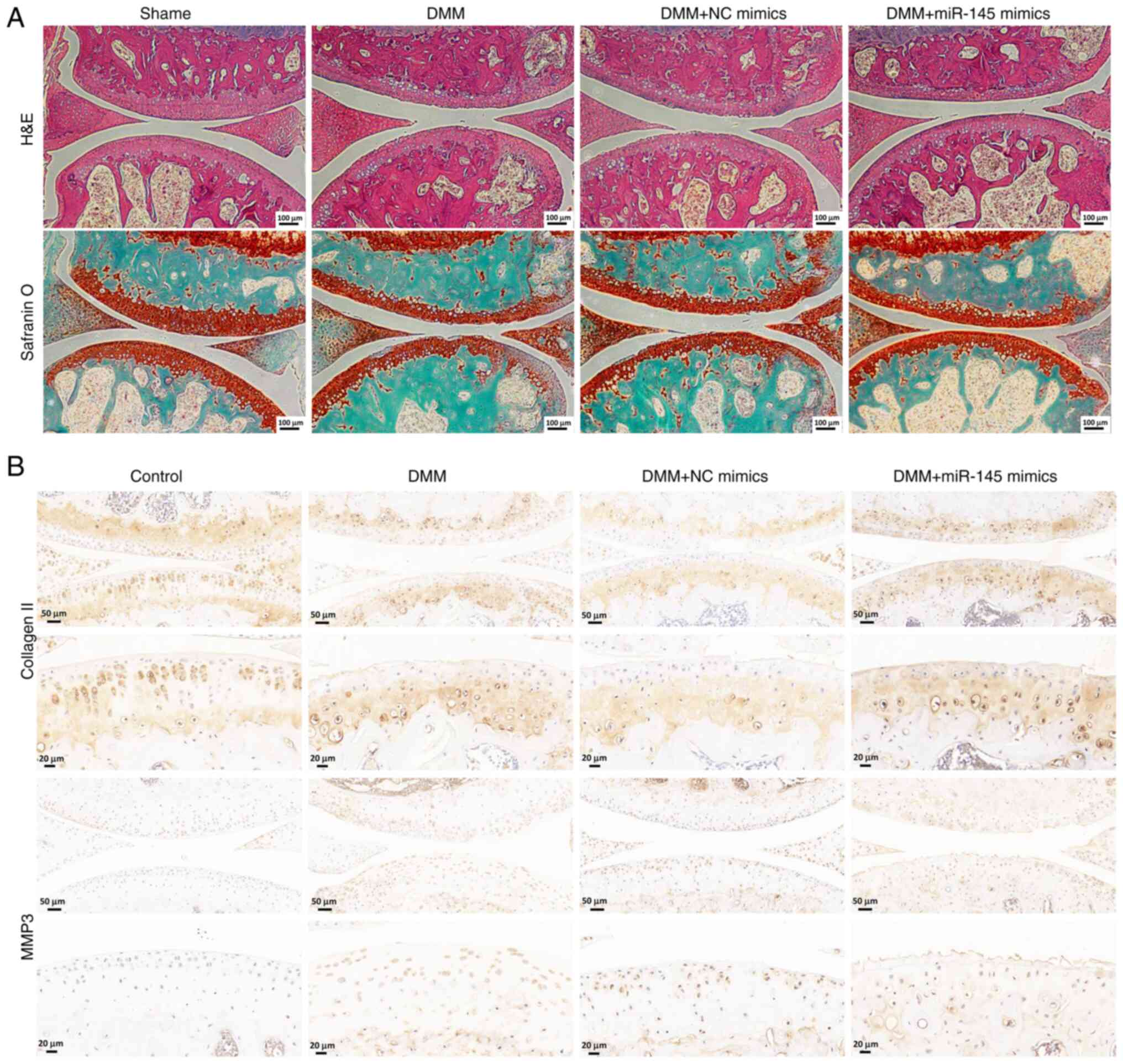
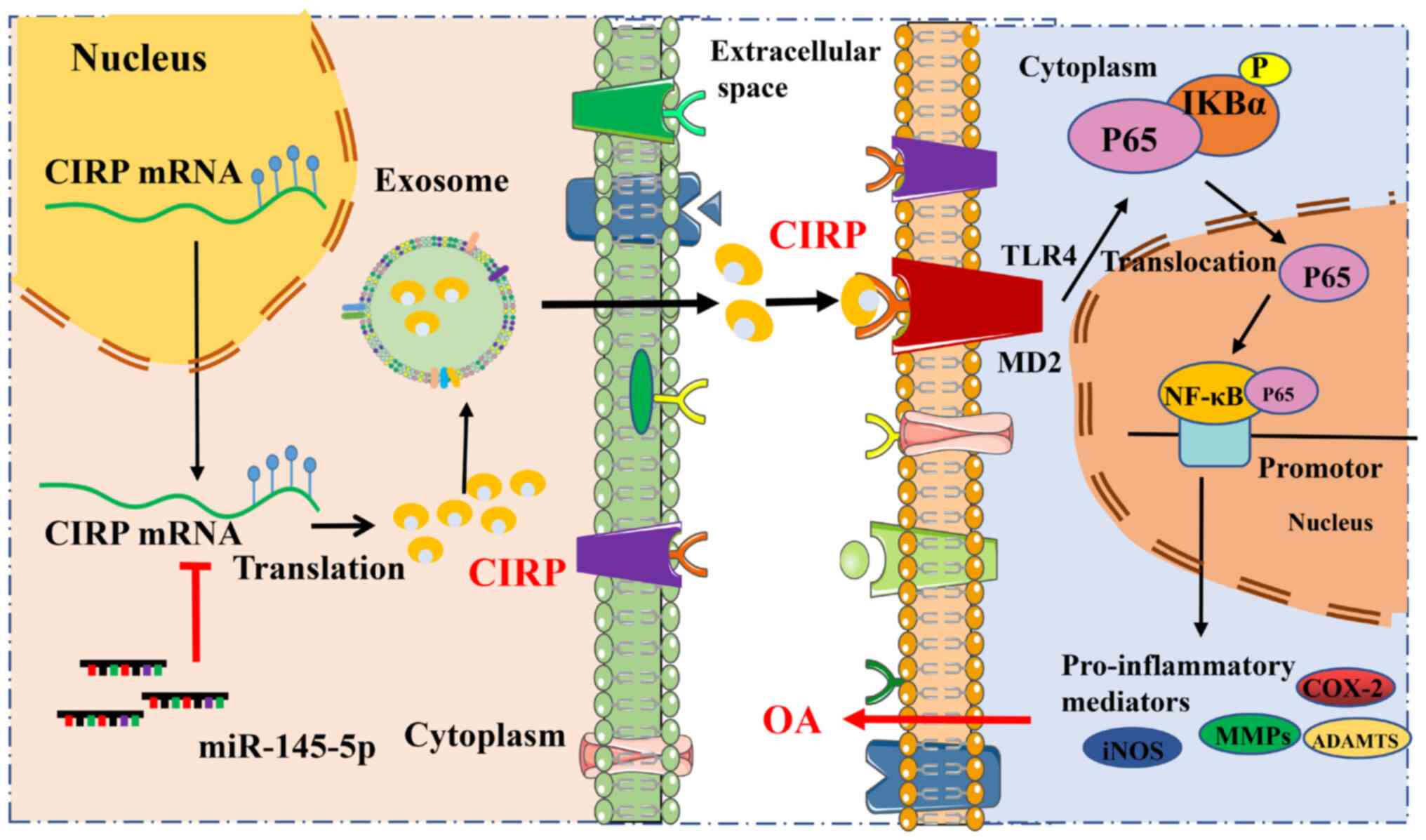
|
1
|
Martel-Pelletier J, Barr AJ, Cicuttini FM,
Conaghan PG, Cooper C, Goldring MB, Goldring SR, Jones G, Teichtahl
AJ and Pelletier JP: Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2:160722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR and
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:1697–1707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F and Lafeber FP:
Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice.
Lancet. 377:2115–2126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis. Lancet.
386:376–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang B, Kang X, Xing Y, Dou C, Kang F, Li
J, Quan Y and Dong S: Effect of microRNA-145 on IL-1beta-induced
cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes. FEBS Lett.
588:2344–2352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tu C, Huang X, Xiao Y, Song M, Ma Y, Yan
J, You H and Wu H: Schisandrin A inhibits the IL-1β-Induced
inflammation and cartilage degradation via suppression of MAPK and
NF-κB signal pathways in rat chondrocytes. Front Pharmacol.
10:412019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chabane N, Zayed N, Afif H, Mfuna-Endam L,
Benderdour M, Boileau C, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Duval N
and Fahmi H: Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress
interleukin-1beta-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2
production in human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
16:1267–1274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou S, Liu G, Si Z, Yu L and Hou L:
Glycyrrhizin, an HMGB1 inhibitor, suppresses interleukin-1β-induced
inflammatory responses in chondrocytes from patients with
osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 13(2_Suppl): 947S–955S. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Frommer KW, Schaffler A, Rehart S, Lehr A,
Muller-Ladner U and Neumann E: Free fatty acids: Potential
proinflammatory mediators in rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis.
74:303–310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xu HC, Wu B, Ma YM, Xu H, Shen ZH and Chen
S: Hederacoside-C protects against AGEs-induced ECM degradation in
mice chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 84:1065792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao F and Zhang S: Loratadine alleviates
advanced glycation end Product-induced activation of NLRP3
inflammasome in human chondrocytes. Drug Des Devel Ther.
14:2899–2908. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao Y, Tong L, Tang L and Wu S: The role
of cold-inducible RNA binding protein in cell stress response. Int
J Cancer. 141:2164–2173. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhong P and Huang H: Recent progress in
the research of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein. Future Sci OA.
3:FSO2462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wellmann S, Buhrer C, Moderegger E, Zelmer
A, Kirschner R, Koehne P, Fujita J and Seeger K: Oxygen-regulated
expression of the RNA-binding proteins RBM3 and CIRP by a
HIF-1-independent mechanism. J Cell Sci. 117:1785–1794. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun W, Liao Y, Yi Q, Wu S, Tang L and Tong
L: The mechanism of CIRP in regulation of STAT3 phosphorylation and
Bag-1/S expression Upon UVB radiation. Photochem Photobiol.
94:1234–1239. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aziz M, Brenner M and Wang P:
Extracellular CIRP (eCIRP) and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol.
106:133–146. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qiang X, Yang WL, Wu R, Zhou M, Jacob A,
Dong W, Kuncewitch M, Ji Y, Yang H, Wang H, et al: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein (CIRP) triggers inflammatory responses in
hemorrhagic shock and sepsis. Nat Med. 19:1489–1495. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakurai T, Kashida H, Watanabe T, Hagiwara
S, Mizushima T, Iijima H, Nishida N, Higashitsuji H, Fujita J and
Kudo M: Stress response protein cirp links inflammation and
tumorigenesis in colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Res.
74:6119–6128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou M, Yang WL, Ji Y, Qiang X and Wang P:
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein mediates neuroinflammation in
cerebral ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1840:2253–2261. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vande Walle L, Van Opdenbosch N, Jacques
P, Fossoul A, Verheugen E, Vogel P, Beyaert R, Elewaut D,
Kanneganti TD, van Loo G and Lamkanfi M: Negative regulation of the
NLRP3 inflammasome by A20 protects against arthritis. Nature.
512:69–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McAllister MJ, Chemaly M, Eakin AJ, Gibson
DS and McGilligan VE: NLRP3 as a potentially novel biomarker for
the management of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
26:612–619. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Z, Zhong H, Wei J, Lin S, Zong Z,
Gong F, Huang X, Sun J, Li P, Lin H, et al: Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1
signaling leads to increased activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 21:3002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Q, Zhang D, Hu D, Zhou X and Zhou Y:
The role of mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol
Immunol. 103:115–124. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou K, Cui S, Duan W, Zhang J, Huang J,
Wang L, Gong Z and Zhou Y: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein
contributes to intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury via
TLR4 signaling. Brain Behav. 10:e016182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elliott EI and Sutterwala FS: Initiation
and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly.
Immunol Rev. 265:35–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu L, Li QH, Deng F, Yu ZW, Luo XZ and Sun
JL: Synovial fluid concentrations of cold-inducible RNA-binding
protein are associated with severity in knee osteoarthritis. Clin
Chim Acta. 464:44–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yoo IS, Lee SY, Park CK, Lee JC, Kim Y,
Yoo SJ, Shim SC, Choi YS, Lee Y and Kang SW: Serum and synovial
fluid concentrations of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 21:148–154.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Felekkis K, Pieri M and Papaneophytou C:
Exploring the feasibility of circulating miRNAs as diagnostic and
prognostic biomarkers in osteoarthritis: Challenges and
opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 24:131442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin Z, Jiang T, Zheng W, Zhang J, Li A, Lu
C and Liu W: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase
WTAP-mediated miR-92b-5p accelerates osteoarthritis progression.
Cell Commun Signal. 21:1992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mao G, Zhang Z, Hu S, Zhang Z, Chang Z,
Huang Z, Liao W and Kang Y: Exosomes derived from
miR-92a-3p-overexpressing human mesenchymal stem cells enhance
chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via targeting
WNT5A. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:2472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen H, Yao H, Chi J, Li C, Liu Y, Yang J,
Yu J, Wang J, Ruan Y, Pi J and Xu JF: Engineered exosomes as drug
and RNA co-delivery system: New hope for enhanced therapeutics?
Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 11:12543562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang M, Jike Y, Liu K, Gan F, Zhang K,
Xie M, Zhang J, Chen C, Zou X, Jiang X, et al: Exosome-mediated
miR-144-3p promotes ferroptosis to inhibit osteosarcoma
proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating ZEB1. Mol
Cancer. 22:1132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Liu N, Wu W, Li H, Lu W
and Guo X: Umbilical cord Blood-derived M1 macrophage exosomes
loaded with cisplatin target ovarian cancer in vivo and reverse
cisplatin resistance. Mol Pharm. 20:5440–5453. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu G, Zhao X, Wang C, Geng Y, Zhao J, Xu
J, Zuo B, Zhao C, Wang C and Zhang X: MicroRNA-145 attenuates
TNF-α-driven cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via
direct suppression of MKK4. Cell Death Dis. 8:e31402017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhou J, Sun J, Markova DZ, Li S, Kepler
CK, Hong J, Huang Y, Chen W, Xu K, Wei F and Ye W: MicroRNA-145
overexpression attenuates apoptosis and increases matrix synthesis
in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 221:274–283. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tian K, Deng B, Han X, Zheng H, Lin T,
Wang Z, Zhang Y and Wang G: Over-expression of microRNA-145
elevating autophagy activities via downregulating FRS2 expression.
Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 27:127–135. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Lu W, Xia X, Zhu Y, Ge C, Guo X,
Zhang N, Chen H and Xu S: Selenomethionine mitigate PM2.5-induced
cellular senescence in the lung via attenuating inflammatory
response mediated by cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ
Saf. 247:1142662022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen Z, Zhang M, Zhao Y, Xu W, Xiang F, Li
X, Zhang T, Wu R and Kang X: Hydrogen sulfide contributes to
uterine quiescence through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome
activation by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB signalling pathway. J
Inflamm Res. 14:2753–2768. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang S, Li W, Zhang P, Wang Z, Ma X, Liu
C, Vasilev K, Zhang L, Zhou X, Liu L, et al: Mechanical overloading
induces GPX4-regulated chondrocyte ferroptosis in osteoarthritis
via Piezo1 channel facilitated calcium influx. J Adv Res. 41:63–75.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gong T, Wang QD, Loughran PA, Li YH, Scott
MJ, Billiar TR, Liu YT and Fan J: Mechanism of lactic
acidemia-promoted pulmonary endothelial cells death in sepsis: Role
for CIRP-ZBP1-PANoptosis pathway. Mil Med Res. 11:712024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou M, Aziz M, Yen HT, Ma G, Murao A and
Wang P: Extracellular CIRP dysregulates macrophage bacterial
phagocytosis in sepsis. Cell Mol Immunol. 20:80–93. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang P, Bai L, Tong Y, Guo S, Lu W, Yuan
Y, Wang W, Jin Y, Gao P, Liu J, et al: CIRP attenuates acute kidney
injury after hypothermic cardiovascular surgery by inhibiting
PHD3/HIF-1α-mediated ROS-TGF-β1/p38 MAPK activation and
mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. Mol Med. 29:612023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ye L, Tang X, Liu F, Wei T, Xu T, Jiang Z,
Xu L, Xiang C, Yuan X, Shen L, et al: Targeting CIRP and
IL-6R-mediated microglial inflammation to improve outcomes in
intracerebral hemorrhage. J Adv Res. Sep 9–2025. View Article : Google Scholar : Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
45
|
Han J, Zhang Y, Ge P, Dakal TC, Wen H,
Tang S, Luo Y, Yang Q, Hua B, Zhang G, et al: Exosome-derived CIRP:
An amplifier of inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol.
14:10667212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Palazzo C, Nguyen C, Lefevre-Colau MM,
Rannou F and Poiraudeau S: Risk factors and burden of
osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 59:134–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Carr AJ, Robertsson O, Graves S, Price AJ,
Arden NK, Judge A and Beard DJ: Knee replacement. Lancet.
379:1331–1340. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu J, Wu X, Lu J, Huang G, Dang L, Zhang
H, Zhong C, Zhang Z, Li D, Li F, et al: Exosomal transfer of
osteoclast-derived miRNAs to chondrocytes contributes to
osteoarthritis progression. Nat Aging. 1:368–384. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun W, Bergmeier AP, Liao Y, Wu S and Tong
L: CIRP sensitizes cancer cell responses to ionizing radiation.
Radiat Res. 195:93–100. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang F, Yang WL, Brenner M and Wang P:
Attenuation of hemorrhage-associated lung injury by adjuvant
treatment with C23, an oligopeptide derived from Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 83:690–697. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Murao A, Tan C, Jha A, Wang P and Aziz M:
Exosome-mediated eCIRP release from macrophages to induce
inflammation in sepsis. Front Pharmacol. 12:7916482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ying X, Peng L, Chen H, Shen Y, Yu K and
Cheng S: Cordycepin prevented IL-β-induced expression of
inflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int
Orthop. 38:1519–1526. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Schmidt N, Pautz A, Art J, Rauschkolb P,
Jung M, Erkel G, Goldring MB and Kleinert H: Transcriptional and
post-transcriptional regulation of iNOS expression in human
chondrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:722–732. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Stannus O, Jones G, Cicuttini F,
Parameswaran V, Quinn S, Burgess J and Ding C: Circulating levels
of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic
osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1441–1447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao Y, Li Y, Qu R, Chen X, Wang W, Qiu C,
Liu B, Pan X, Liu L, Vasilev K, et al: Cortistatin binds to TNF-α
receptors and protects against osteoarthritis. EBioMedicine.
41:556–570. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhou M, Aziz M, Denning NL, Yen HT, Ma G
and Wang P: Extracellular CIRP induces macrophage endotoxin
tolerance through IL-6R-mediated STAT3 activation. JCI Insight.
5:e1337152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Denning NL, Aziz M, Murao A, Gurien SD,
Ochani M, Prince JM and Wang P: Extracellular CIRP as an endogenous
TREM-1 ligand to fuel inflammation in sepsis. JCI Insight.
5:e1341722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gomez R, Villalvilla A, Largo R, Gualillo
O and Herrero-Beaumont G: TLR4 signalling in osteoarthritis-finding
targets for candidate DMOADs. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 11:159–170. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Barreto G, Senturk B, Colombo L, Brück O,
Neidenbach P, Salzmann G, Zenobi-Wong M and Rottmar M: Lumican is
upregulated in osteoarthritis and contributes to TLR4-induced
pro-inflammatory activation of cartilage degradation and macrophage
polarization. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 28:92–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Liu L, Gu H, Liu H, Jiao Y, Li K, Zhao Y,
An L and Yang J: Protective effect of resveratrol against
IL-1β-induced inflammatory response on human osteoarthritic
chondrocytes partly via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway: An
'in vitro study'. Int J Mol Sci. 15:6925–6940. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang A, Wang P, Ma X, Yin X, Li J, Wang
H, Jiang W, Jia Q and Ni L: Mechanisms that lead to the regulation
of NLRP3 inflammasome expression and activation in human dental
pulp fibroblasts. Mol Immunol. 66:253–262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang C, Gao Y, Zhang Z, Chen C, Chi Q, Xu
K and Yang L: Ursolic acid protects chondrocytes, exhibits
anti-inflammatory properties via regulation of the NF-κB/NLRP3
inflammasome pathway and ameliorates osteoarthritis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 130:1105682020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Dougherty U, Mustafi R, Zhu H, Zhu X, Deb
D, Meredith SC, Ayaloglu-Butun F, Fletcher M, Sanchez A, Pekow J,
et al: Upregulation of polycistronic microRNA-143 and microRNA-145
in colonocytes suppresses colitis and Inflammation-associated colon
cancer. Epigenetics. 16:1317–1334. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Tang J, Yi S and Liu Y: Long non-coding
RNA PVT1 can regulate the proliferation and inflammatory responses
of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting
microRNA-145-5p. Hum Cell. 33:1081–1090. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu Z, Tao B, Fan S, Pu Y, Xia H and Xu L:
MicroRNA-145 protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury via CaMKII-Mediated antiapoptotic and Anti-inflammatory
pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:89486572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li Y, Wu X, Miao S and Cao Q: MiR-383-5p
promotes apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells by targeting CIRP
through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
306:501–512. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lin TY, Jia JS, Luo WR, Lin XL, Xiao SJ,
Yang J, Xia JW, Zhou C, Zhou ZH, Lin SJ, et al:
ThermomiR-377-3p-induced suppression of Cirbp expression is
required for effective elimination of cancer cells and cancer
stem-like cells by hyperthermia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 43:622024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|