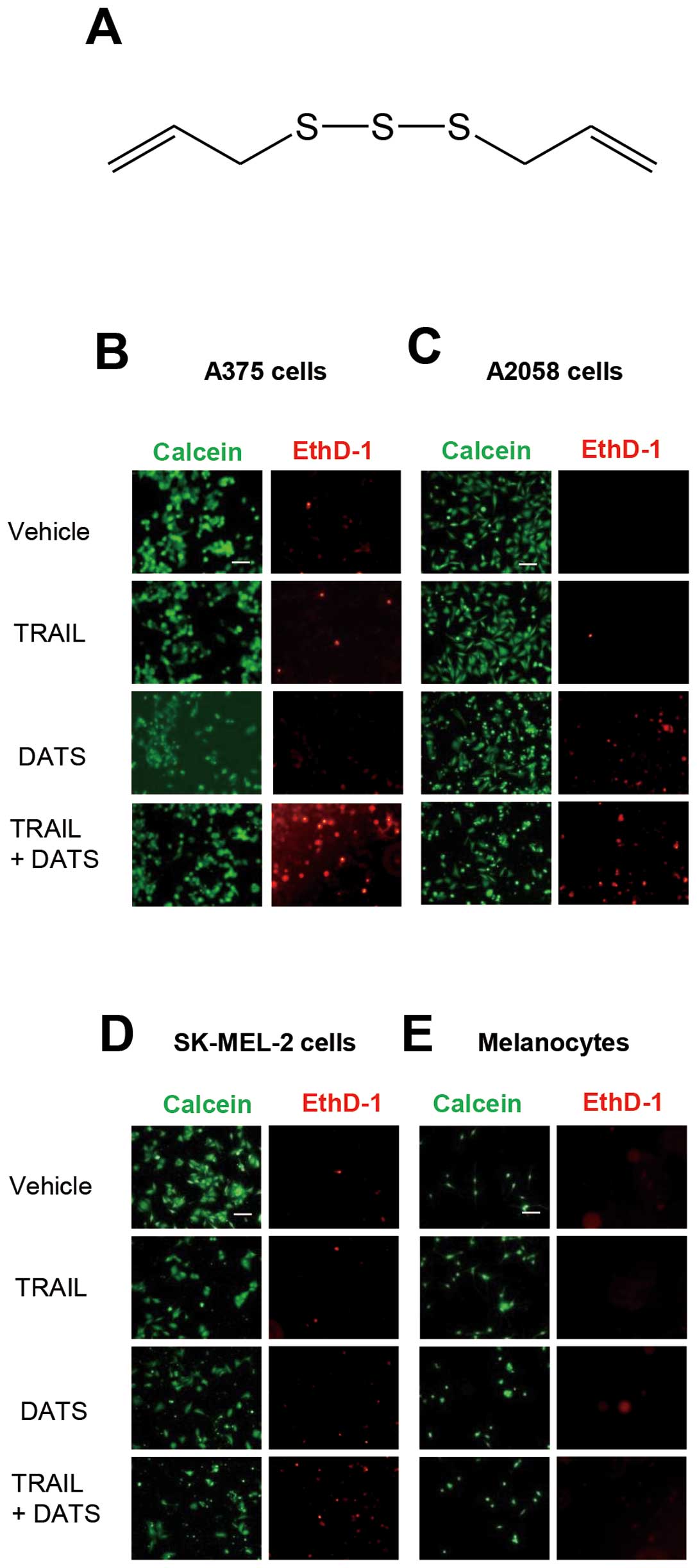
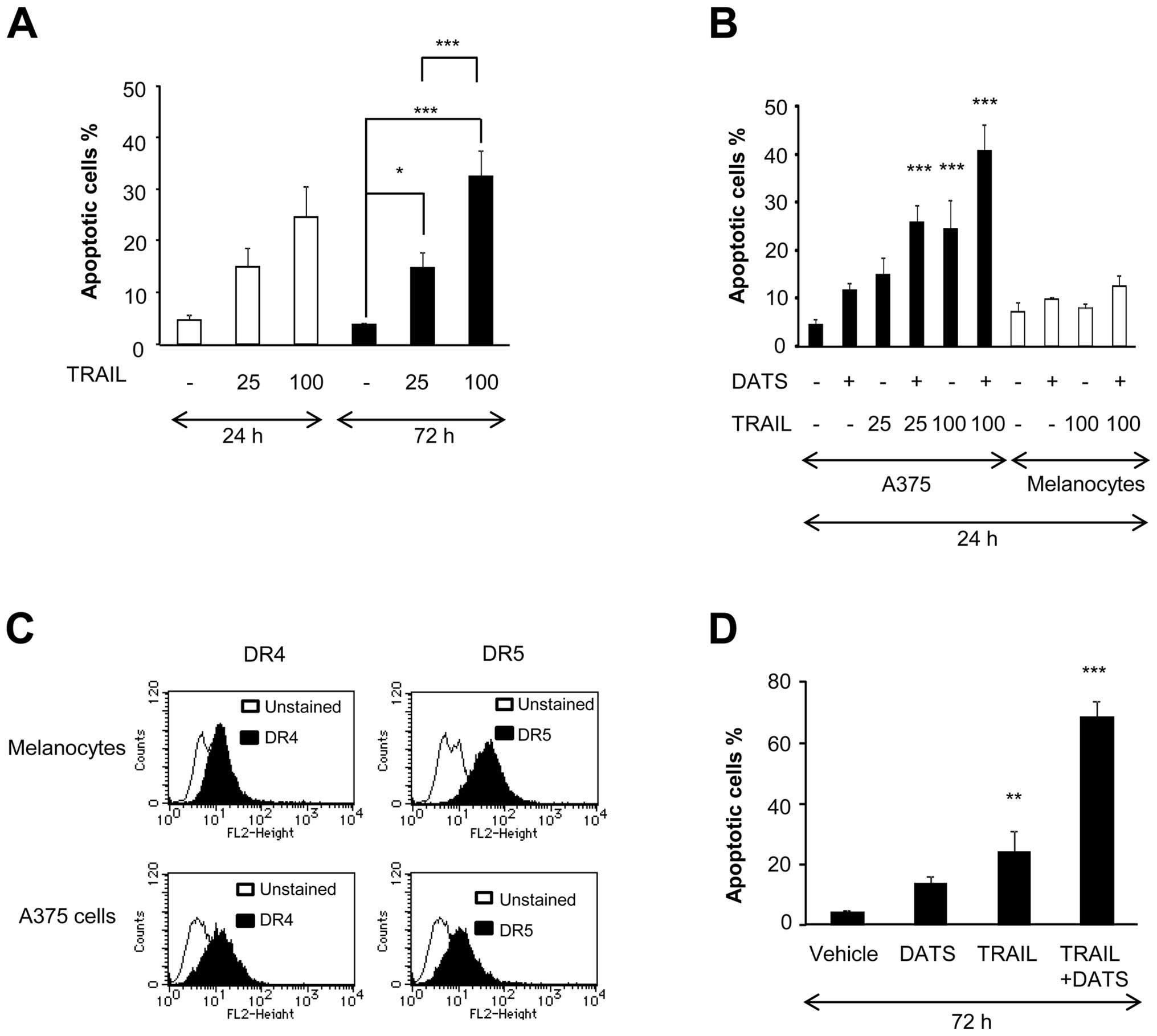
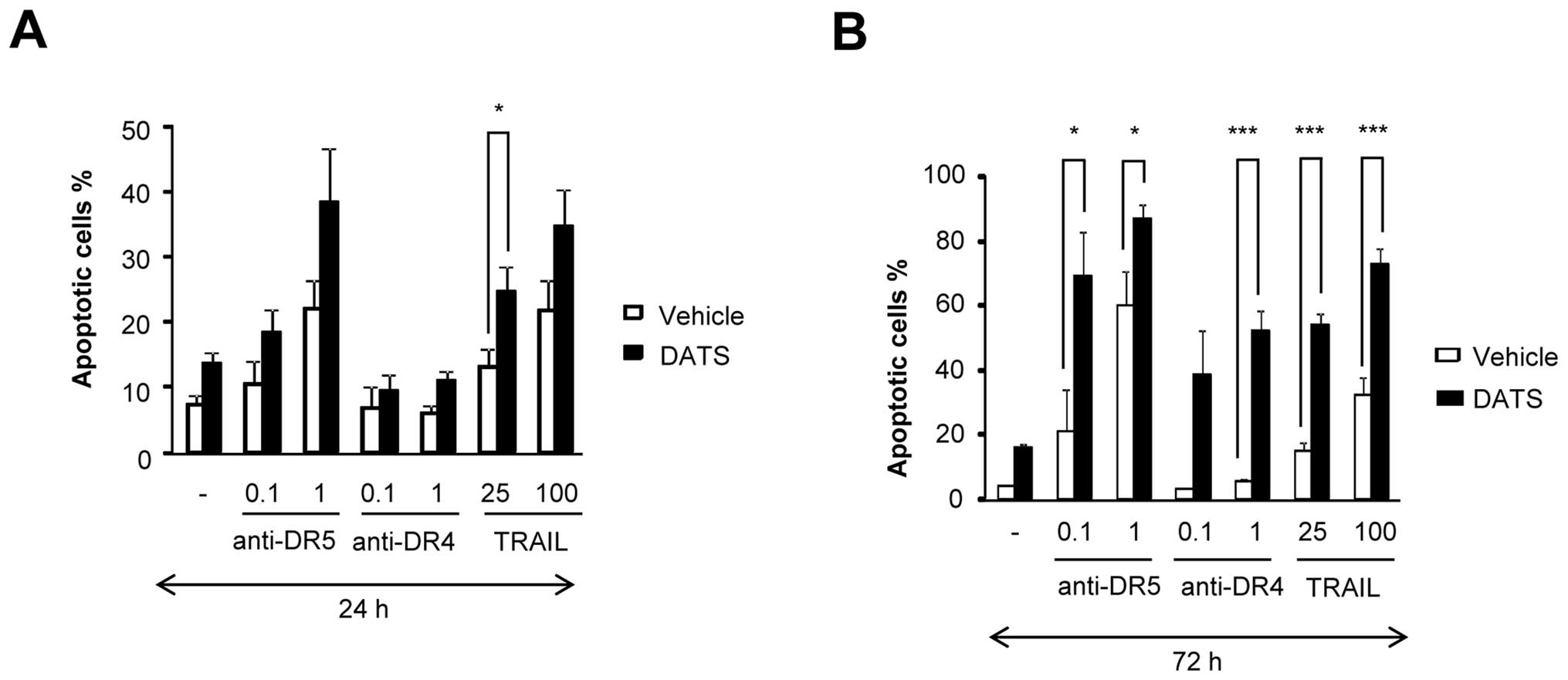
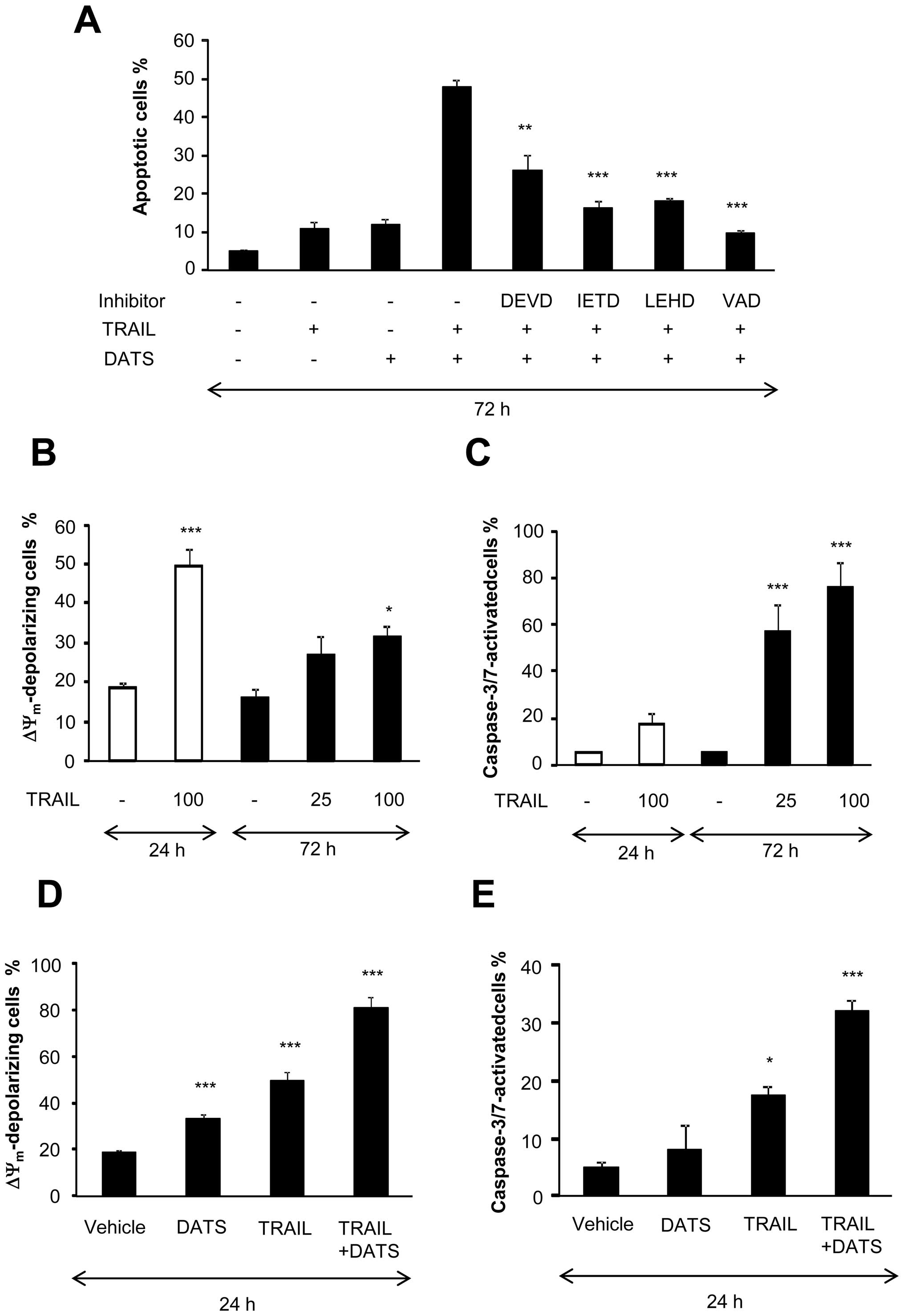
|
1.
|
LeBlanc HN and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL
and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 10:66–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ and Smyth MJ: The
TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 8:782–798. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Wang S: The promise of cancer therapeutics
targeting the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and TRAIL
receptor pathway. Oncogene. 27:6207–6215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Sayers TJ: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptosis signaling pathway for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 60:1173–1180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Dyer MJ, MacFarlane M and Cohen GM:
Barriers to effective TRAIL-targeted therapy of malignancy. J Clin
Oncol. 25:4505–4506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Das A, Banik NL and Ray SK: Garlic
compounds generate reactive oxygen species leading to activation of
stress kinases and cysteine proteases for apoptosis in human
glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells. Cancer. 110:1083–1095. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Kim YA, Xiao D, Xiao H, et al:
Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by diallyl trisulfide in human
prostate cancer cells is associated with generation of reactive
oxygen species and regulated by Bax/Bak. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:1599–1609. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Powlny AA and Singh SV: Multitargeted
prevention and therapy of cancer by diallyl trisulfide and related
Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds. Cancer Lett.
269:305–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Shankar S, Chen Q, Ganapathy S, Singh KP
and Srivastava RK: Diallyl trisulfide increases the effectiveness
of TRAIL and inhibits prostate cancer growth in an orthotropic
model: molecular mechanisms. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2328–2338. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Suzuki Y, Inoue T, Murai M,
Suzuki-Karasaki M, Ochiai T and Ra C: Depolarization potentiates
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells: role for
ATP-sensitive K+ channels and endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Int J Oncol. 41:465–475. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Suzuki Y, Yoshimaru T, Inoue T and Ra C:
Mitochondrial Ca2+ flux is a critical determinant of the
Ca2+ dependence of mast cell degranulation. J Leukoc
Biol. 79:508–518. 2006.
|
|
12.
|
Griffith TS, Rauch CT, Smolak PJ, et al:
Functional analysis of TRAIL receptors using monoclonal antibodies.
J Immunol. 162:2597–2605. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Tinel A, et al:
Death receptor recruitment of endogenous caspase-10 and apoptosis
initiation in the absence of caspase-8. J Biol Chem.
276:46639–46646. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R, et al:
HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody,
induces cell death in multiple tumour types in vitro and in vivo.
Br J Cancer. 92:1430–1441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Humphreys R, et al:
Activity of selective fully human agonistic antibodies to the TRAIL
death receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in primary and cultured
lymphoma cells: induction of apoptosis and enhancement of
doxorubicin-and bortezomib-induced cell death. Br J Haematol.
130:501–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Breckenridge DG, Germain M, Mathai JP, et
al: Regulation of apoptosis by endoplasmic reticulum pathways.
Oncogene. 22:8608–8618. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Groenendyk J and Michalak M: Endoplasmic
reticulum quality control and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Pol.
52:381–395. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Chen LH, Jiang CC, Kiejda KA, et al:
Thapsigargin sensitizes human melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis by up-regulation of TRAIL-R2 through the unfolded protein
response. Carcinogenesis. 28:2328–2336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Mahalingam D, Szegezdi E, Keane M, de Jong
S and Samali A: TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: are we on
the right TRAIL? Cancer Treat Rev. 35:280–288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Merino D, Lalaoui N, Morizot A, Schneider
P, Solary E and Micheau O: Differential inhibition of
TRAIL-mediated DR5-DISC formation by decoy receptors 1 and 2. Mol
Cell Biol. 26:7046–7055. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Busch C, Jacob C, Anwar A, et al:
Diallylpolysulfides induce growth arrest and apoptosis. Int J
Oncol. 36:743–749. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lee BC, Park BH, Kim SY and Lee YJ: Role
of Bim in diallyl trisulfide-induced cytotoxicity in human cancer
cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:118–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Balch CM, Buzzaid AC, Soong SJ, et al:
Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging
system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 19:3635–3648.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, et al:
Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and
cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Szegezdi E, Fitzgerald U and Samali A:
Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: the story so far. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1010:186–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Rutkowski DT and Kaufman RJ: A trip to the
ER: coping with stress. Trends Cell Biol. 14:20–28. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hersey P and Zhang XD: Adaptation to ER
stress as a driver of malignancy and resistance to therapy in human
melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21:358–367. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Liu H, Jiang CC, Lavis CJ, et al:
2-Deoxy-D-glucose enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human
melanoma cells through XBP-1-mediated up-regulation of TRAIL-R2.
Mol Cancer. 8:1222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Ferri KF and Kroemer G: Organelle-specific
initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol. 3:E255–E263.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Rao RV, Castro-Obregon S, Frankowski H, et
al: Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death
program. An Apaf-1-independent intrinsic pathway. J Biol Chem.
277:21836–21842. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H,
Shibata T and Yasuhiko Y: An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific
caspase cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation
of caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem. 277:34287–34294. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Xie Q, Khaoustov VI, Chung CC, et al:
Effect of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced caspase-12 activation. Hepatology. 36:592–601. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Mandic A, Hansson J, Linder S and Shoshan
MC: Cisplatin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and
nucleus-independent apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem.
278:9100–9106. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Shellman YG, Howe WR, Miller LA, et al:
Hyperthermia induces endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis in
melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer cells. J Invest Dermatol.
128:949–956. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|