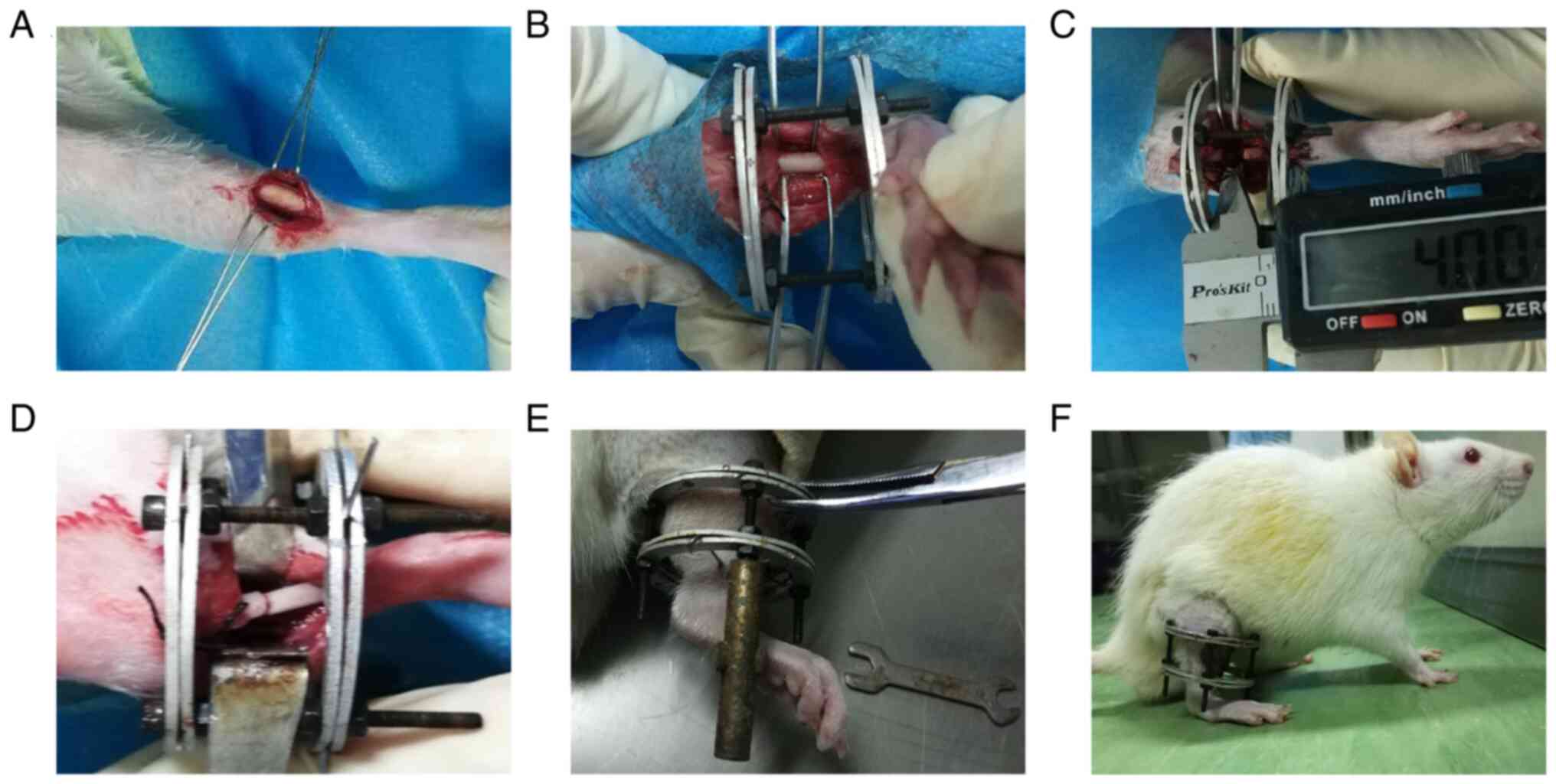
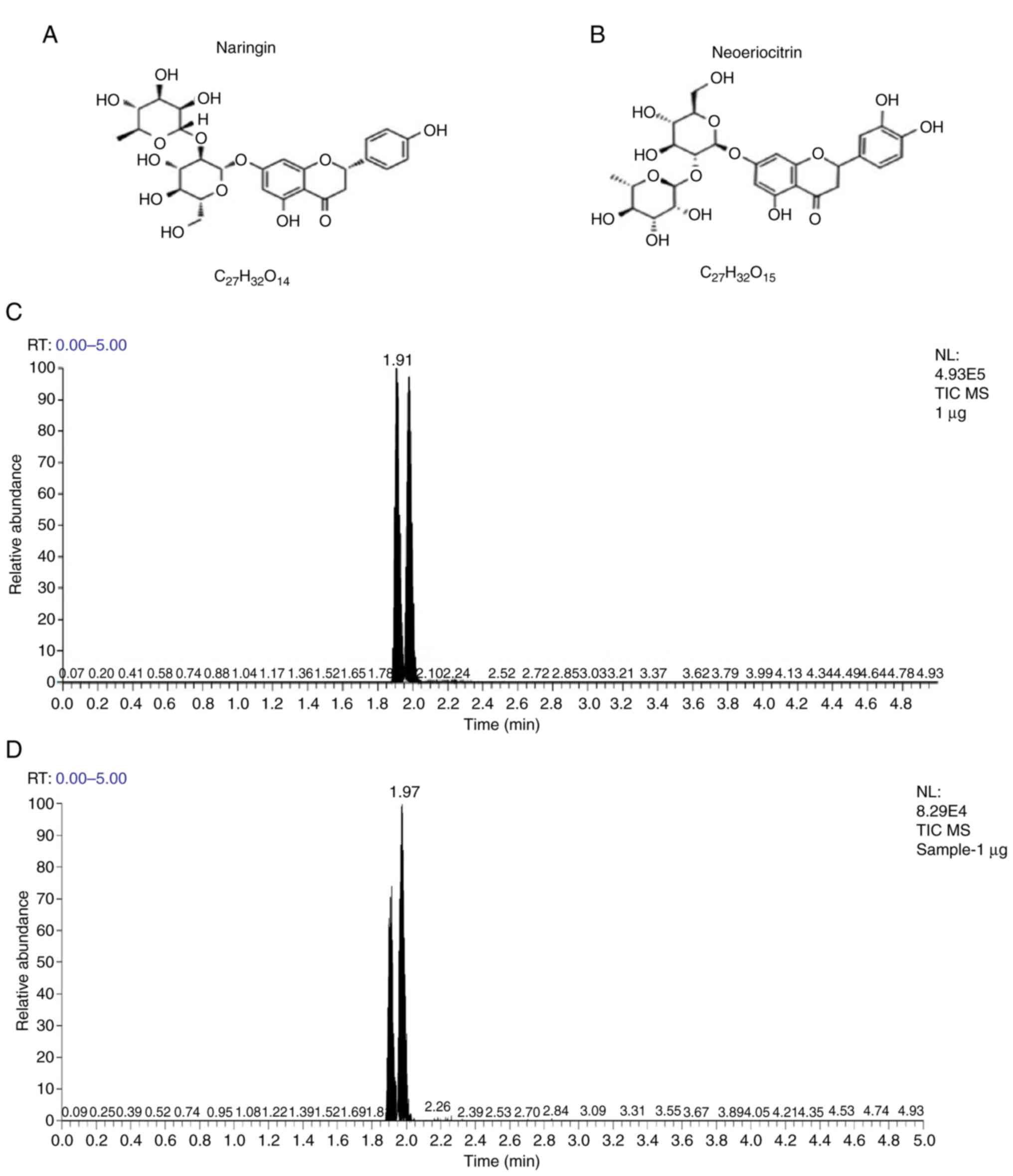
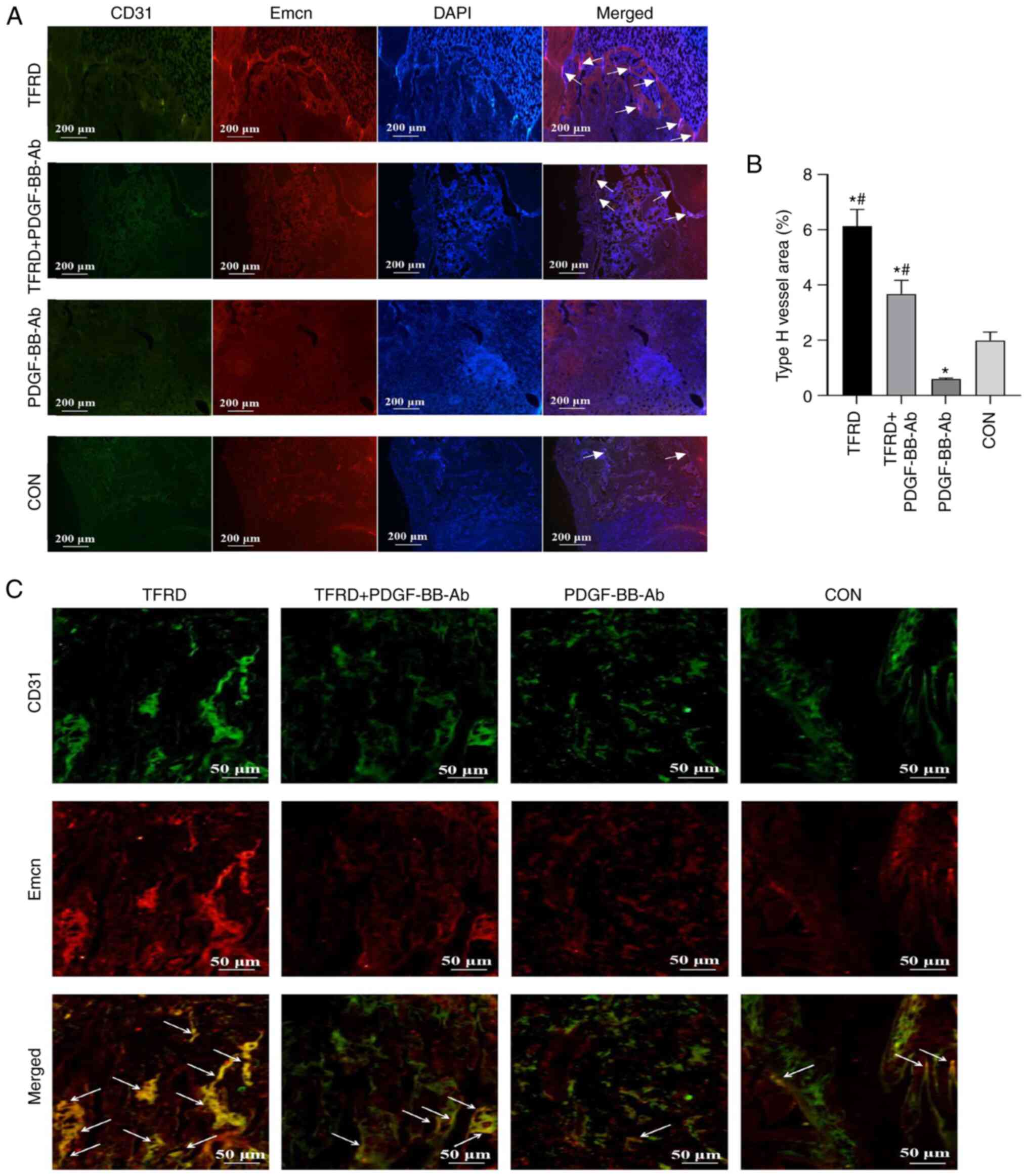
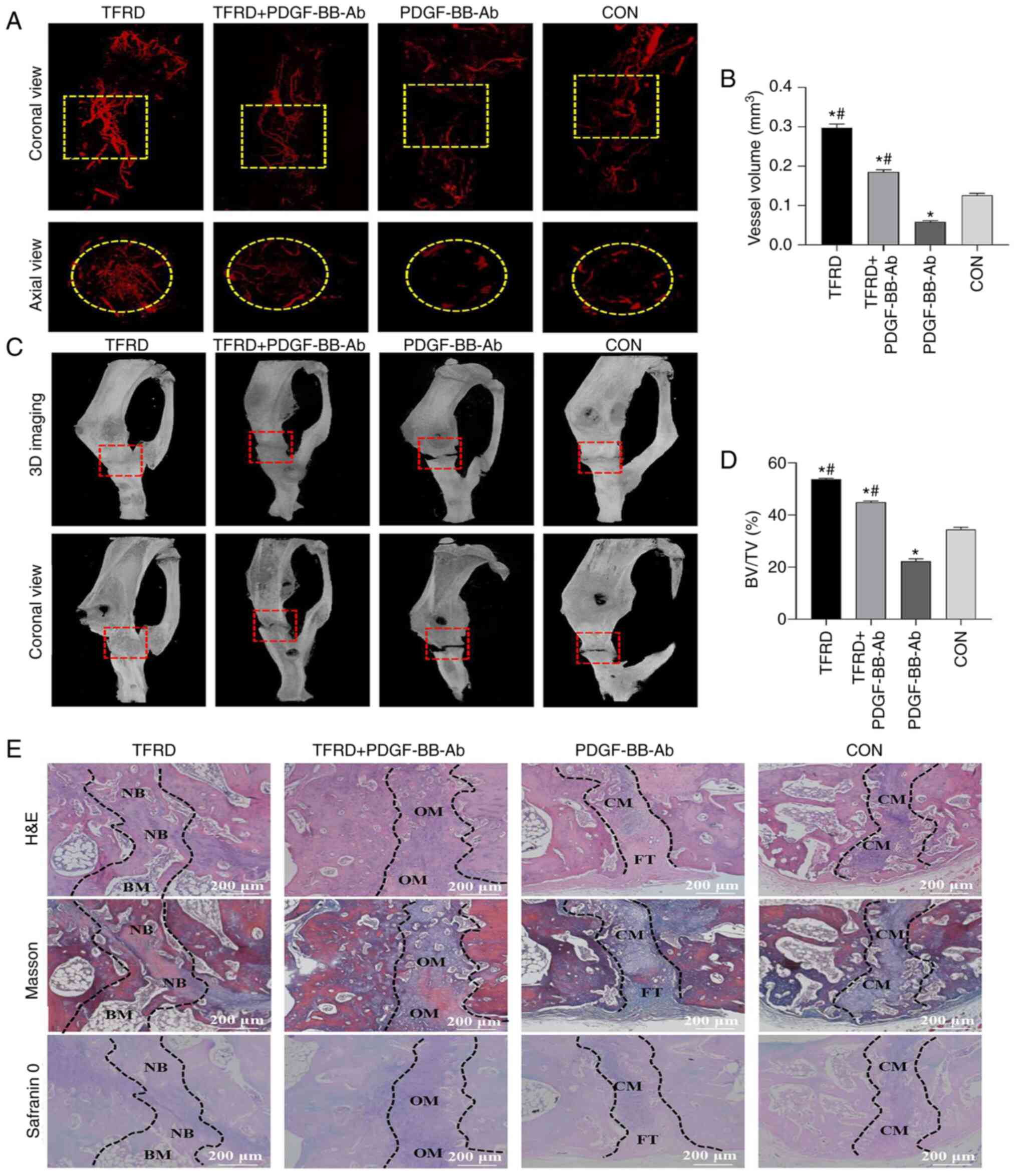
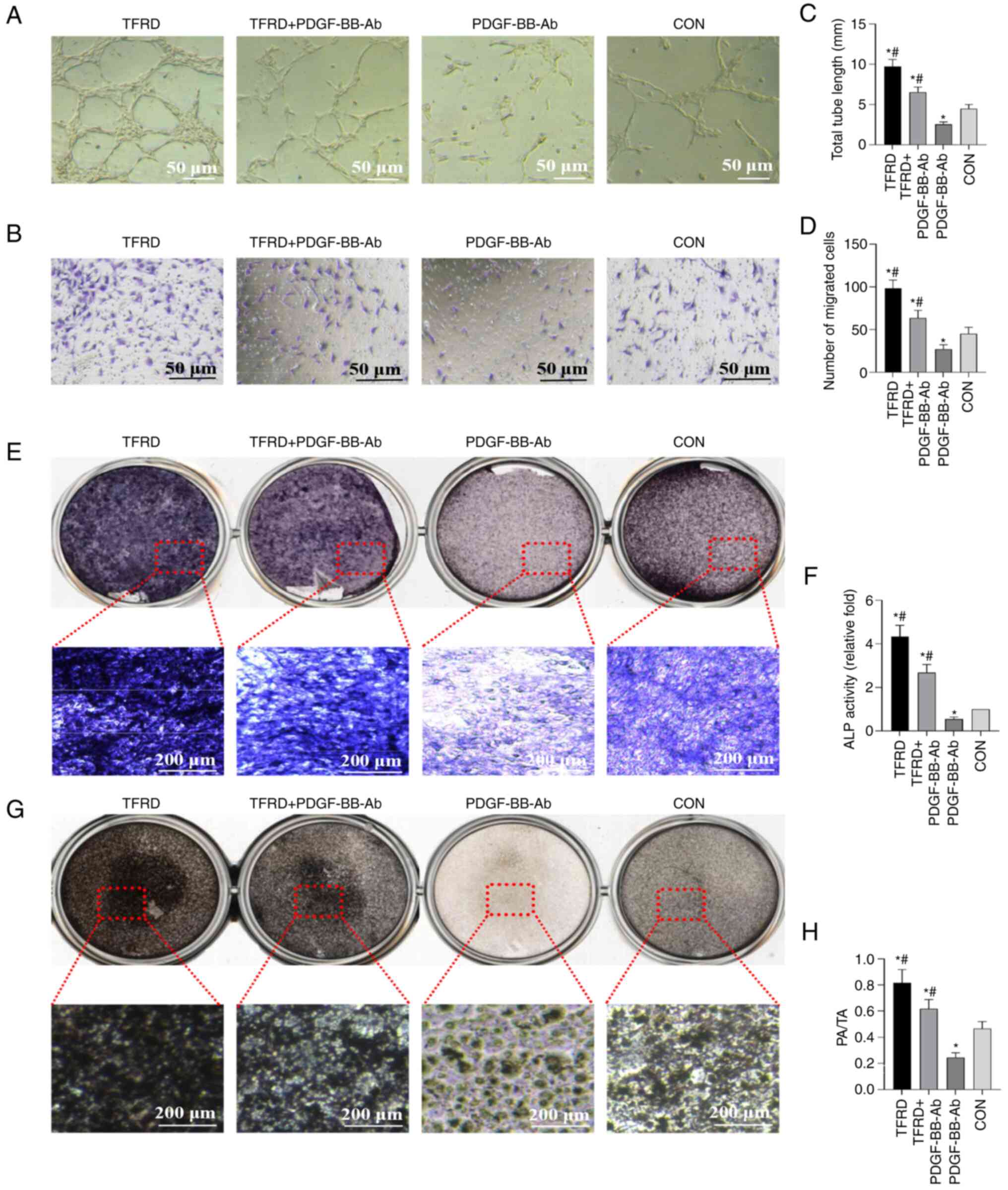
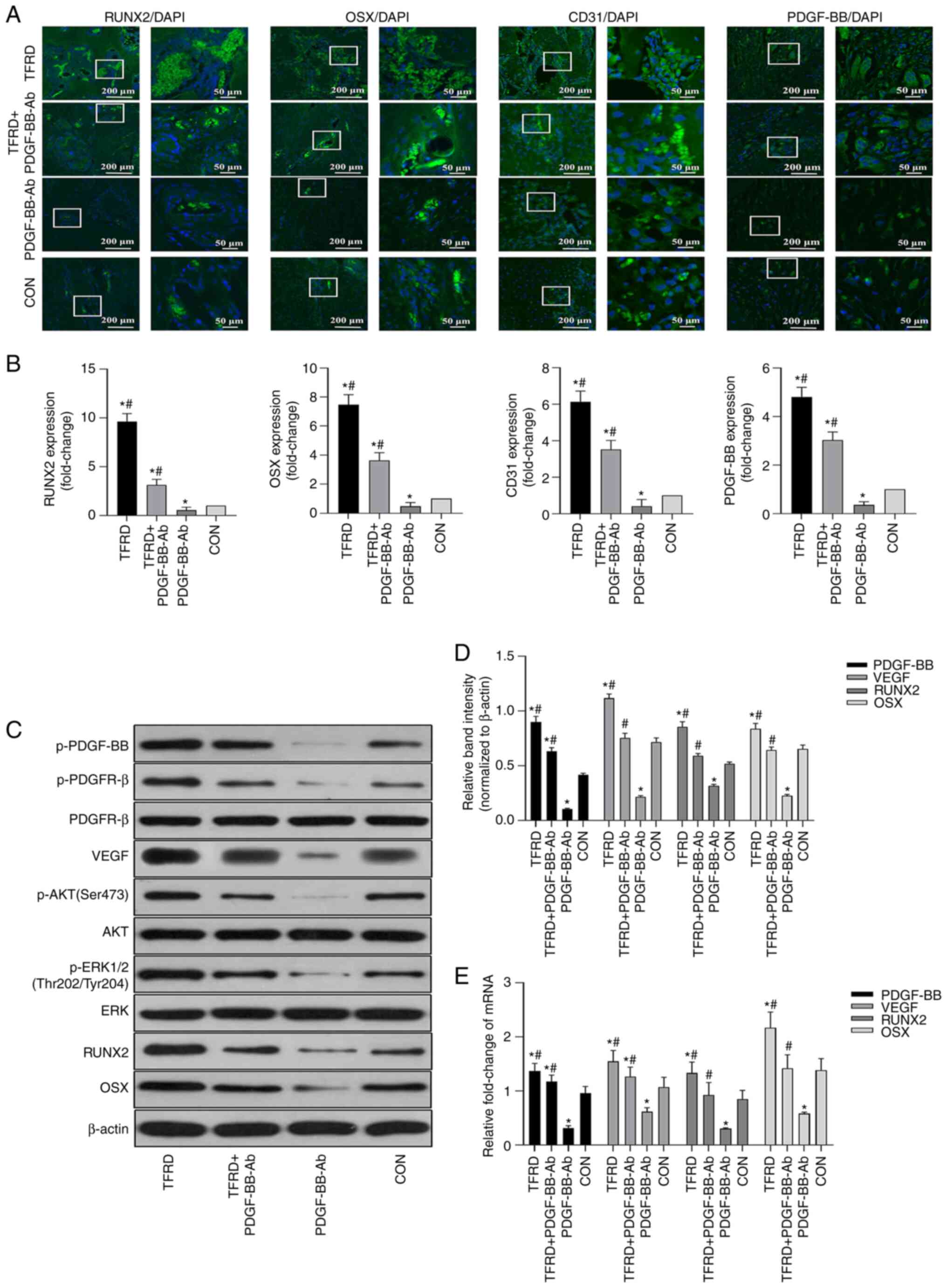
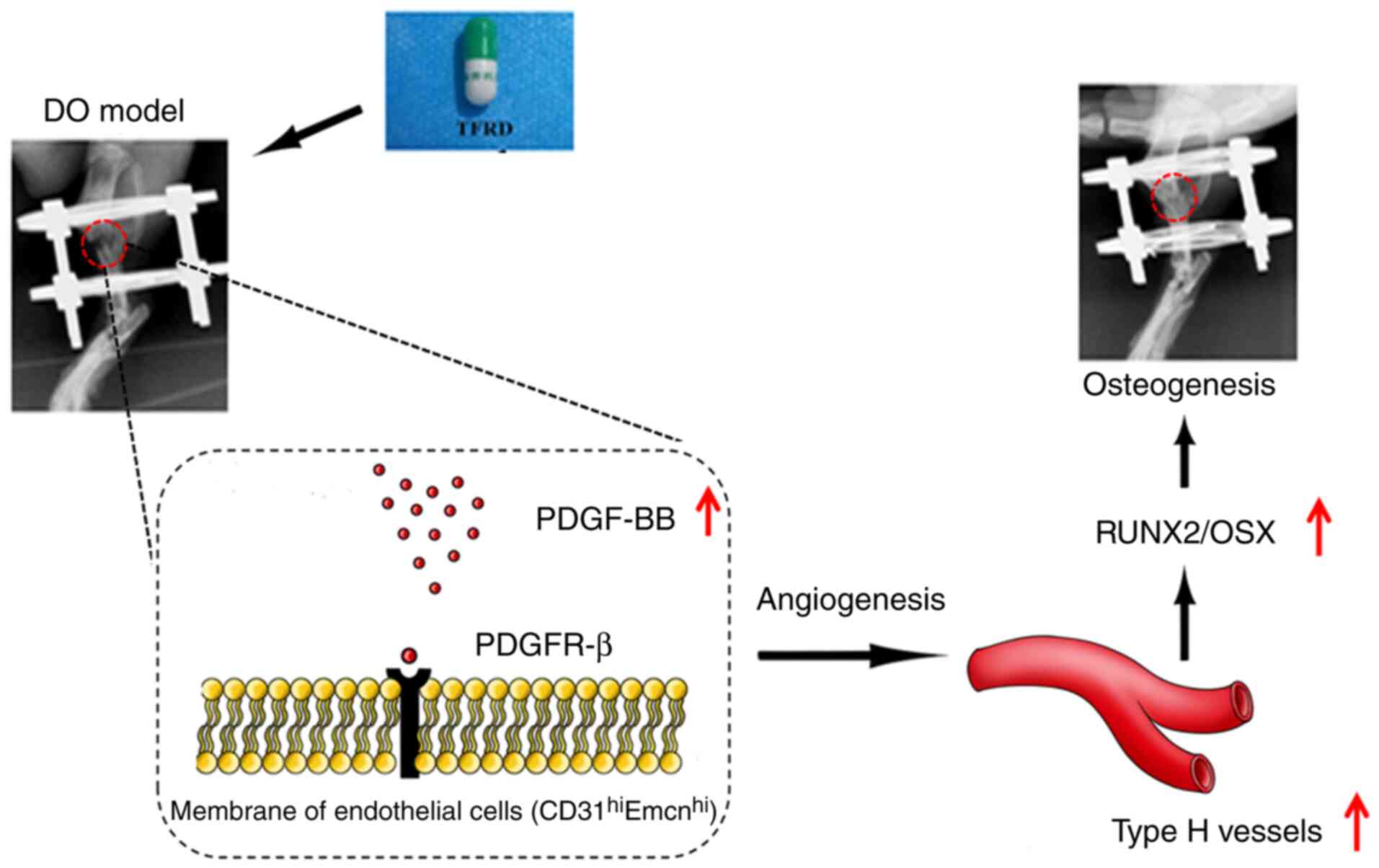
|
1
|
Nauth A, McKee MD, Einhorn TA, Watson JT,
Li R and Schemitsch EH: Managing bone defects. J Orthop Trauma.
25:462–466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mauffrey C, Barlow BT and Smith W:
Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.
23:143–153. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li W, Zhu S and Hu J: Bone regeneration is
promoted by orally administered bovine lactoferrin in a rabbit
tibial distraction osteogenesis model. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
473:2383–2393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Xu J, Xu L, Zhang J, Chan K, Pan X
and Li G: MiR-503 promotes bone formation in distraction
osteogenesis through suppressing smurf1 expression. Sci Rep.
7:4092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun YX, Zhang JF, Xu J, Xu LL, Wu TY, Wang
B, Pan XH and Li G: MiRNA-144-3p inhibits bone formation in
distraction osteogenesis through targeting Connexin 43. Oncotarget.
8:89913–89922. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jia Y, Qiu S, Xu J, Kang Q and Chai Y:
Exosomes secreted by young mesenchymal stem cells promote new bone
formation during distraction osteogenesis in older rats. Calcif
Tissue Int. 106:509–517. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jia YC, Zhu Y, Qiu S, Xu J and Chai Y:
Exosomes secreted by endothelial progenitor cells accelerate bone
regeneration during distraction osteogenesis by stimulating
angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Montes-Medina L, Hernández-Fernández A,
Gutiérrez-Rivera A, Ripalda-Cemboráin P, Bitarte N, Pérez-López V,
Granero-Moltó F, Prosper F and Izeta A: Effect of bone marrow
stromal cells in combination with biomaterials in early phases of
distraction osteogenesis: An experimental study in a rabbit femur
model. Injury. 49:1979–1986. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paley D: Problems, obstacles, and
complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 250:81–104. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dhaliwal R, Kunchur K and Farhadieh R:
Review of the cellular and biological principles of distraction
osteogenesis: An in vivo bioreactor tissue engineering model. J
Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 69:e19–e26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tomlinson RE and Silva MJ: Skeletal blood
flow in bone repair and maintenance. Bone Res. 1:311–322. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gerber HP and Ferrara N: Angiogenesis and
bone growth. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 10:223–228. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Saran U, Piperni SG and Chatterjee S: Role
of angiogenesis in bone repair. Arch Biochem Biophys. 561:109–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brandi ML and Collin-Osdoby P: Vascular
biology and the skeleton. J Bone Miner Res. 21:183–192. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grosso A, Burger MG, Lunger A, Schaefer
DJ, Banfi A and Maggio ND: It takes two to tango: Coupling of
angiogenesis and osteogenesis for bone regeneration. Front Bioeng
Biotechnol. 5:682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang TD, Salim A, Xia W, Nacamuli RP,
Guccione S, Song HM, Carano RA, Filvaroff EH, Bednarski MD, Giaccia
AJ and Longaker MT: Angiogenesis is required for successful bone
induction during distraction osteogenesis. J Bone Miner Res.
20:1114–1124. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK and Adams RH:
Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel
subtype in bone. Nature. 507:323–328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramasamy SK, Kusumbe AP, Wang L and Adams
RH: Endothelial notch activity promotes angiogenesis and
osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 507:376–380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng Y, Wu S, Li Y and Crane JL: Type H
blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics.
10:426–436. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang J, Yin H, Rao SS, Xie PL, Cao X, Rao
T, Liu SY, Wang ZX, Cao J, Hu Y, et al: Harmine enhances type H
vessel formation and prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice.
Theranostics. 8:2435–2446. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu R, Yallowitz A, Qin A, Wu Z, Shin DY,
Kim JM, Debnath S, Ji G, Bostrom MP, Yang X, et al: Targeting
skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat Med. 24:823–833.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Gao Y, Cheng P, Li D, Jiang H, Ji
C, Zhang S, Shen C, Li J, Song Y, et al:
CD31hiEmcnhi Vessels support new trabecular
bone formation at the frontier growth area in the bone defect
repair process. Sci Rep. 7:49902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fan YG and Zhan HS: Orthopaedics of
traditional chinese medicine. People's Medical Publishing House,
Beijing. 29–31. 2005.
|
|
24
|
Yao W, Zhang H, Jiang X, Mehmood K, Iqbal
M, Li A, Zhang J, Wang Y, Waqas M, Shen Y and Li J: Effect of total
flavonoids of on tibial dyschondroplasia by regulating BMP-2 and
Runx2 expression in chickens. Front Pharmacol. 9:12512018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen LL, Lei LH, Ding PH, Tang Q and Wu
YM: Osteogenic effect of Drynariae rhizoma extracts and Naringin on
MC3T3-E1 cells and an induced rat alveolar bone resorption model.
Arch Oral Biol. 56:1655–1662. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song S, Gao Z, Lei X, Niu Y, Zhang Y, Li
C, Lu Y, Wang Z and Shang P: Total flavonoids of drynariae rhizoma
prevent bone loss induced by hindlimb unloading in rats. Molecules.
22:10332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen Z, Jiang ZW, Li D, Zhang Y, Li ZG,
Chen HM, et al: Comparison of two types of tonifying kidney in the
mechanism of angiogenesis and osteogenesis coupling based on
distraction osteogenesis. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm.
34:2150–2155. 2019.
|
|
28
|
Shen Z, Lin H, Chen G, Zhang Y, Li Z, Li
D, Xie L, Li Y, Huang F and Jiang Z: Comparison between the induced
membrane technique and distraction osteogenesis in treating
segmental bone defects: An experimental study in a rat model. PLoS
One. 14:e02268392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song SH, Zhai YK, Li CQ, Yu Q, Lu Y, Zhang
Y, Hua WP, Wang ZZ and Shang P: Effects of total flavonoids from
Drynariae Rhizoma prevent bone loss in vivo and in vitro. Bone Rep.
5:262–273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan Y, Chen H, Zhang H, Guo C, Yang K,
Chen K, Cheng R, Qian N, Sandler N, Zhang YS, et al: Vascularized
3D printed scaffolds for promoting bone regeneration. Biomaterials.
190–191. 97–110. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang M, Ahn W, Kim S, Hong HS, Quan C and
Son Y: Endothelial precursor cells stimulate pericyte-like coverage
of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through
platelet-derived growth factor-BB induction, which is enhanced by
substance P. Microcirculation. 24:e123942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Naruse K, Yamada T, Sai XR, Hamaguchi M
and Sokabe M: Pp125FAK is required for stretch dependent
morphological response of endothelial cells. Oncogene. 17:455–463.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ilizarov GA: The tension-stress effect on
the genesis and growth of tissues. Part I. The influence of
stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 238:249–281. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stegen S, van Gastel N and Carmeliet G:
Bringing new life to damaged bone: The importance of angiogenesis
in bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 70:19–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang L, Zhou F, Zhang P, Wang H, Qu Z, Jia
P, Yao Z, Shen G, Li G, Zhao G, et al: Human type H vessels are a
sensitive biomarker of bone mass. Cell Death Dis. 8:e27602017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie H, Cui Z, Wang L, Xia Z, Hu Y, Xian L,
Li C, Xie L, Crane J, Wan M, et al: PDGF-BB secreted by
preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with
osteogenesis. Nat Med. 20:1270–1278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu L, Zong C, Li B, Shen D, Tang Z, Chen
J, Zheng Q, Tong X, Gao C and Wang J: The interaction between β1
integrins and ERK1/2 in osteogenic differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells under fluid shear stress modelled by a
perfusion system. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 8:85–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee DY, Cho TJ, Kim JA, Lee HR, Yoo WJ,
Chung CY and Choi IH: Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells
in fracture healing and distraction osteogenesis. Bone. 42:932–941.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Yin Y, Li W, Zhao X, Yu Y, Zhu J,
Qin Z, Wang Q, Wang K, Lu W, et al: Over-expression of PDGFR-β
promotes PDGF-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of
EPCs through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. PLoS One. 7:e305032012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Caplan AI and Correa D: PDGF in bone
formation and regeneration: New insights into a novel mechanism
involving MSCs. J Orthop Res. 29:1795–1803. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heldin CH, Lennartsson J and Westermark B:
Involvement of platelet-derived growth factor ligands and receptors
in tumorigenesis. J Intern Med. 283:16–44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee SJ, Namkoong S and Kim YM, Kim CK, Lee
H, Ha KS, Chung HT, Kwon YG and Kim YM: Fractalkine stimulates
angiogenesis by activating the Raf-1/MEK/ERK-and PI3K/Akt/
eNOS-dependent signal pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
291:H2836–H2846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang J, Guan J, Qi X, Ding H, Yuan H, Xie
Z, Chen C, Li X, Zhang C and Huang Y: Dimethyloxaloxaloylglycine
promotes the angiogenic activity of mesenchymal stem cells derived
from iPSCs via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway for bone
regeneration. Int J Biol Sci. 12:639–652. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kuang MJ, Zhang WH, He WW, Sun L, Ma JX,
Wang D and Ma XL: Naringin regulates bone metabolism in
glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the
Akt/Bad signal cascades. Chem Biol Interact. 304:97–105. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang P, Dai KR, Yan SG, Yan WQ, Zhang C,
Chen DQ, Xu B and Xu ZW: Effects of naringin on the proliferation
and osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cell.
Eur J Pharmacol. 607:1–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|