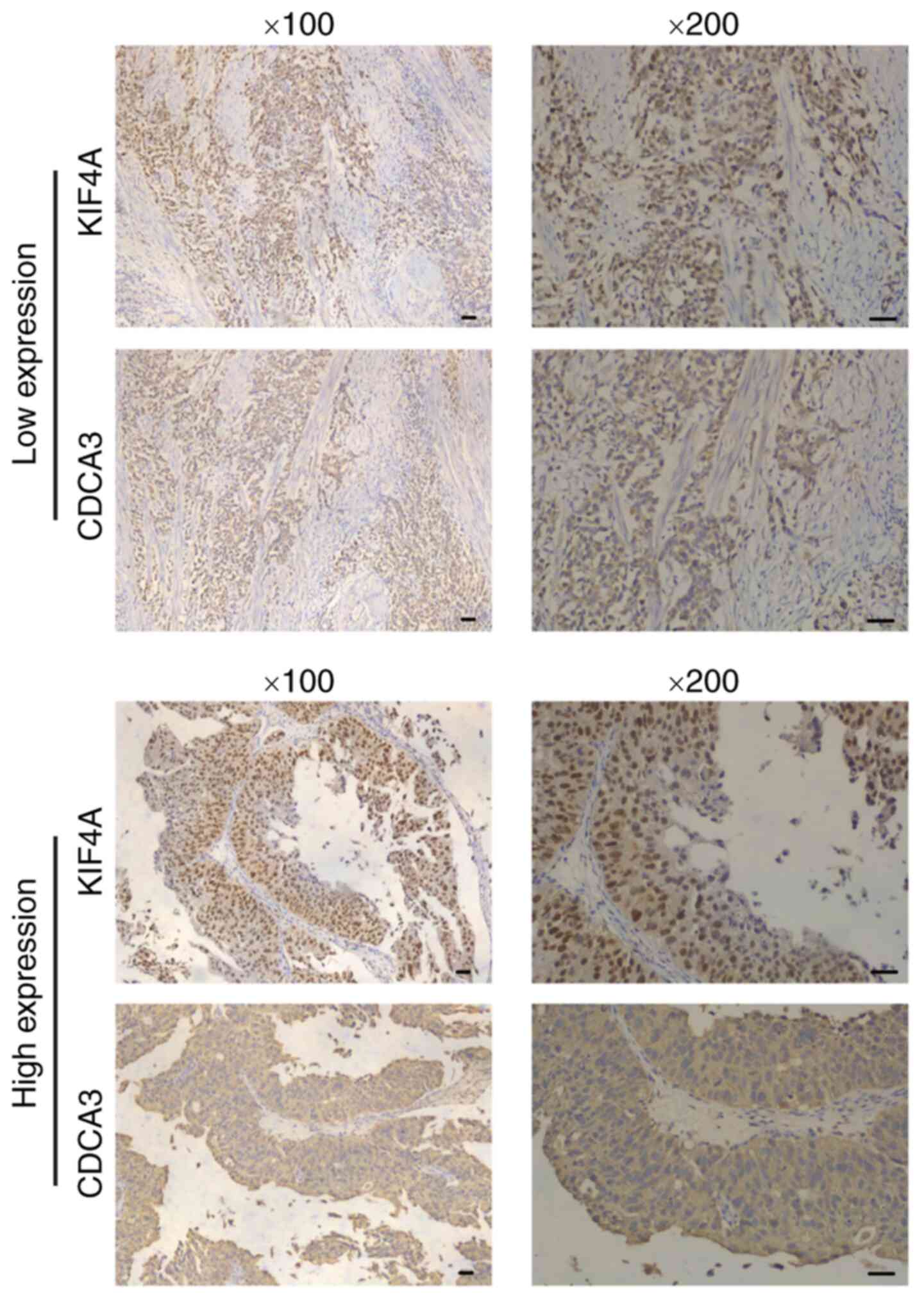
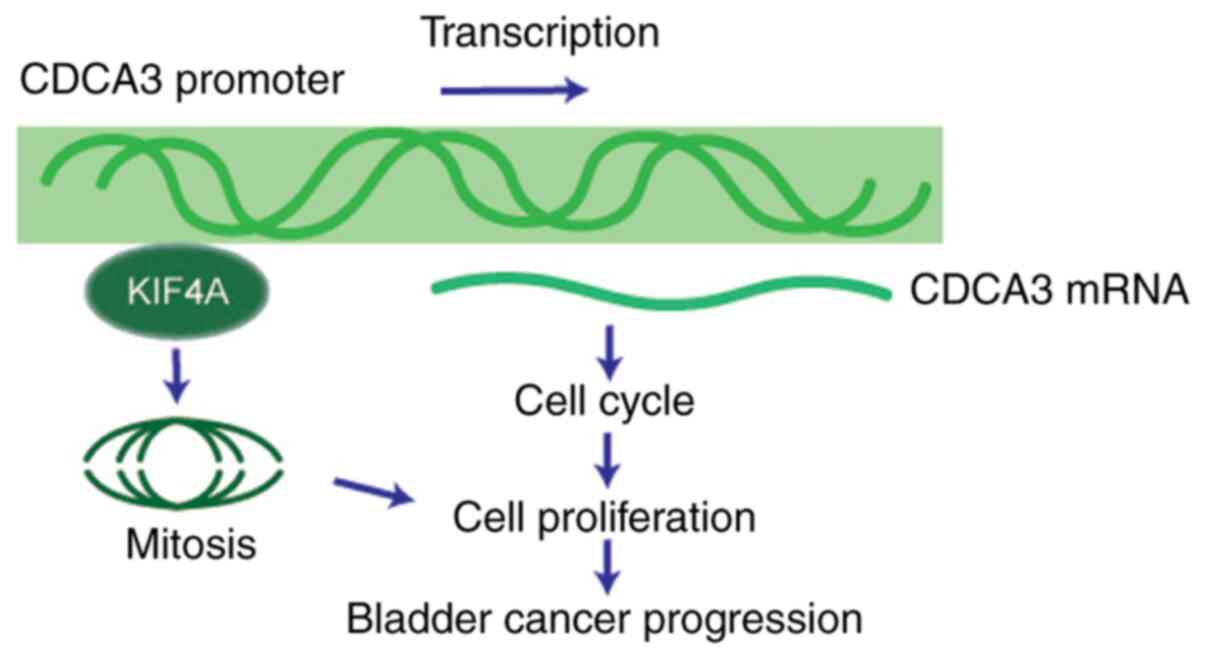
|
1
|
Williams SB, Shan Y, Jazzar U, Mehta HB,
Baillargeon JG, Huo J, Huo J, Senagore AJ, Orihuela E, Tyler DS, et
al: Comparing survival outcomes and costs associated with radical
cystectomy and trimodal therapy for older adults with
Muscle-Invasive bladder cancer. JAMA Surg. 153:881–889. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giulietti M, Occhipinti G, Righetti A,
Bracci M, Conti A, Ruzzo A, Cerigioni E, Cacciamani T, Principato G
and Piva F: Emerging biomarkers in bladder cancer identified by
network analysis of transcriptomic data. Front Oncol. 8:4502018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Terzic M, Ladjevic IL, Ladjevic N, Terzic
S, Dotlic J, Cekerevac M, Arsenovic N, Laganà AS and Vereczkey A:
Anaplastic T-cell lymphoma of the urinary bladder with unspecific
clinical and radiological characteristics - a unique case report.
Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 40:136–139. 2019.
|
|
4
|
Tan WS, Rodney S, Lamb B, Feneley M and
Kelly J: Management of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A
comprehensive analysis of guidelines from the United States, Europe
and Asia. Cancer Treat Rev. 47:22–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Chang Q and Li Y: Racial
differences in Urinary bladder cancer in the United States. Sci
Rep. 8:125212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Crabb SJ and Douglas J: The latest
treatment options for bladder cancer. Br Med Bull. 128:85–95. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakaguchi M, Maebayashi T, Aizawa T,
Ishibashi N and Saito T: Clinical results for bladder cancer
treated by radiotherapy without concurrent standard chemotherapy.
Anticancer Res. 36:5519–5525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li R, Metcalfe MJ, Ferguson JE III,
Mokkapati S, Nogueras Gonzalez GM, Dinney CP, Navai N, McConkey DJ,
Sahai SK and Kamat AM: Effects of thiazolidinedione in patients
with active bladder cancer. BJU Int. 121:244–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
DeGeorge KC, Holt HR and Hodges SC:
Bladder cancer: Diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician.
96:507–514. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abbosh PH, McConkey DJ and Plimack ER:
Targeting signaling transduction pathways in bladder cancer. Curr
Oncol Rep. 17:582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang YJ and Yang WX: Kinesins in MAPK
cascade: How kinesin motors are involved in the MAPK pathway? Gene.
684:1–9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rath O and Kozielski F: Kinesins and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:527–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chudy A, Gajewska B, Gutowicz M and
Baranczyk-Kuzma A: Intracellular transport proteins:
Classification, structure and function of kinesins. Postepy Hig Med
Dosw (Online). 65:588–596. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Heintz TG, Heller JP, Zhao R, Caceres A,
Eva R and Fawcett JW: Kinesin KIF4A transports integrin β1 in
developing axons of cortical neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 63:60–71.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu G and Chen PL: Structural requirements
of chromokinesin Kif4A for its proper function in mitosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 372:454–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mazumdar M, Sundareshan S and Misteli T:
Human chromokinesin KIF4A functions in chromosome condensation and
segregation. J Cell Biol. 166:613–620. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tipton AR, Wren JD, Daum JR, Siefert JC
and Gorbsky GJ: GTSE1 regulates spindle microtubule dynamics to
control Aurora B kinase and Kif4A chromokinesin on chromosome arms.
J Cell Biol. 216:3117–3132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang F, Pan MH, Lu Y, Wan X, Zhang Y and
Sun SC: Involvement of Kif4a in Spindle formation and chromosome
segregation in Mouse Oocytes. Aging Dis. 9:623–633. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu G, Zhou L, Khidr L, Guo XE, Kim W, Lee
YM, Krasieva T and Chen PL: A novel role of the chromokinesin Kif4A
in DNA damage response. Cell Cycle. 7:2013–2020. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsumoto Y, Saito M, Saito K, Kanke Y,
Watanabe Y, Onozawa H, Hayase S, Sakamoto W, Ishigame T, Momma T,
et al: Enhanced expression of KIF4A in colorectal cancer is
associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncol Lett. 15:2188–2194.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taniwaki M, Takano A, Ishikawa N, Yasui W,
Inai K, Nishimura H, Tsuchiya E, Kohno N, Nakamura Y and Daigo Y:
Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic
target for lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6624–6631. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou G, Dong C, Dong Z, Liu G, Xu H, Chen
L, Liu L, Wang H and Zhou W: Upregulate KIF4A enhances
proliferation, invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma and indicates
poor prognosis across human cancer types. Sci Rep. 7:41482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Phan NN, Wang CY, Li KL, Chen CF, Chiao
CC, Yu HG, Huang PL and Lin YC: Distinct expression of CDCA3,
CDCA5, and CDCA8 leads to shorter relapse free survival in breast
cancer patient. Oncotarget. 9:6977–6992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Yin W, Cao W, Chen P, Bian L and
Ni Q: CDCA3 is a potential prognostic marker that promotes cell
proliferation in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 41:2471–2481.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dou D, Ren X, Han M, Xu X, Ge X, Gu Y,
Wang X and Zhao S: CircUBE2D2 (hsa_circ_0005728) promotes cell
proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance in triple-negative
breast cancer by regulating miR-512-3p/CDCA3 axis. Cancer Cell Int.
20:4542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Q, Zhou L, Ye X, Tao M and Wu J:
MiR-145-5p suppresses proliferation, metastasis and EMT of
colorectal cancer by targeting CDCA3. Pathol Res Pract.
216:1528722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yamaoka T, Kusumoto S, Ando K, Ohba M and
Ohmori T: Receptor tyrosine kinase-targeted cancer therapy. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:34912018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
He YT, Li DJ, Liang D, Zheng RS, Zhang SW,
Zeng HM, Chen WQ and He J: Incidence and mortality of BC in China.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 40:647–652. 2018.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Y, Zhao Z, Xie C and Zhao Y:
Dual-targeting liposome modified by glutamic hexapeptide and folic
acid for bone metastatic breast cancer. Chem Phys Lipids.
228:1048822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao Z, Zhao Y, Xie C, Chen C, Lin D, Wang
S, Lin D, Cui X, Guo Z and Zhou J: Dual-active targeting liposomes
drug delivery system for bone metastatic breast cancer: Synthesis
and biological evaluation. Chem Phys Lipids. 223:1047852019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soria F, Krabbe LM, Todenhofer T, Dobruch
J, Mitra AP, Inman BA, Gust KM, Lotan Y and Shariat SF: Molecular
markers in bladder cancer. World J Urol. 37:31–40. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Dong Z, Zhu C, Zhan Q and Jiang W: Cdk
phosphorylation licenses Kif4A chromosome localization required for
early mitotic progression. J Mol Cell Biol. 10:358–370. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nunes Bastos R, Gandhi SR, Baron RD,
Gruneberg U, Nigg EA and Barr FA: Aurora B suppresses microtubule
dynamics and limits central spindle size by locally activating
KIF4A. J Cell Biol. 202:605–621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wan Q, Shen Y, Zhao H, Wang B, Zhao L,
Zhang Y, Bu X, Wan M and Shen C: Impaired DNA double-strand breaks
repair by kinesin family member 4A inhibition renders human H1299
non-small-cell lung cancer cells sensitive to cisplatin. J Cell
Physiol. 234:10360–10371. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang Y, Wang H, Lian Y, Wu X, Zhou L,
Wang J, Deng M and Huang Y: Upregulation of kinesin family member
4A enhanced cell proliferation via activation of Akt signaling and
predicted a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death
Dis. 9:1412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Minakawa Y, Kasamatsu A, Koike H, Higo M,
Nakashima D, Kouzu Y, Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H
and Uzawa K: Kinesin family member 4A: A potential predictor for
progression of human oral cancer. PLoS One. 8:e859512013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Lu C, Li Q, Xie J, Chen T, Tan Y,
Wu C and Jiang J: The role of Kif4A in doxorubicin-induced
apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Mol Cells. 37:812–818. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao J, Sai N, Wang C, Sheng X, Shao Q,
Zhou C, Shi Y, Sun S, Qu X and Zhu C: Overexpression of
chromokinesin KIF4 inhibits proliferation of human gastric
carcinoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. 32:53–61.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee YM and Kim W: Association of human
kinesin superfamily protein member 4 with BRCA2-associated factor
35. Biochem J. 374:497–503. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao H, Chen X, Cai Q, Shang Z and Niu Y:
Increased KIF4A expression is a potential prognostic factor in
prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:7941–7947. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li S, Liu X, Liu T, Meng X, Yin X, Fang C,
Huang D, Cao Y, Weng H, Zeng X and Wang X: Identification of
biomarkers correlated with the TNM staging and overall survival of
patients with bladder cancer. Front Physiol. 8:9472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li B, Liu B, Zhang X, Liu H and He L:
KIF18B promotes the proliferation of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma via activating the expression of CDCA8. J Cell
Physiol. 235:4227–4238. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen J, Zhu S, Jiang N, Shang Z, Quan C
and Niu Y: HoxB3 promotes prostate cancer cell progression by
transactivating CDCA3. Cancer Lett. 330:217–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Uchida F, Uzawa K, Kasamatsu A, Takatori
H, Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H and Bukawa H:
Overexpression of cell cycle regulator CDCA3 promotes oral cancer
progression by enhancing cell proliferation with prevention of G1
phase arrest. BMC Cancer. 12:3212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang W, Lu Y and Li X, Zhang J, Zheng L,
Zhang W, Lin C, Lin W and Li X: CDCA3 promotes cell proliferation
by activating the NF-κB/cyclin D1 signaling pathway in colorectal
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 500:196–203. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Takeuchi H, Taoka R, Mmeje CO, Jinesh GG,
Safe S and Kamat AM: Urol Oncol. CDODA-Me decreases specificity
protein transcription factors and induces apoptosis in bladder
cancer cells through induction of reactive oxygen species. Urol
Oncol. 34:337.e11–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Takeuchi H, Tanaka M, Tanaka A, Tsunemi A
and Yamamoto H: Predominance of M2-polarized macrophages in bladder
cancer affects angiogenesis, tumor grade and invasiveness. Oncol
Lett. 11:3403–3408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takeuchi H, Mmeje CO, Jinesh GG, Taoka R
and Kamat AM: Sequential gemcitabine and tamoxifen treatment
enhances apoptosis and blocks transformation in bladder cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 34:2738–2744. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|