|
1.
|
Anzola M: Hepatocellular carcinoma: role
of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses proteins in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Viral Hepat. 11:383–393. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kasprzak A and Adamek A: Role of hepatitis
C virus proteins (C, NS3, NS5A) in hepatic oncogenesis. Hepatol
Res. 38:1–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Wang F, Yoshida I, Takamatsu M, Fujita T,
Oka K and Hotta H: Complex formation between hepatitis C virus core
protein and p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
273:479–484. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Chang SC, Yen JH, Kang HY, Jang MH and
Chang MF: Nuclear localization signals in the core protein of
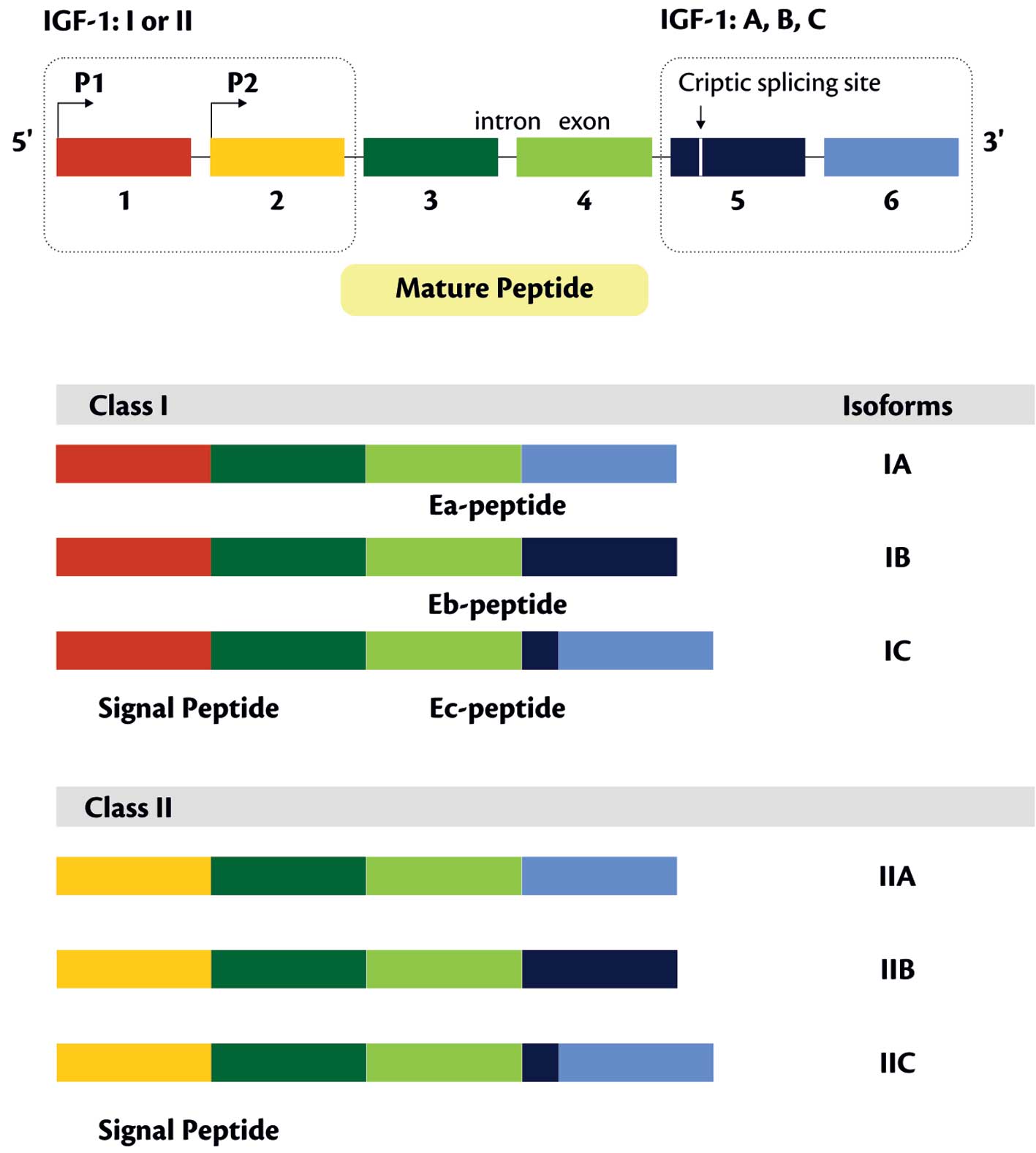
hepatitis C virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 205:1284–1290. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Suzuki R, Sakamoto S, Tsutsumi T, et al:
Molecular determinants for subcellular localization of hepatitis C
virus core protein. J Virol. 79:1271–1281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yamanaka T, Uchida M and Doi T: Innate
form of HCV core protein plays an important role in the
localization and the function of HCV core protein. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 294:521–527. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Nielsen SU, Bassendine MF, Burt AD, Bevitt
DJ and Toms GL: Characterization of the genome and structural
proteins of hepatitis C virus resolved from infected human liver. J
Gen Virol. 85:1497–1507. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Cho JW, Baek WK, Suh SI, Yang SH, Chang J,
Sung YC and Suh MH: Hepatitis C virus core protein promotes cell
proliferation through the upregulation of cyclin E expression
levels. Liver. 21:137–142. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Jung EY, Lee MN, Yang HY, Yu D and Jang
KL: The repressive activity of hepatitis C virus core protein on
the transcription of p21(waf1) is regulated by protein kinase
A-mediated phosphorylation. Virus Res. 79:109–115. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
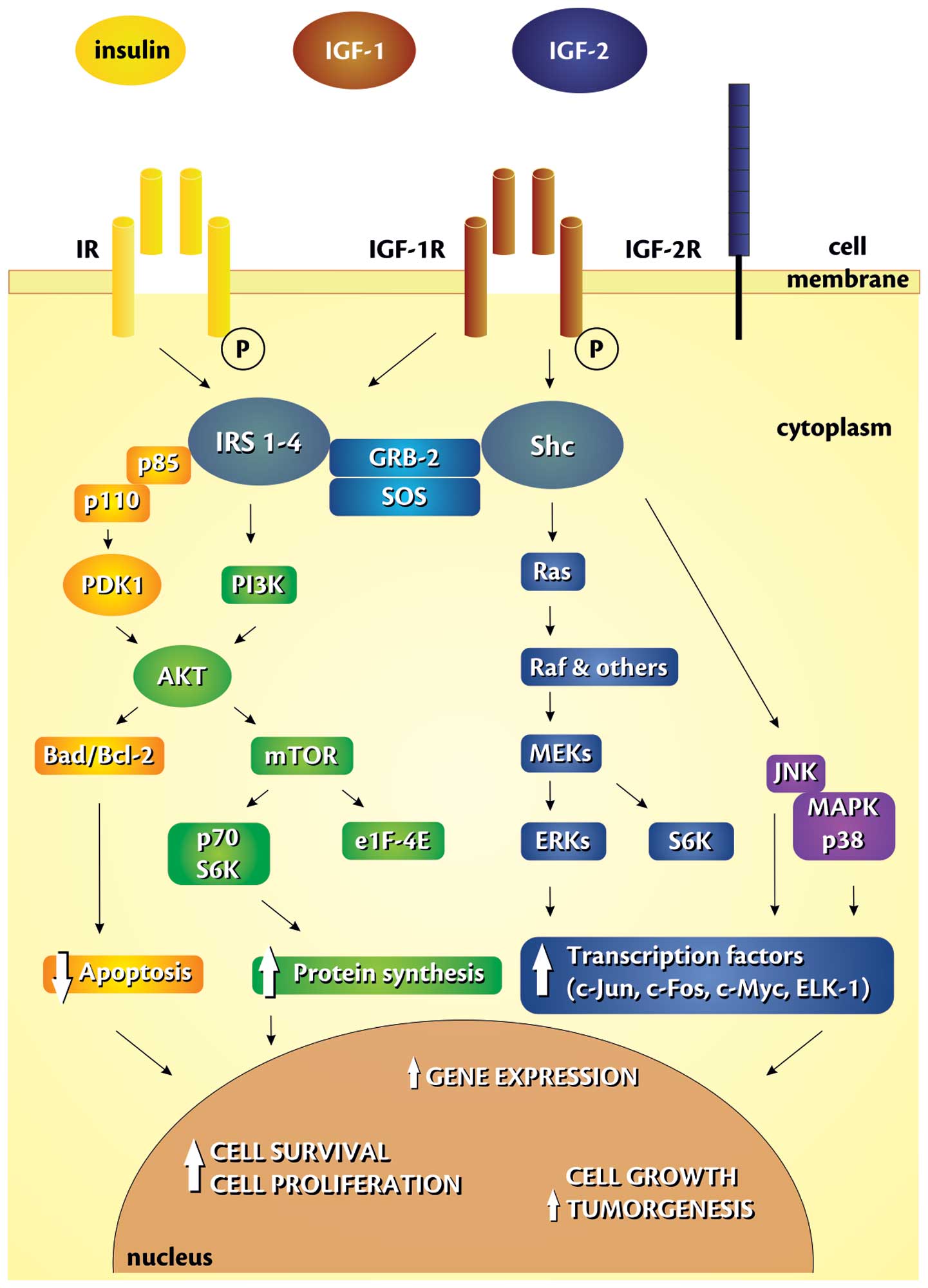
10.
|
Kwun HJ, Jung EY, Ahn JY, Lee MN and Jang
KL: p53-dependent transcriptional repression of p21 (waf1) by
hepatitis C virus NS3. J Gen Virol. 82:2235–2241. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Taniguchi H, Kato N, Otsuka M, Goto T,
Yoshida H, Shiratori Y and Omata M: Hepatitis C virus core protein
upregulates transforming growth factor-beta 1 transcription. J Med
Virol. 72:52–59. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Sato Y, Kato J, Takimoto R, et al:
Hepatitis C virus core protein promotes proliferation of human
hepatoma cells through enhancement of transforming growth factor
alpha expression via activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Gut.
55:1801–1808. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
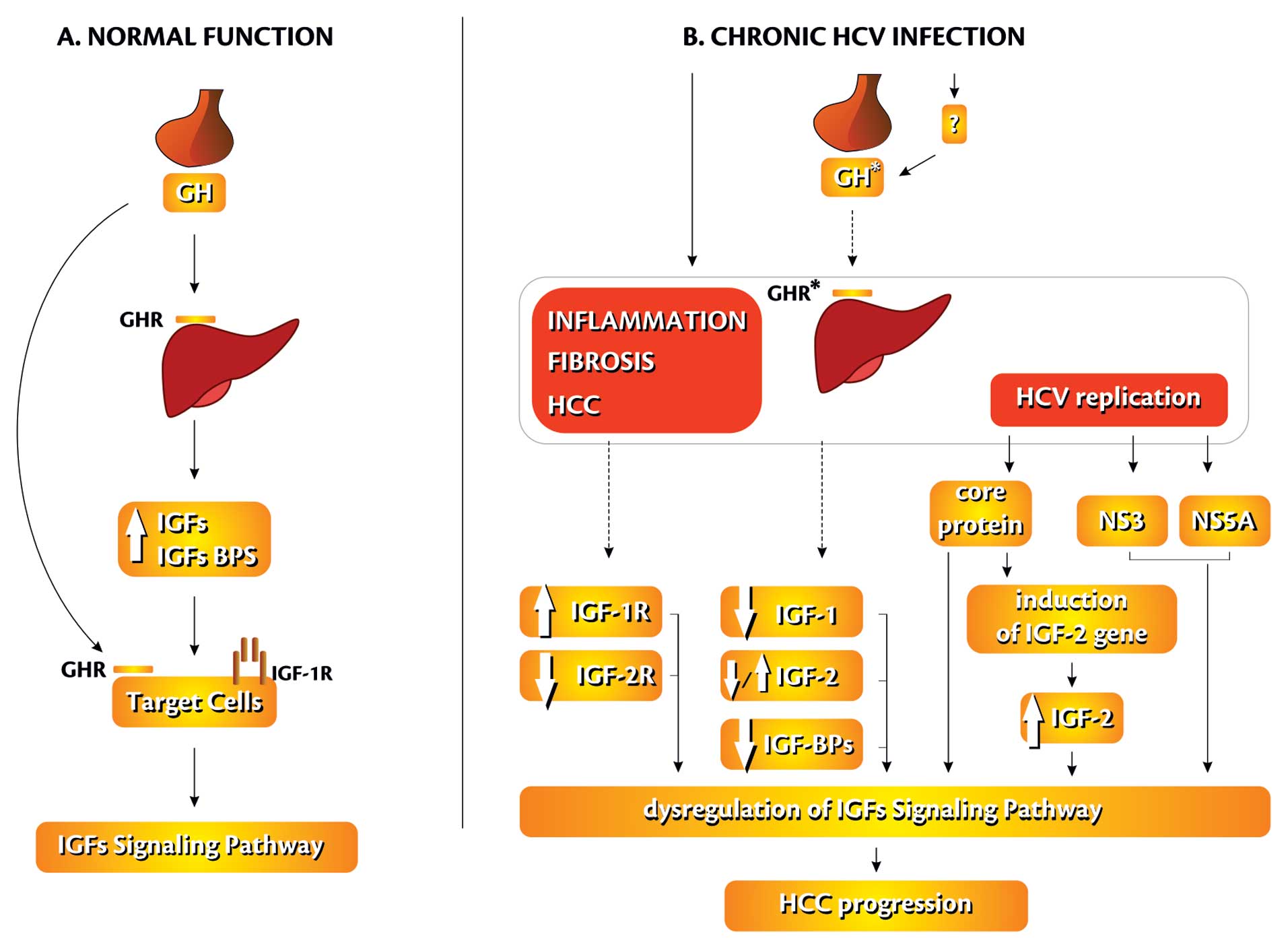
|
Kasprzak A, Adamek A, Biczysko W, et al:
Intracellular expression of the proliferative marker Ki-67 and
viral proteins (NS3, NS5A and C) in chronic, long lasting hepatitis
C virus (HCV) infection. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 45:357–366.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Breuhahn K, Longerich T and Schirmacher P:
Dysregulation of growth factor signalling in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 25:3787–3800. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Daughday WH and Rotweien P: Insulin-like
growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and
gene structures, serum and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev.
10:68–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Rotwein P, Naylor SL and Chirgwin JM:
Human insulin-related DNA sequences map to chromosomes 2 and 11.
Somat Cell Mol Genet. 12:625–631. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Zarilli R, Bruni CB and Riccio A: Multiple
levels of control of insulin-like growth factor gene expression.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 101:R1–R14. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Murphy LJ: Insulin-like growth
factor-binding proteins: functional diversity or redundancy? J Mol
Endocrinol. 21:97–107. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kostecka Z and Blahovec J: Insulin-like
growth factor binding proteins and their functions (minireview).
Endocr Regul. 33:90–94. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Scharf JG, Dombrowski F and Ramadori G:
The IGF axis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Pathol. 54:138–144.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Huynh H, Chow PKH, Ooi LLP and Soo KC: A
possible role for insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3
autocrine/paracrine loops in controlling hepatocellular carcinoma
cell proliferation. Cell Growth Differ. 13:115–122. 2002.
|
|
22.
|
Rechler MM and Clemmonds DR: Regulatory
actions of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 9:176–183. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Baserga R: The insulin-like growth factor
I receptor: a key to tumor growth? Cancer Res. 55:249–255.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Höppener JW, de Pagter-Holthuizen P,
Geurts van Kessel AHM, et al: The human gene encoding insulin- like
growth factor I is located on chromosome 12. Hum Genet. 69:157–160.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Bell GI, Stempien MM, Fong NM and Rall LB:
Sequences of liver cDNAs encoding two different mouse insulin-like
growth factor 1 precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 14:7873–7882. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Adamo ML: Regulation of insulin-like
growth factor I gene expression. Implications for normal and
pathological growth. Diabetes Rev. 3:2–27. 1995.
|
|
27.
|
Temmerman L, Slonimsky E and Rosenthal N:
Class 2 IGF-1 isoforms are dispensabile for viability, growth and
maintenance of IGF-1 serum levels. Growth Horm IGF Res. 20:255–263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Matheny RW Jr, Nindl BC and Adamo ML:
Minireview: Mechano-Growth Factor: a putative product of IGF-I gene
expression involved in tissue repair and regeneration.
Endocrinology. 151:865–875. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Adamo ML, Ben-Hur H, LeRoith D and Roberts
CT Jr: Transcription initiation in the two leader exons of the rat
IGF-1 gene occurs from disperse versus localized sites. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 176:887–893. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Simmons JG, Van Wyk JJ, Hoyt EC and Lund
PK: Multiple transcription start sites in the rat insulin-like
growth factor-I gene give rise to IGF-I mRNAs that encode different
IGF-I precursors and are processed differently in vitro. Growth
Factors. 9:205–221. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Jansen M, van Schaik FM, Ricker AT, et al:
Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I
precursor. Nature. 306:609–611. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Roberts CT Jr, Lasky SR, Lowe WI Jr,
Seaman WT and LeRoith D: Molecular cloning of rat insulin-like
growth factor I complementary deoxyribonucleic acids: differential
messenger ribonucleic acid processing and regulation by growth
hormone in extrahepatic tissues. Mol Endocrinol. 1:243–248. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Chew SL, Lavender P, Clark AJ and Ross RJ:
An alternatively spliced human insulin-like growth factor-1
transcript with hepatic tissue expression that diverts away from
mitogenic IBE1 peptide. Endocrinology. 136:1939–1944.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Rotwein P: Two insulin-like growth factor
I messenger RNAs are expressed in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 83:77–81. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Shavlakadze T, Winn N, Rosenthal N and
Grounds MD: Reconciling data from transgenic mice that overexpress
IGF-I specifically in skeletal muscle. Growth Horm IGF Res.
15:4–18. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Winn N, Paul A, Musaro A and Rosenthal N:
Insulin-like growth factor isoforms in skeletal muscle aging,
regeneration, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol.
67:507–518. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Rotwein P: Molecular biology of IGF-1 and
IGF-2. The IGF System. Rosenfeld RG and Roberts CT Jr: Humana
Press; Totowa, NJ: pp. 19–35. 1999, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Siegfried JM, Kasprzyk PG, Treston AM,
Mulshine JL, Quinn KA and Cuttitta F: A mitogenic peptide amide
encoded within the E peptide domain of the insulin-like growth
factor IB prohormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:8107–8111. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Barton ER: The ABCs of IGF-I isoforms:
impact on muscle hypertrophy and implications for repair. Appl
Physiol Nutr Metab. 31:791–797. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Barton ER: Viral expression of
insulin-like growth factor-1 isoforms promotes different responses
in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 100:1778–1784. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Rotwein P, Pollock KM, Didier DK and Krivi
GG: Organization and sequence of the human insulin-like growth
factor I gene. Alternative RNA processing produces two insulin-like
growth factor I precursor peptides. J Biol Chem. 261:4828–4832.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Bach MA, Roberts CT Jr, Smith EP and
LeRoith D: Alternative splicing produces messenger RNAs encoding
insulin-like growth factor-I prohormones that are differentially
glycosylated in vitro. Mol Endocrinol. 4:899–904. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Hameed M, Lange KH, Andersen JL,
Schjerling P, Kjaer M, Harridge SD and Goldspink G: The effect of
recombinant human growth hormone and resistance training of IGF-I
mRNA expression in the muscles of elderly men. J Physiol.
555:231–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Tan DS, Cook A and Chew SL: Nucleolar
localization of an isoform of the IGF-I precursor. BMC Cell Biol.
3:172003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Adamo ML, Neuenschwander S, LeRoith D and
Roberts CT Jr: Structure, expression, and regulation of the IGF-I
gene. Adv Exp Med Biol. 343:1–11. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Wang X, Yang Y and Adamo ML:
Characterization of the rat insulin-like growth factor I gene
promoters and identification of a minimal exon 2 promoter.
Endocrionology. 138:1528–1536. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Mittanck DW, Kim SW and Rotweien P:
Essential promoter elements are located within the 5′ untranslated
region of human insulin-like growth factor-I exon I. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 126:153–163. 1997.
|
|
48.
|
Nolten LA, van Schaik FM, Steenbergh PH
and Sussenbach JS: Expression of the insulin-like growth factor I
gene is stimulated by the liver-enriched transcription factors
C/EBP alpha and LAP. Mol Endocrinol. 8:1636–1645. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Nolten LA, Steenbergh PH and Sussenbach
JS: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha activates promoter 1 of the
human insulin-like growth factor I gene via two distinct binding
sites. Mol Endocrinol. 9:1488–1499. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Armakolas A, Philippou A, Panteleakou Z,
Nezos A, Sourla A, Petraki C and Koutsilieris M: Preferential
expression of IGF-IEc (MGF) transcript in cancerous tissues of
human prostate: evidence for a novel and autonomous growth factor
activity of MGF E peptide in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate.
70:1233–1242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Koczorowska MM, Kwasniewska A and
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A: IGF1 mRNA isoform expression in the cervix of
HPV-positive woman with pre-cancerous and cancer lesions. Exp Ther
Med. 2:149–156. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Górecki DC, Beresewicz M and Zabłocka B:
Neuroprotective effects of short peptides derived from the
Insulin-like growth factor 1. Neurochem Int. 51:451–458.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Juul A, Bang P, Hertel NT, et al: Serum
insulin-like growth factor-I in 1030 healthy children, adolescents,
and adults: relation to age, stage of puberty, testicular size, and
body mass index. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 78:744–752.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Brabant G, von zur Muhlen A, Wurster Ch,
et al: Serum Insulin-like Growth factor I reference values for an
automated chemiluminescence immunoassay system: results from a
multi-center study. Horm Res. 60:53–60. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55.
|
Aimaretti G, Boschetti M, Corneli G, et
al: Normal age-dependent values of serum insulin growth factor-I:
results from a healthy Italian population. J Endocrinol Invest.
31:445–449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Rosario P: Normal values of serum IGF-1 in
adults: results from a Brazilian population. Arq Bras Endocrinol
Metab. 54:477–481. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Andreassen M, Nielsen K, Raymond I,
Kristensen LØ and Faber J: Characteristics and reference ranges of
Insulin-Like Growth factor-I measured with a commercially avaible
immunoassay in 724 healthy adult Caucasians. Scand J Clin Lab
Invest. 69:880–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Yu H, Mistry J, Nicar MJ, Khosravi MJ,
Diamandis A, van Doorn J and Juul A: Insulin-like growth factors
(IGF-I, free IGF-I, and IGF-II) and insulin-like growth factor
binding proteins (IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, IGFBP-6, and ALS) in blood
circulation. J Clin Lab Anal. 13:166–172. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Holmes MD, Pollak MN and Hankinson SE:
Lifestyle correlates of plasma insulin-like growth factor I and
insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 concentrations. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:862–867. 2002.
|
|
60.
|
Schneider HJ, Saller B, Klotsche J, März
W, Erwa W, Wittchen HU and Stalla GK: Oposite associations of
age-dependent insulin-like growth factor-I standard deviation
scores with nutritional state in normal weight and obese subject.
Eur J Endocrinol. 154:699–706. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Platz EA, Pollak MN, Rimm EB, Majeed N,
Tao Y, Willett WC and Giovannucci E: Racial variation in
insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3 concentrations
in middlle-aged men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prevent.
8:1107–1110. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Lecomte P, Lecureuil N, Lecureuil M,
Lemonnier Y, Mariotte N, Valat C and Garrigue MA: Sex differences
in the control of sex-hormone-binding globulin in the elderly: role
of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin. Eur J Endocrinol.
139:178–183. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Sandhu MS, Heald AH, Gibson JM,
Cruickshank JK, Dunger DB and Wareham NJ: Circulating
concentrations of insulin like growth factor-I and development of
glucose intolerance: a prospective observational study. Lancet.
359:1740–1745. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Sesti G, Sciacqua A, Cardellini M, et al:
Plasma concentration of IGF-I is independently associated with
insulin sensitivity in subjects with different degrees of glucose
tolerance. Diabetes Care. 28:120–125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Livingstone C and Ferns G: Insulin-like
growth factor-related proteins and diabetic complications. Br J
Diabetes Vasc Dis. 3:326–331. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66.
|
Froesch E, Hussain M, Schmid Ch and Zapf
J: Insulin-like growth factor I: physiology, metabolic effects and
clinical uses. Diabetes Metab Rev. 12:195–215. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Pao CI, Farmer PK, Begovic S, Goldstein S,
Wu GJ and Philips LS: Expression of hepatic insulin-like growth
factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 genes is
transcriptionally regulated in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Mol
Endocrinol. 6:969–977. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
LeRoith D, Bondy C, Yakar S, Liu JL and
Butler A: The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr Rev. 22:53–74.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69.
|
Blum W, Albertsson-Wikland K, Rosberg S
and Ranke M: Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) and
IGF binding protein 3 reflect spontaneous growth hormone secretion.
J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 76:1610–1616. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A
and Friend KE: The effects of insulin-like growth factors on
tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 21:215–244. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
O’Dell SD and Day IN: Insulin-like growth
factor II (IGF-II). Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 30:767–771. 1998.
|
|
72.
|
Szebenyi G and Rotweien P: The mouse
insulin-like growth factor II/cation-independent mannose
6-phosphate (IGF-II/MPR) receptor gene: molecular cloning and
genomic organization. Genomics. 19:120–129. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, et al:
Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity
insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:3278–3288. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Stewart CEH and Rotwein P: Growth,
differentiation, and survival: multiple physiological functions for
insulin-like growth factors. Physiol Rev. 76:1005–1026.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Baserga R: The IGF-1 receptor in cancer
biology. Int J Cancer. 107:873–877. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Grimberg A: Mechanisms by which IGF-I may
promote cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2:630–635. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Delafontaine P, Song YH and Li Y:
Expression, regulation, and function of IGF-1, IGF-1R, and IGF-1
binding proteins in blood vessels. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
24:435–444. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Yu H and Rohan T: Role of the insulin-like
growth factor family in cancer development and progression. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1472–1489. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D and Brodt P:
The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis:
overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 28:20–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Laureys G, Barton DE, Ullrich A and
Francke U: Chromosomal mapping of the gene for the type II
insulin-like growth factor receptor/cation-independent mannose
6-phosphate receptor in man and mouse. Genomics. 3:224–229. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81.
|
Morgan DO, Edman JC, Standring DN, Fried
VA, Smith MC, Roth RA and Rutter WJ: Insulin-like growth factor II
receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 329:301–307.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82.
|
Lau MM, Stewart CE, Liu Z, Bhatt H,
Rotwein P and Stewart CL: Loss of the imprinted
IGF2/cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor results in
fetal overgrowth and perinatal lethality. Genes Dev. 8:2953–2963.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83.
|
Sun H, Chua M-S, Yang D, Tsalenko A, Peter
B and So S: Antibody arrays identify potential diagnostic markers
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark Insights. 3:1–18.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84.
|
Tovar V, Alsinet C, Villanueva A, et al:
IGF activation in a molecular subclass of hepatocellular carcinoma
and pre-clinical efficacy of IGF-1R blockage. J Hepatol.
52:550–559. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85.
|
Weng CJ, Hsieh YH, Tsai CM, et al:
Relationship of insulin-like growth factors system gene
polymorphisms with the susceptibility and pathological development
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1808–1815. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86.
|
Scharf JG, Schmidt-Sandte W, Pahernik SA,
Ramadori G, Braulke T and Hartmann H: Characterization of the
insulin-like growth factor axis in a human hepatoma cell line
(PLC). Carcinogenesis. 19:2121–2128. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87.
|
Tsai TF, Yauk YK, Chou CK, et al: Evidence
of autocrine regulation in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 153:39–45. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88.
|
Tanaka S, Mohr L, Schmidt EV, Sugimachi K
and Wands JR: Biological effects of human insulin receptor
substrate-1 over-expression in hepatocytes. Hepatology. 26:598–604.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89.
|
Nishiyama M and Wands JR: Cloning and
increased expression of an insulin receptor substrate-1-like gene
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
183:280–285. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90.
|
Coutant A, Rescan C, Gilot D, Loyer P,
Guguen-Guillouzo C and Baffet G: PI3K- FRAP/mTOR pathway is
critical for hepatocyte proliferation whereas MEK/ERK supports both
proliferation and survival. Hepatology. 36:1079–1088. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91.
|
Alexia C, Fallot G, Lasfer M,
Schweizer-Groyer G and Groyer A: An evaluation of the role of
insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and of type-I IGF receptor
signaling in hepatocarcinogenesis and in the resistance of
hepatocellular cells against drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem
Pharmacol. 86:1003–1015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92.
|
LeRoith D: Insulin-like growth factor I
receptor signaling-overlapping or redundant pathways.
Endocrinology. 141:1287–1288. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93.
|
Knittel T, Dinter C, Kobold D, Neubauer K,
Mehde M, Eichhorst S and Ramadori G: Expression and regulation of
cell adhesion molecules by hepatic stellate cells (HSC) of rat
liver: involvement of HSC in recruitment of inflammatory cells
during hepatic tissue repair. Am J Pathol. 154:153–167. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94.
|
Wu JC, Daughaday WH, Lee SD, et al:
Radioimmunoassay of serum IGF-I and IGF-II in patients with chronic
liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma with or without
hypoglycemia. J Lab Clin Med. 112:589–594. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95.
|
Kratzsch J, Blum WF, Schenker E and Keller
E: Regulation of growth hormone (GH), insulin-like growth factor
(IGF) I, IGF binding proteins -1, -2, -3 and GH binding protein
during progression of liver cirrhosis. Exp Clin Endocrinol
Diabetes. 103:285–291. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96.
|
Nikolić JA, Todorović V, Bozić M, et al:
Serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II is more closely
associated with liver disfunction than is IGF-I in patients with
cirrhosis. Clin Chim Acta. 294:169–177. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97.
|
Okan A, Comlekci A, Akpinar H, Okan I,
Yesil S, Tankurt E and Simsek I: Serum concentration of
insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-3 in patients with chronic hepatitis. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 35:1212–1215. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98.
|
Stuver SO, Kuper H, Tzonou A, Lagiou P,
Spanos E and Hsieh CC: Insulin-like growth factor 1 in
hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic liver cancer in men. Int J
Cancer. 87:118–121. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99.
|
Vyzantiadis T, Theodoridou S, Giouleme O,
Harsoulis P, Evgenidis N and Vyzantiadis A: Serum concentrations of
insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in patients with liver
cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 50:814–816. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100.
|
Lorenzo-Zúñiga V, Bartoli R, Masnou H,
Montoliu S, Morillas RM and Planas R: Serum concentration of
insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) as a marker of liver fibrosis
in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci. 52:3245–3250.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101.
|
Mahdy KA, Ahmed HH, Mannaa F and
Abdel-Shaheed A: Clinical benefits of biochemical markers of bone
turnover in Egyptian children with chronic liver diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:785–790. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102.
|
Mazziotti G, Sorvillo F, Morisco F, et al:
Serum insulin-growth factor I evaluation as a useful tool for
predicting the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in
patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis: a prospective
study. Cancer. 95:2539–2545. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103.
|
Wu YL, Ye J, Zhang S, Zhong J and Xi RP:
Clinical significance of serum IGF-I, IGF-II and IGFBP-3 in liver
cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2740–2743. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104.
|
Weber MM, Auernhammer CJ, Lee PD,
Engelhardt D and Zachoval R: Insulin-like growth factors and
insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in adult patients with
severe liver disease before and after orthotropic liver
transplantation. Horm Res. 57:105–112. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105.
|
Ranke MB, Maier KP, Schweizer R, Stadler
B, Schleicher S, Elmlinger MW and Flehmig B: Pilot study of
elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 as
indicators of hepatocellular carcinoma. Horm Res. 60:174–180. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106.
|
Morali G, Shitrit AB, Eran M, Freier S,
Reinus C and Braverman D: Hepatic production of insulin-like growth
factors in normal and diseased liver. Hepatogastroenterology.
52:1511–1515. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107.
|
Nordstedt G, Levinovitz A, Möller C,
Eriksson LC and Anderson G: Expression of insulin-like growth
factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-II mRNA during hepatic development,
proliferation and carcinogenesis in the rat. Carcinogenesis.
9:209–213. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108.
|
Couvert P, Carrie A, Paries J, et al:
Liver insulin-like growth factor 2 methylation in hepatitis C virus
cirrhosis and further occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. World
J Gastroenterol. 14:5419–5427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109.
|
Price JA, Kovach SJ, Johnson T, Koniaris
LG, Cahill PA, Sitzmann JV and McKillop IH: Insulin-like growth
factor I is a comitogen for hepatocytes growth factor in a rat
model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 36:1089–1097. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110.
|
Kim SO, Park JG and Lee YI: Increased
expression of the insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptor
gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines: implications of the
IGF-I receptor gene activation by hepatitis B virus X gene product.
Cancer Res. 56:3831–3836. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111.
|
Nardone G, Romano M, Calabro A, et al:
Activation of fetal promoters of insulin-like growth factors II
gene in hepatitis C virus-related chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 23:1304–1312. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112.
|
Sohda T, Kamimura S, Iwata K, Shijo H and
Okumura M: Immunohistochemical evidence of insulin-like growth
factor II in human small hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis C
virus infection: relationship to fatty change in carcinoma cells. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:224–228. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113.
|
Chin E, Zhou J, Dai J, Baxter RC and Bondy
CA: Cellular localization and regulation of gene expression for
components of the insulin-like growth factor ternary binding
protein complex. Endocrinology. 134:2498–2504. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114.
|
Arany E, Afford S, Strain AJ, Winwood PJ,
Arthur MJ and Hill DJ: Differential cellular synthesis of
insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) and IGFBP-3
within human liver. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 79:1871–1876.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115.
|
Ross RJM, Chew SL, D’Souza Li L, et al:
Expression of IGF-I and IGF-binding protein genes in cirrhotic
liver. J Endocrinol. 149:209–216. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116.
|
Völzke H, Nauck M, Rettig R, Dörr M,
Higham C, Brabant G and Wallaschofski H: Association between
hepatic steatosis and serum IGF1 and IGFBP-3 levels in a
population-based sample. Eur J Endocrinol. 161:705–713.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117.
|
Colakoğlu O, Taşkiran B, Colakoğlu G,
Kizildağ S, Ari Ozkan F and Unsal B: Serum insulin like growth
factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin growth factor binding protein-3
(IGFBP-3) levels in liver cirrhosis. Turk J Gastroenterol.
18:245–249. 2007.
|
|
118.
|
Mattera D, Capuano G, Colao A, Pivonello
R, Manguso F, Puzziello A and D’Agostino L: Increased IGF-I :
IGFBP-3 ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin
Endocrinol. 59:699–706. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119.
|
Moller S, Juul A, Becker U, Flyvbjerg A,
Skakkebaek NE and Henriksen JH: Concentrations, release, and
disposal of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins
(IGFBP), IGF-I, and growth hormone in different vascular beds in
patients with cirrhosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 80:1148–1157.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120.
|
Juul A, Dalgaard P, Blum WF, et al: Serum
levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3
(IGFBP-3) in healthy infants, children, and adolescents: the
relation to IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, age, sex, body mass
index, and pubertal maturation. J Clin Endocrin Metabol.
80:2534–2542. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121.
|
Raslan HM, Ezzat WM, Ahmed MM and Rasheed
EA: Insulin growth factor-1 and insulin growth factor binding
protein-3 in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C. Arch Med
Sci. 3:46–51. 2007.
|
|
122.
|
Shin SY, Lee JR, Noh GW, Kim HJ, Kang WJ,
Kim SH and Chung JK: Analysis of serum levels of anti-Mullerian
hormone, inhibin B, insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like
growth factor binding protein-3, and follicle-stimulating hormone
with respect to age and menopausal status. J Korean Med Sci.
23:104–110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123.
|
Okabe H, Satoh S, Kato T, et al:
Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in human hepatocellular
carcionamas using cDNA microarray: identification of genes involved
in viral carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Cancer Res.
61:2129–2137. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124.
|
Su TS, Liu WY, Han SH, Jansen M, Yang-Fen
TL, P’eng FK and Chou CK: Transcripts of the insulin-like growth
factors I and II in human hepatoma. Cancer Res. 49:1773–1777.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125.
|
Ng IO, Lee J MF, Srivastava G and Ng M:
Expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:152–157. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126.
|
Cariani E, Lasserre C, Seurin D, et al:
Differential expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in
human primary liver cancers, benign liver tumors, and liver
cirrhosis. Cancer Res. 48:6844–6849. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127.
|
Lamas E, Le Bail B, Housset C, Boucher O
and Brechot C: Localization of insulin-like growth factor-II and
hepatitis B virus mRNAs and proteins in human hepatocellular
carcinomas. Lab Invest. 64:98–104. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128.
|
Lamas E, Zindy F, Seurin D,
Guguen-Guillouzo and Brechot C: Expression of insulin-like growth
factor II and receptors for insulin-like growth factor II,
insulin-like growth factor I and insulin in isolated and cultured
rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 13:936–940. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129.
|
D’Errico A, Grignioni WF, Fiorentino M, et
al: Expression of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) in human
hepatocellular carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study. Pathol Int.
44:131–137. 1994.
|
|
130.
|
Iizuka N, Oka M, Tamesa T, Hamamoto Y and
Yamada-Okabe H: Imbalance in expression levels of insulin-like
growth factor 2 and H19 transcripts linked to progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 24:4085–4089.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131.
|
Sedlaczek N, Hasilik A, Neuhaus P,
Schuppan D and Herbst H: Focal overexpression of insulin-like
growth factor 2 by hepatocytes and cholangiocytes in viral liver
cirrhosis. Br J Cancer. 88:733–739. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132.
|
Caro JF, Poulos J, Ittoop O, Pories WJ,
Flickinger EG and Sinha MK: Insulin-like growth factor binding in
hepatocytes from human liver, human hepatoma, and normal,
regenerating, and fetal rat liver. J Clin Invest. 81:976–981. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133.
|
Verspohl EJ, Maddux BA and Goldfine ID:
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I regulate the same
biological functions in HEP-G2 cells via their own specific
receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 67:169–174. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134.
|
Zhang YC, Wang XP, Zhang LY, Song AL, Kou
ZM and Li XS: Effect of blocking IGF-I receptor on growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol.
12:3977–3982. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135.
|
Lee YI, Han YJ, Lee SY, et al: Activation
of insulin-like growth factor II signaling by mutant type p53.
Physiological implications for potentiation of IGF-II signaling by
p53 mutant 249. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 203:51–63. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136.
|
Lee YI, Lee S, Das GC, Park US and Park
SM: Activation of the insulin-like growth factor II transcription
by aflatoxin B1 induced p53 mutant 249 is caused by activation of
transcription complexes; implications for a gain-of-function during
formation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 19:3717–3726.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137.
|
De Souza AT, Hankins GR, Washington MK,
Orton TC and Jirtle RL: M6P/IGF2R gene is mutated in human
hepatocellular carcinomas with loss of heterozygosity. Nat Genet.
11:447–449. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138.
|
Su WW, Lee KT, Yeh YT, Soon MS, Wang CL,
Yu ML and Wang SN: Association of circulating insulin-like growth
factor 1 with hepatocellular carcinoma: one cross-sectional
correlation study. J Clin Lab Anal. 24:195–200. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139.
|
Plöckinger U, Krüger D, Bergk A,
Wiedenmann B and Berg T: Hepatitis-C patients have reduced growth
hormone (GH) secretion which improves during long-term therapy with
pegylated interferon-alpha. Am J Gastroenterol. 102:2724–2731.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140.
|
Helaly GF, Hussein NG, Refai W and Ibrahim
M: Relation of serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels
with hepatitis C virus infection and insulin resistance. Transl
Res. 158:155–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141.
|
Adamek A, Kasprzak A, Seraszek A, Mikos H,
Bura A and Mozer-Lisewska I: Alterations of serum levels of
insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and estradiol in chronic
hepatitis C. Onkol Wspol. 16:234–239. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142.
|
Conchillo M, Prieto J and Quiroga J:
Insulin like growth factor I (IGF-I) and liver cirrhosis. Rev Esp
Enferm Dig. 99:156–164. 2007.(In Spanish).
|
|
143.
|
Hung CH, Wang JH, Hu TH, et al: Insulin
resistance is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic
hepatitis C infection. World J Gastroenterol. 16:2265–2271. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144.
|
Stefano JT, Correa-Giannella ML, Ribeiro
CMF, Alves VAF, Massarollo PCB, Machado MCC and Giannella-Neto D:
Increased hepatic expression of insulin-like growth factor-I
receptor in chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol.
28:3821–3828. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145.
|
Tanaka S, Takenaka K, Matsumata T, Mori R
and Sugimachi K: Hepatitis C virus replication is associated with
expression of transforming growth factor-alpha and insulin-like
growth factor-II in cirrhotic livers. Dig Dis Sci. 41:208–215.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146.
|
Sohda T, Oka Y, Iwata K, et al:
Co-localisation of insulin-like growth factor II and the
proliferation marker MIB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Clin
Pathol. 50:135–137. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147.
|
Yakar S, LeRoith D and Brodt P: The role
of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis in tumor
growth and progression: lessons from animal models. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 16:407–420. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148.
|
Wu Y, Brodt P, Sun H, et al: Insulin-like
growth factor-I regulates the liver microenvironment in obese mice
and promotes liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 70:57–67. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149.
|
Lee S, Park U and Lee YI: Hepatitis C
virus core protein transactivates insulin-like growth factor II
gene transcription through acting concurrently on Egr1 and Sp1
sites. Virology. 283:167–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150.
|
Kasprzak A, Adamek A, Przybyszewska W, et
al: Expression of IGF-I and viral proteins (C, NS3, NS5A) in the
livers of patients with chronic HCV infection. Adv Clin Exp Med.
20:263–273. 2011.
|