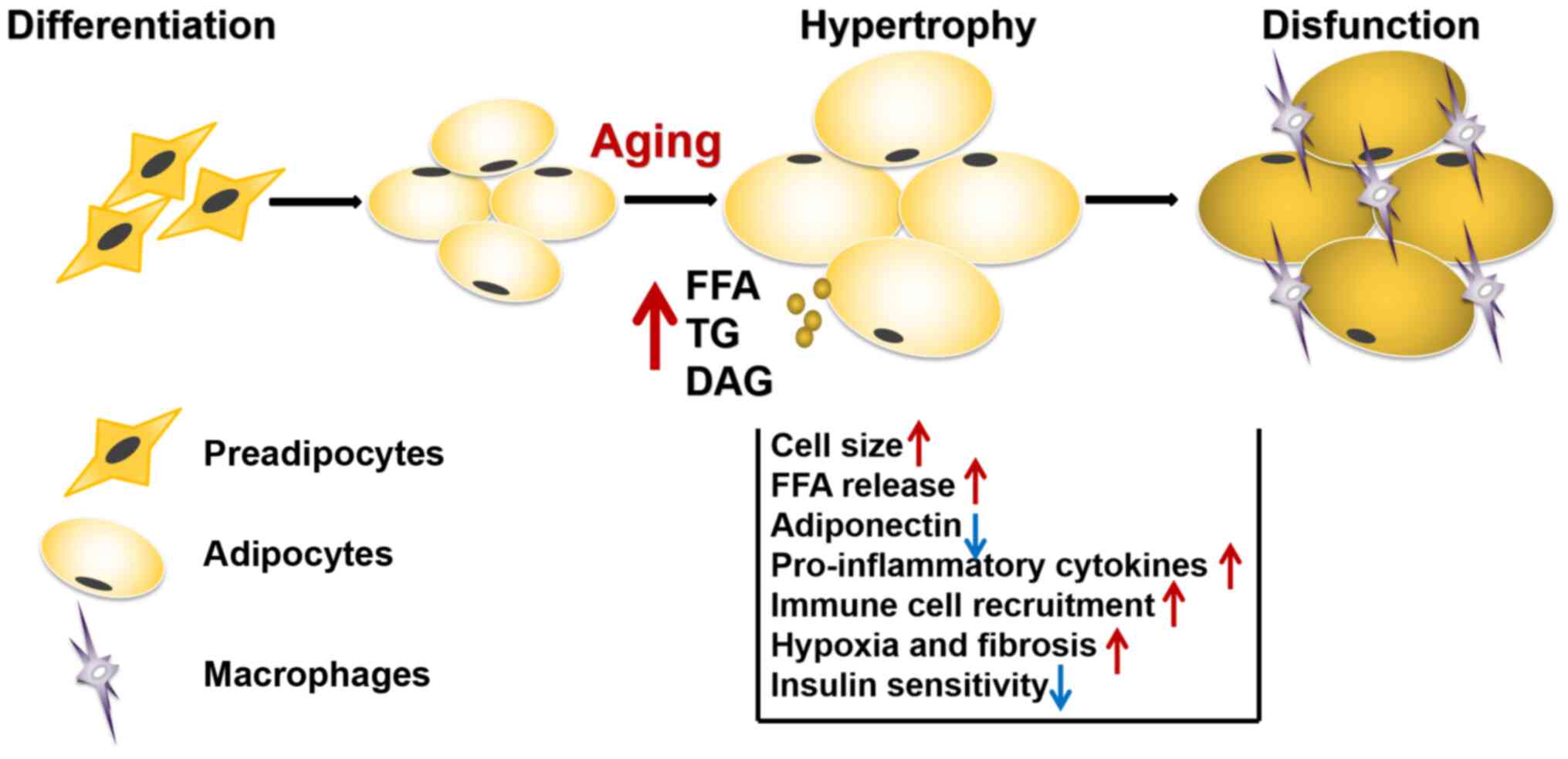
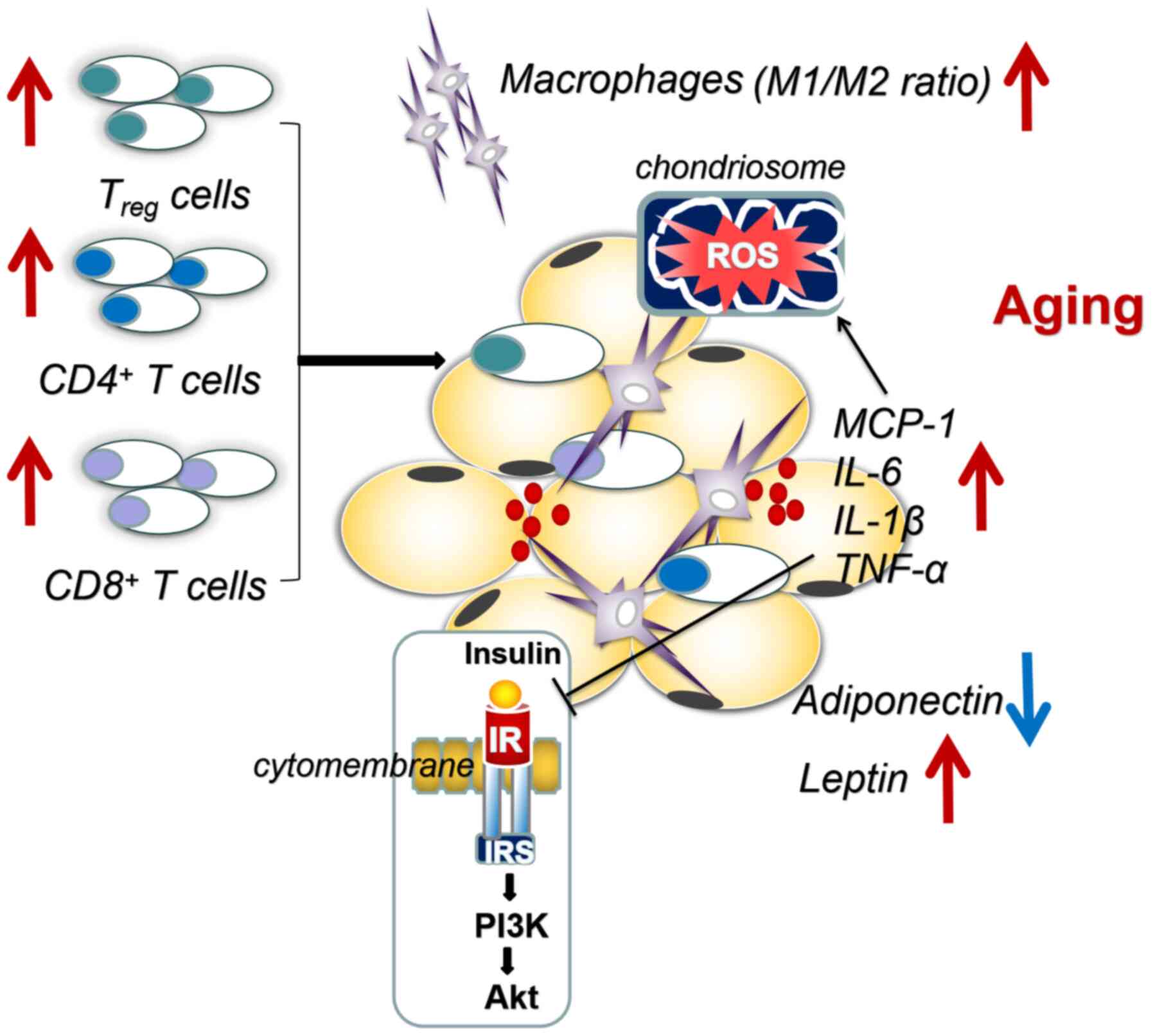
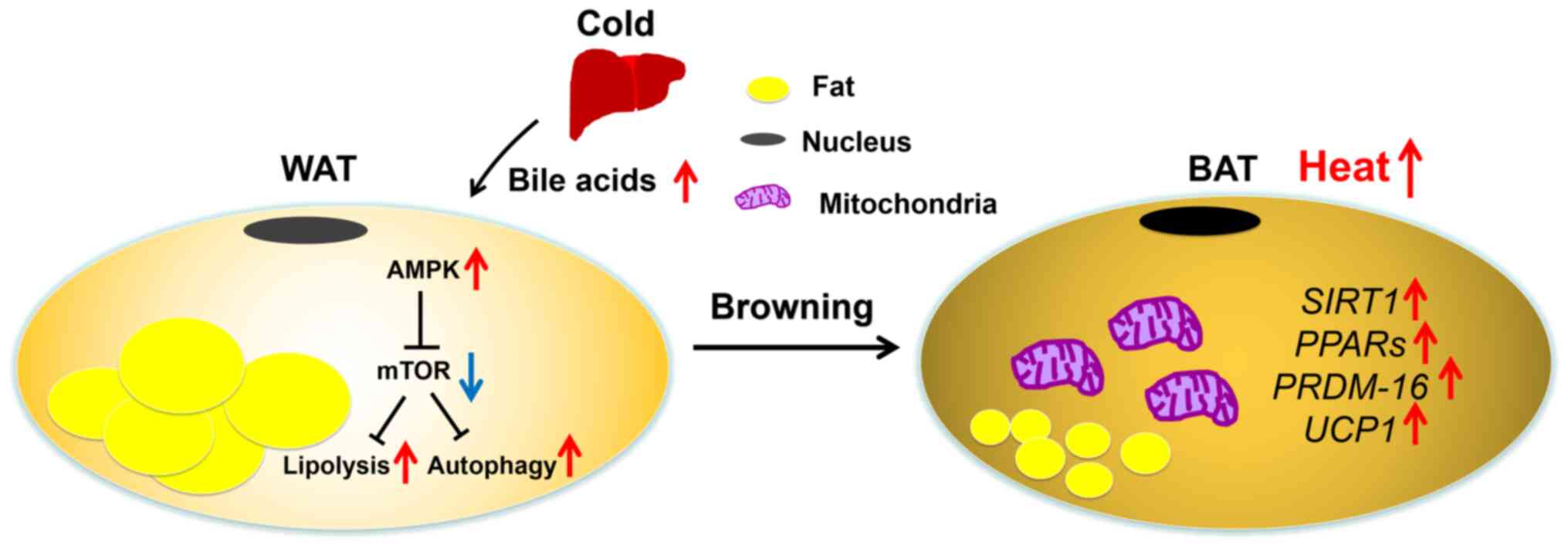
|
1
|
Ikemura M, Nishikawa M, Hyoudou K,
Kobayashi Y, Yamashita F and Hashida M: Improvement of insulin
resistance by removal of systemic hydrogen peroxide by PEGylated
catalase in obese mice. Mol Pharm. 7:2069–2076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo S: Insulin signaling, resistance, and
the metabolic syndrome: Insights from mouse models into disease
mechanisms. J Endocrinol. 220:T1–T23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tarantino G, Citro V and Capone D:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A challenge from mechanisms to
therapy. J Clin Med. 9:152019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Czech MP: Insulin action and resistance in
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Med. 23:804–814. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qi X, Yun C, Sun L, Xia J, Wu Q, Wang Y,
Wang L, Zhang Y, Liang X, Wang L, et al: Gut microbiota-bile
acid-interleukin-22 axis orchestrates polycystic ovary syndrome.
Nat Med. 25:1225–1233. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Petersen MC and Shulman GI: Mechanisms of
insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol Rev. 98:2133–2223.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Napoli N, Chandran M, Pierroz DD,
Abrahamsen B and Schwartz AV: Mechanisms of diabetes
mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 13:208–219.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chow HM, Shi M, Cheng A, Gao Y, Chen G,
Song X, So RWL, Zhang J and Herrup K: Age-related hyperinsulinemia
leads to insulin resistance in neurons and cell-cycle-induced
senescence. Nat Neurosci. 22:1806–1819. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barzilai N and Ferrucci L: Insulin
resistance and aging: A cause or a protective response? J Gerontol
A Biol Sci Med Sci. 67:1329–1331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rosen ED and Spiegelman BM: Adipocytes as
regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature.
444:847–853. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun R, Wu Y, Hou W, Sun Z, Wang Y, Wei H,
Mo W and Yu M: Bromodomain-containing protein 2 induces insulin
resistance via the mTOR/Akt signaling pathway and an inflammatory
response in adipose tissue. Cell Signal. 30:92–103. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zong J, Li S, Wang Y, Mo W, Sun R and Yu
M: Bromodomain-containing protein 2 promotes lipolysis via ERK/HSL
signalling pathway in white adipose tissue of mice. Gen Comp
Endocrinol. 281:105–116. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bapat SP, Myoung Suh J, Fang S, Liu S,
Zhang Y, Cheng A, Zhou C, Liang Y, LeBlanc M, Liddle C, et al:
Depletion of fat-resident Treg cells prevents age-associated
insulin resistance. Nature. 528:137–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sierra Rojas JX, Garcia-San Frutos M,
Horrillo D, Lauzurica N, Oliveros E, Carrascosa JM,
Fernández-Agulló T and Ros M: Differential development of
inflammation and insulin resistance in different adipose tissue
depots along aging in wistar rats: Effects of caloric restriction.
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 71:310–322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park A, Kim WK and Bae KH: Distinction of
white, beige and brown adipocytes derived from mesenchymal stem
cells. World J Stem Cells. 6:33–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Giralt M and Villarroya F: White, brown,
beige/brite: Different adipose cells for different functions?
Endocrinology. 154:2992–3000. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Palmer AK and Kirkland JL: Aging and
adipose tissue: Potential interventions for diabetes and
regenerative medicine. Exp Gerontol. 86:97–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Madonna R and De Caterina R: In vitro
neovasculogenic potential of resident adipose tissue precursors. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C1271–1280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chon SH and Pappas A: Differentiation and
characterization of human facial subcutaneous adipocytes.
Adipocyte. 4:13–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frontini A and Cinti S: Distribution and
development of brown adipocytes in the murine and human adipose
organ. Cell Metab. 11:253–256. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cedikova M, Kripnerová M, Dvorakova J,
Pitule P, Grundmanova M, Babuska V, Mullerova D and Kuncova J:
Mitochondria in white, brown, and beige adipocytes. Stem Cells Int.
2016:60673492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ye L, Wu J, Cohen P, Kazak L, Khandekar
MJ, Jedrychowski MP, Zeng X, Gygi SP and Spiegelman BM: Fat cells
directly sense temperature to activate thermogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:12480–12485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cypess AM, White AP, Vernochet C, Schulz
TJ, Xue R, Sass CA, Huang TL, Roberts-Toler C, Weiner LS, Sze C, et
al: Anatomical localization, gene expression profiling and
functional characterization of adult human neck brown fat. Nat Med.
19:635–639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mailloux RJ and Harper ME: Uncoupling
proteins and the control of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species
production. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1106–1115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu J, Boström P, Sparks LM, Ye L, Choi JH,
Giang AH, Khandekar M, Virtanen KA, Nuutila P, Schaart G, et al:
Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in
mouse and human. Cell. 150:366–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pyrzak B, Demkow U and Kucharska AM: Brown
adipose tissue and browning agents: Irisin and FGF21 in the
development of obesity in children and adolescents. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 866:25–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Okla M, Ha JH, Temel RE and Chung S: BMP7
drives human adipogenic stem cells into metabolically active beige
adipocytes. Lipids. 50:111–120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Palmer AK, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK,
Chini EN, Xu M and Kirkland JL: Cellular senescence in type 2
diabetes: A therapeutic opportunity. Diabetes. 64:2289–2298. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zoico E, Rubele S, De Caro A, Nori N,
Mazzali G, Fantin F, Rossi A and Zamboni M: Brown and beige adipose
tissue and aging. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:3682019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO,
Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O, Blomqvist L, Hoffstedt J,
Näslund E, Britton T, et al: Dynamics of fat cell turnover in
humans. Nature. 453:783–787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eckel-Mahan K, Ribas Latre A and Kolonin
MG: Adipose stromal cell expansion and exhaustion: Mechanisms and
consequences. Cells. 9:8632020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Tchkonia T, Morbeck DE, Von Zglinicki T,
Van Deursen J, Lustgarten J, Scrable H, Khosla S, Jensen MD and
Kirkland JL: Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence. Aging
Cell. 9:667–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Caso G, McNurlan MA, Mileva I, Zemlyak A,
Mynarcik DC and Gelato MC: Peripheral fat loss and decline in
adipogenesis in older humans. Metabolism. 62:337–340. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bukowska J, Frazier T, Smith S, Brown T,
Bender R, McCarthy M, Wu X, Bunnell BA and Gimble JM: Bone marrow
adipocyte developmental origin and biology. Curr Osteoporos Rep.
16:312–319. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ahmed AS, Sheng MH, Wasnik S, Baylink DJ
and Lau KW: Effect of aging on stem cells. World J Exp Med. 7:1–10.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T, Pirtskhalava T,
Han J and Karagiannides I: Adipogenesis and aging: Does aging make
fat go MAD? Exp Gerontol. 37:757–767. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gill LE, Bartels SJ and Batsis JA: Weight
management in older adults. Curr Obes Rep. 4:379–388. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sepe A, Tchkonia T, Thomou T, Zamboni M
and Kirkland JL: Aging and regional differences in fat cell
progenitors-a mini-review. Gerontology. 57:66–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pischon T, Boeing H, Hoffmann K, Bergmann
M, Schulze MB, Overvad K, van der Schouw YT, Spencer E, Moons KG,
Tjønneland A, et al: General and abdominal adiposity and risk of
death in Europe. N Engl J Med. 359:2105–2120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Preis SR, Massaro JM, Robins SJ, Hoffmann
U, Vasan RS, Irlbeck T, Meigs JB, Sutherland P, D'Agostino RB Sr,
O'Donnell CJ and Fox CS: Abdominal subcutaneous and visceral
adipose tissue and insulin resistance in the Framingham heart
study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 18:2191–2198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Paradis ME, Hogue MO, Mauger JF, Couillard
C, Couture P, Bergeron N and Lamarche B: Visceral adipose tissue
accumulation, secretory phospholipase A2-IIA and atherogenecity of
LDL. Int J Obes (Lond). 30:1615–1622. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Giorgino F: Adipose tissue function and
dysfunction: Organ cross talk and metabolic risk. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 297:E975–E976. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Capurso C and Capurso A: From excess
adiposity to insulin resistance: The role of free fatty acids.
Vascul Pharmacol. 57:91–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ibrahim MM: Subcutaneous and visceral
adipose tissue: Structural and functional differences. Obes Rev.
11:11–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Niu Z, Lin N, Gu R, Sun Y and Feng Y:
Associations between insulin resistance, free fatty acids, and
oocyte quality in polycystic ovary syndrome during in vitro
fertilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:E2269–E2276. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chait A and den Hartigh LJ: Adipose tissue
distribution, inflammation and its metabolic consequences,
including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Front Cardiovasc
Med. 7:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Coppé JP, Patil CK, Rodier F, Sun Y, Muñoz
DP, Goldstein J, Nelson PS, Desprez PY and Campisi J:
Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal
cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor
suppressor. PLoS Biol. 6:2853–2868. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu M, Palmer AK, Ding H, Weivoda MM,
Pirtskhalava T, White TA, Sepe A, Johnson KO, Stout MB, Giorgadze
N, et al: Targeting senescent cells enhances adipogenesis and
metabolic function in old age. Elife. 4:e129972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu M, Tchkonia T, Ding H, Ogrodnik M,
Lubbers ER, Pirtskhalava T, White TA, Johnson KO, Stout MB, Mezera
V, et al: JAK inhibition alleviates the cellular
senescence-associated secretory phenotype and frailty in old age.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E6301–E6310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park SS and Seo YK: Excess accumulation of
lipid impairs insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:19492020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Pincus Z, Smith-Vikos T and Slack FJ:
MicroRNA predictors of longevity in caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS
Genet. 7:e10023062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mori MA, Raghavan P, Thomou T, Boucher J,
Robida-Stubbs S, Macotela Y, Russell SJ, Kirkland JL, Blackwell TK
and Kahn CR: Role of microRNA processing in adipose tissue in
stress defense and longevity. Cell Metab. 16:336–347. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mori MA, Thomou T, Boucher J, Lee KY,
Lallukka S, Kim JK, Torriani M, Yki-Järvinen H, Grinspoon SK,
Cypess AM and Kahn CR: Altered miRNA processing disrupts
brown/white adipocyte determination and associates with
lipodystrophy. J Clin Invest. 124:3339–3351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mori MA, Ludwig RG, Garcia-Martin R,
Brandão BB and Kahn CR: Extracellular miRNAs: From biomarkers to
mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab. 30:656–673. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fontes-Carvalho R, Fontes-Oliveira M,
Sampaio F, Mancio J, Bettencourt N, Teixeira M, Rocha Gonçalves F,
Gama V and Leite-Moreira A: Influence of epicardial and visceral
fat on left ventricular diastolic and systolic functions in
patients after myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 114:1663–1669.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mancuso P and Bouchard B: The impact of
aging on adipose function and adipokine synthesis. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 10:1372019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Chandrasekar B, Boylston WH, Venkatachalam
K, Webster NJ, Prabhu SD and Valente AJ: Adiponectin blocks
interleukin-18-mediated endothelial cell death via APPL1-dependent
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and
IKK/NF-kappaB/PTEN suppression. J Biol Chem. 283:24889–24898. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jura M and Kozak LP: Obesity and related
consequences to ageing. Age (Dordr). 38:232016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, Lee Y, Ahn JY,
Kim SJ, Koh Y and Shin EK: Simvastatin improves flow-mediated
dilation but reduces adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity in
hypercholesterolemic patients. Diabetes Care. 31:776–782. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Isobe T, Saitoh S, Takagi S, Takeuchi H,
Chiba Y, Katoh N and Shimamoto K: Influence of gender, age and
renal function on plasma adiponectin level: The Tanno and Sobetsu
study. Eur J Endocrinol. 153:91–98. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Takenouchi Y, Kobayashi T, Matsumoto T and
Kamata K: Gender differences in age-related endothelial function in
the murine aorta. Atherosclerosis. 206:397–404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li JB, Nishida M, Kaimoto K, Asakawa A,
Chaolu H, Cheng KC, Li YX, Terashi M, Koyama KI, Amitani H, et al:
Effects of aging on the plasma levels of nesfatin-1 and
adiponectin. Biomed Rep. 2:152–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nigro E, Scudiero O, Monaco ML, Palmieri
A, Mazzarella G, Costagliola C, Bianco A and Daniele A: New insight
into adiponectin role in obesity and obesity-related diseases.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:6589132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Carter S, Caron A, Richard D and Picard F:
Role of leptin resistance in the development of obesity in older
patients. Clin Interv Aging. 8:829–844. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Katsiki N, Mikhailidis DP and Banach M:
Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 39:1176–1188. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Doherty GH: Obesity and the ageing brain:
Could leptin play a role in neurodegeneration? Curr Gerontol
Geriatr Res. 2011:7081542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lehrke M, Reilly MP, Millington SC, Iqbal
N, Rader DJ and Lazar MA: An inflammatory cascade leading to
hyperresistinemia in humans. PLoS Med. 1:e452004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gencer B, Auer R, de Rekeneire N, Butler
J, Kalogeropoulos A, Bauer DC, Kritchevsky SB, Miljkovic I,
Vittinghoff E, Harris T and Rodondi N: Association between resistin
levels and cardiovascular disease events in older adults: The
health, aging and body composition study. Atherosclerosis.
245:181–186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rea IM, Gibson DS, McGilligan V, McNerlan
SE, Alexander HD and Ross OA: Age and age-related diseases: Role of
inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front Immunol. 9:5862018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
de Heredia FP, Gómez-Martinez S and Marcos
A: Obesity, inflammation and the immune system. Proc Nutr Soc.
71:332–338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lumeng CN, Liu J, Geletka L, Delaney C,
Delproposto J, Desai A, Oatmen K, Martinez-Santibanez G, Julius A,
Garg S and Yung RL: Aging is associated with an increase in T cells
and inflammatory macrophages in visceral adipose tissue. J Immunol.
187:6208–6216. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL and Saltiel AR:
Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage
polarization. J Clin Invest. 117:175–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Russo L and Lumeng CN: Properties and
functions of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity. Immunology.
155:407–417. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Olefsky JM and Glass CK: Macrophages,
inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:219–246.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Fang W, Deng Z, Benadjaoud F, Yang D, Yang
C and Shi GP: Regulatory T cells promote adipocyte beiging in
subcutaneous adipose tissue. FASEB J. 34:9755–9770. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Schenk S, Saberi M and Olefsky JM: Insulin
sensitivity: Modulation by nutrients and inflammation. J Clin
Invest. 118:2992–3002. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lumeng CN, Deyoung SM and Saltiel AR:
Macrophages block insulin action in adipocytes by altering
expression of signaling and glucose transport proteins. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 292:E166–E174. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Gustafson B and Smith U: Cytokines promote
Wnt signaling and inflammation and impair the normal
differentiation and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J
Biol Chem. 281:9507–9516. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Woo CY, Jang JE, Lee SE, Koh EH and Lee
KU: Mitochondrial dysfunction in adipocytes as a primary cause of
adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetes Metab J. 43:247–256. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
van de Ven RAH, Santos D and Haigis MC:
Mitochondrial sirtuins and molecular mechanisms of aging. Trends
Mol Med. 23:320–331. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Tao Y, Huang C, Huang Y, Hong L, Wang H,
Zhou Z and Qiu Y: SIRT4 suppresses inflammatory responses in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 15:217–223.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Argmann C and Auwerx J: Insulin secretion:
SIRT4 gets in on the act. Cell. 126:837–839. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bartelt A, Bruns OT, Reimer R, Hohenberg
H, Ittrich H, Peldschus K, Kaul MG, Tromsdorf UI, Weller H,
Waurisch C, et al: Brown adipose tissue activity controls
triglyceride clearance. Nat Med. 17:200–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yoneshiro T, Aita S, Matsushita M,
Okamatsu-Ogura Y, Kameya T, Kawai Y, Miyagawa M, Tsujisaki M and
Saito M: Age-related decrease in cold-activated brown adipose
tissue and accumulation of body fat in healthy humans. Obesity
(Silver Spring). 19:1755–1760. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Tan CY, Virtue S, Bidault G, Dale M, Hagen
R, Griffin JL and Vidal-Puig A: Brown adipose tissue thermogenic
capacity is regulated by Elovl6. Cell Rep. 13:2039–2047. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Rogers NH, Landa A, Park S and Smith RG:
Aging leads to a programmed loss of brown adipocytes in murine
subcutaneous white adipose tissue. Aging Cell. 11:1074–1083. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Valle A, Guevara R, Garcia-Palmer FJ, Roca
P and Oliver J: Caloric restriction retards the age-related decline
in mitochondrial function of brown adipose tissue. Rejuvenation
Res. 11:597–604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Detmer SA and Chan DC: Functions and
dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:870–879. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lin AL, Coman D, Jiang L, Rothman DL and
Hyder F: Caloric restriction impedes age-related decline of
mitochondrial function and neuronal activity. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 34:1440–1443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Fitzgibbons TP, Kogan S, Aouadi M,
Hendricks GM, Straubhaar J and Czech MP: Similarity of mouse
perivascular and brown adipose tissues and their resistance to
diet-induced inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H1425–H1437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Villarroya F, Cereijo R, Villarroya J,
Gavaldà-Navarro A and Giralt M: Toward an understanding of how
immune cells control brown and beige adipobiology. Cell Metab.
27:954–961. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lorenzo M, Fernández-Veledo S, Vila-Bedmar
R, Garcia-Guerra L, De Alvaro C and Nieto-Vazquez I: Insulin
resistance induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in myocytes and
brown adipocytes. J Anim Sci. 86:E94–E104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Amitani M, Amitani H, Cheng KC, Kairupan
TS, Sameshima N, Shimoshikiryo I, Mizuma K, Rokot NT, Nerome Y,
Owaki T, et al: The role of ghrelin and ghrelin signaling in aging.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:15112017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Lee JY, Takahashi N, Yasubuchi M, Kim YI,
Hashizaki H, Kim MJ, Sakamoto T, Goto T and Kawada T:
Triiodothyronine induces UCP-1 expression and mitochondrial
biogenesis in human adipocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
302:C463–C472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Weiner J, Hankir M, Heiker JT, Fenske W
and Krause K: Thyroid hormones and browning of adipose tissue. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 458:156–159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Gustafson B, Hedjazifar S, Gogg S,
Hammarstedt A and Smith U: Insulin resistance and impaired
adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 26:193–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kajimura S, Seale P, Tomaru T,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Cooper MP, Ruas JL, Chin S, Tempst P, Lazar MA
and Spiegelman BM: Regulation of the brown and white fat gene
programs through a PRDM16/CtBP transcriptional complex. Genes Dev.
22:1397–1409. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Becerril S, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Martin M,
Moncada R, Sesma P, Burrell MA and Frühbeck G: Role of PRDM16 in
the activation of brown fat programming. Relevance to the
development of obesity. Histol Histopathol. 28:1411–1425.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Khanh VC, Zulkifli AF, Tokunaga C,
Yamashita T, Hiramatsu Y and Ohneda O: Aging impairs beige
adipocyte differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via the reduced
expression of Sirtuin 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 500:682–690.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A,
Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Boström EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, et al: A
PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of
white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 481:463–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Niranjan SB, Belwalkar SV, Tambe S,
Venkataraman K and Mookhtiar KA: Recombinant irisin induces weight
loss in high fat DIO mice through increase in energy consumption
and thermogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 519:422–429. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Shankar K, Kumar D, Gupta S, Varshney S,
Rajan S, Srivastava A, Gupta A, Gupta AP, Vishwakarma AL, Gayen JR
and Gaikwad AN: Role of brown adipose tissue in modulating adipose
tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat diet fed
mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 854:354–364. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wang W and Seale P: Control of brown and
beige fat development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:691–702. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
He L, Tang M, Xiao T, Liu H, Liu W, Li G,
Zhang F, Xiao Y, Zhou Z, Liu F and Hu F: Obesity-associated
miR-199a/214 cluster inhibits adipose browning via PRDM16-PGC-1α
transcriptional network. Diabetes. 67:2585–2600. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Yao L, Cui X, Chen Q, Yang X, Fang F,
Zhang J, Liu G, Jin W and Chang Y: Cold-inducible SIRT6 regulates
thermogenesis of brown and beige fat. Cell Rep. 20:641–654. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Gollisch KS, Brandauer J, Jessen N, Toyoda
T, Nayer A, Hirshman MF and Goodyear LJ: Effects of exercise
training on subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in normal- and
high-fat diet-fed rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
297:E495–E504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Knudsen JG, Murholm M, Carey AL, Biensø
RS, Basse AL, Allen TL, Hidalgo J, Kingwell BA, Febbraio MA, Hansen
JB and Pilegaard H: Role of IL-6 in exercise training- and
cold-induced UCP1 expression in subcutaneous white adipose tissue.
PLoS One. 9:e849102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Thirupathi A, da Silva Pieri BL, Queiroz
JAMP, Rodrigues MS, de Bem Silveira G, de Souza DR, Luciano TF,
Silveira PCL and De Souza CT: Strength training and aerobic
exercise alter mitochondrial parameters in brown adipose tissue and
equally reduce body adiposity in aged rats. J Physiol Biochem.
75:101–108. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Vosselman MJ, Hoeks J, Brans B,
Pallubinsky H, Nascimento EB, van der Lans AA, Broeders EP,
Mottaghy FM, Schrauwen P and van Marken Lichtenbelt WD: Low brown
adipose tissue activity in endurance-trained compared with lean
sedentary men. Int J Obes (Lond). 39:1696–1702. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Orava J, Nuutila P, Lidell ME, Oikonen V,
Noponen T, Viljanen T, Scheinin M, Taittonen M, Niemi T, Enerbäck S
and Virtanen KA: Different metabolic responses of human brown
adipose tissue to activation by cold and insulin. Cell Metab.
14:272–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Nirengi S, Homma T, Inoue N, Sato H,
Yoneshiro T, Matsushita M, Kameya T, Sugie H, Tsuzaki K, Saito M,
et al: Assessment of human brown adipose tissue density during
daily ingestion of thermogenic capsinoids using near-infrared
time-resolved spectroscopy. J Biomed Opt. 21:0913052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Kim SM, Jung YJ, Kwon ON, Cha KH, Um BH,
Chung D and Pan CH: A potential commercial source of fucoxanthin
extracted from the microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Appl
Biochem Biotechnol. 166:1843–1855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Bonet ML, Ribot J, Galmés S, Serra F and
Palou A: Carotenoids and carotenoid conversion products in adipose
tissue biology and obesity: Pre-clinical and human studies. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1865:1586762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hilgendorf KI, Johnson CT, Mezger A, Rice
SL, Norris AM, Demeter J, Greenleaf WJ, Reiter JF, Kopinke D and
Jackson PK: Omega-3 fatty acids activate ciliary FFAR4 to control
adipogenesis. Cell. 179:1289–1305.e21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Jiménez-Aranda A, Fernández-Vázquez G,
Campos D, Tassi M, Velasco-Perez L, Tan DX, Reiter RJ and Agil A:
Melatonin induces browning of inguinal white adipose tissue in
Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Pineal Res. 55:416–423. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zhang Y, Goldman S, Baerga R, Zhao Y,
Komatsu M and Jin S: Adipose-specific deletion of autophagy-related
gene 7 (atg7) in mice reveals a role in adipogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:19860–19865. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Martinez-Lopez N, Athonvarangkul D, Sahu
S, Coletto L, Zong H, Bastie CC, Pessin JE, Schwartz GJ and Singh
R: Autophagy in Myf5+ progenitors regulates energy and
glucose homeostasis through control of brown fat and skeletal
muscle development. EMBO Rep. 14:795–803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Tran CM, Mukherjee S, Ye L, Frederick DW,
Kissig M, Davis JG, Lamming DW, Seale P and Baur JA: Rapamycin
blocks induction of the thermogenic program in white adipose
tissue. Diabetes. 65:927–941. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Liu D, Bordicchia M, Zhang C, Fang H, Wei
W, Li JL, Guilherme A, Guntur K, Czech MP and Collins S: Activation
of mTORC1 is essential for β-adrenergic stimulation of adipose
browning. J Clin Invest. 126:1704–1716. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wada S, Neinast M, Jang C, Ibrahim YH, Lee
G, Babu A, Li J, Hoshino A, Rowe GC, Rhee J, et al: The tumor
suppressor FLCN mediates an alternate mTOR pathway to regulate
browning of adipose tissue. Genes Dev. 30:2551–2564. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|