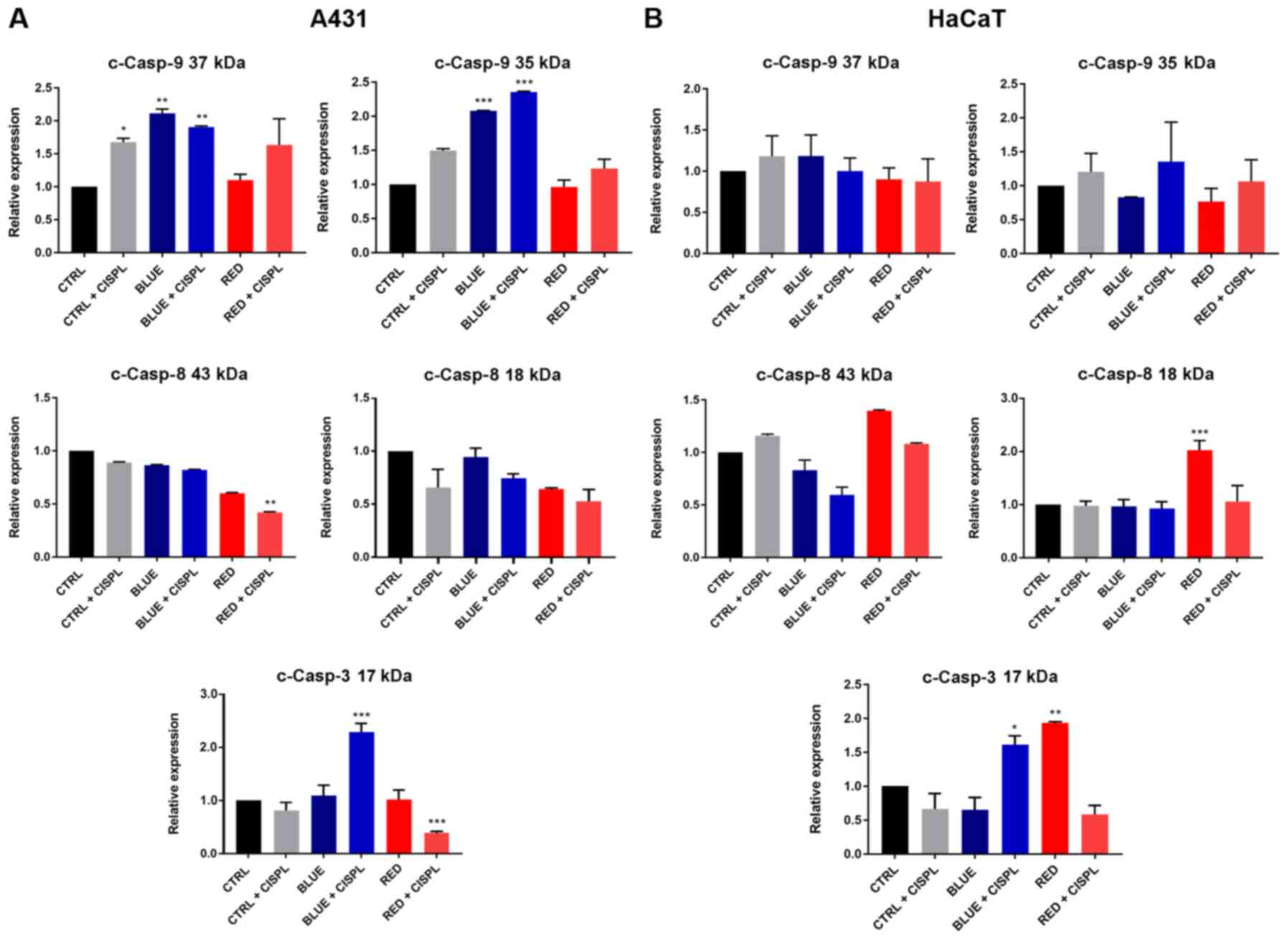
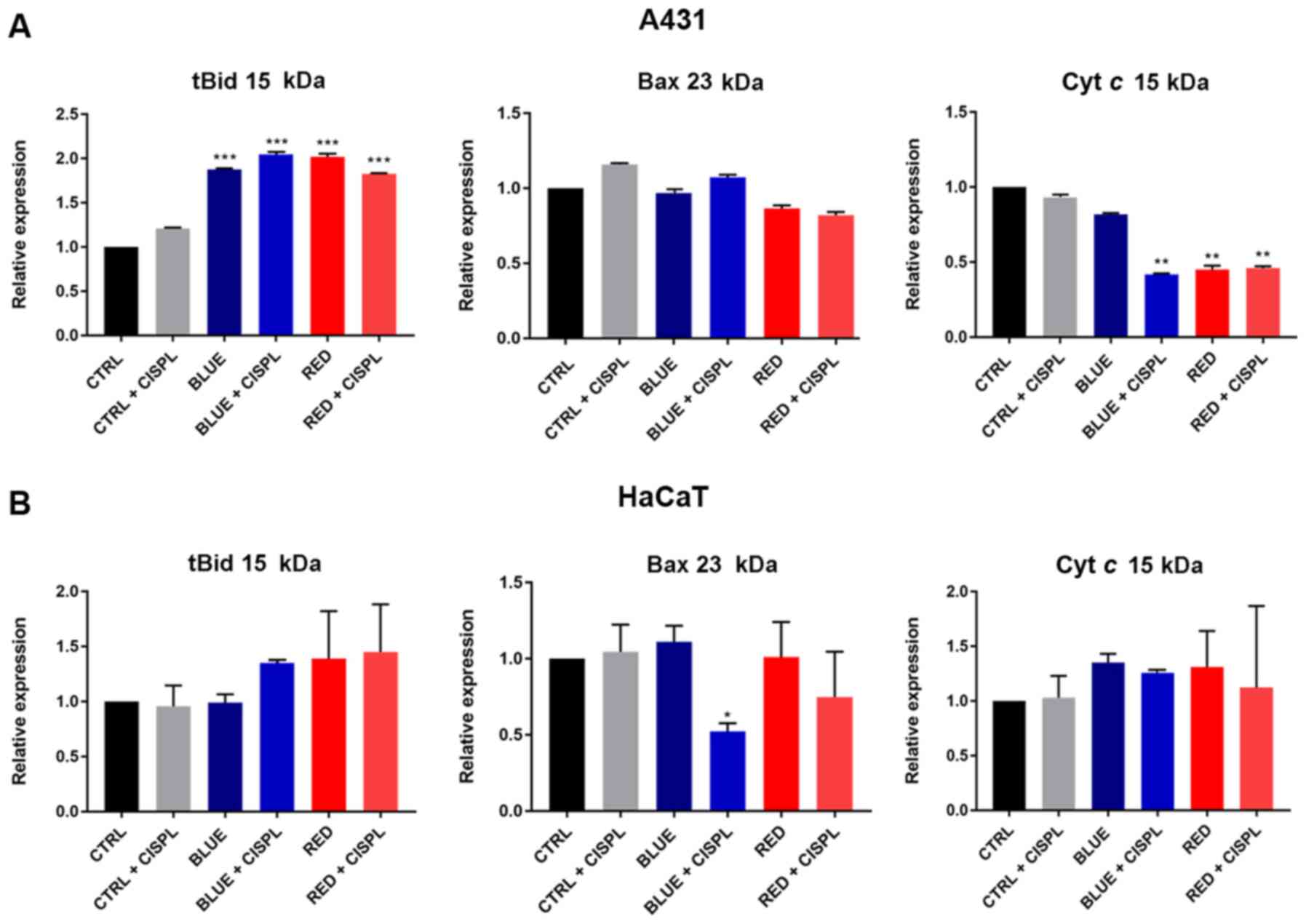
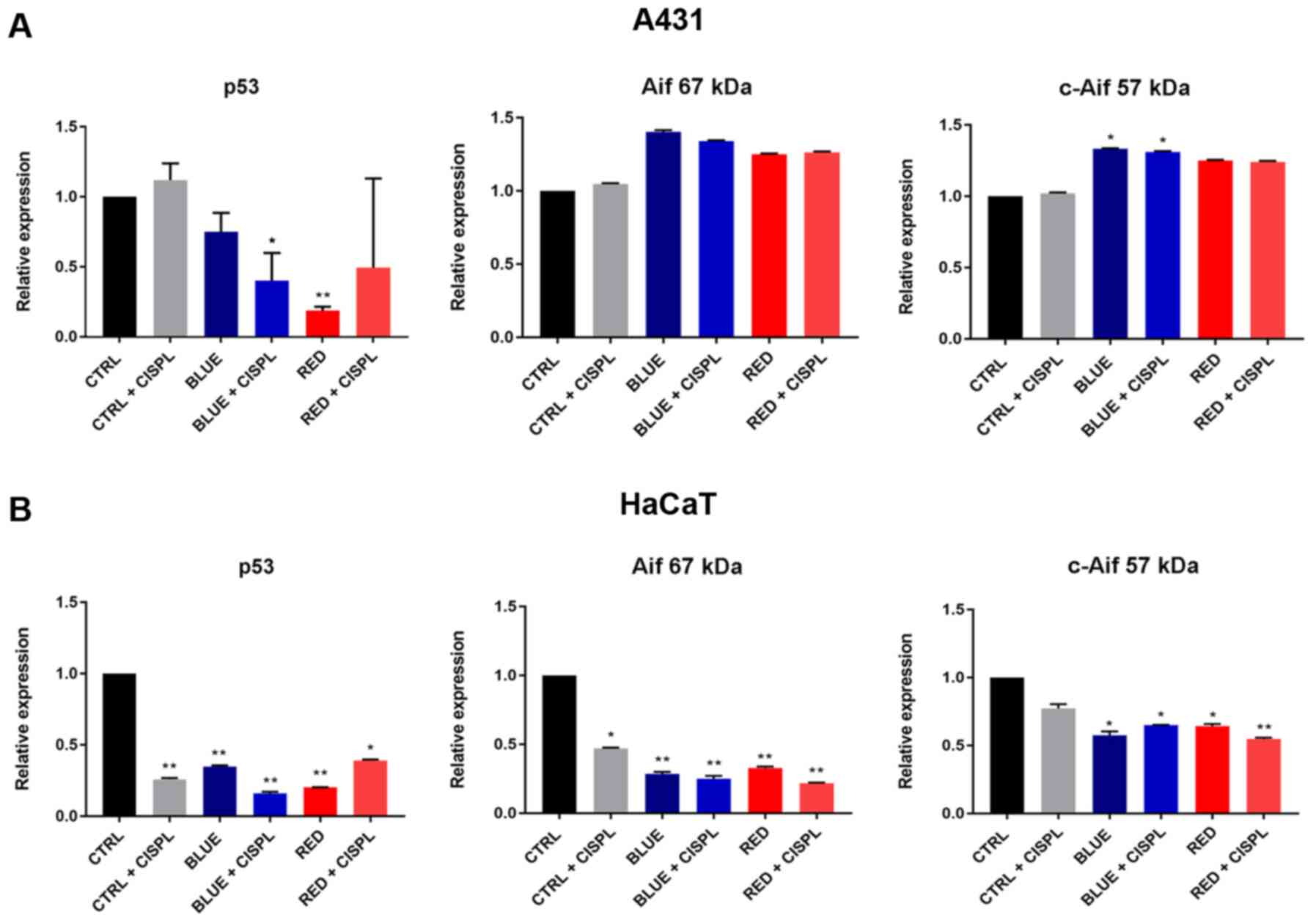
|
1
|
Barolet D, Roberge CJ, Auger FA, Boucher A
and Germain L: Regulation of skin collagen metabolism in vitro
using a pulsed 660 nm LED light source: Clinical correlation with a
single-blinded study. J Invest Dermatol. 129:2751–2759. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mateus C: Cutaneous squamous cell
carcinoma. Rev Prat. 64:45–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parekh V and Seykora JT: Cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Lab Med. 37:503–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smoller BR: Squamous cell carcinoma: From
precursor lesions to high-risk variants. Mod Pathol. 19(Suppl 2):
S88–S92. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palme CE, MacKay SG, Kalnins I, Morgan GJ
and Veness MJ: The need for a better prognostic staging system in
patients with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the
head and neck. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 15:103–106.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garcia-Zuazaga J and Olbricht SM:
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Adv Dermatol. 24:33–57. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kyrgidis A, Tzellos TG, Kechagias N,
Patrikidou A, Xirou P, Kitikidou K, Bourlidou E, Vahtsevanos K and
Antoniades K: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head
and neck: Risk factors of overall and recurrence-free survival. Eur
J Cancer. 46:1563–1572. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Clayman GL, Lee JJ, Holsinger FC, Zhou X,
Duvic M, El-Naggar AK, Prieto VG, Altamirano E, Tucker SL, Strom
SS, et al: Mortality risk from squamous cell skin cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 23:759–765. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sreedhar A, Li J and Zhao Y: Next-gen
therapeutics for skin cancer: Nutraceuticals. Nutr Cancer.
70:697–709. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Burton KA, Ashack KA and Khachemoune A:
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A review of high-risk and
metastatic disease. Am J Clin Dermatol. 17:491–508. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Que SKT, Zwald FO and Schmults CD:
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Management of advanced and
high-stage tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 78:249–261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Compagnin C, Mognato M, Celotti L, Canti
G, Palumbo G and Reddi E: Cell proliferation and cell cycle
alterations in oesophageal p53-mutated cancer cells treated with
cisplatin in combination with photodynamic therapy. Cell Prolif.
43:262–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bray FN, Simmons BJ, Wolfson AH and Nouri
K: Acute and chronic cutaneous reactions to ionizing radiation
therapy. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 6:185–206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, Shinoda M, Ozawa
S, Shimizu H, Nakamura T, Yabusaki H, Aoyama N, Kurita A, et al: A
randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with
cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for
localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic
esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 19:68–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Salman M and Naseem I: Riboflavin as
adjuvant with cisplatin: Study in mouse skin cancer model. Front
Biosci (Elite Ed). 7:242–254. 2015.
|
|
16
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mego M, Svetlovska D, Miskovska V,
Obertova J, Palacka P, Rajec J, Sycova-Mila Z, Chovanec M,
Rejlekova K, Zuzák P, et al: Phase II study of everolimus in
refractory testicular germ cell tumors. Urol Oncol.
34:122.e17–122.e22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Terenziani M, De Pasquale MD, Bisogno G,
Biasoni D, Boldrini R, Collini P, Conte M, Dall'Igna P, Inserra A,
Melchionda F, et al: Malignant testicular germ cell tumors in
children and adolescents: The AIEOP (Associazione Italiana
Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica) protocol. Urol Oncol.
36:502.e7–502.e13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi T, Jiang R, Yu J, Yang H, Tu D, Dai Z,
Shen Y, Zhang Y, Cheng X, Jia H, et al: Addition of intraperitoneal
cisplatin and etoposide to first-line chemotherapy for advanced
ovarian cancer: A randomised, phase 2 trial. Br J Cancer.
119:12–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tempfer CB, Giger-Pabst U, Seebacher V,
Petersen M, Dogan A and Rezniczek GA: A phase I, single-arm,
open-label, dose escalation study of intraperitoneal cisplatin and
doxorubicin in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer and
peritoneal carcinomatosis. Gynecol Oncol. 150:23–30. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gupta S, Maheshwari A, Parab P,
Mahantshetty U, Hawaldar R, Sastri Chopra S, Kerkar R, Engineer R,
Tongaonkar H, Ghosh J, et al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by
radical surgery versus concomitant chemotherapy and radiotherapy in
patients with stage IB2, IIA, or IIB squamous cervical cancer: A
randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 36:1548–1555. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kitagawa R, Katsumata N, Shibata T, Kamura
T, Kasamatsu T, Nakanishi T, Nishimura S, Ushijima K, Takano M,
Satoh T and Yoshikawa H: Paclitaxel Plus carboplatin versus
paclitaxel plus cisplatin in metastatic or recurrent cervical
cancer: The open-label randomized phase III trial JCOG0505. J Clin
Oncol. 33:2129–2135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rosen VM, Guerra I, McCormack M,
Nogueira-Rodrigues A, Sasse A, Munk VC and Shang A: Systematic
review and network meta-analysis of bevacizumab plus first-line
topotecan-paclitaxel or cisplatin-paclitaxel versus
non-bevacizumab-containing therapies in persistent, recurrent, or
metastatic cervical cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 27:1237–1246.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Small W Jr, Bacon MA, Bajaj A, Chuang LT,
Fisher BJ, Harkenrider MM, Jhingran A, Kitchener HC, Mileshkin LR,
Viswanathan AN and Gaffney DK: Cervical cancer: A global health
crisis. Cancer. 123:2404–2412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Noronha V, Joshi A, Patil VM, Agarwal J,
Ghosh-Laskar S, Budrukkar A, Murthy V, Gupta T, D'Cruz AK, Banavali
S, et al: Once-a-week versus once-every-3-weeks cisplatin
chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer: A phase
III randomized noninferiority trial. J Clin Oncol. 36:1064–1072.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Strojan P, Vermorken JB, Beitler JJ, Saba
NF, Haigentz M Jr, Bossi P, Worden FP, Langendijk JA, Eisbruch A,
Mendenhall WM, et al: Cumulative cisplatin dose in concurrent
chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: A systematic review.
Head Neck. 38(Suppl 1): E2151–E2158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Szturz P, Wouters K, Kiyota N, Tahara M,
Prabhash K, Noronha V, Castro A, Licitra L, Adelstein D and
Vermorken JB: Weekly low-dose versus three-weekly high-dose
cisplatin for concurrent chemoradiation in locoregionally advanced
non-nasopharyngeal head and neck cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of aggregate data. Oncologist. 22:1056–1066. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gridelli C, Morabito A, Cavanna L, Luciani
A, Maione P, Bonanno L, Filipazzi V, Leo S, Cinieri S, Ciardiello
F, et al: Cisplatin-based first-line treatment of elderly patients
with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Joint analysis of MILES-3
and MILES-4 phase III trials. J Clin Oncol. 36:2585–2592. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rossi A and Di Maio M: Platinum-based
chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Optimal number
of treatment cycles. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 16:653–660. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sarin N, Engel F, Kalayda GV, Mannewitz M,
Cinatl J Jr, Rothweiler F, Michaelis M, Saafan H, Ritter CA, Jaehde
U and Frötschl R: Cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung
cancer cells is associated with an abrogation of cisplatin-induced
G2/M cell cycle arrest. PLoS One. 12:e01810812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu L, Fan J, Ai G, Liu J, Luo N, Li C and
Cheng Z: Berberine in combination with cisplatin induces
necroptosis and apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Biol Res.
52:372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Freitas LM, Soares CP and Fontana CR:
Synergistic effect of photodynamic therapy and cisplatin: A novel
approach for cervical cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 140:365–373.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oun R, Moussa YE and Wheate NJ: The side
effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: A review for
chemists. Dalton Trans. 47:6645–6653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Crul M, van Waardenburg RC, Beijnen JH and
Schellens JH: DNA-based drug interactions of cisplatin. Cancer
Treat Rev. 28:291–303. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fuertes MA, Alonso C and Pérez JM:
Biochemical modulation of cisplatin mechanisms of action:
Enhancement of antitumor activity and circumvention of drug
resistance. Chem Rev. 103:645–662. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oh PS and Jeong HJ: Therapeutic
application of light emitting diode: Photo-oncomic approach. J
Photochem Photobiol B. 192:1–7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sorbellini E, Rucco M and Rinaldi F:
Photodynamic and photobiological effects of light-emitting diode
(LED) therapy in dermatological disease: An update. Lasers Med Sci.
33:1431–1439. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brancaleon L and Moseley H: Laser and
non-laser light sources for photodynamic therapy. Lasers Med Sci.
17:173–186. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ost D: Photodynamic therapy in lung
cancer. A review Methods Mol Med. 75:507–526. 2003.
|
|
40
|
Sutedja TG and Postmus PE: Photodynamic
therapy in lung cancer. A review. J Photochem Photobiol B.
36:199–204. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Silva JN, Filipe P, Morlière P, Mazière
JC, Freitas JP, Gomes MM and Santus R: Photodynamic therapy:
Dermatology and ophthalmology as main fields of current
applications in clinic. Biomed Mater Eng. 18:319–327.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Breskey JD, Lacey SE, Vesper BJ, Paradise
WA, Radosevich JA and Colvard MD: Photodynamic therapy:
Occupational hazards and preventative recommendations for clinical
administration by healthcare providers. Photomed Laser Surg.
31:398–407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
del Olmo-Aguado S, Manso AG and Osborne
NN: Light might directly affect retinal ganglion cell mitochondria
to potentially influence function. Photochem Photobiol.
88:1346–1355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chui C, Hiratsuka K, Aoki A, Takeuchi Y,
Abiko Y and Izumi Y: Blue LED inhibits the growth of Porphyromonas
gingivalis by suppressing the expression of genes associated with
DNA replication and cell division. Lasers Surg Med. 44:856–864.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rybchyn MS, De Silva WGM, Sequeira VB,
McCarthy BY, Dilley AV, Dixon KM, Halliday GM and Mason RS:
Enhanced repair of UV-induced DNA damage by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3 in skin is linked to pathways that control cellular energy. J
Invest Dermatol. 138:1146–1156. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Suh SS, Lee SG, Youn UJ, Han SJ, Kim IC
and Kim S: Comprehensive expression profiling and functional
network analysis of porphyra-334, one mycosporine-like amino acid
(MAA), in human keratinocyte exposed with UV-radiation. Mar Drugs.
15:1962017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Muhammad S, Qasid SH, Rehman S and Rai AB:
Visible light communication applications in healthcare. Technol
Health Care. 24:135–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tsibadze A, Chikvaidze E, Katsitadze A,
Kvachadze I, Tskhvediani N and Chikviladze A: Visible light and
human skin (Review). Georgian Med News. 46–53. 2015.In Russian.
|
|
49
|
Gegotek A, Atalay S, Domingues P and
Skrzydlewska E: The differences in the proteome profile of
cannabidiol-treated skin fibroblasts following UVA or UVB
irradiation in 2D and 3D cell cultures. Cells. 8:9952019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Zhang C, Yuchi H, Sun L, Zhou X and Lin J:
Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against UVA
irradiation-induced human dermal fibroblast senescence, in vitro.
Mol Med Rep. 16:2016–2022. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Patel AD, Rotenberg S, Messer RL, Wataha
JC, Ogbureke KU, McCloud VV, Lockwood P, Hsu S and Lewis JB: Blue
light activates phase 2 response proteins and slows growth of a431
epidermoid carcinoma xenografts. Anticancer Res. 34:6305–6313.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Niu T, Tian Y, Wang G, Guo G, Tong Y and
Shi Y: Inhibition of ROS-NF-κB-dependent autophagy enhances
hypocrellin A united LED red light-induced apoptosis in squamous
carcinoma A431 cells. Cell Signal. 69:1095502020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Meulemans J, Delaere P and Vander Poorten
V: Photodynamic therapy in head and neck cancer: Indications,
outcomes, and future prospects. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 27:136–141. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kerr C, Adhikary G, Grun D, George N and
Eckert RL: Combination cisplatin and sulforaphane treatment reduces
proliferation, invasion, and tumor formation in epidermal squamous
cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 57:3–11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hwang H, Biswas R, Chung PS and Ahn JC:
Modulation of EGFR and ROS induced cytochrome c release by
combination of photodynamic therapy and carboplatin in human
cultured head and neck cancer cells and tumor xenograft in nude
mice. J Photochem Photobiol B. 128:70–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang X, Liu X, Kang S, Liu C and Hao Y:
Resveratrol enhances the effects of ALA-PDT on skin squamous cells
A431 through p38/MAPK signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark.
21:797–803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Tampucci S, Carpi S, Digiacomo M, Polini
B, Fogli S, Burgalassi S, Macchia M, Nieri P, Manera C and Monti D:
Diclofenac-derived hybrids for treatment of actinic keratosis and
squamous cell carcinoma. Molecules. 24:17932019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Carbone C, Martins-Gomes C, Pepe V, Silva
AM, Musumeci T, Puglisi G, Furneri PM and Souto EB: Repurposing
itraconazole to the benefit of skin cancer treatment: A combined
azole-DDAB nanoencapsulation strategy. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 167:337–344. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen H, Pan J, Zhang L, Chen L, Qi H,
Zhong M, Shi X, Du J and Li Q: Downregulation of estrogen-related
receptor alpha inhibits human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
cell proliferation and migration by regulating EMT via fibronectin
and STAT3 signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 825:133–142. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ou C, Liu H, Ding Z and Zhou L:
Chloroquine promotes gefitinib-induced apoptosis by inhibiting
protective autophagy in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med
Rep. 20:4855–4866. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fusenig NE and Boukamp P: Multiple stages
and genetic alterations in immortalization, malignant
transformation, and tumor progression of human skin keratinocytes.
Mol Carcinog. 23:144–158. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Colombo I, Sangiovanni E, Maggio R,
Mattozzi C, Zava S, Corbett Y, Fumagalli M, Carlino C, Corsetto PA,
Scaccabarozzi D, et al: HaCaT cells as a reliable in vitro
differentiation model to dissect the inflammatory/repair response
of human keratinocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2017:74356212017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Cordero RR, Damiani A, Seckmeyer G,
Jorquera J, Caballero M, Rowe P, Ferrer J, Mubarak R, Carrasco J,
Rondanelli R, et al: The solar spectrum in the atacama det. Sci
Rep. 6:224572016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Faurschou A, Gniadecki R, Calay D and Wulf
HC: TNF-alpha impairs the S-G2/M cell cycle checkpoint and
cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer repair in premalignant skin cells:
Role of the PI3K-Akt pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 128:2069–2077.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schug ZT, Gonzalvez F, Houtkooper RH, Vaz
FM and Gottlieb E: BID is cleaved by caspase-8 within a native
complex on the mitochondrial membrane. Cell Death Differ.
18:538–548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Huang C and Yu Y: Synergistic cytotoxicity
of β-elemene and cisplatin in gingival squamous cell carcinoma by
inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 23:1507–1513.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tao JX, Zhou WC and Zhu XG: Mitochondria
as potential targets and initiators of the blue light hazard to the
retina. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:64353642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hientz K, Mohr A, Bhakta-Guha D and
Efferth T: The role of p53 in cancer drug resistance and targeted
chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 8:8921–8946. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Batchelor E and Loewer A: Recent progress
and open challenges in modeling p53 dynamics in single cells. Curr
Opin Syst Biol. 3:54–59. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Batchelor E, Loewer A, Mock C and Lahav G:
Stimulus-dependent dynamics of p53 in single cells. Mol Syst Biol.
7:4882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Paek AL, Liu JC, Loewer A, Forrester WC
and Lahav G: Cell-to-cell variation in p53 dynamics leads to
fractional killing. Cell. 165:631–642. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bowen AR, Hanks AN, Allen SM, Alexander A,
Diedrich MJ and Grossman D: Apoptosis regulators and responses in
human melanocytic and keratinocytic cells. J Invest Dermatol.
120:48–55. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Laubach V, Kaufmann R, Bernd A,
Kippenberger S and Zöller N: Extrinsic or intrinsic apoptosis by
curcumin and light: Still a mystery. Int J Mol Sci. 20:9052019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Cives M, Mannavola F, Lospalluti L, Sergi
MC, Cazzato G, Filoni E, Cavallo F, Giudice G, Stucci LS, Porta C
and Tucci M: Non-melanoma skin cancers: Biological and clinical
features. Int J Mol Sci. 21:53942020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Gargiulo M, Papa A, Capasso P, Moio M,
Cubicciotti E and Parascandolo S: Electrochemotherapy for
non-melanoma head and neck cancers: Clinical outcomes in 25
patients. Ann Surg. 255:1158–1164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Goggins CA and Khachemoune A: The use of
electrochemotherapy in combination with immunotherapy in the
treatment of metastatic melanoma: A focused review. Int J Dermatol.
58:865–870. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Montuori M, Santurro L, Feliziani A, DE
Sanctis F, Ricciardi E, Gaudio D, Campione E, Bianchi L, Silvi MB
and Rossi P: Electrochemotherapy for basocellular and
squamocellular head and neck cancer: preliminary experience in day
surgery unit. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 153:19–25. 2018.
|
|
78
|
Grzelak A, Rychlik B and Bartosz G:
Light-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species in cell
culture media. Free Radic Biol Med. 30:1418–1425. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Stockley JH, Evans K, Matthey M, Volbracht
K, Agathou S, Mukanowa J, Burrone J and Káradóttir RT: Surpassing
light-induced cell damage in vitro with novel cell culture media.
Sci Rep. 7:8492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|