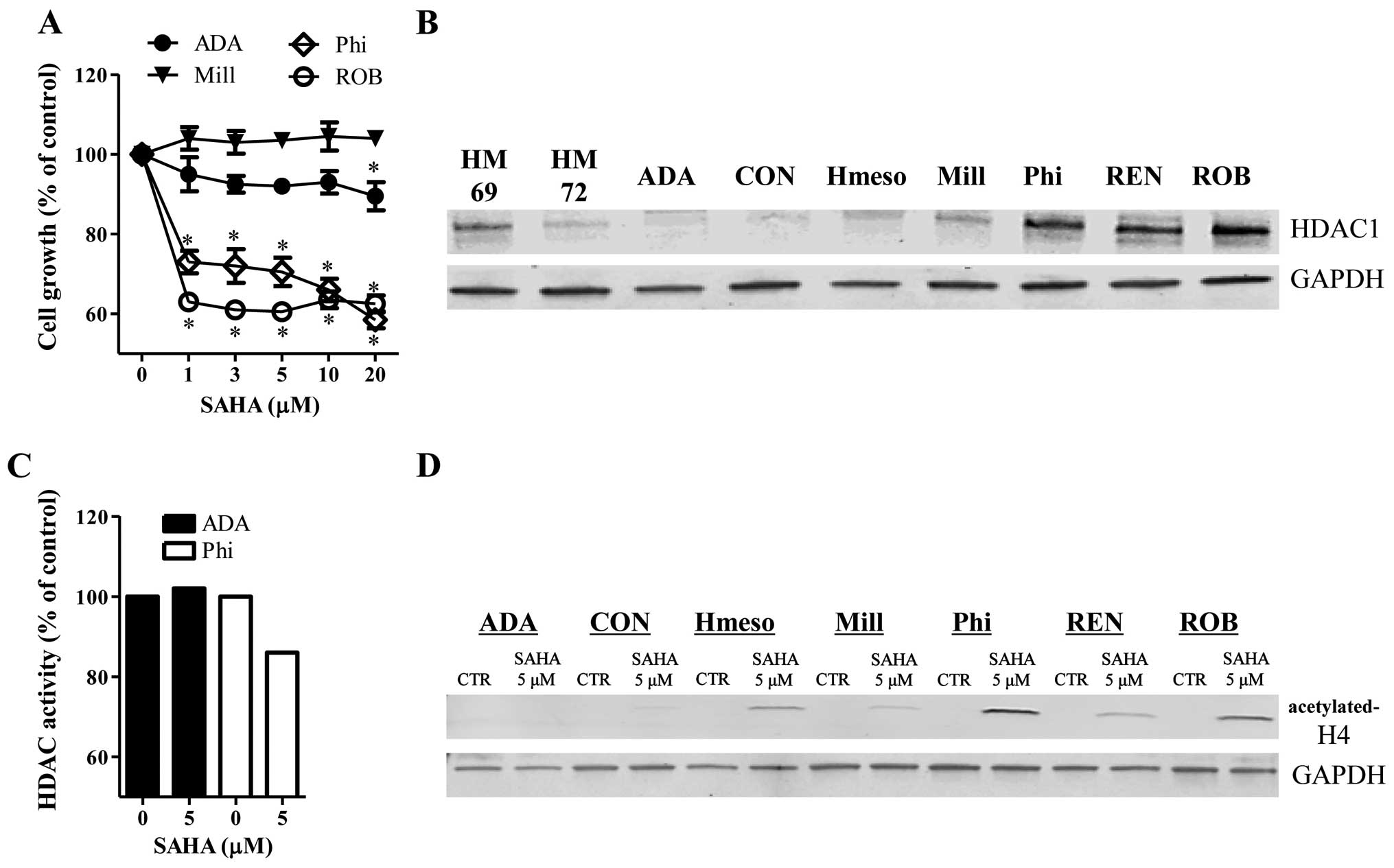
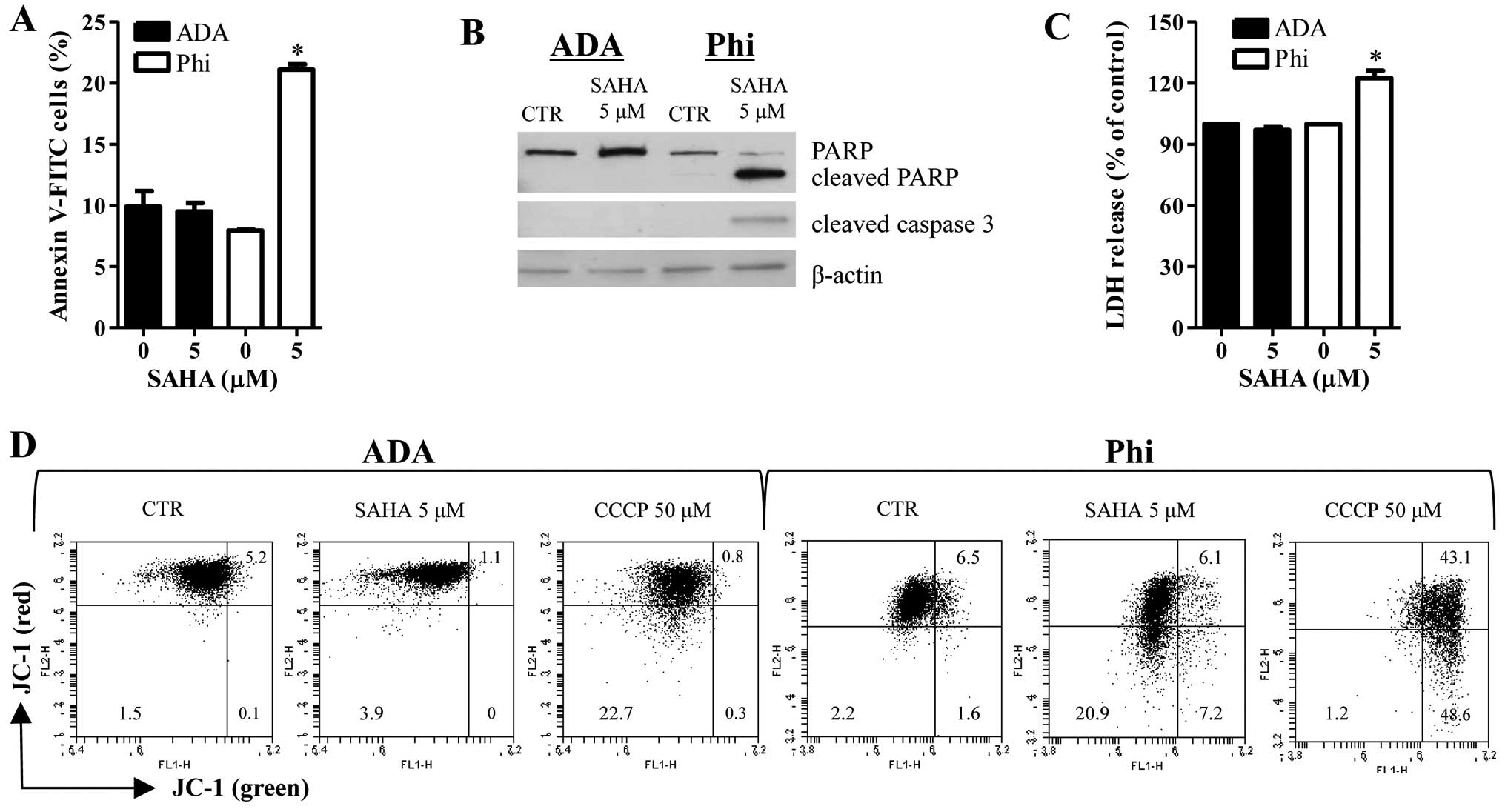
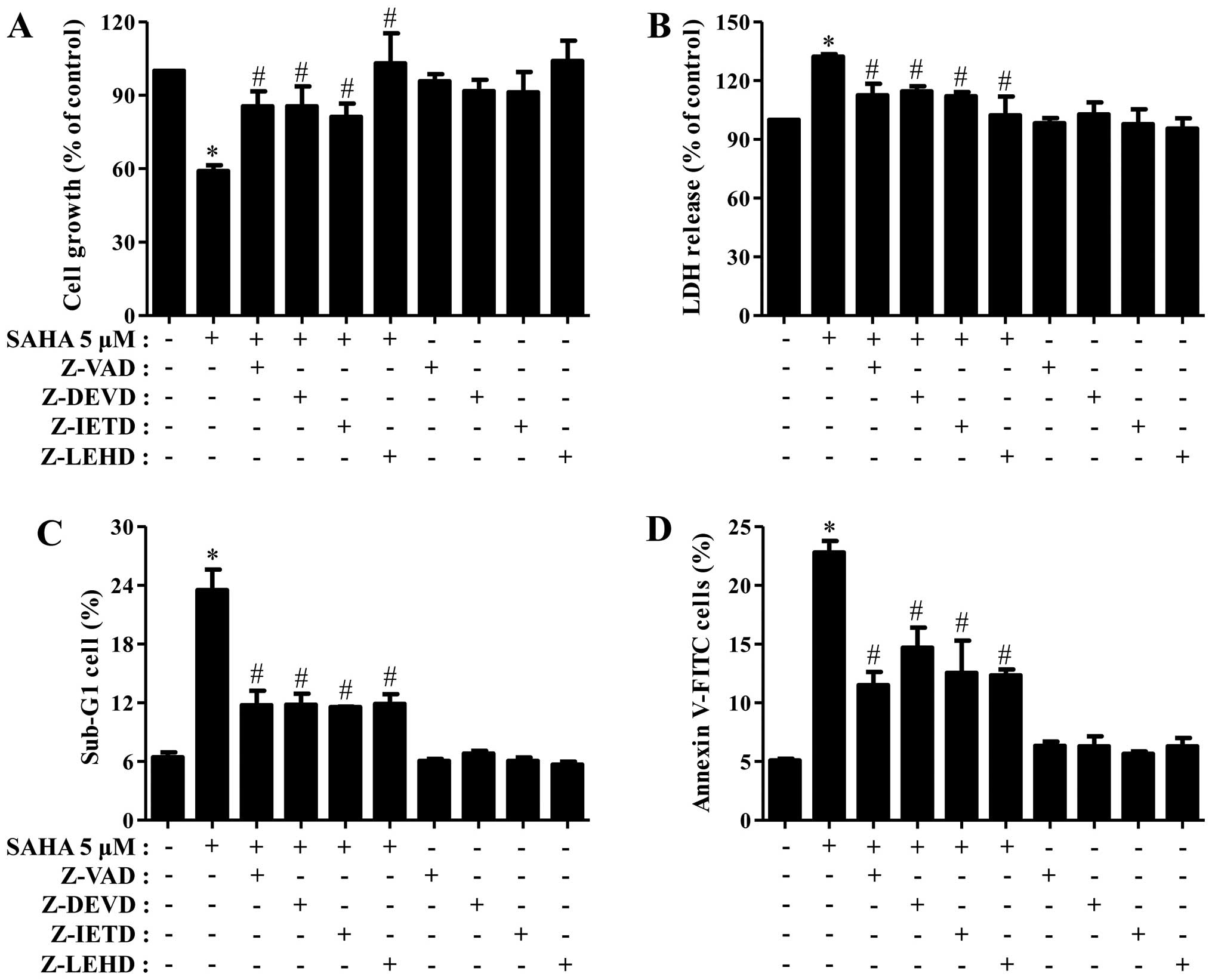
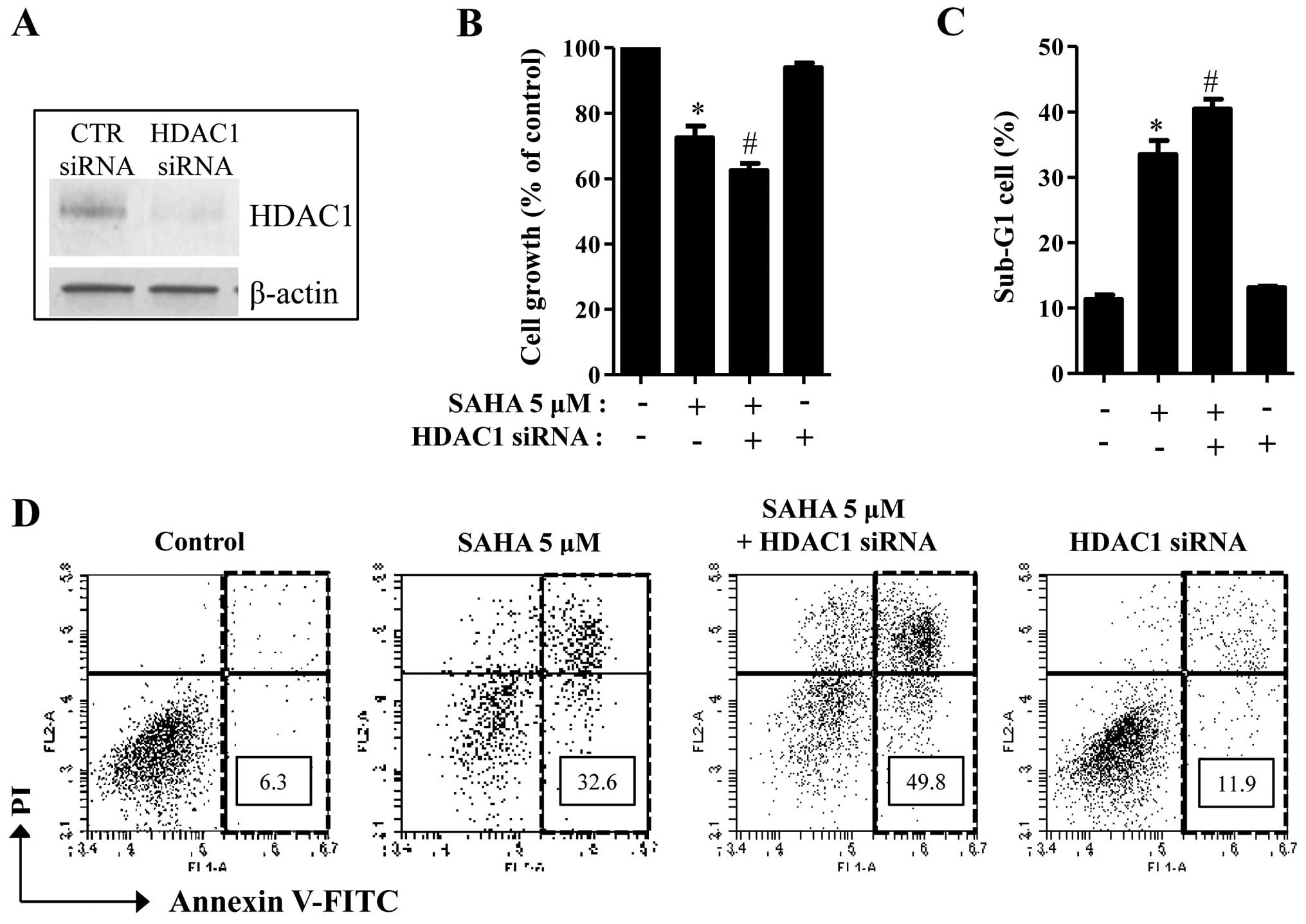
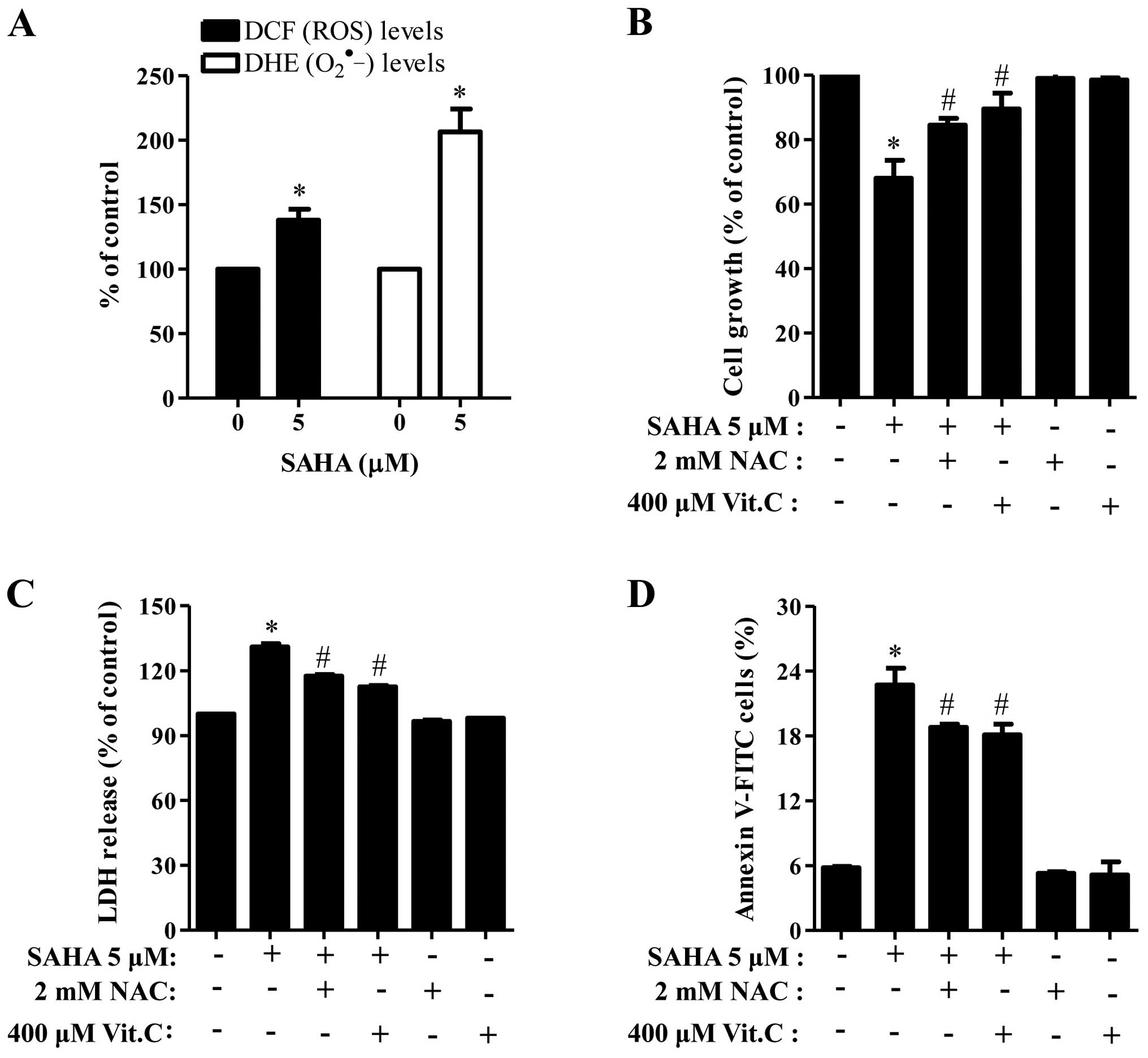
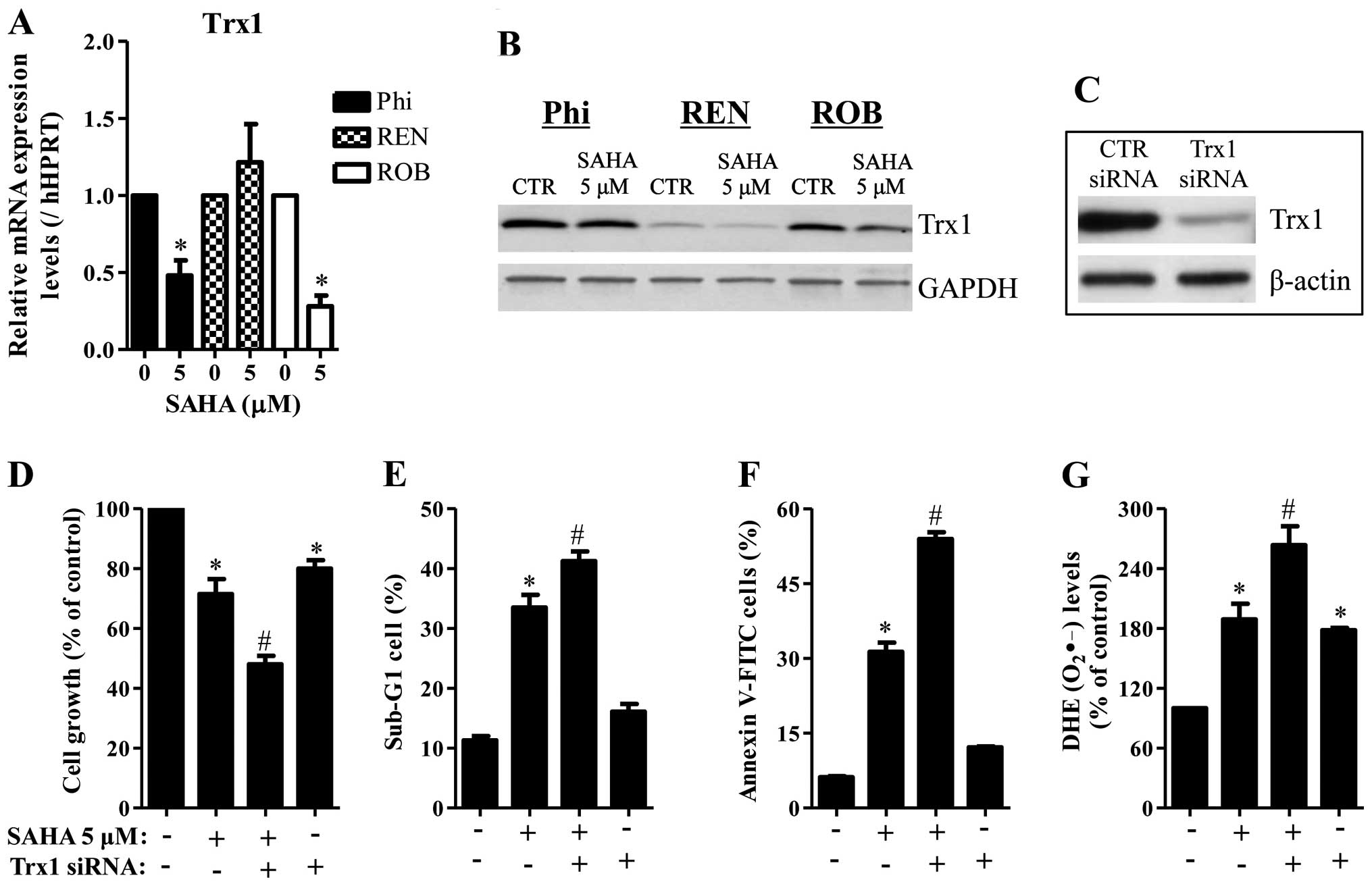
|
1
|
Comertpay S, Pastorino S, Tanji M,
Mezzapelle R, Strianese O, Napolitano A, Baumann F, Weigel T,
Friedberg J, Sugarbaker P, et al: Evaluation of clonal origin of
malignant mesothelioma. J Transl Med. 12:3012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carbone M and Yang H: Molecular pathways:
Targeting mechanisms of asbestos and erionite carcinogenesis in
mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. 18:598–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Matsuzaki H, Maeda M, Lee S, Nishimura Y,
Kumagai-Takei N, Hayashi H, Yamamoto S, Hatayama T, Kojima Y,
Tabata R, et al: Asbestos-induced cellular and molecular alteration
of immuno-competent cells and their relationship with chronic
inflammation and carcinogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:4926082012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Christensen BC, Houseman EA, Godleski JJ,
Marsit CJ, Longacker JL, Roelofs CR, Karagas MR, Wrensch MR, Yeh
RF, Nelson HH, et al: Epigenetic profiles distinguish pleural
mesothelioma from normal pleura and predict lung asbestos burden
and clinical outcome. Cancer Res. 69:227–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karczmarski J, Rubel T, Paziewska A,
Mikula M, Bujko M, Kober P, Dadlez M and Ostrowski J: Histone H3
lysine 27 acetylation is altered in colon cancer. Clin Proteomics.
11:242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kalari S, Moolky N, Pendyala S, Berdyshev
EV, Rolle C, Kanteti R, Kanteti A, Ma W, He D, Husain AN, et al:
Sphingosine kinase 1 is required for mesothelioma cell
proliferation: Role of histone acetylation. PLoS One. 7:e453302012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim NH, Kim SN and Kim YK: Involvement of
HDAC1 in E-cadherin expression in prostate cancer cells; its
implication for cell motility and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 404:915–921. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hayashi A, Horiuchi A, Kikuchi N, Hayashi
T, Fuseya C, Suzuki A, Konishi I and Shiozawa T: Type-specific
roles of histone deacetylase (HDAC) overexpression in ovarian
carcinoma: HDAC1 enhances cell proliferation and HDAC3 stimulates
cell migration with downregulation of E-cadherin. Int J Cancer.
127:1332–1346. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paik PK and Krug LM: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Preclinical rationale
and clinical trials. J Thorac Oncol. 5:275–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Katafygiotis P, Giaginis C, Patsouris E
and Theocharis S: Histone deacetylase inhibitors as potential
therapeutic agents for the treatment of malignant mesothelioma.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:476–482. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tabata C, Terada T, Tabata R, Yamada S,
Eguchi R, Fujimori Y and Nakano T: Serum thioredoxin-1 as a
diagnostic marker for malignant peritoneal mesothelioma. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 47:e7–e11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Thompson JK, Westbom CM, MacPherson MB,
Mossman BT, Heintz NH, Spiess P and Shukla A: Asbestos modulates
thioredoxin-thioredoxin interacting protein interaction to regulate
inflammasome activation. Part Fibre Toxicol. 11:242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murthy S, Adamcakova-Dodd A, Perry SS,
Tephly LA, Keller RM, Metwali N, Meyerholz DK, Wang Y, Glogauer M,
Thorne PS, et al: Modulation of reactive oxygen species by Rac1 or
catalase prevents asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L846–L855. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Powis G and Kirkpatrick DL: Thioredoxin
signaling as a target for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
7:392–397. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Yang H, Li W, Xu H, Yang X and Gan
L: Thioredoxin 1 upregulates FOXO1 transcriptional activity in drug
resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:395–405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Min A, Im SA, Kim DK, Song SH, Kim HJ, Lee
KH, Kim TY, Han SW, Oh DY, Kim TY, et al: Histone deacetylase
inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), enhances
anti-tumor effects of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)
inhibitor olaparib in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res. 17:332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ding L, Zhang Z, Liang G, Yao Z, Wu H,
Wang B, Zhang J, Tariq M, Ying M and Yang B: SAHA triggered MET
activation contributes to SAHA tolerance in solid cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 356:828–836. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hurwitz JL, Stasik I, Kerr EM, Holohan C,
Redmond KM, McLaughlin KM, Busacca S, Barbone D, Broaddus VC, Gray
SG, et al: Vorinostat/SAHA-induced apoptosis in malignant
mesothelioma is FLIP/caspase 8-dependent and HR23B-independent. Eur
J Cancer. 48:1096–1107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Pyrogallol inhibits the growth of lung cancer Calu-6 cells via
caspase-dependent apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact. 177:107–114. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
You BR and Park WH: Gallic acid-induced
lung cancer cell death is related to glutathione depletion as well
as reactive oxygen species increase. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1356–1362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
You BR, Kim SH and Park WH: Reactive
oxygen species, glutathione, and thioredoxin influence suberoyl
bishydroxamic acid-induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 36:3429–3439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
You BR, Shin HR, Han BR and Park WH: PX-12
induces apoptosis in Calu-6 cells in an oxidative stress-dependent
manner. Tumour Biol. 36:2087–2095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Butler LM, Zhou X, Xu WS, Scher HI,
Rifkind RA, Marks PA and Richon VM: The histone deacetylase
inhibitor SAHA arrests cancer cell growth, up-regulates
thioredoxin-binding protein-2, and down-regulates thioredoxin. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:11700–11705. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Crisanti MC, Wallace AF, Kapoor V,
Vandermeers F, Dowling ML, Pereira LP, Coleman K, Campling BG,
Fridlender ZG, Kao GD, et al: The HDAC inhibitor panobinostat
(LBH589) inhibits mesothelioma and lung cancer cells in vitro and
in vivo with particular efficacy for small cell lung cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 8:2221–2231. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie HJ, Noh JH, Kim JK, Jung KH, Eun JW,
Bae HJ, Kim MG, Chang YG, Lee JY, Park H, et al: HDAC1 inactivation
induces mitotic defect and caspase-independent autophagic cell
death in liver cancer. PLoS One. 7:e342652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cacan E, Ali MW, Boyd NH, Hooks SB and
Greer SF: Inhibition of HDAC1 and DNMT1 modulate RGS10 expression
and decrease ovarian cancer chemoresistance. PLoS One.
9:e874552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chae JS, Gil Hwang S, Lim DS and Choi EJ:
Thioredoxin-1 functions as a molecular switch regulating the
oxidative stress-induced activation of MST1. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:2335–2343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ungerstedt J, Du Y, Zhang H, Nair D and
Holmgren A: In vivo redox state of human thioredoxin and redox
shift by the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide
hydroxamic acid (SAHA). Free Radic Biol Med. 53:2002–2007. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|