|
1
|
Yang Z, Kulkarni K, Zhu W, et al:
Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of genistein: mechanistic
studies on its ADME. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 10:1264–1280.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Banerjee S, Li Y, Wang Z, et al:
Multi-targeted therapy of cancer by genistein. Cancer Lett.
2:226–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang Z, Wang CZ, Du GJ, et al: Genistein
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via atm/p53-dependent
pathway in human colon cancer cell. Int J Oncol. 1:289–296.
2013.
|
|
4
|
Ullah MF, Ahmad A, Zubair H, et al: Soy
isoflavone genistein induces cell death in breast cancer cells
through mobilization of endogenous copper ions and generation of
reactive oxygen species. Mol Nutr Food Res. 4:553–559. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mizushina Y, Shiomi K, Kuriyama I, et al:
Inhibitory effects of a major soy isoflavone, genistein, on human
DNA topoisomerase II activity and cancer cell proliferation. Int J
Oncol. 4:1117–1124. 2013.
|
|
6
|
Hwang KA, Kang NH, Yi BR, et al:
Genistein, a soy phytoestrogen, prevents the growth of BG-1 ovarian
cancer cells induced by 17beta-estradiol or bisphenol A via the
inhibition of cell cycle progression. Int J Oncol. 2:733–740.
2013.
|
|
7
|
Xia J, Cheng L, Mei C, et al: Genistein
inhibits cell growth and invasion through regulation of mir-27a in
pancreatic cancer cells. Curr Pharm Des. 33:5348–5353. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
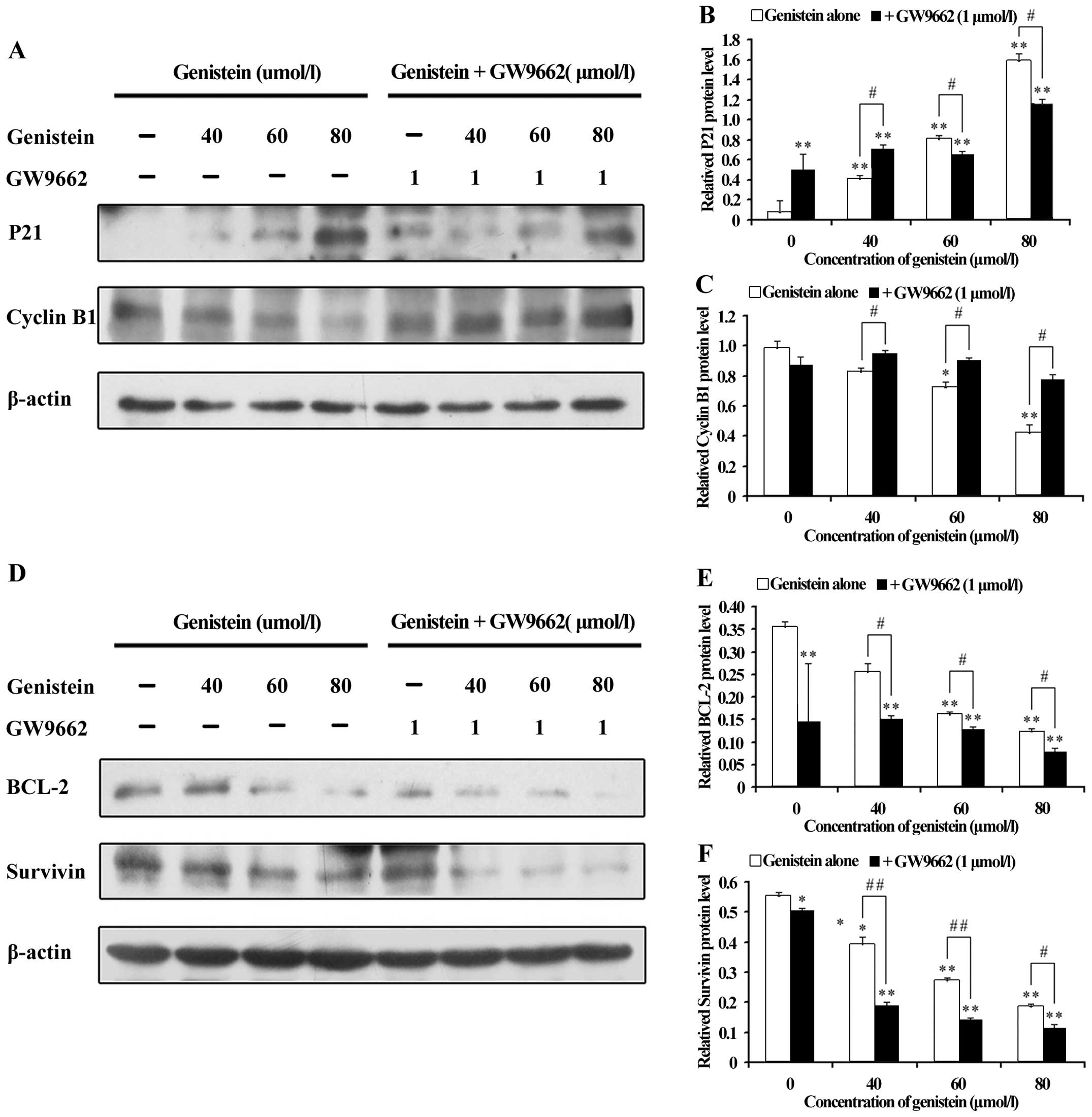
|
8
|
Hilakivi-Clarke L, Onojafe I, Raygada M,
et al: Prepubertal exposure to zearalenone or genistein reduces
mammary tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 11:16821999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhou JR, Mukherjee P, Gugger ET, et al:
Inhibition of murine bladder tumorigenesis by soy isoflavones via
alterations in the cell cycle, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. Cancer
Res. 22:5231–5238. 1998.
|
|
10
|
Li C, Teng RH, Tsai YC, et al: H-Ras
oncogene counteracts the growth-inhibitory effect of genistein in
T24 bladder carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 1:80–88. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Yang CH, Murti A, Pfeffer SR, et al:
Interferon α/β promotes cell survival by activating nuclear factor
κB through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt. J Biol Chem.
17:13756–13761. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Yamashita K, Suzuki M, Iwata H, et al:
Tyrosine phosphorylation is crucial for growth signaling by tissue
inhibitors of metalloproteinases. FEBS Lett. 1:103–107. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nikitovic D, Tsatsakis AM, Karamanos NK,
et al: The effects of genistein on the synthesis and distribution
of glycosaminoglycans/proteoglycans by two osteosarcoma cell lines
depends on tyrosine kinase and the estrogen receptor density.
Anticancer Res. 23(1A): 459–464. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morris C, Thorpe J, Ambrosio L, et al: The
soybean isoflavone genistein induces differentiation of MG63 human
osteosarcoma osteoblasts. J Nutr. 5:1166–1170. 2006.
|
|
15
|
Zhang B, Shi ZL, Liu B, et al: Enhanced
anticancer effect of gemcitabine by genistein in osteosarcoma: the
role of Akt and nuclear factor-κB. Anticancer Drugs. 3:288–296.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liang C, Li H, Shen C, et al: Genistein
potentiates the anti-cancer effects of gemcitabine in human
osteosarcoma via the downregulation of Akt and nuclear
factor-kappaB pathway. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 5:554–563. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nakamura A, Aizawa J, Sakayama K, et al:
Genistein inhibits cell invasion and motility by inducing cell
differentiation in murine osteosarcoma cell line LM8. BMC Cell
Biol. 1:242012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rickard DJ, Monroe DG, Ruesink TJ, et al:
Phytoestrogen genistein acts as an estrogen agonist on human
osteoblastic cells through estrogen receptors alpha and beta. J
Cell Biochem. 3:633–646. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Salvatori L, Caporuscio F, Coroniti G, et
al: Down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor induced by
estrogens and phytoestrogens promotes the differentiation of U2OS
human osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1:35–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Djiogue S, Njamen D, Halabalaki M, et al:
Estrogenic properties of naturally occurring prenylated isoflavones
in U2OS human osteosarcoma cells: Structure-activity relationships.
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 4–5:184–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nakamura H, Wang Y, Kurita T, et al:
Genistein increases epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and
promotes tumor progression in advanced human prostate cancer. PLoS
One. 5:e200342011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dang ZC, Audinot V, Papapoulos SE, et al:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma as a molecular
target for the soy phytoestrogen genistein. J Biol Chem. 2:962–967.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mezei O, Banz WJ, Steger RW, et al: Soy
isoflavones exert anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic effects through
the PPAR pathways in obese Zucker rats and murine RAW 264.7 cells.
J Nutr. 5:1238–1243. 2003.
|
|
24
|
Xiang Q, Lin G, Fu X, et al: The role of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ and estrogen receptors
in genistein-induced regulation of vascular tone in female rat
aortas. Pharmacology. 2:117–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Youssef J and Badr M: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors and cancer: challenges and
opportunities. Br J Pharmacol. 1:68–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Willson TM, Lambert MH and Kliewer SA:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and metabolic
disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 70:341–367. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Berger J and Moller DE: The mechanisms of
action of PPARs. Annu Rev Med. 53:409–435. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bundscherer A, Reichle A, Hafner C, et al:
Targeting the tumor stroma with peroxisome proliferator activated
receptor agonists. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 7:816–821. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rumi MA, Ishihara S, Kazumori H, et al:
Can PPAR gamma ligands be used in cancer therapy? Curr Med Chem
Anticancer Agents. 6:465–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tontonoz P, Singer S, Forman BM, et al:
Terminal differentiation of human liposarcoma cells induced by
ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and
the retinoid X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1:237–241. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kubota T, Koshizuka K, Williamson EA, et
al: Ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma has
potent antitumor effect against human prostate cancer both in vitro
and in vivo. Cancer Res. 15:3344–3352. 1998.
|
|
32
|
Asou H, Verbeek W, Williamson E, et al:
Growth inhibition of myeloid leukemia cells by troglitazone, a
ligand for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma, and
retinoids. Int J Oncol. 5:1027–1031. 1999.
|
|
33
|
Kitamura S, Miyazaki Y, Shinomura Y, et
al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma induces growth
arrest and differentiation markers of human colon cancer cells. Jpn
J Cancer Res. 1:75–80. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Elstner E, Muller C, Koshizuka K, et al:
Ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorgamma and
retinoic acid receptor inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of human
breast cancer cells in vitro and in BNX mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 15:8806–8811. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mueller E, Sarraf P, Tontonoz P, et al:
Terminal differentiation of human breast cancer through PPAR gamma.
Mol Cell. 3:465–470. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chang TH and Szabo E: Induction of
differentiation and apoptosis by ligands of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 4:1129–1138. 2000.
|
|
37
|
Ali AA, Weinstein RS, Stewart SA, et al:
Rosiglitazone causes bone loss in mice by suppressing osteoblast
differentiation and bone formation. Endocrinology. 3:1226–1235.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rzonca SO, Suva LJ, Gaddy D, et al: Bone
is a target for the antidiabetic compound rosiglitazone.
Endocrinology. 1:401–406. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rajkumar T and Yamuna M: Multiple pathways
are involved in drug resistance to doxorubicin in an osteosarcoma
cell line. Anticancer Drugs. 3:257–265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yamaguchi K, Whitlock NC, Liggett JL, et
al: Molecular characterisation of canine nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene. Vet J. 1:89–95. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
He BC, Chen L, Zuo GW, et al: Synergistic
antitumor effect of the activated PPARgamma and retinoid receptors
on human osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2235–2245. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Haydon RC, Luu HH and He TC: Osteosarcoma
and osteoblastic differentiation: a new perspective on oncogenesis.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 454:237–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Haydon RC, Zhou L, Feng T, et al: Nuclear
receptor agonists as potential differentiation therapy agents for
human osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 5:1288–1294. 2002.
|
|
44
|
Yu LX, Yan HX, Liu Q, et al: Endotoxin
accumulation prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes
liver tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology. 4:1322–1333. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lv L, Xiao XY, Gu ZH, et al: Silencing
USP22 by asymmetric structure of interfering RNA inhibits
proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in bladder cancer
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1–2:11–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lu Q, Lu S, Gao X, et al: Norisoboldine,
an alkaloid compound isolated from Radix Linderae, inhibits
synovial angiogenesis in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats by
moderating Notch1 pathway-related endothelial tip cell phenotype.
Exp Biol Med. 8:919–932. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Seargent JM, Yates EA and Gill JH: GW9662,
a potent antagonist of PPARgamma, inhibits growth of breast tumour
cells and promotes the anticancer effects of the PPARgamma agonist
rosiglitazone, independently of PPARgamma activation. Br J
Pharmacol. 8:933–937. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Patel L, Pass I, Coxon P, et al: Tumor
suppressor and anti-inflammatory actions of PPARgamma agonists are
mediated via upregulation of PTEN. Curr Biol. 10:764–768. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wu ZX, Song TB, Li DM, et al:
Overexpression of PTEN suppresses growth and induces apoptosis by
inhibiting the expression of survivin in bladder cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 1:9–15. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mikhail M, Velazquez E, Shapiro R, et al:
PTEN expression in melanoma: relationship with patient survival,
Bcl-2 expression, and proliferation. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5153–5157.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Raffoul JJ, Wang Y, Kucuk O, et al:
Genistein inhibits radiation-induced activation of NF-kappaB in
prostate cancer cells promoting apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle
arrest. BMC Cancer. 6:1072006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ouyang G, Yao L, Ruan K, et al: Genistein
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human ovarian
cancer cells via activation of DNA damage checkpoint pathways. Cell
Biol Int. 12:1237–1244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wagner ER, He BC, Chen L, et al:
Therapeutic implications of PPARgamma in human osteosarcoma. PPAR
Res. 9564272010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Miao J, Wu S, Peng Z, et al: MicroRNAs in
osteosarcoma: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Tumour Biol.
4:2093–2098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Weng L, Brown J and Eng C: PTEN induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through
phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt-dependent and -independent pathways.
Hum Mol Genet. 3:237–242. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Waite KA, Sinden MR and Eng C:
Phytoestrogen exposure elevates PTEN levels. Hum Mol Genet.
11:1457–1463. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Choi YH, Lee WH, Park KY, et al:
p53-independent induction of p21, reduction of Cyclin B1 and G2/M
arrest by the isoflavone genistein in human prostate carcinoma
cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2:164–173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Mayo LD and Donner DB: The PTEN, Mdm2, p53
tumor suppressor-oncoprotein network. Trends Biochem Sci.
9:462–467. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang T, Wang F, Xu H-X, et al: Activation
of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and PPARγ plays a
role in the genis-tein-mediated attenuation of oxidative
stress-induced endothelial cell injury. Br J Nutr. 2:223–235. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Halasova E, Adamkov M, Matakova T, et al:
Expression of Ki-67, Bcl-2, survivin and p53 proteins in patients
with pulmonary carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 756:15–21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gao Q, Yang S and Kang MQ: Influence of
survivin and Bcl-2 expression on the biological behavior of
non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Med Rep. 6:1409–1414. 2012.
|
|
62
|
Ma Y and Wang HS: Correlations of Bcl-2
and survivin gene protein expressions in colorectal cancer. Applied
Mech Mater. 423–426:362–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kumar P, Miller AI and Polverini PJ: p38
MAPK mediates gamma-irradiation-induced endothelial cell apoptosis,
and vascular endothelial growth factor protects endothelial cells
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-Bcl-2 pathway. J Biol
Chem. 41:43352–43360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Fong WH, Tsai HD, Chen YC, et al:
Anti-apoptotic actions of PPAR-gamma against ischemic stroke. Mol
Neurobiol. 2–3:180–186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Ren Y, Sun C, Sun Y, et al: PPAR gamma
protects cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress and apoptosis via
Bcl-2 upregulation. Vascul Pharmacol. 2–3:169–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kim YJ, Park KJ, Song JK, et al: The
PPARgamma agonist protects cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress and
apoptosis via thioredoxin overexpression. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 12:2181–2187. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|