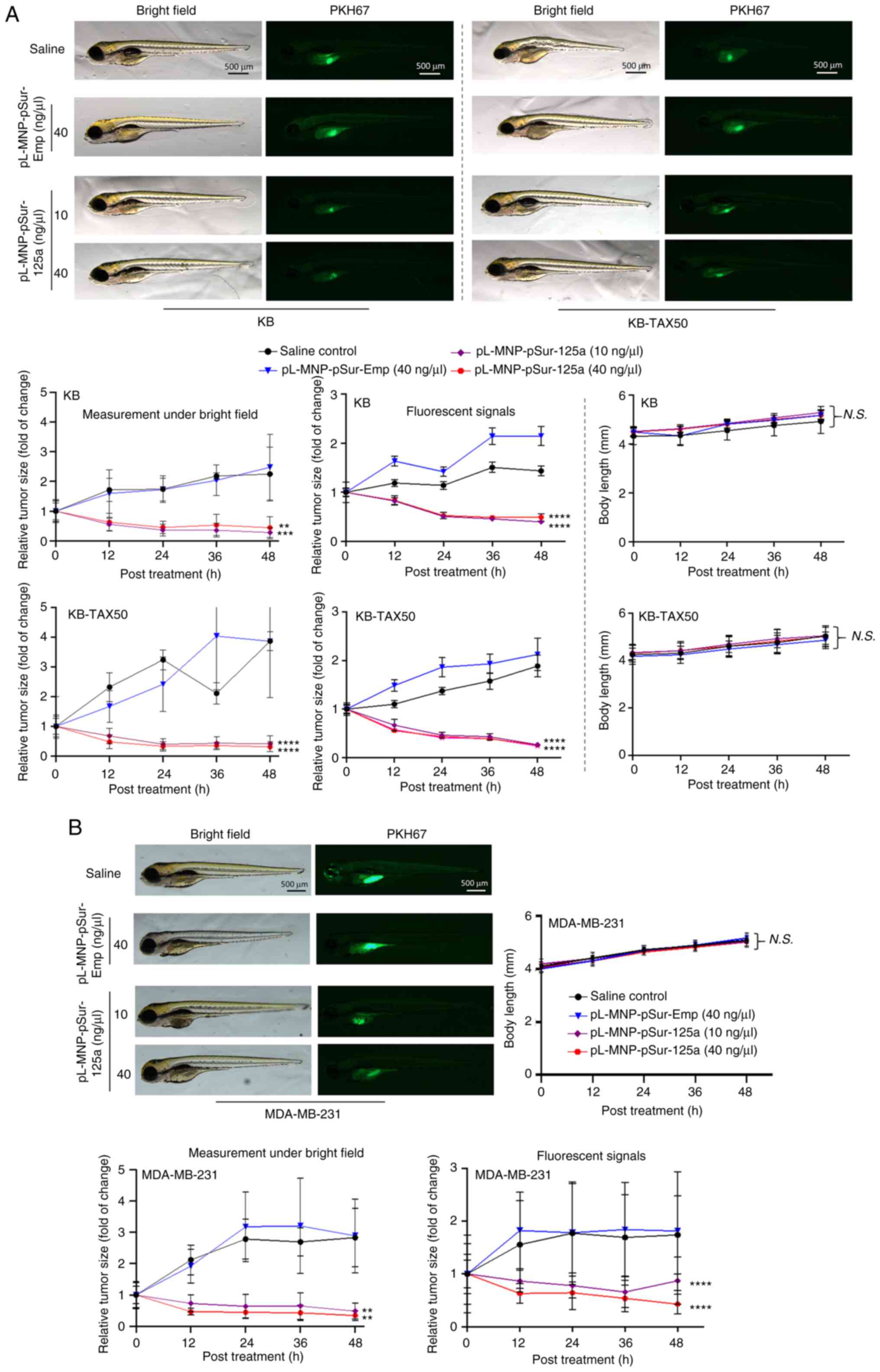
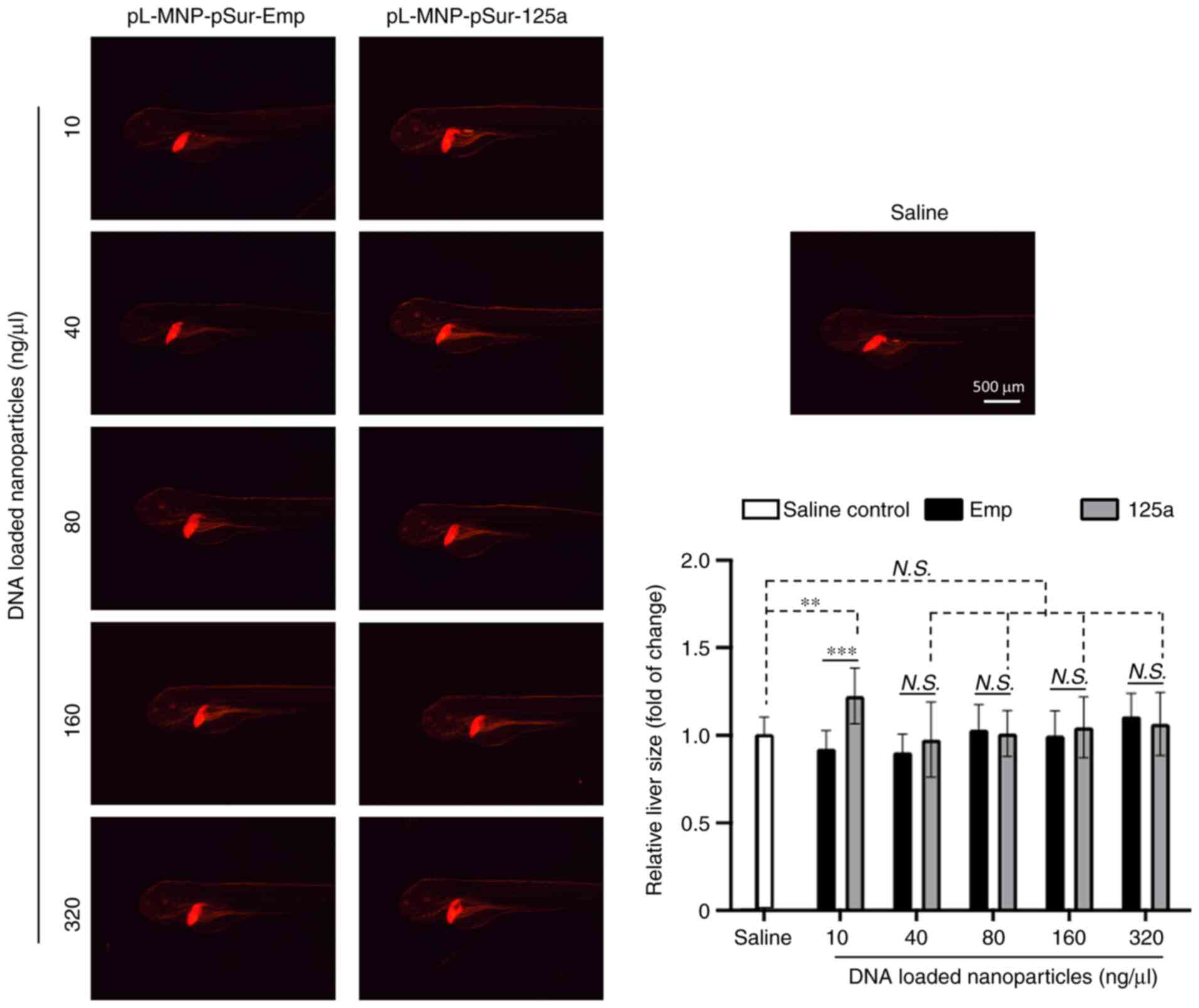
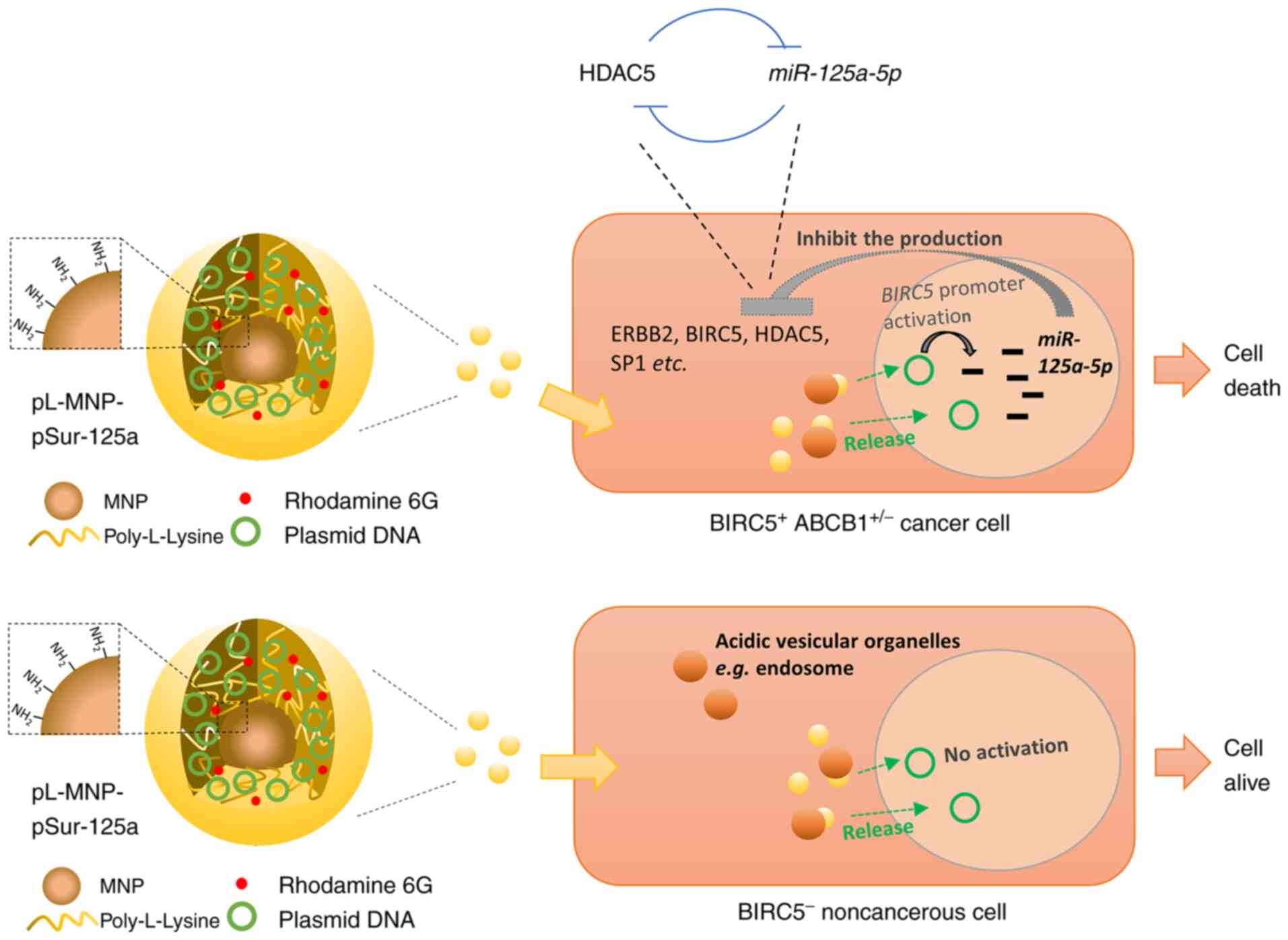
|
1
|
Groenendijk FH and Bernards R: Drug
resistance to targeted therapies: Déjà vu all over again. Mol
Oncol. 8:1067–1083. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie L and Bourne PE: Developing
multi-target therapeutics to fine-tune the evolutionary dynamics of
the cancer ecosystem. Front Pharmacol. 6:2092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Antolin AA, Workman P, Mestres J and
Al-Lazikani B: Polypharmacology in precision oncology: Current
applications and future prospects. Curr Pharm Design. 22:6935–6945.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nishida N, Mimori K, Fabbri M, Yokobori T,
Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Ishii H, Doki Y and Mori M:
MicroRNA-125a-5p is an independent prognostic factor in gastric
cancer and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells
in combination with trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2725–2733.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hsieh TH, Hsu CY, Tsai CF, Long CY, Chai
CY, Hou MF, Lee JN, Wu DC, Wang SC and Tsai EM: miR-125a-5p is a
prognostic biomarker that targets HDAC4 to suppress breast
tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 6:4942014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Vo DT, Karanam NK, Ding L, Saha D, Yordy
JS, Giri U, Heymach JV and Story MD: miR-125a-5p functions as tumor
suppressor microRNA and is a marker of locoregional recurrence and
poor prognosis in head and neck cancer. Neoplasia. 21:849–862.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang Z, Pan Q, Zhang Z, Huang C, Yan Z,
Zhang Y and Li J: MicroRNA-125a-5p controls the proliferation,
apoptosis, migration and PTEN/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 20:4507–4514. 2019.
|
|
8
|
Yan L, Yu MC, Gao GL, Liang HW, Zhou XY,
Zhu ZT, Zhang CY, Wang YB and Chen X: MiR-125a-5p functions as a
tumour suppressor in breast cancer by downregulating BAP1. J Cell
Biochem. 119:8773–8783. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tang L, Zhou L, Wu S, Shi X, Jiang G, Niu
S and Ding D: miR-125a-5p inhibits colorectal cancer cell
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration by
targeting TAZ. Onco Targets Ther. 12:3481–3489. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tong Z, Liu N, Lin L, Guo X, Yang D and
Zhang Q: miR-125a-5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces
apoptosis in colon cancer via targeting BCL2, BCL2L12 and MCL1.
Biomed Pharmacother. 75:129–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhong L, Sun S, Shi J, Cao F, Han X and
Chen Z: MicroRNA-125a-5p plays a role as a tumor suppressor in lung
carcinoma cells by directly targeting STAT3. Tumor Biol.
39:10104283176975792017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hsieh TH, Hsu CY, Tsai CF, Long CY, Wu CH,
Wu DC, Lee JN, Chang WC and Tsai EM: HDAC inhibitors target HDAC5,
upregulate microRNA-125a-5p and induce apoptosis in breast cancer
cells. Mol Ther. 23:656–666. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Xu Y, Zheng Y, Duan Y, Ma L and Nan P:
MicroRNA-125a-5p targets LIM kinase 1 to inhibit cisplatin
resistance of cervical cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 21:3922021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Cao Q, Wang N, Ren L, Tian J, Yang S and
Cheng H: miR-125a-5p post-transcriptionally suppresses GALNT7 to
inhibit proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer cells via the
EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 20:1172020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Huang WT, Tsai YH, Chen SH, Kuo CW, Kuo
YL, Lee KT, Chen WC, Wu PC, Chuang CY, Cheng SM, et al: HDAC2 and
HDAC5 up-regulations modulate survivin and miR-125a-5p expressions
and promote hormone therapy resistance in estrogen receptor
positive breast cancer cells. Front Pharmacol. 8:9022017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Li A, Shi J, Fang Y, Gu C, Cai J,
Lin C, Zhao L and Liu S: Imbalanced LIMK1 and LIMK2 expression
leads to human colorectal cancer progression and metastasis via
promoting β-catenin nuclear translocation. Cell Death Dis.
9:7492018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cheung CH, Chen HH, Kuo CC, Chang CY,
Coumar MS, Hsieh HP and Chang JY: Survivin counteracts the
therapeutic effect of microtubule de-stabilizers by stabilizing
tubulin polymers. Mol Cancer. 8:432009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mahalaxmi I and Santhy KS: Role and
hallmarks of Sp1 in promoting ovarian cancer. J Oncol Sci.
4:102–105. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jiang Y, de Bruin A, Caldas H, Fangusaro
J, Hayes J, Conway EM, Robinson ML and Altura RA: Essential role
for survivin in early brain development. J Neurosci. 25:6962–6970.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vischioni B, van der Valk P, Span SW,
Kruyt FAE, Rodriguez JA and Giaccone G: Nuclear localization of
survivin is a positive prognostic factor for survival in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 15:1654–1660. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Yan R, Zhang Q, Wang H, Kang X,
Li J, Yang S, Zhang J, Liu Z and Yang X: Survivin, a key component
of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, contributes to traumatic
brain injury-induced adult neurogenesis in the mouse dentate gyrus.
Int J Mol Med. 32:867–875. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bao R, Connolly DC, Murphy M, Green J,
Weinstein JK, Pisarcik DA and Hamilton TC: Activation of
cancer-specific gene expression by the survivin promoter. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 94:522–528. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang L, Cao Z, Li F, Post DE, Van Meir EG,
Zhong H and Wood WC: Tumor-specific gene expression using the
survivin promoter is further increased by hypoxia. Gene Ther.
11:1215–1223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Siddharth S, Das S, Nayak A and Kundu CN:
Survivin as a marker for quiescent-breast cancer stem cells-An
intermediate, adherent, pre-requisite phase of breast cancer
metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 33:661–675. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carter BZ, Qiu Y, Huang X, Diao L, Zhang
N, Coombes KR, Mak DH, Konopleva M, Cortes J, Kantarjian HM, et al:
Survivin is highly expressed in CD34+38-leukemic stem/progenitor
cells and predicts poor clinical outcomes in AML. Blood.
120:173–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Yan H, Li R, Guo Y and Zheng R:
High expression of survivin predicts poor prognosis in cervical
squamous cell carcinoma treated with paclitaxel and carboplatin.
Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e156072019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Onodi F, Maherzi-Mechalikh C, Mougel A,
Hamouda NB, Taboas C, Gueugnon F, Tran T, Nozach H, Marcon E, Gey
A, et al: High therapeutic efficacy of a new survivin LSP-cancer
vaccine containing CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell epitopes. Front Oncol.
8:5172018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Voges Y, Michaelis M, Rothweiler F,
Schaller T, Schneider C, Politt K, Mernberger M, Nist A, Stiewe T,
Wass MN, et al: Effects of YM155 on survivin levels and viability
in neuroblastoma cells with acquired drug resistance. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e24102016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Nakahara T, Kita A, Yamanaka K, Mori M,
Amino N, Takeuchi M, Tominaga F, Hatakeyama S, Kinoyama I,
Matsuhisa A, et al: YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin
suppressant, induces regression of established human
hormone-refractory prostate tumor xenografts. Cancer Res.
67:8014–8021. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hansen JB, Fisker N, Westergaard M,
Kjaerulff LS, Hansen HF, Thrue CA, Rosenbohm C, Wissenbach M, Orum
H and Koch T: SPC3042: A proapoptotic survivin inhibitor. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:2736–2745. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tolcher AW, Mita A, Lewis LD, Garrett CR,
Till E, Daud AI, Patnaik A, Papadopoulos K, Takimoto C, Bartels P,
et al: Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of YM155, a small-molecule
inhibitor of survivin. J Clin Oncol. 26:5198–5203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheung CHA, Sun X, Kanwar JR, Bai JZ,
Cheng L and Krissansen GW: A cell-permeable dominant-negative
survivin protein induces apoptosis and sensitizes prostate cancer
cells to TNF-α therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 10:362010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tsai SL, Chang YC, Sarvagalla S, Wang S,
Coumar MS and Cheung CHA: Cloning, expression, and purification of
the recombinant pro-apoptotic dominant-negative survivin T34A-C84A
protein in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 160:73–83. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Quispe PA, Lavecchia MJ and León IE: On
the discovery of a potential survivin inhibitor combining
computational tools and cytotoxicity studies. Heliyon.
5:e022382019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Arigita C, Zuidam NJ, Crommelin DJ and
Hennink WE: Association and dissociation characteristics of
polymer/DNA complexes used for gene delivery. Pharm Res.
16:1534–1541. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin KY, Cheng SM, Tsai SL, Tsai JY, Lin CH
and Cheung CHA: Delivery of a survivin promoter-driven antisense
survivin-expressing plasmid DNA as a cancer therapeutic: A
proof-of-concept study. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2601–2613.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheung CH, Lin WH, Hsu JTA, Hour TC, Yeh
TK, Ko S, Lien TW, Coumar MS, Liu JF, Lai WY, et al: BPR1K653, a
novel Aurora kinase inhibitor, exhibits potent anti-proliferative
activity in MDR1 (P-gp170)-mediated multidrug-resistant cancer
cells. PLoS One. 6:e234852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chang YC, Kondapuram SK, Yang TH, Syed SB,
Cheng SM, Lin TY, Lin YC, Coumar MS, Chang JY, Leung E and Cheung
CHA: The SMAC mimetic LCL161 is a direct ABCB1/MDR1-ATPase activity
modulator and BIRC5/Survivin expression down-regulator in cancer
cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 401:1150802020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee PC, Lee HJ, Kakadiya R, Sanjiv K, Su
TL and Lee TC: Multidrug-resistant cells overexpressing
P-glycoprotein are susceptible to DNA crosslinking agents due to
attenuated Src/nuclear EGFR cascade-activated DNA repair activity.
Oncogene. 32:1144–1154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yu HJ, Tsai TC, Hsieh TS and Chiu TY:
Characterization of a newly established human bladder carcinoma
cell line, NTUB1. J Formos Med Assoc. 91:608–613. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Leung E, Kannan N, Krissansen GW, Findlay
MP and Baguley BC: MCF-7 breast cancer cells selected for tamoxifen
resistance acquire new phenotypes differing in DNA content,
phospho-HER2 and PAX2 expression, and rapamycin sensitivity. Cancer
Biol Ther. 9:717–724. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jiang G, Ren B, Xu L, Song S, Zhu C and Ye
F: Survivin may enhance DNA double-strand break repair capability
by up-regulating Ku70 in human KB cells. Anticancer Res.
29:223–228. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheng Q, Ling X, Haller A, Nakahara T,
Yamanaka K, Kita A, Koutoku H, Takeuchi M, Brattain MG and Li F:
Suppression of survivin promoter activity by YM155 involves
disruption of Sp1-DNA interaction in the survivin core promoter.
Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 3:179–197. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Al-Sharif I, Remmal A and Aboussekhra A:
Eugenol triggers apoptosis in breast cancer cells through
E2F1/survivin down-regulation. BMC Cancer. 13:6002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Meng F, Cheng R, Deng C and Zhong Z:
Intracellular drug release nanosystems. Materials Today.
15:436–442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
de Iudicibus RC, Tomek P, Palmer BD,
Tijono SM, Flanagan JU and Ching LM: Parallel discovery of
selective and dual inhibitors of tryptophan dioxygenases IDO1 and
TDO2 with a newly-modified enzymatic assay. Bioorg Med Chem.
39:1161602021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sari S, Tomek P, Leung E and Reynisson J:
Discovery and characterisation of dual inhibitors of tryptophan
2,3-Dioxygenase (TDO2) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1)
using virtual screening. Molecules. 24:43462019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Gong Y, Li Y, Abdolmaleky HM, Li L and
Zhou JR: Tanshinones inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells
through epigenetic modification of aurora a expression and
function. PLoS One. 7:e336562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tai CJ, Chin-Sheng H, Kuo LJ, Wei PL, Lu
HH, Chen HA, Liu TZ, Liu JJ, Liu DZ, Ho YS, et al:
Survivin-mediated cancer cell migration through GRP78 and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker expression in
mahlavu cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:336–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Al-Thani HF, Shurbaji S and Yalcin HC:
Zebrafish as a model for anticancer nanomedicine studies.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 14. pp. 6252021, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Letrado P, de Miguel I, Lamberto I,
Díez-Martínez R and Oyarzabal J: Zebrafish: Speeding up the cancer
drug discovery process. Cancer Res. 78:6048–6058. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hason M and Bartůněk P: Zebrafish models
of cancer-new insights on modeling human cancer in a non-mammalian
vertebrate. Genes (Basel). 10. pp. 9352019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
He JH, Guo SY, Zhu F, Zhu JJ, Chen YX,
Huang CJ, Gao JM, Dong QX, Xuan YX and Li CQ: A zebrafish
phenotypic assay for assessing drug-induced hepatotoxicity. J
Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 67:25–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Vliegenthart ADB, Tucker CS, Pozo JD and
Dear JW: Zebrafish as model organisms for studying drug-induced
liver injury. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 78:1217–1227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mechetner E, Kyshtoobayeva A, Zonis S, Kim
H, Stroup R, Garcia R, Parker RJ and Fruehauf JP: Levels of
multidrug resistance (MDR1) P-glycoprotein expression by human
breast cancer correlate with in vitro resistance to taxol and
doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res. 4:389–398. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Duan Z, Brakora KA and Seiden MV:
Inhibition of ABCB1 (MDR1) and ABCB4 (MDR3) expression by small
interfering RNA and reversal of paclitaxel resistance in human
ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:833–838. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Krisnamurti DGB, Louisa M, Anggraeni E and
Wanandi SI: Drug efflux transporters are overexpressed in
short-term tamoxifen-induced MCF7 breast cancer cells. Adv
Pharmacol Sci. 2016:67024242016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Vaidyanathan A, Sawers L, Gannon AL,
Chakravarty P, Scott AL, Bray SE, Ferguson MJ and Smith G: ABCB1
(MDR1) induction defines a common resistance mechanism in
paclitaxel- and olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 115:431–441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Park E, Gang EJ, Hsieh YT, Schaefer P,
Chae S, Klemm L, Huantes S, Loh M, Conway EM, Kang ES, et al:
Targeting survivin overcomes drug resistance in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Blood. 118:2191–2199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Xue Y, Lian W, Zhi J, Yang W, Li Q, Guo X,
Gao J, Qu H, Lin W, Li Z, et al: HDAC5-mediated deacetylation and
nuclear localisation of SOX9 is critical for tamoxifen resistance
in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 121:1039–1049. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kang HJ, Yi YW, Hong YB, Kim HJ, Jang YJ,
Seong YS and Bae I: HER2 confers drug resistance of human breast
cancer cells through activation of NRF2 by direct interaction. Sci
Rep. 4:72012014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Liu Q, Zhai J, Kong X, Wang X, Wang Z,
Fang Y and Wang J: Comprehensive analysis of the expressionand
prognosis for TDO2 in breast cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
17:153–168. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Miyazaki T, Chung S, Sakai H, Ohata H,
Obata Y, Shiokawa D, Mizoguchi Y, Kubo T, Ichikawa H, Taniguchi H,
et al: Stemness and immune evasion conferred by the TDO2-AHR
pathway are associated with liver metastasis of colon cancer.
Cancer Sci. 113:170–181. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wanek J, Gaisberger M, Beyreis M, Mayr C,
Helm K, Primavesi F, Jäger T, Fazio PD, Jakab M, Wagner A, et al:
Pharmacological inhibition of class IIA HDACs by LMK-235 in
pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cells. Int J Mol Sci. 19:31282018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Dhatchinamoorthy K, Colbert JD and Rock
KL: Cancer immune evasion through loss of MHC class I antigen
presentation. Front Immunol. 12:6365682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ogris M, Steinlein P, Kursa M, Mechtler K,
Kircheis R and Wagner E: The size of DNA/transferrin-PEI complexes
is an important factor for gene expression in cultured cells. Gene
Ther. 5:1425–1433. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Ogris M, Steinlein P, Carotta S, Brunner S
and Wagner E: DNA/polyethylenimine transfection particles:
Influence of ligands, polymer size, and PEGylation on
internalization and gene expression. AAPS PharmSci. 3:E212001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kalyane D, Raval N, Maheshwari R, Tambe V,
Kalia K and Tekade RK: Employment of enhanced permeability and
retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for
targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater Sci
Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 98:1252–1276. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Kulkarni SA and Feng SS: Effects of
particle size and surface modification on cellular uptake and
biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. Pharm
Res. 30:2512–2522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Talekar M, Trivedi M, Shah P, Ouyang Q,
Oka A, Gandham S and Amiji MM: Combination wt-p53 and MicroRNA-125b
transfection in a genetically engineered lung cancer model using
dual CD44/EGFR-targeting nanoparticles. Mol Ther. 24:759–769. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Li Z, Zhang L, Tang C and Yin C:
Co-delivery of doxorubicin and survivin shRNA-expressing plasmid
via microenvironment-responsive dendritic mesoporous silica
nanoparticles for synergistic cancer therapy. Pharm Res.
34:2829–2841. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
El-Boubbou K, Ali R, Al-Zahrani H,
Trivilegio T, Alanazi AH, Khan AL, Boudjelal M and AlKushi A:
Preparation of iron oxide mesoporous magnetic microparticles as
novel multidrug carriers for synergistic anticancer therapy and
deep tumor penetration. Sci Rep. 9:94812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Behzadi S, Serpooshan V, Tao W, Hamaly MA,
Alkawareek MY, Dreaden EC, Brown D, Alkilany AM, Farokhzad OC and
Mahmoudi M: Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: Journey inside the
cell. Chem Soc Rev. 46:4218–4244. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Blanc-Brude OP, Teissier E, Castier Y,
Lesèche G, Bijnens AP, Daemen M, Staels B, Mallat Z and Tedgui A:
IAP survivin regulates atherosclerotic macrophage survival.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:901–907. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|