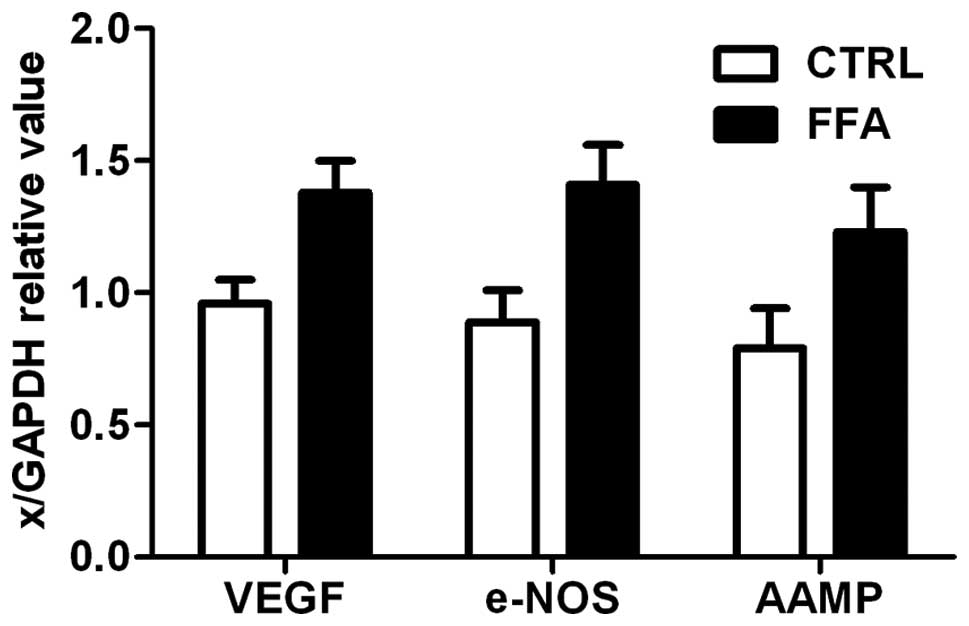
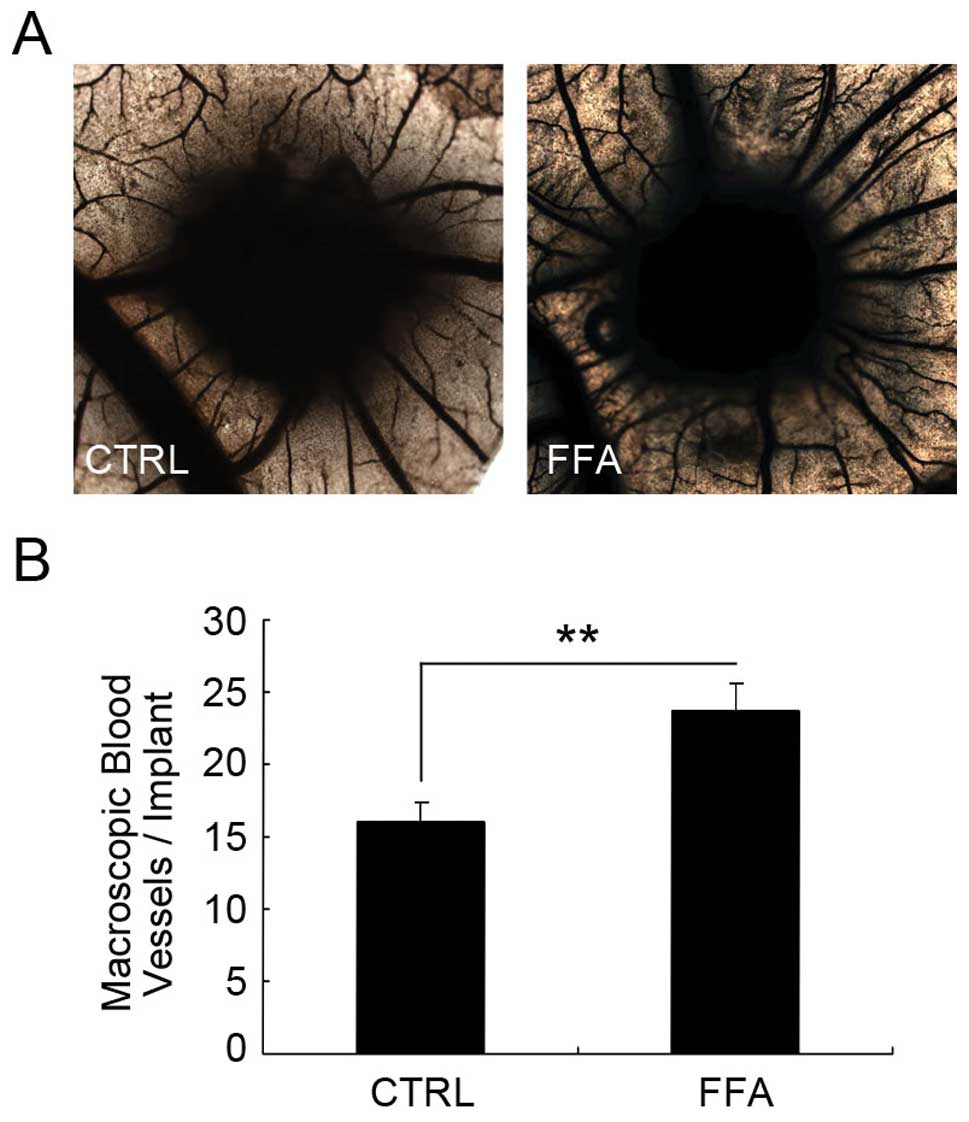
|
1
|
Tonnesen MG, Feng X and Clark RA:
Angiogenesis in wound healing. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc.
5:40–46. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Breier G: Angiogenesis in embryonic
development - a review. Placenta. 21(Suppl A): S11–S15. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Costa C, Incio J and Soares R:
Angiogenesis and chronic inflammation: cause or consequence?
Angiogenesis. 10:149–166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trayhurn P and Wood IS: Adipokines:
inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J
Nutr. 92:347–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wubben DP and Adams AK: Metabolic
syndrome: what’s in a name? WMJ. 105:17–20. 2006.
|
|
9
|
Tan TT and Coussens LM: Humoral immunity,
inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol. 19:209–216. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Otani A, Takagi H, Oh H, Koyama S,
Matsumura M and Honda Y: Expressions of angiopoietins and Tie2 in
human choroidal neovascular membranes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
40:1912–1920. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Benelli R, Lorusso G, Albini A and Noonan
DM: Cytokines and chemokines as regulators of angiogenesis in
health and disease. Curr Pharm Des. 12:3101–3115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nathan C: Points of control in
inflammation. Nature. 420:846–852. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mrowietz U and Boehncke WH: Leukocyte
adhesion: a suitable target for anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr Pharm
Des. 12:2825–2831. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee FH, Haskell C, Charo IF and Boettiger
D: Receptor-ligand binding in the cell-substrate contact zone: a
quantitative analysis using CX3CR1 and CXCR1 chemokine receptors.
Biochemistry. 43:7179–7186. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pacifico F and Leonardi A: NF-kappaB in
solid tumors. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1142–1152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nam NH: Naturally occurring NF-kappaB
inhibitors. Mini Rev Med Chem. 6:945–951. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Flower RJ: Drugs which inhibit
prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 26:33–67. 1974.
|
|
19
|
Naziroglu M, Luckhoff A and Jungling E:
Antagonist effect of flufenamic acid on TRPM2 cation channels
activated by hydrogen peroxide. Cell Biochem Funct. 25:383–387.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peppiatt-Wildman CM, Albert AP, Saleh SN
and Large WA: Endothelin-1 activates a Ca2+-permeable
cation channel with TRPC3 and TRPC7 properties in rabbit coronary
artery myocytes. J Physiol. 580:755–764. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Farrugia G, Rae JL, Sarr MG and
Szurszewski JH: Potassium current in circular smooth muscle of
human jejunum activated by fenamates. Am J Physiol. 265:G873–G879.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Doughty JM, Miller AL and Langton PD:
Non-specificity of chloride channel blockers in rat cerebral
arteries: block of the L-type calcium channel. J Physiol.
507:433–439. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Greenwood IA and Large WA: Comparison of
the effects of fenamates on Ca-activated chloride and potassium
currents in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol.
116:2939–2948. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Inoue R, Okada T, Onoue H, et al: The
transient receptor potential protein homologue TRP6 is the
essential component of vascular alpha(1)-adrenoceptor-activated
Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel. Circ Res. 88:325–332.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jung S, Strotmann R, Schultz G and Plant
TD: TRPC6 is a candidate channel involved in receptor-stimulated
cation currents in A7r5 smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 282:C347–C359. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poteser M, Graziani A, Eder P, et al:
Identification of a rare subset of adipose tissue-resident
progenitor cells, which express CD133 and TRPC3 as a VEGF-regulated
Ca2+ entry channel. FEBS Lett. 582:2696–2702. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hamdollah Zadeh MA, Glass CA, Magnussen A,
Hancox JC and Bates DO: VEGF-mediated elevated intracellular
calcium and angiogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells
in vitro are inhibited by dominant negative TRPC6.
Microcirculation. 15:605–614. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ge R, Tai Y, Sun Y, et al: Critical role
of TRPC6 channels in VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Lett.
283:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ribatti D, Nico B, Vacca A and Presta M:
The gelatin sponge-chorioallantoic membrane assay. Nat Protoc.
1:85–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schober W, Wiskirchen J, Kehlbach R, et
al: Flufenamic acid: growth modulating effects on human aortic
smooth muscle cells in vitro. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 13:89–96. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tiemann U, Neels P, Pohland R, Walzel H
and Lohrke B: Influence of inhibitors on increase in intracellular
free calcium and proliferation induced by platelet-activating
factor in bovine oviductal cells. J Reprod Fertil. 116:63–72. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weiser T and Wienrich M: Investigations on
the mechanism of action of the antiproliferant and ion channel
antagonist flufenamic acid. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
353:452–460. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wilson BD, Ii M, Park KW, et al: Netrins
promote developmental and therapeutic angiogenesis. Science.
313:640–644. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chi Y, Li K, Yan Q, et al: Nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drug flufenamic acid is a potent activator of
AMP-activated protein kinase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 339:257–266.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Towler MC and Hardie DG: AMP-activated
protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ
Res. 100:328–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Del Carratore R, Carpi A, Beffy P, et al:
Itraconazole inhibits HMEC-1 angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother.
66:312–317. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aoki C, Hattori Y, Tomizawa A, Jojima T
and Kasai K: Anti-inflammatory role of cilostazol in vascular
smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo. J Atheroscler Thromb.
7:503–509. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shin MJ, Lee YP, Kim DW, et al: Transduced
PEP-1-AMPK inhibits the LPS-induced expression of COX-2 and iNOS in
Raw264. 7 cells. BMB Rep. 43:40–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kongsuphol P, Cassidy D, Hieke B, et al:
Mechanistic insight into control of CFTR by AMPK. J Biol Chem.
284:5645–5653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kréneisz O, Benoit JP, Bayliss DA and
Mulkey DK: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits TREK channels. J
Physiol. 587:5819–5830. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Klein H, Garneau L, Trinh NTN, et al:
Inhibition of the KCa3. 1 channels by AMP-activated protein kinase
in human airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
296:C285–C295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schlichter LC, Sakellaropoulos G, Ballyk
B, Pennefather PS and Phipps DJ: Properties of K+ and
Cl− channels and their involvement in proliferation of
rat microglial cells. Glia. 17:225–236. 1996.
|
|
43
|
Guilbert A, Gautier M, Dhennin-Duthille I,
Haren N, Sevestre H and Ouadid-Ahidouch H: Evidence that TRPM7 is
required for breast cancer cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 297:C493–C502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang SL, Cao Q, Zhou KC, Feng YJ and Wang
YZ: Transient receptor potential channel C3 contributes to the
progression of human ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 28:1320–1328. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schilling T and Eder C: Non-selective
cation channel activity is required for
lysophosphatidylcholine-induced monocyte migration. J Cell Physiol.
221:325–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fiedler U, Reiss Y, Scharpfenecker M, et
al: Angiopoietin-2 sensitizes endothelial cells to TNF-alpha and
has a crucial role in the induction of inflammation. Nat Med.
12:235–239. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fiedler U and Augustin HG: Angiopoietins:
a link between angiogenesis and inflammation. Trends Immunol.
27:552–558. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Noonan DM, De Lerma Barbaro A, Vannini N,
Mortara L and Albini A: Inflammation, inflammatory cells and
angiogenesis: decisions and indecisions. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
27:31–40. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|