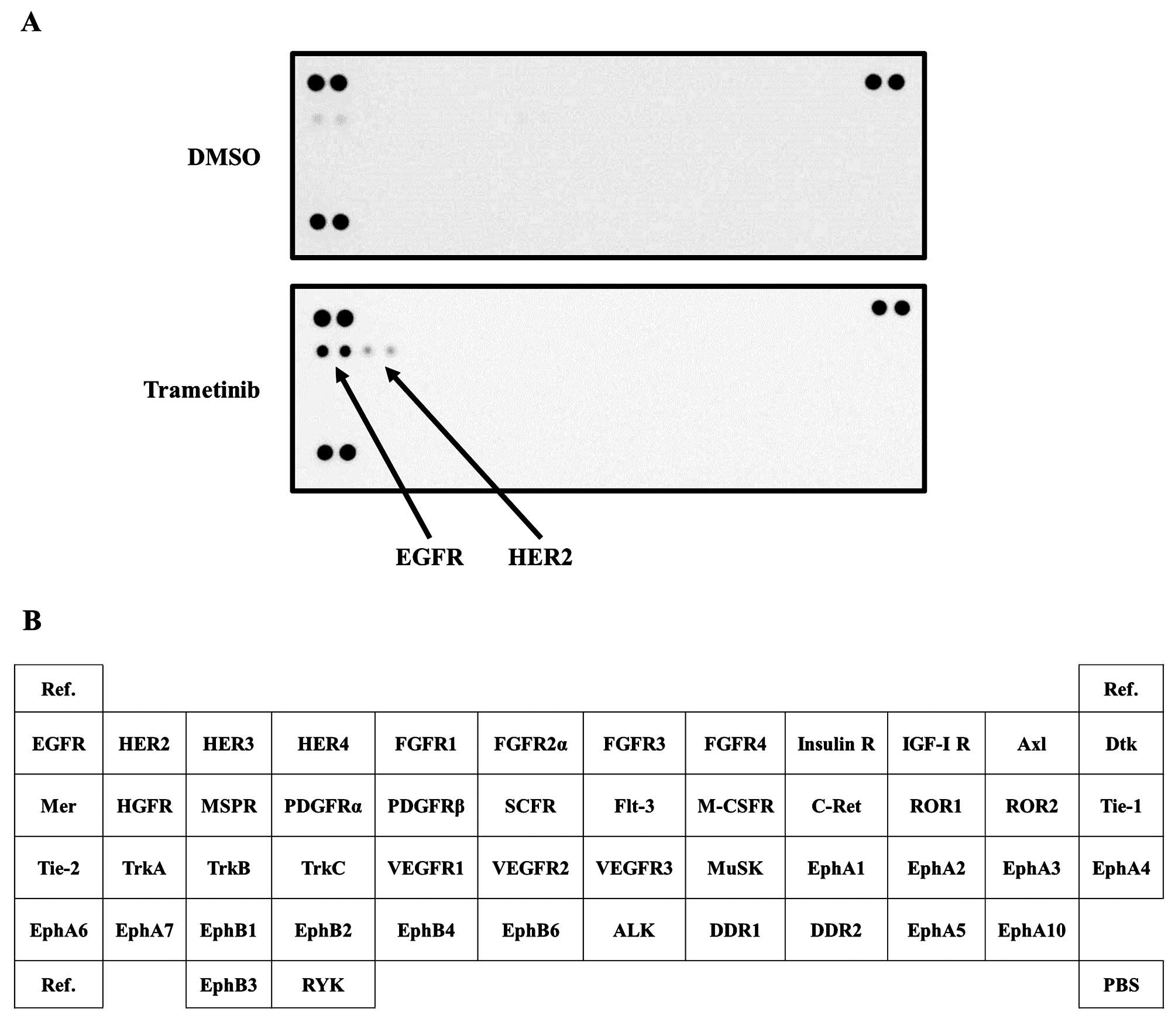
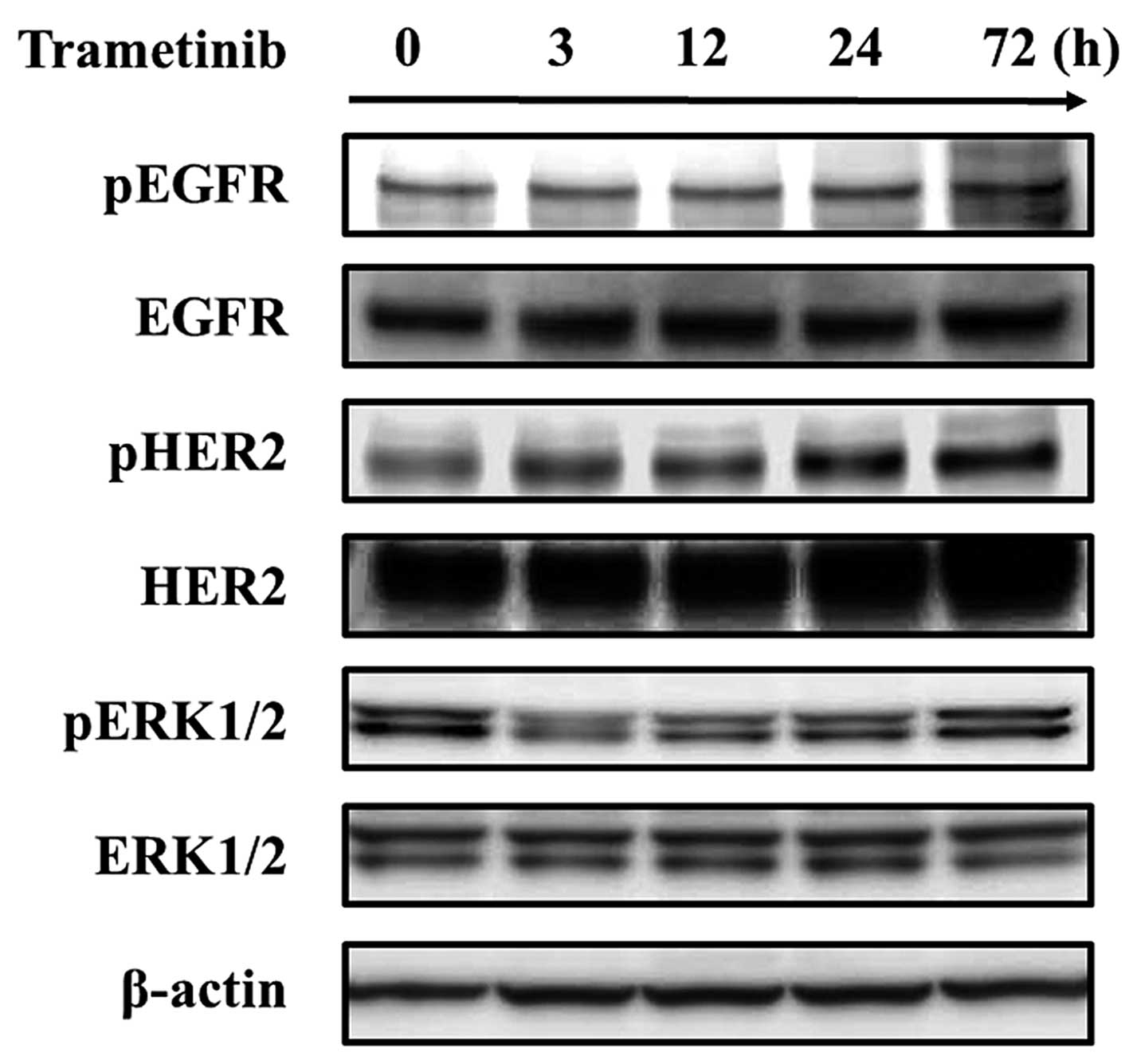
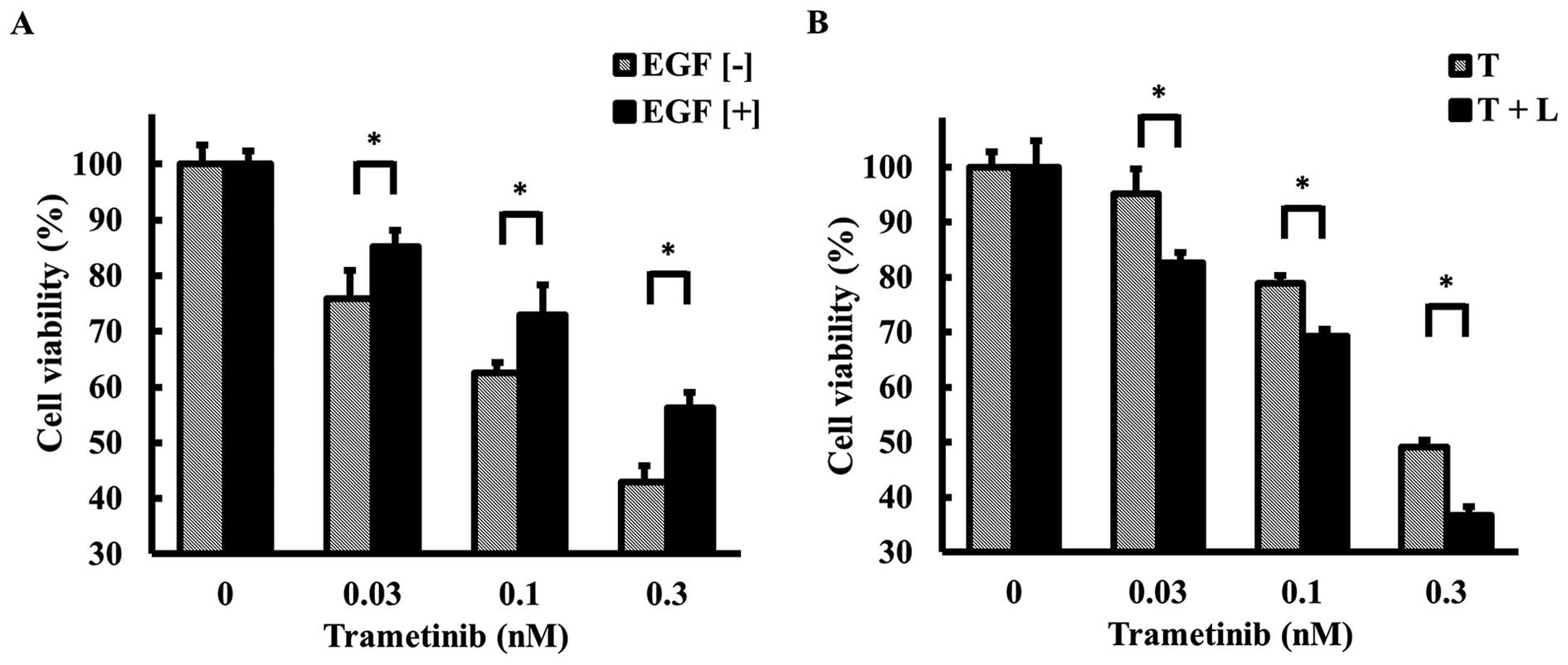
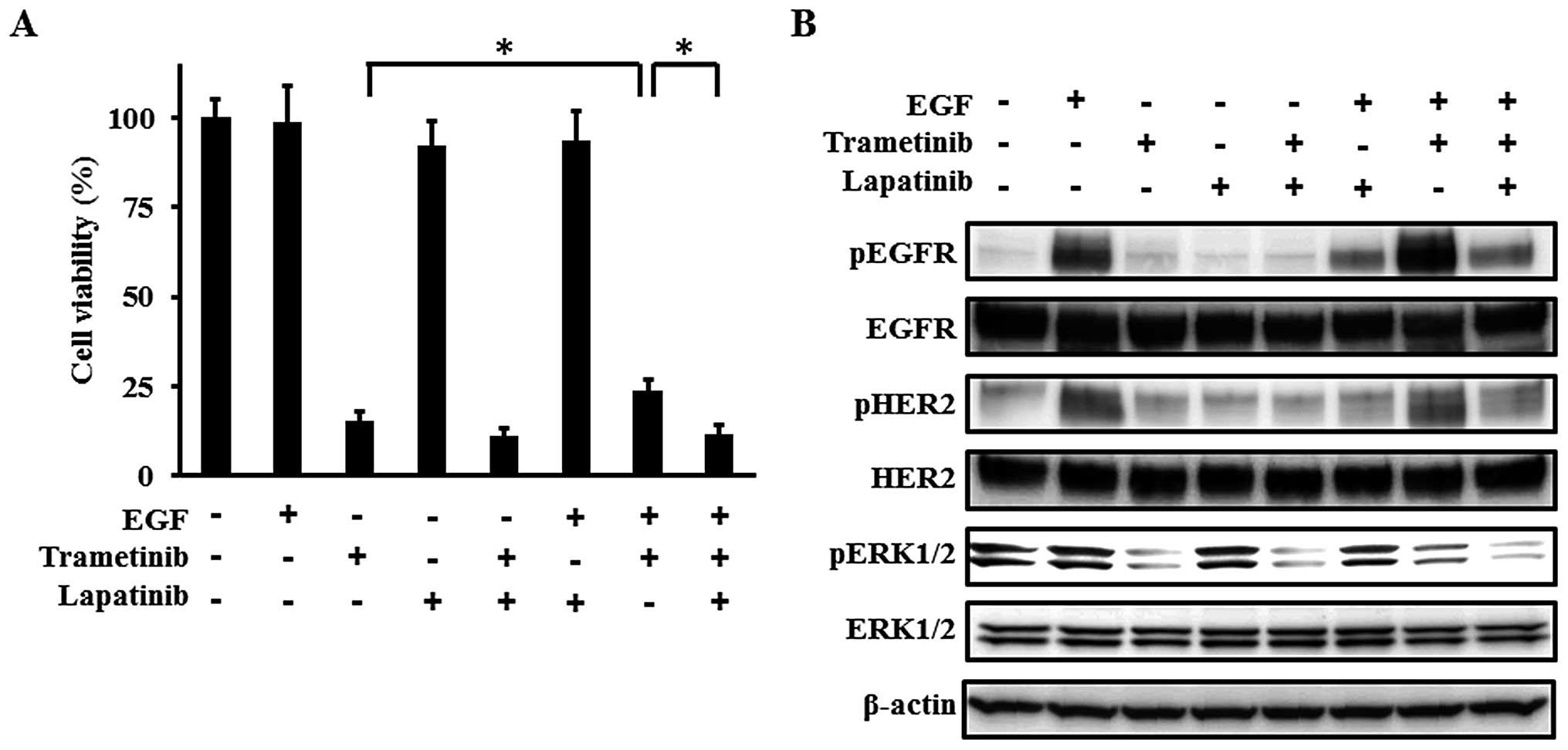
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S,
Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, Rodrigues A, Fodor M, Chao Y, Voznyi
E, et al; V325 Study Group. Phase III study of docetaxel and
cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and
fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A
report of the V325 Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 24:4991–4997. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T,
Nicolson M, Coxon F, Middleton G, Daniel F, Oates J and Norman AR;
Upper Gastrointestinal Clinical Studies Group of the National
Cancer Research Institute of the United Kingdom. Capecitabine and
oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med.
358:36–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, Takagane A,
Akiya T, Takagi M, Miyashita K, Nishizaki T, Kobayashi O, Takiyama
W, et al: S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line
treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): A phase III
trial. Lancet Oncol. 9:215–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al; ToGA Trial Investigators. Trastuzumab in combination with
chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of
HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sakai K, Mori S, Kawamoto T, Taniguchi S,
Kobori O, Morioka Y, Kuroki T and Kano K: Expression of epidermal
growth factor receptors on normal human gastric epithelia and
gastric carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 77:1047–1052.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yano T, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Hashizume
K, Nakanishi M and Ochiai A: Comparison of HER2 gene amplification
assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and HER2 protein
expression assessed by immunohistochemistry in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 15:65–71. 2006.
|
|
8
|
Gravalos C and Jimeno A: HER2 in gastric
cancer: A new prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target. Ann
Oncol. 19:1523–1529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Hamaguchi T, Shimada
Y, Kato K, Oda I, Taniguchi H, Koizumi F, Yanagihara K, Sasaki H,
et al: FGFR2 gene amplification and clinicopathological features in
gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:727–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kawakami H, Okamoto I, Arao T, Okamoto W,
Matsumoto K, Taniguchi H, Kuwata K, Yamaguchi H, Nishio K, Nakagawa
K, et al: MET amplification as a potential therapeutic target in
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 4:9–17. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang K, Yuen ST, Xu J, Lee SP, Yan HH, Shi
ST, Siu HC, Deng S, Chu KM, Law S, et al: Whole-genome sequencing
and comprehensive molecular profiling identify new driver mutations
in gastric cancer. Nat Genet. 46:573–582. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kakiuchi M, Nishizawa T, Ueda H, Gotoh K,
Tanaka A, Hayashi A, Yamamoto S, Tatsuno K, Katoh H, Watanabe Y, et
al: Recurrent gain-of-function mutations of RHOA in diffuse-type
gastric carcinoma. Nat Genet. 46:583–587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P,
Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W,
et al: Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature.
417:949–954. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J,
Ibrahim PN, Cho H, Spevak W, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Habets G, et al:
Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in
BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature. 467:596–599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A,
McArthur GA, Sosman JA, O’Dwyer PJ, Lee RJ, Grippo JF, Nolop K, et
al: Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N
Engl J Med. 363:809–819. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pao W and Girard N: New driver mutations
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 12:175–180. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Estep AL, Palmer C, McCormick F and Rauen
KA: Mutation analysis of BRAF, MEK1 and MEK2 in 15 ovarian cancer
cell lines: Implications for therapy. PLoS One. 2:e12792007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marks JL, Gong Y, Chitale D, Golas B,
McLellan MD, Kasai Y, Ding L, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, Solit D, et al:
Novel MEK1 mutation identified by mutational analysis of epidermal
growth factor receptor signaling pathway genes in lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:5524–5528. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bentivegna S, Zheng J, Namsaraev E,
Carlton VE, Pavlicek A, Moorhead M, Siddiqui F, Wang Z, Lee L,
Ireland JS, et al: Rapid identification of somatic mutations in
colorectal and breast cancer tissues using mismatch repair
detection (MRD). Hum Mutat. 29:441–450. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sogabe S, Togashi Y, Kato H, Kogita A,
Mizukami T, Sakamoto Y, Banno E, Terashima M, Hayashi H, de Velasco
MA, et al: MEK inhibitor for gastric cancer with MEK1 gene
mutations. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:3098–3106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Emery CM, Vijayendran KG, Zipser MC,
Sawyer AM, Niu L, Kim JJ, Hatton C, Chopra R, Oberholzer PA,
Karpova MB, et al: MEK1 mutations confer resistance to MEK and
B-RAF inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:20411–20416. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Little AS, Balmanno K, Sale MJ, Newman S,
Dry JR, Hampson M, Edwards PA, Smith PD and Cook SJ: Amplification
of the driving oncogene, KRAS or BRAF, underpins acquired
resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer cells. Sci
Signal. 4:ra172011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Corcoran RB, Dias-Santagata D, Bergethon
K, Iafrate AJ, Settleman J and Engelman JA: BRAF gene amplification
can promote acquired resistance to MEK inhibitors in cancer cells
harboring the BRAF V600E mutation. Sci Signal.
3:ra842010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Walters DM, Lindberg JM, Adair SJ, Newhook
TE, Cowan CR, Stokes JB, Borgman CA, Stelow EB, Lowrey BT,
Chopivsky ME, et al: Inhibition of the growth of patient-derived
pancreatic cancer xenografts with the MEK inhibitor trametinib is
augmented by combined treatment with the epidermal growth factor
receptor/ HER2 inhibitor lapatinib. Neoplasia. 15:143–155. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun C, Hobor S, Bertotti A, Zecchin D,
Huang S, Galimi F, Cottino F, Prahallad A, Grernrum W, Tzani A, et
al: Intrinsic resistance to MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant lung and
colon cancer through transcriptional induction of ERBB3. Cell Rep.
7:86–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Togashi Y, Sakamoto H, Hayashi H,
Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Fujita Y, Kodera Y, Sakai K, Tomida S,
Kitano M, et al: Homozygous deletion of the activin A receptor,
type IB gene is associated with an aggressive cancer phenotype in
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:1262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaneda H, Arao T, Tanaka K, Tamura D,
Aomatsu K, Kudo K, Sakai K, De Velasco MA, Matsumoto K, Fujita Y,
et al: FOXQ1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and enhances
tumorigenicity and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 70:2053–2063. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hingorani SR, Jacobetz MA, Robertson GP,
Herlyn M and Tuveson DA: Suppression of BRAF(V599E) in human
melanoma abrogates transformation. Cancer Res. 63:5198–5202.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Freeman AK and Morrison DK: Mechanisms and
potential therapies for acquired resistance to inhibitors targeting
the Raf or MEK kinases in cancer. Molecular Mechanisms of Tumor
Cell Resistance to Chemotherapy: Targeted Therapies to Reverse
Resistance. Bonavita B: pp. 47–67. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Prahallad A, Sun C, Huang S, Di
Nicolantonio F, Salazar R, Zecchin D, Beijersbergen RL, Bardelli A
and Bernards R: Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E)
inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nature.
483:100–103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Van Schaeybroeck S, Karaiskou-McCaul A,
Kelly D, Longley D, Galligan L, Van Cutsem E and Johnston P:
Epidermal growth factor receptor activity determines response of
colorectal cancer cells to gefitinib alone and in combination with
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7480–7489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li T, Ling YH, Goldman ID and Perez-Soler
R: Schedule-dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and
erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:3413–3422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|