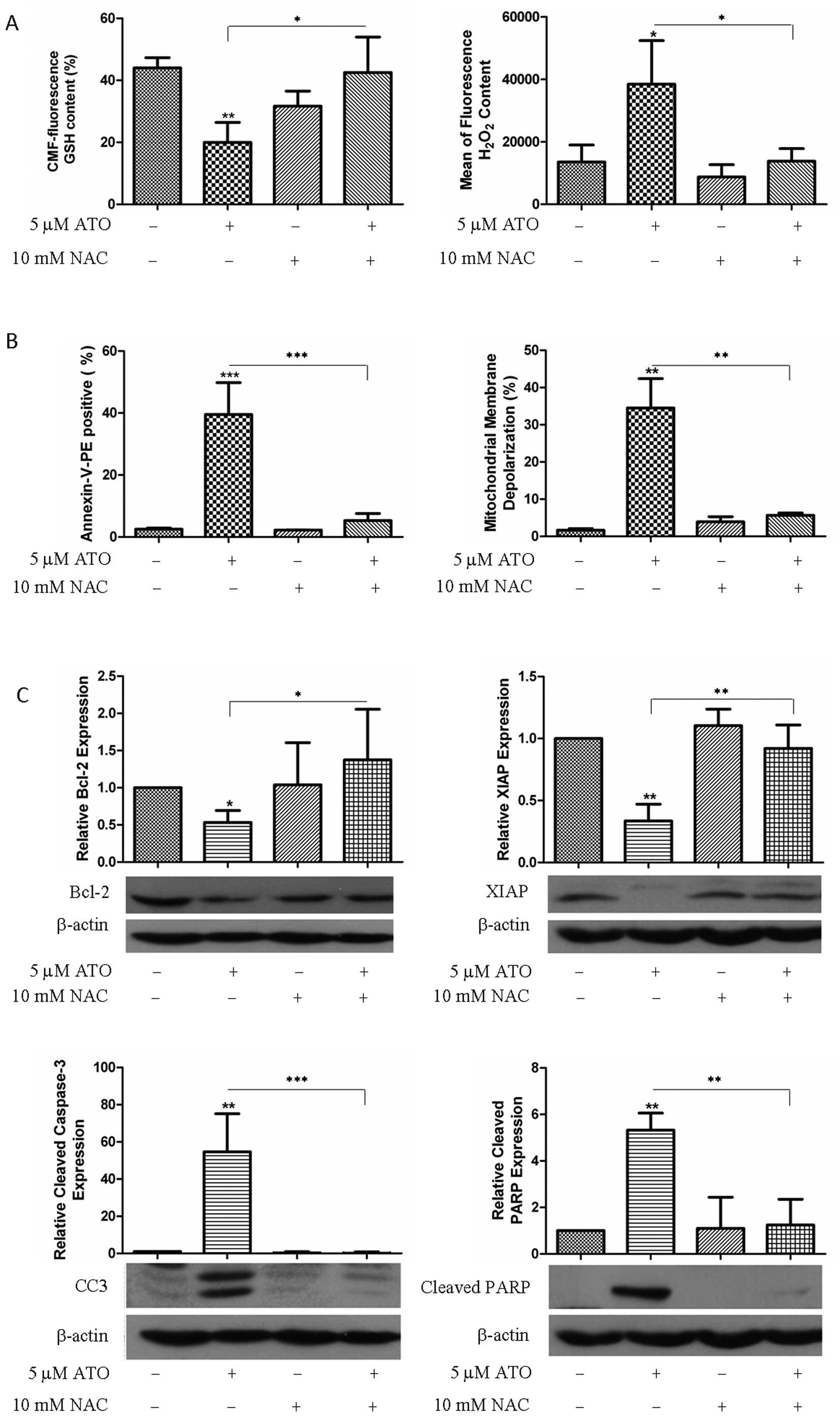
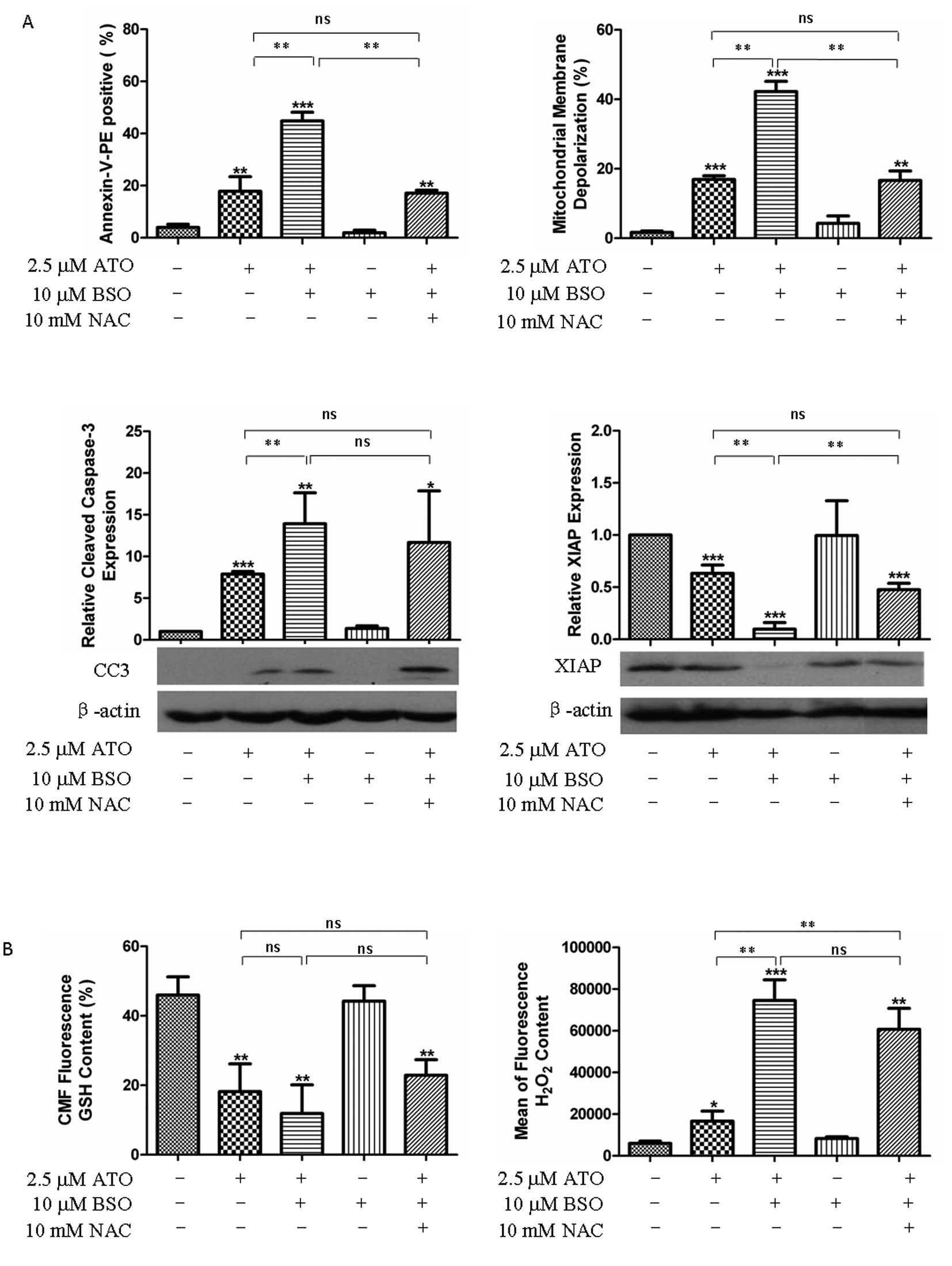
|
1
|
Lally BE, Urbanic JJ, Blackstock AW,
Miller AA and Perry MC: Small cell lung cancer: have we made any
progress over the last 25 years? Oncologist. 12:1096–1104. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, et al: Use of
arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of
acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and
pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 89:3354–3360.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen GQ, Shi XG, Tang W, et al: Use of
arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of
acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): I. As2O3
exerts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells. Blood.
89:3345–3353. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoda A, Toyoshima K, Watanabe Y, et al:
Arsenic trioxide augments Chk2/p53-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting
oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 283:18969–18979. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Qu X, Qu J, et al: Arsenic trioxide
induces apoptosis and G2/M phase arrest by inducing Cbl to inhibit
PI3K/Akt signaling and thereby regulate p53 activation. Cancer
Lett. 284:208–215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scholz C, Richter A, Lehmann M,
Schulze-Osthoff K, Dorken B and Daniel PT: Arsenic trioxide induces
regulated, death receptor-independent cell death through a
Bcl-2-controlled pathway. Oncogene. 24:7031–7042. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, et al: In vitro
studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide
(As2O3) in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4
cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and
modulation of PML-RAR alpha/PML proteins. Blood. 88:1052–1061.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang YH, Yi MJ, Kim MJ, et al:
Caspase-independent cell death by arsenic trioxide in human
cervical cancer cells: reactive oxygen species-mediated
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation signals apoptosis-inducing
factor release from mitochondria. Cancer Res. 64:8960–8967. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen ZY, Shen J, Cai WJ, Hong C and Zheng
MH: The alteration of mitochondria is an early event of arsenic
trioxide induced apoptosis in esophageal carcinoma cells. Int J Mol
Med. 5:155–158. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dalton WS: Targeting the mitochondria: an
exciting new approach to myeloma therapy. Commentary re: NJ Bahlis
et al: Feasibility and correlates of arsenic trioxide combined with
ascorbic acid-mediated depletion of intracellular glutathione for
the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer
Res. 8:3658–3668. 2002.
Clin Cancer Res. 8:3643–3645. 2002.
|
|
11
|
Bhalla S, Gordon LI, David K, et al:
Glutathione depletion enhances arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis
in lymphoma cells through mitochondrial-independent mechanisms. Br
J Haematol. 150:365–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Davison K, Cote S, Mader S and Miller WH:
Glutathione depletion overcomes resistance to arsenic trioxide in
arsenic-resistant cell lines. Leukemia. 17:931–940. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walker AM, Stevens JJ, Ndebele K and
Tchounwou PB: Arsenic trioxide modulates DNA synthesis and
apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
7:1996–2007. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu GP, Xiu QY, Li B, Liu YA and Zhang LZ:
Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of human lung cancer cell
lines via cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis at both
normoxia and hypoxia. Toxicol Ind Health. 25:505–515. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Induction of apoptosis in arsenic trioxide-treated lung cancer A549
cells by buthionine sulfoximine. Mol Cells. 26:158–164.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lam SK, Li YY, Zheng CY, Leung LL and Ho
JC: E2F1 downregulation by arsenic trioxide in lung adenocarcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 45:2033–2043. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lam SK, Mak JC, Zheng CY, Li YY, Kwong YL
and Ho JC: Downregulation of thymidylate synthase with arsenic
trioxide in lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 44:2093–2102.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lam SK, Li YY, Zheng CY and Ho JC:
Downregulation of thymidylate synthase and E2F1 by arsenic trioxide
in mesothelioma. Int J Oncol. 46:113–122. 2015.
|
|
19
|
Li H, Zhu X, Zhang Y, Xiang J and Chen H:
Arsenic trioxide exerts synergistic effects with cisplatin on
non-small cell lung cancer cells via apoptosis induction. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 28:1102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chien CW, Yao JH, Chang SY, Lee PC and Lee
TC: Enhanced suppression of tumor growth by concomitant treatment
of human lung cancer cells with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and
arsenic trioxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 257:59–66. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park JH, Kim EJ, Jang HY, et al:
Combination treatment with arsenic trioxide and sulindac enhances
apoptotic cell death in lung cancer cells via activation of
oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Oncol Rep.
20:379–384. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pettersson HM, Pietras A, Munksgaard
Persson M, et al: Arsenic trioxide is highly cytotoxic to small
cell lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:160–170. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer
J and Waxman S: Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer
Res. 62:3893–3903. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carney DA: Arsenic trioxide mechanisms of
action - looking beyond acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 49:1846–1851. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chouchane S and Snow ET: In vitro effect
of arsenical compounds on glutathione-related enzymes. Chem Res
Toxicol. 14:517–522. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu J, Chew EH and Holmgren A: Targeting
thioredoxin reductase is a basis for cancer therapy by arsenic
trioxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:12288–12293. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim HJ, Chae HZ, Kim YJ, et al:
Preferential elevation of Prx I and Trx expression in lung cancer
cells following hypoxia and in human lung cancer tissues. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 19:285–298. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hedley D, Pintilie M, Woo J, et al:
Up-regulation of the redox mediators thioredoxin and
apurinic/apyrimidinic excision (APE)/Ref-1 in hypoxic microregions
of invasive cervical carcinomas, mapped using multispectral,
wide-field fluorescence image analysis. Am J Pathol. 164:557–565.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi JH, Kim TN, Kim S, et al:
Overexpression of mitochondrial thioredoxin reductase and
peroxiredoxin III in hepatocellular carcinomas. Anticancer Res.
22:3331–3335. 2002.
|
|
30
|
Powis G, Mustacich D and Coon A: The role
of the redox protein thioredoxin in cell growth and cancer. Free
Radic Biol Med. 29:312–322. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tonissen KF and Di Trapani G: Thioredoxin
system inhibitors as mediators of apoptosis for cancer therapy. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 53:87–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zheng CY, Lam SK, Li YY, Fong BM, Mak JC
and Ho JC: Combination of arsenic trioxide and chemotherapy in
small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 82:222–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tauskela JS, Hewitt K, Kang LP, et al:
Evaluation of glutathione-sensitive fluorescent dyes in cortical
culture. Glia. 30:329–341. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sordet O, Liao Z, Liu H, et al:
Topoisomerase I-DNA complexes contribute to arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:33968–33975. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Watson WH, Pohl J, Montfort WR, et al:
Redox potential of human thioredoxin 1 and identification of a
second dithiol/disulfide motif. J Biol Chem. 278:33408–33415. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Go YM and Jones DP: Thioredoxin redox
western analysis. Curr Protoc Toxicol. Chapter 17(Unit 17.12)
View Article : Google Scholar : 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun RC, Board PG and Blackburn AC:
Targeting metabolism with arsenic trioxide and dichloroacetate in
breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:1422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Askar N, Cirpan T, Toprak E, et al:
Arsenic trioxide exposure to ovarian carcinoma cells leads to
decreased level of topoisomerase II and cytotoxicity. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 16:1552–1556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wen X, Li D, Zhang Y, Liu S, Ghali L and
Iles RK: Arsenic trioxide induces cervical cancer apoptosis, but
specifically targets human papillomavirus-infected cell
populations. Anticancer Drugs. 23:280–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lam HK, Li K, Chik KW, et al: Arsenic
trioxide mediates intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest in acute megakaryocytic leukemia. Int J Oncol.
27:537–545. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Delavallee L, Cabon L, Galan-Malo P,
Lorenzo HK and Susin SA: AIF-mediated caspase-independent
necroptosis: a new chance for targeted therapeutics. IUBMB Life.
63:221–232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cande C, Cecconi F, Dessen P and Kroemer
G: Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): key to the conserved
caspase-independent pathways of cell death? J Cell Sci.
115:4727–4734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, et al:
Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing
factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lorenzo HK and Susin SA: Therapeutic
potential of AIF-mediated caspase-independent programmed cell
death. Drug Resist Updat. 10:235–255. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ye H, Cande C, Stephanou NC, et al: DNA
binding is required for the apoptogenic action of apoptosis
inducing factor. Nat Struct Biol. 9:680–684. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Choi YJ, Park JW, Suh SI, et al: Arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis in U937 cells involve generation of
reactive oxygen species and inhibition of Akt. Int J Oncol.
21:603–610. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Calvino E, Estan MC, Simon GP, et al:
Increased apoptotic efficacy of lonidamine plus arsenic trioxide
combination in human leukemia cells. Reactive oxygen species
generation and defensive protein kinase (MEK/ERK, Akt/mTOR)
modulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:1619–1629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xiao G, Tang X, Yao C and Wang C:
Potentiation of arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis by
8-bromo-7-methoxychrysin in human leukemia cells involves depletion
of intracellular reduced glutathione. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin.
43:712–721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Konig H, Hartel N, Schultheis B, et al:
Enhanced Bcr-Abl-specific antileukemic activity of arsenic trioxide
(Trisenox) through glutathione-depletion in imatinib-resistant
cells. Haematologica. 92:838–841. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ramos AM, Fernandez C, Amran D, Sancho P,
de Blas E and Aller P: Pharmacologic inhibitors of PI3K/Akt
potentiate the apoptotic action of the antileukemic drug arsenic
trioxide via glutathione depletion and increased peroxide
accumulation in myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 105:4013–4020. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hu XM, Hirano T and Oka K: Arsenic
trioxide induces apoptosis in cells of MOLT-4 and its
daunorubicin-resistant cell line via depletion of intracellular
glutathione, disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and
activation of caspase-3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 52:47–58.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH
and Park WH: Effects of arsenic trioxide on cell death, reactive
oxygen species and glutathione levels in different cell types. Int
J Mol Med. 25:121–128. 2010.
|
|
54
|
Yi J, Yang J, He R, et al: Emodin enhances
arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis via generation of reactive
oxygen species and inhibition of survival signaling. Cancer Res.
64:108–116. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Morales AA, Gutman D, Cejas PJ, Lee KP and
Boise LH: Reactive oxygen species are not required for an arsenic
trioxide-induced antioxidant response or apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
284:12886–12895. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sun SY: N-acetylcysteine, reactive oxygen
species and beyond. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:109–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Guha P, Dey A, Sen R, Chatterjee M,
Chattopadhyay S and Bandyopadhyay SK: Intracellular GSH depletion
triggered mitochondrial Bax translocation to accomplish
resveratrol-induced apoptosis in the U937 cell line. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 336:206–214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Voehringer DW and Meyn RE: Redox aspects
of Bcl-2 function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2:537–550. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hochman A, Sternin H, Gorodin S, et al:
Enhanced oxidative stress and altered antioxidants in brains of
Bcl-2-deficient mice. J Neurochem. 71:741–748. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rajesh K, Vedamurthy J, Prakash D,
Thammanna Gowda SS, Satish BP and Dinesha R: Antioxidant activity
of spathodea campanulata in prevention of TBOOH and
H2O2 induced DNA damage. Int J Curr
Pharmaceut Res. 3:32011.
|
|
61
|
Keser S, Celik S, Turkoglu S, Yilmaz Ö and
Turkoglu I: Hydrogen peroxide radical scavenging and total
antioxidant activity of Hawthorn. Chem J. 2:42012.
|
|
62
|
Cherouny PH, Ghodgaonkar RB, Gurtner GH
and Dubin NH: The effect of the antioxidant, butylated hydroxy
anisole, on peroxide-induced and spontaneous activity of the uterus
from the pregnant rat. Biol Reprod. 41:98–103. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gulcin I, Alici HA and Cesur M:
Determination of in vitro antioxidant and radical scavenging
activities of propofol. Chem Pharm Bull. 53:281–285. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lushchak VI: Glutathione homeostasis and
functions: potential targets for medical interventions. J Amino
Acids. 7368372012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Patrick L: Toxic metals and antioxidants:
Part II. The role of antioxidants in arsenic and cadmium toxicity.
Altern Med Rev. 8:106–128. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ and Park WH:
Apoptosis in arsenic trioxide-treated Calu-6 lung cells is
correlated with the depletion of GSH levels rather than the changes
of ROS levels. J Cell Biochem. 104:862–878. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Reliene R and Schiestl RH: Glutathione
depletion by buthionine sulfoximine induces DNA deletions in mice.
Carcinogenesis. 27:240–244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Tian C, Gao P, Zheng Y, et al: Redox
status of thioredoxin-1 (TRX1) determines the sensitivity of human
liver carcinoma cells (HepG2) to arsenic trioxide-induced cell
death. Cell Res. 18:458–471. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kang YH and Lee SJ: The role of p38 MAPK
and JNK in arsenic trioxide-induced mitochondrial cell death in
human cervical cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 217:23–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH
and Park WH: The effect of MAPK inhibitors on arsenic
trioxide-treated Calu-6 lung cells in relation to cell death, ROS
and GSH levels. Anticancer Res. 29:3837–3844. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang S, Guo W, Ren TT, Lu XC, Tang GQ and
Zhao FL: Arsenic trioxide inhibits Ewing’s sarcoma cell
invasiveness by targeting p38(MAPK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
Anticancer Drugs. 23:108–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Chiu HW, Ho SY, Guo HR and Wang YJ:
Combination treatment with arsenic trioxide and irradiation
enhances autophagic effects in U118-MG cells through increased
mitotic arrest and regulation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. Autophagy. 5:472–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ellington AA, Berhow MA and Singletary KW:
Inhibition of Akt signaling and enhanced ERK1/2 activity are
involved in induction of macroautophagy by triterpenoid B-group
soyasaponins in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 27:298–306.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|