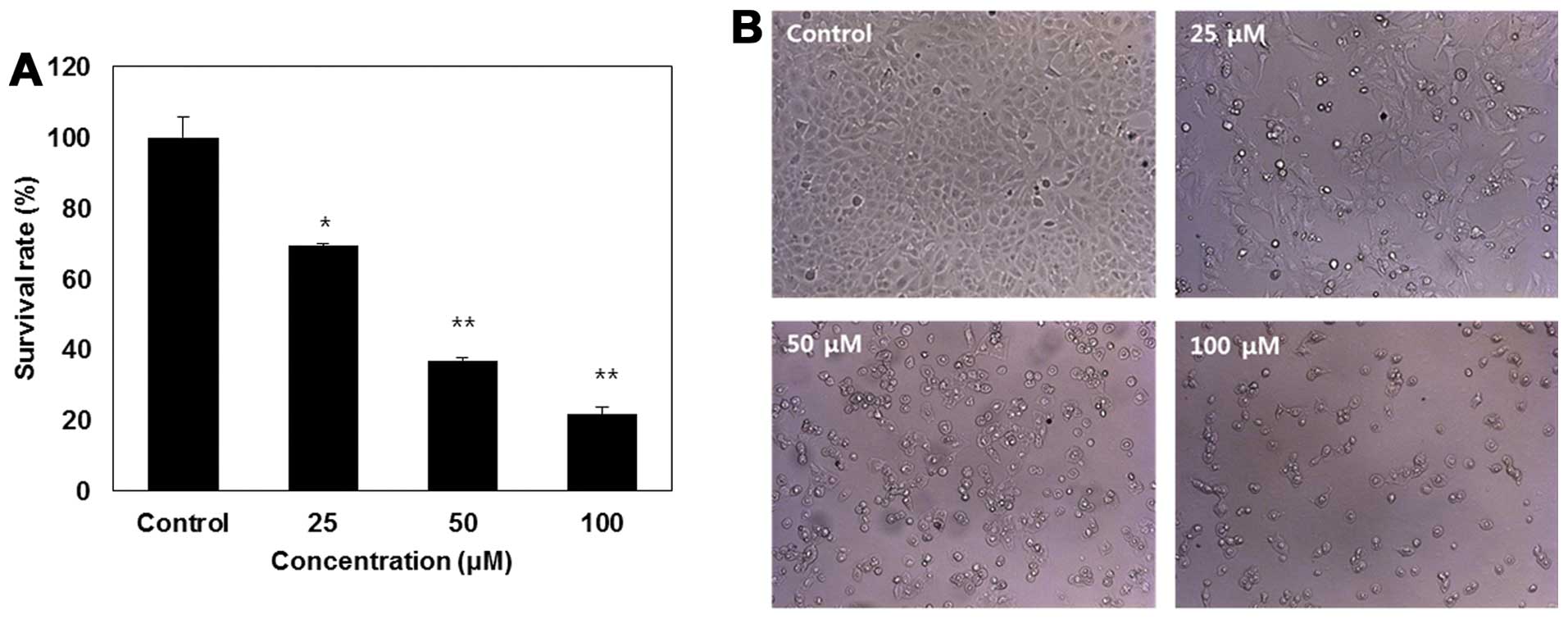
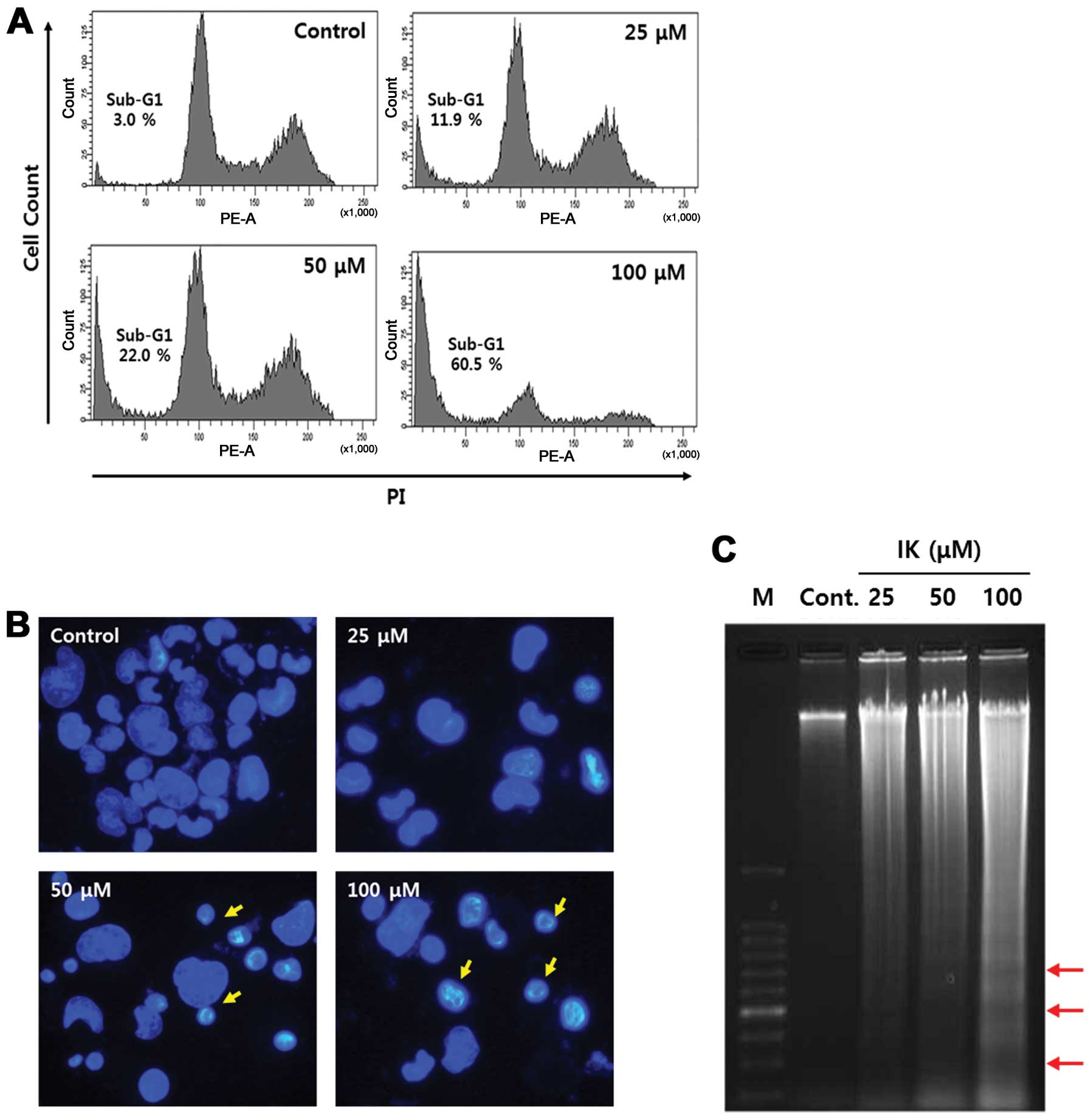
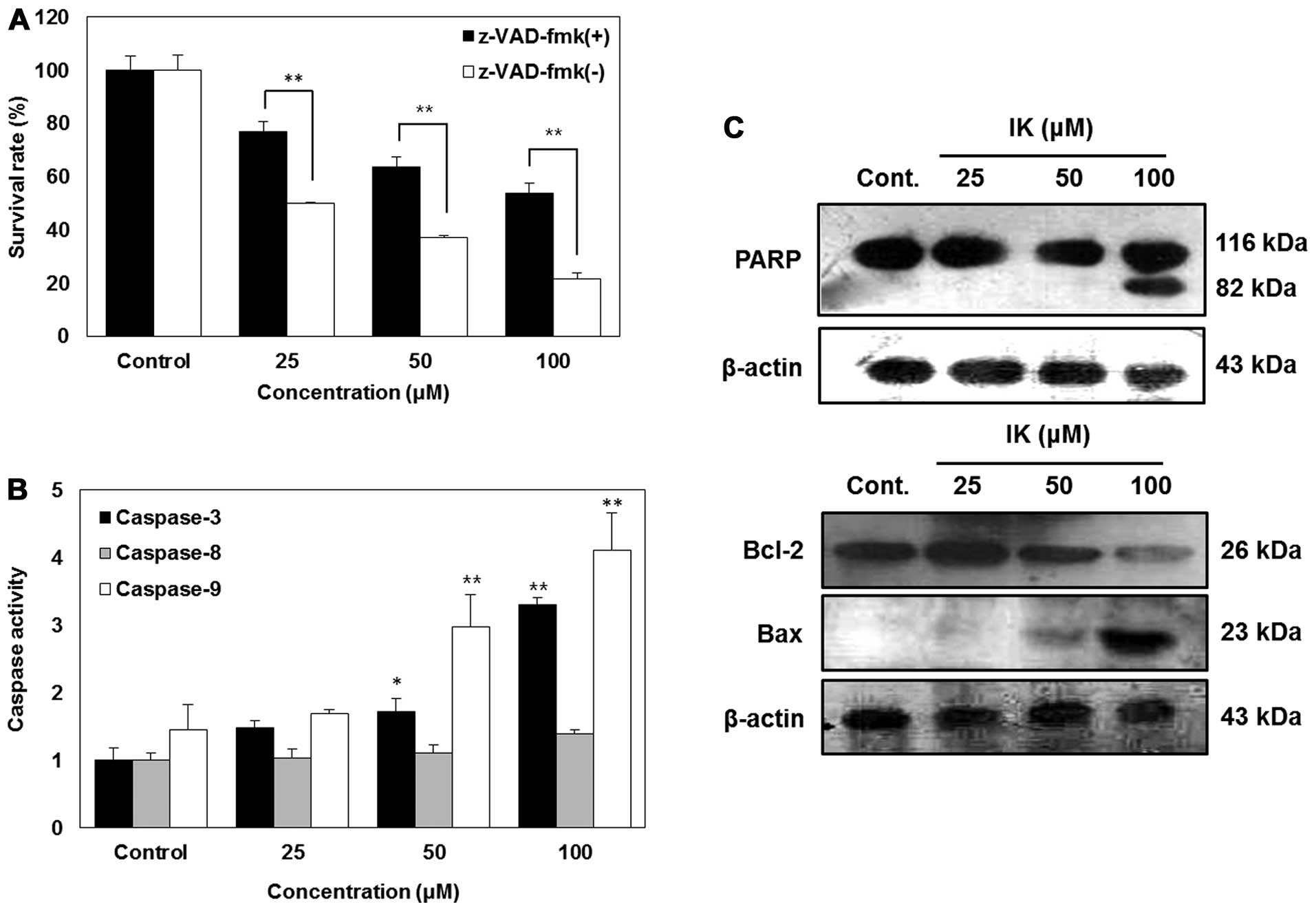
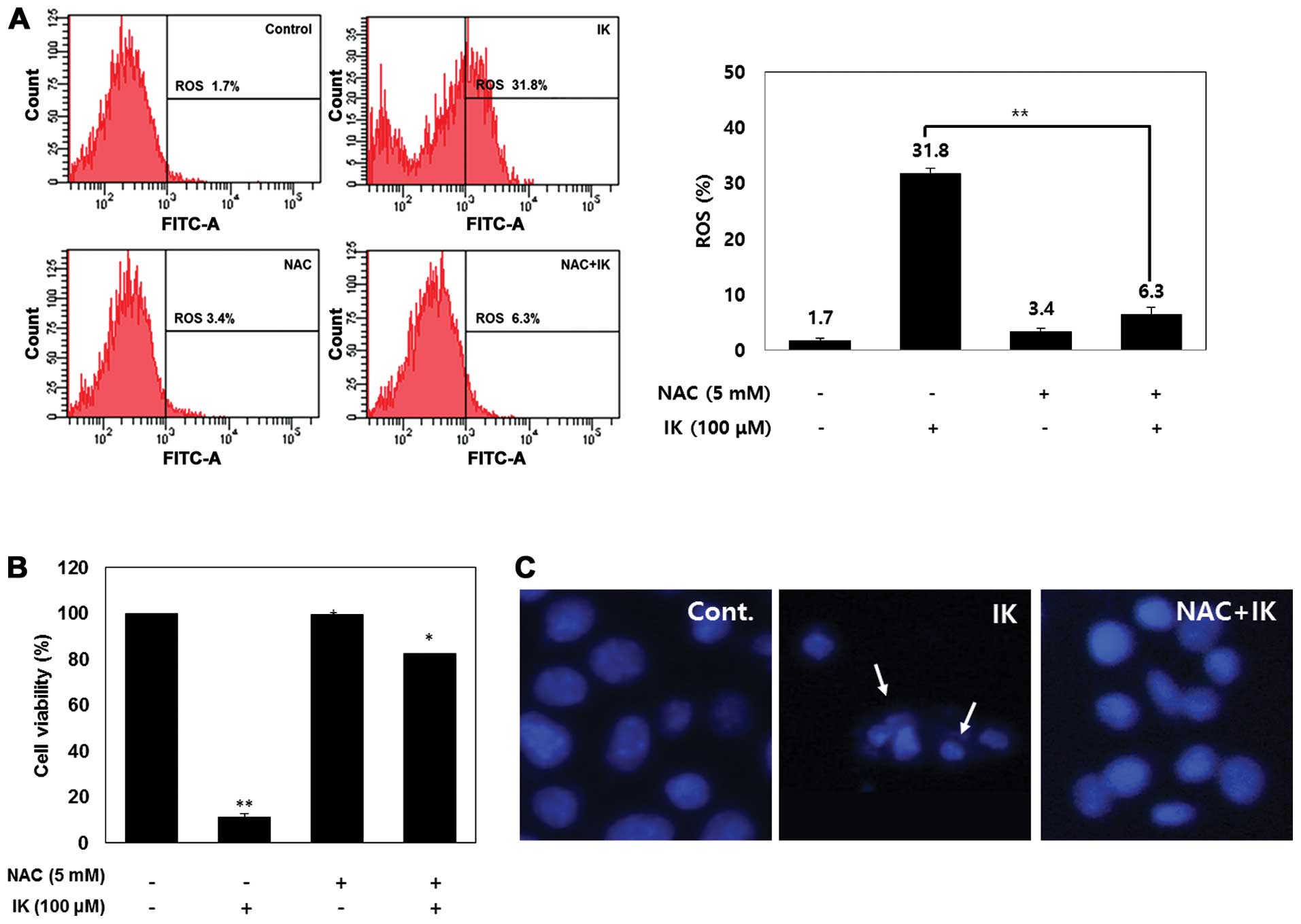
|
1
|
Park K, Nam D, Yun H, et al:
B-caryophyllene oxide inhibits growth and induces apoptosis through
the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 pathways and ROS-mediated
MAPKs activation. Cancer Lett. 312:178–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seo WH and Baek HH: Characteristic
aroma-active compounds of korean perilla (perilla frutescens
britton) leaf. J Agric Food Chem. 57:11537–11542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choung M, Kwon Y and Kwak Y: Test of
components related to quality in perilla leaves: II. test of
volatile flavor components in perilla leaves. RDA J Agric Sci.
40:127–132. 1998.
|
|
4
|
Lee B: Comparison of analytical methods
for volatile flavor compounds in leaf of perilla frutescens.
Korean J Crop Sci. 44:154–158. 1999.
|
|
5
|
Lim S, Seo Y, Lee Y and Baek N: Isolation
of volatile allelochemicals from leaves of perilla
frutescens and artemisia asiatica. Agricult Chem
Biotechnol. 37:115–123. 1994.
|
|
6
|
Park YD, Jin CH, Choi DS, Byun M and Jeong
IY: Biological evaluation of isoegomaketone isolated from
perilla frutescens and its synthetic derivatives as
anti-inflammatory agents. Arch Pharm Res. 34:1277–1282.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho BO, Jin CH, Park YD, Ryu HW, Byun MW,
Seo KI and Jeong IY: Isoegomaketone induces apoptosis through
caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways in human DLD1
cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 75:1306–1311. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Devasagayam TP, Tilak JC, Boloor KK, Sane
KS, Ghaskadbi SS and Lele RD: Free radicals and antioxidants in
human health: current status and future prospects. J Assoc
Physicians India. 52:794–804. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simon H, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sander C, Hamm F, Elsner P and Thiele J:
Oxidative stress in malignant melanoma and non-melanoma skin
cancer. Br J Dermatol. 148:913–922. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ralph SJ, Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Neuzil J
and Moreno-Sánchez R: Bioenergetic pathways in tumor mitochondria
as targets for cancer therapy and the importance of the ROS-induced
apoptotic trigger. Mol Aspects Med. 31:29–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raj L, Ide T, Gurkar AU, et al: Selective
killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the stress
response to ROS. Nature. 475:231–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morgensztern D and McLeod HL:
PI3K/akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer
Drugs. 16:797–803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F,
de Bono JS and Workman P: Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway:
progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8:393–412.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, et al:
Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:520–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vara JÁF, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P,
Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/akt signalling pathway
and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brugge J, Hung M and Mills GB: A new
mutational aktivation in the PI3K pathway. Cancer Cell. 12:104–107.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Agarwal R, Carey M, Hennessy B and Mills
GB: PI3K pathway-directed therapeutic strategies in cancer. Curr
Opin Investig Drugs. 11:615–628. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee Y, Jeong H, Kim Y, et al: Reactive
oxygen species and PI3K/akt signaling play key roles in the
induction of Nrf2-driven heme oxygenase-1 expression in
sulforaphane-treated human mesothelioma MSTO-211H cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 50:116–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu C, Gong K, Mao X and Li W: Tetrandrine
induces apoptosis by activating reactive oxygen species and
repressing akt activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 129:1519–1531. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mao X, Yu CR, Li WH and Li WX: Induction
of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in
bcr/abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells. Cell
Res. 18:879–888. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ka H, Park H, Jung H, Choi J, Cho K, Ha J
and Lee K: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated
mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 196:143–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin CH, Lee HJ, Park YD, et al:
Isoegomaketone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide
production in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the heme oxygenase-1
induction and inhibition of the interferon-beta-STAT-1 pathway. J
Agric Food Chem. 58:860–867. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, et al:
New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:1107–1112. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park SY, Cho SJ, Kwon HC, Lee KR, Rhee DK
and Pyo S: Caspase-independent cell death by allicin in human
epithelial carcinoma cells: involvement of PKA. Cancer Lett.
224:123–132. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ricote M, Garcia-Tunon I, Fraile B,
Fernandez C, Aller P, Paniagua R and Royuela M: P38 MAPK protects
against TNF-alpha-provoked apoptosis in LNCaP prostatic cancer
cells. Apoptosis. 11:1969–1975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim JY, Park KW, Moon KD, et al: Induction
of apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer cells by crude saponin from
platycodi radix. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:3753–3758. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Chang CH and Lin CC: The
mechanism of ellipticine-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in
human breast MCF-7 cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 223:293–301. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen CY, Liu TZ, Liu YW, et al: 6-shogaol
(alkanone from ginger) induces apoptotic cell death of human
hepatoma p53 mutant mahlavu subline via an oxidative
stress-mediated caspase-dependent mechanism. J Agric Food Chem.
55:948–954. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wan CK, Wang C, Cheung HY, Yang M and Fong
WF: Triptolide induces bcl-2 cleavage and mitochondria dependent
apoptosis in p53-deficient HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 241:31–41.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alnemri ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW,
Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW and Yuan J: Human ICE/CED-3
protease nomenclature. Cell. 87:1711996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsujimoto Y: Role of bcl-2 family proteins
in apoptosis: apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells. 3:697–707.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Candé C, Cecconi F, Dessen P and Kroemer
G: Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): key to the conserved
caspase-independent pathways of cell death? J Cell Sci.
115:4727–4734. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alvarez M, Roman E, Santos ES and Raez LE:
New targets for non-small-cell lung cancer therapy. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 7:1423–1437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Di Cosimo S, Scaltriti M, Val D, et al:
The PI3-K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a target for breast cancer therapy. J
Clin Oncol. 25(Suppl 18): 35112007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin C, Kuo C, Wang J, Cheng J, Huang Z and
Chen C: Growth inhibitory and apoptosis inducing effect of
Perilla frutescens extract on human hepatoma HepG2 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 112:557–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Osakabe N, Yasuda A, Natsume M and
Yoshikawa T: Rosmarinic acid inhibits epidermal inflammatory
responses: anticarcinogenic effect of perilla frutescens
extract in the murine two-stage skin model. Carcinogenesis.
25:549–557. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM and Kaufmann SH:
Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and
functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:383–424. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Köhler C, Orrenius S and Zhivotovsky B:
Evaluation of caspase activity in apoptotic cells. J Immunol
Methods. 265:97–110. 2002.
|
|
42
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, et al:
Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing
factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Su C, Lin J, Li T, et al: Curcumin-induced
apoptosis of human colon cancer colo 205 cells through the
production of ROS, Ca2 and the activation of caspase-3. Anticancer
Res. 26:4379–4389. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hwang J, Ha J, Park I, Lee S, Baik HW, Kim
YM and Park OJ: Apoptotic effect of EGCG in HT-29 colon cancer
cells via AMPK signal pathway. Cancer Lett. 247:115–121. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang J, Wu L, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Reactive oxygen species mediate oridonin-induced HepG2
apoptosis through p53, MAPK, and mitochondrial signaling pathways.
J Pharmacol Sci. 107:370–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Q, Wang Y, Xu K, et al: Curcumin
induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells through a
reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway.
Oncol Rep. 23:397–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, et al:
Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade:
hierarchical activation of caspases-2,-3,-6,-7,-8, and-10 in a
caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 144:281–292.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brunet A, Datta SR and Greenberg ME:
Transcription-dependent and-independent control of neuronal
survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
11:297–305. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Madhunapantula SV, Mosca PJ and Robertson
GP: The akt signaling pathway: an emerging therapeutic target in
malignant melanoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:1032–1049. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chang F, Lee J, Navolanic P, et al:
Involvement of PI3K/akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Osaki M, Oshimura Ma and Ito H: PI3K-akt
pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|