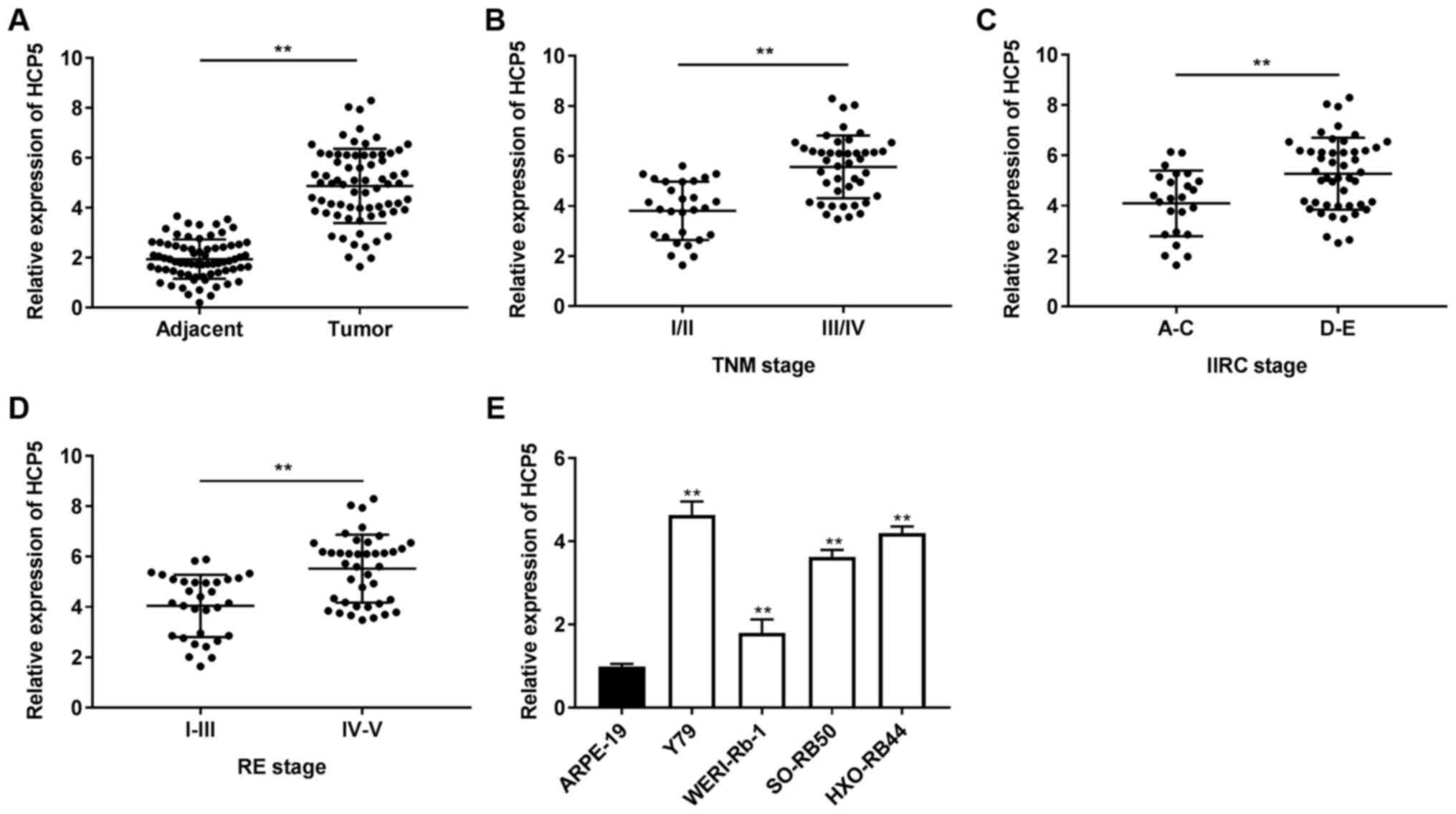
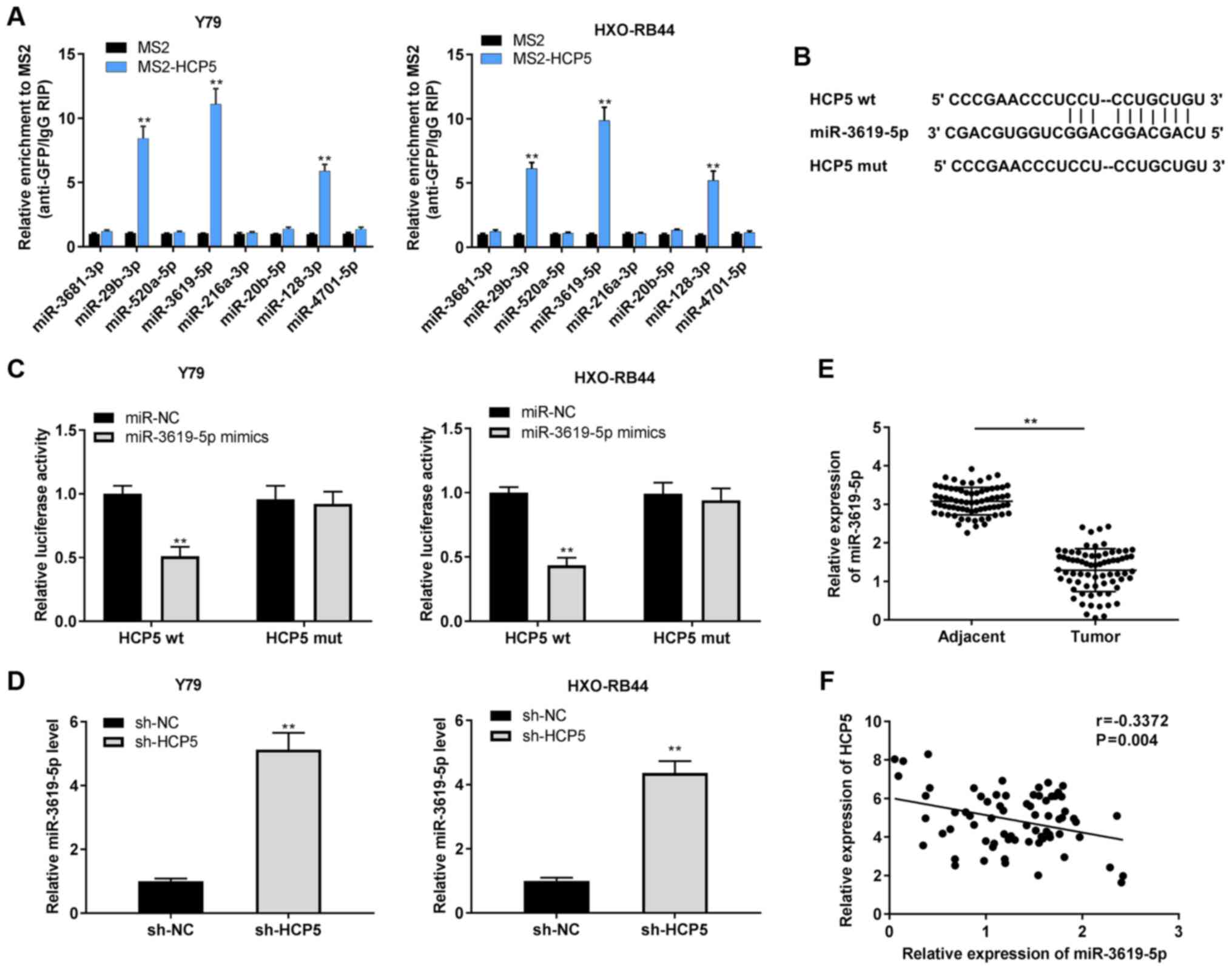
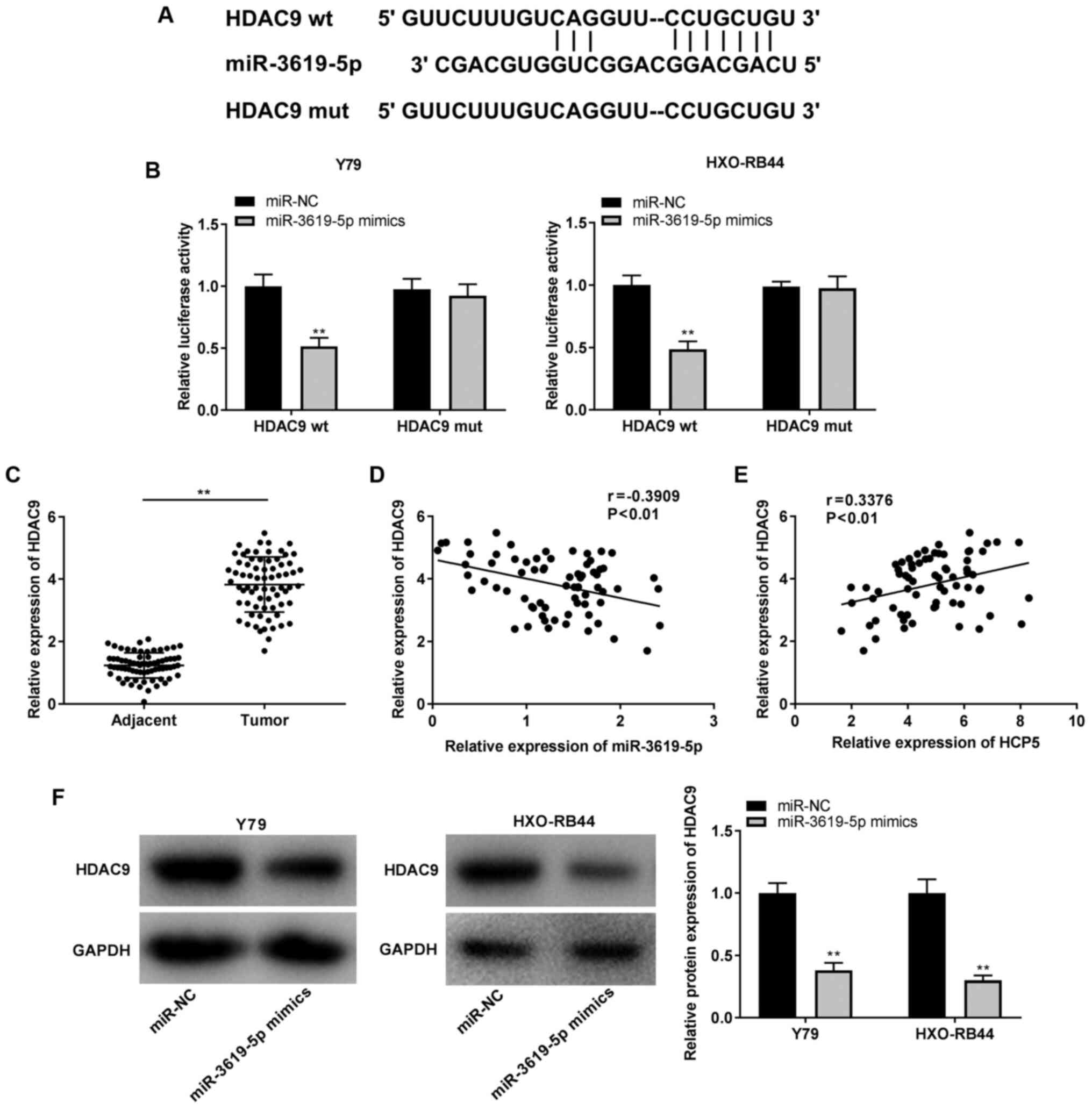
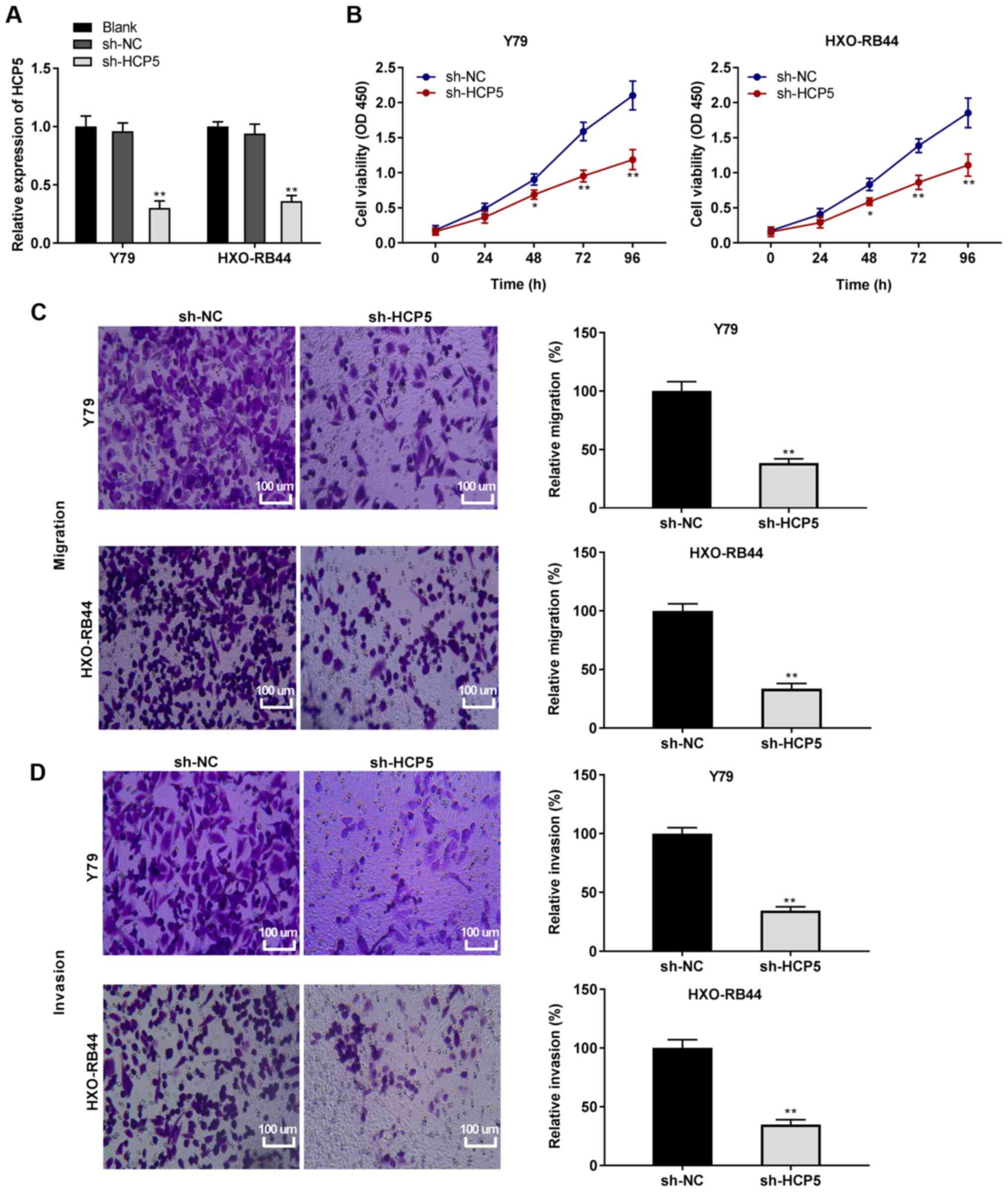
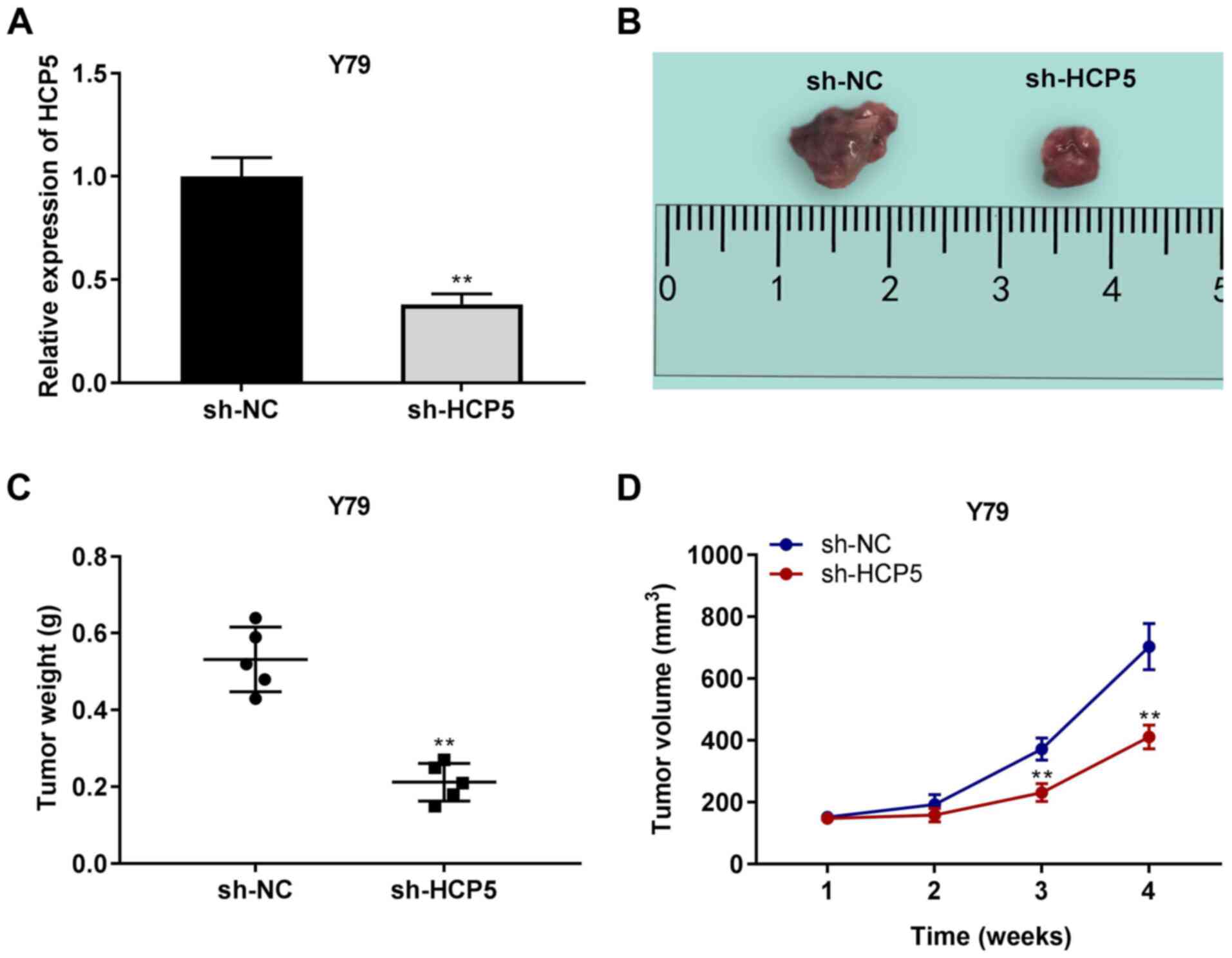
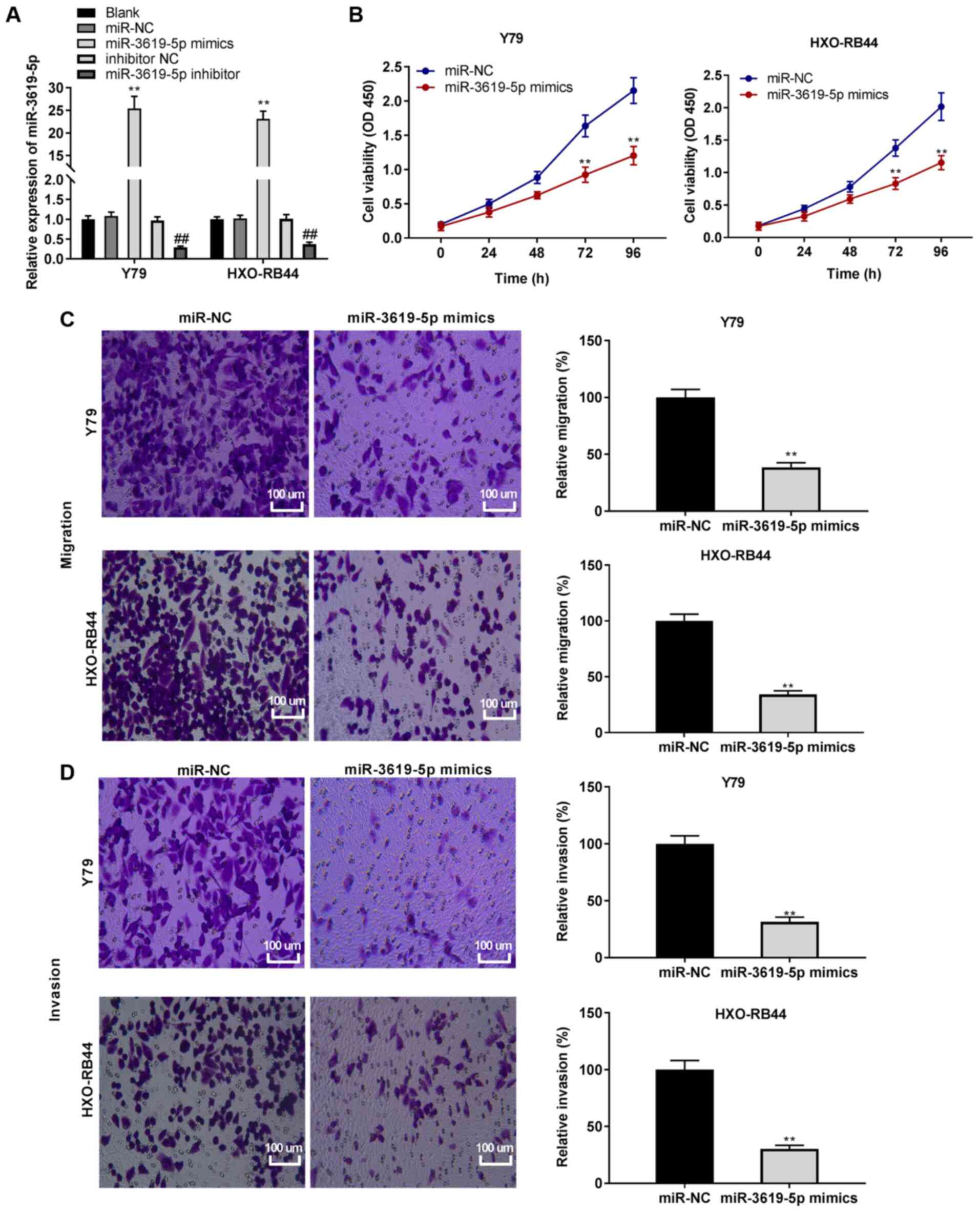
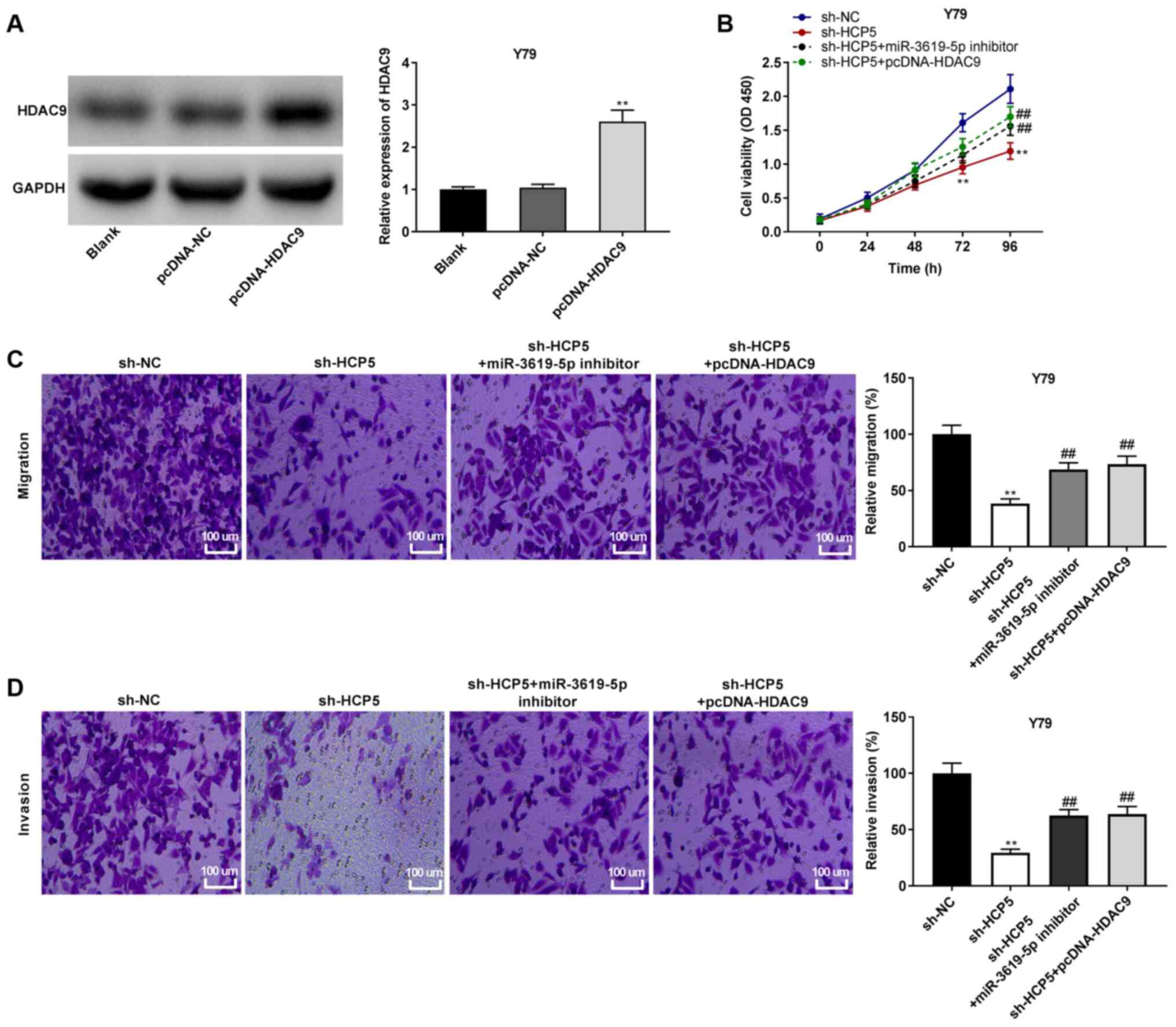
|
1
|
Villegas VM, Hess DJ, Wildner A, Gold AS
and Murray TG: Retinoblastoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 24:581–588.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cimino PJ, Robirds DH, Tripp SR, Pfeifer
JD, Abel HJ and Duncavage EJ: Retinoblastoma gene mutations
detected by whole exome sequencing of merkel cell carcinoma. Mod
Pathol. 27:1073–1087. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Venkatesan N, Deepa PR, Khetan V and
Krishnakumar S: Computational and in vitro investigation of
miRNA-Gene regulations in retinoblastoma pathogenesis: miRNA mimics
strategy. Bioinform Biol Insights. 9:89–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dimaras H, Corson TW, Cobrinik D, White A,
Zhao J, Munier FL, Abramson DH, Shields CL, Chantada GL, Njuguna F
and Gallie BL: Retinoblastoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150212015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okimoto S and Nomura K: Clinical
manifestations and treatment of retinoblastoma in Kobe children's
hospital for 16 years. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 51:222–229.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abu-Ain MS, Shatnawi R, Yousef YA and
Watts P: Heterochromia irides and mistaken identity of
retinoblastoma. BMJ Case Rep. 12:e2310912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jenkinson H: Retinoblastoma: Diagnosis and
management-the UK perspective. Arch Dis Child. 100:1070–1075. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rao R and Honavar SG: Retinoblastoma.
Indian J Pediatr. 84:937–944. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sullivan EM, Wilson MW, Billups CA, Wu J,
Merchant TE, Brennan RC, Haik BG, Shulkin B, Free TM, Given V, et
al: Pathologic risk-based adjuvant chemotherapy for unilateral
retinoblastoma following enucleation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
36:e335–e340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qaddoumi I, Nawaiseh I, Mehyar M, Razzouk
B, Haik BG, Kharma S, Jaradat I, Rodriguez-Galindo C and Wilson MW:
Team management, twinning, and telemedicine in retinoblastoma: A
3-tier approach implemented in the first eye salvage program in
Jordan. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 51:241–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chantada GL, Dunkel IJ, Schaiquevich PS,
Grynszpancholc EL, Francis J, Ceciliano A, Zubizarreta PA, Fandiño
AC and Abramson DH: Twenty-Year collaboration between north
American and South American retinoblastoma programs. J Glob Oncol.
2:347–352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang X, Arai S, Song X, Reichart D, Du K,
Pascual G, Tempst P, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK and Kurokawa R: Induced
ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit
transcription. Nature. 454:126–130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:7–21. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
He X, Chai P, Li F, Zhang L, Zhou C, Yuan
X, Li Y, Yang J, Luo Y, Ge S, et al: A novel LncRNA transcript,
RBAT1, accelerates tumorigenesis through interacting with HNRNPL
and cis-activating E2F3. Mol Cancer. 19:1152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han S, Song L, Chen Y, Hou M, Wei X and
Fan D: The long non-coding RNA ILF3-AS1 increases the proliferation
and invasion of retinoblastoma through the miR-132-3p/SMAD2 axis.
Exp Cell Res. 393:1120872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong Y, Wan G, Yan P, Qian C, Li F and
Peng G: Long noncoding RNA LINC00324 promotes retinoblastoma
progression by acting as a competing endogenous RNA for
microRNA-769-5p, thereby increasing STAT3 expression. Aging (Albany
NY). 12:7729–7746. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vernet C, Ribouchon MT, Chimini G,
Jouanolle AM, Sidibe I and Pontarotti P: A novel coding sequence
belonging to a new multicopy gene family mapping within the human
MHC class I region. Immunogenetics. 38:47–53. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Helms C, Liao W, Zaba LC, Duan S,
Gardner J, Wise C, Miner A, Malloy MJ, Pullinger CR, et al: A
genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
identifies new disease loci. PLoS Genet. 4:e10000412008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bai N, Ma Y, Zhao J and Li B: Knockdown of
lncRNA HCP5 suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer by
miR-299-3p/PFN1/AKT axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:4747–4758. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, He M, Fu L and Jin Y: Role of
lncRNAHCP5/microRNA-525-5p/PRC1 crosstalk in the malignant
behaviors of ovarian cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 394:1121292020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuan B, Guan Q, Yan T, Zhang X, Xu W and
Li J: LncRNA HCP5 regulates pancreatic cancer progression by
miR-140-5p/CDK8 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:711–719. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wan W, Long Y, Li Q, Jin X, Wan G, Zhang
F, Lv Y, Zheng G, Li Z and Zhu Y: MiR-25-3p promotes malignant
phenotypes of retinoblastoma by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1091112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J and You X: MicroRNA758 inhibits
malignant progression of retinoblastoma by directly targeting PAX6.
Oncol Rep. 40:1777–1786. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hao P, Yue F, Xian X, Ren Q, Cui H and
Wang Y: Inhibiting effect of MicroRNA-3619-5p/PSMD10 axis on liver
cancer cell growth in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 254:1176322020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan G, Su Y, Ma Z, Yu L and Chen N: Long
noncoding RNA LINC00202 promotes tumor progression by sponging
miR-3619-5p in retinoblastoma. Cell Struct Funct. 44:51–60. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parra M and Verdin E: Regulatory signal
transduction pathways for class IIa histone deacetylases. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 10:454–460. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Wu D, Xia F, Xian H, Zhu X, Cui H
and Huang Z: Downregulation of HDAC9 inhibits cell proliferation
and tumor formation by inducing cell cycle arrest in
retinoblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:600–606. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin Q, He W, Chen L, Yang Y, Shi K and You
Z: MicroRNA-101-3p inhibits proliferation in retinoblastoma cells
by targeting EZH2 and HDAC9. Exp Ther Med. 16:1663–1670.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu L, Li W, Shi Q, Wang M, Li H, Yang X
and Zhang J: MicroRNA936 inhibits the malignant phenotype of
retinoblastoma by directly targeting HDAC9 and deactivating the
PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Rep. 43:635–645. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
TNM8: The updated TNM classification for
retinoblastoma. Community Eye Health. 31:342018.
|
|
31
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Basic
understanding of current classification and management of
retinoblastoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 17:228–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yousef YA, Al-Hussaini M, Mehyar M, Sultan
I, Jaradat I, AlRawashdeh K, Khurma S, Deebajah R and Nawaiseh I:
Predictive value of tnm classification, international
classification, and reese-ellsworth staging of retinoblastoma for
the likelihood of high-risk pathologic features. Retina.
35:1883–1889. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yu Y, Shen HM, Fang DM, Meng QJ and Xin
YH: LncRNA HCP5 promotes the development of cervical cancer by
regulating MACC1 via suppression of microRNA-15a. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:4812–4819. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu R and Lu Z: Long noncoding RNA HCP5
promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by acting as the sponge
of miR4656 to modulate CEMIP expression. Oncol Rep. 43:328–336.
2020.
|
|
36
|
Zhao J, Bai X, Feng C, Shang X and Xi Y:
Long non-coding RNA HCP5 facilitates cell invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma
by miR-140-5p/SOX4 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 11:10455–10462. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang L, Luan T, Zhou S, Lin J, Yang Y, Liu
W, Tong X and Jiang W: LncRNA HCP5 promotes triple negative breast
cancer progression as a ceRNA to regulate BIRC3 by sponging
miR-219a-5p. Cancer Med. 8:4389–4403. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Niu X, Liu S, Jia L and Chen J: Role of
MiR-3619-5p in β-catenin-mediated non-small cell lung cancer growth
and invasion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:1527–1536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lv MH, Mao QX, Li JT, Qiao J, Chen X and
Luo S: Knockdown of LINC00665 inhibits proliferation and invasion
of breast cancer via competitive binding of miR-3619-5p and
inhibition of catenin beta 1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 25:432020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu S, Chu B, Cai C, Wu X, Yao W, Wu Z,
Yang Z, Li F, Liu Y, Dong P and Gong W: DGCR5 promotes gallbladder
cancer by sponging MiR-3619-5p via MEK/ERK1/2 and JNK/p38 MAPK
pathways. J Cancer. 11:5466–5477. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu C, Hu Y, Ning Y, Zhao A, Zhang G and
Yan L: Long noncoding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1
regulates cisplatin resistance via miR-3619-5p/TBL1XR1 axis in
gastric cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:741–752. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|