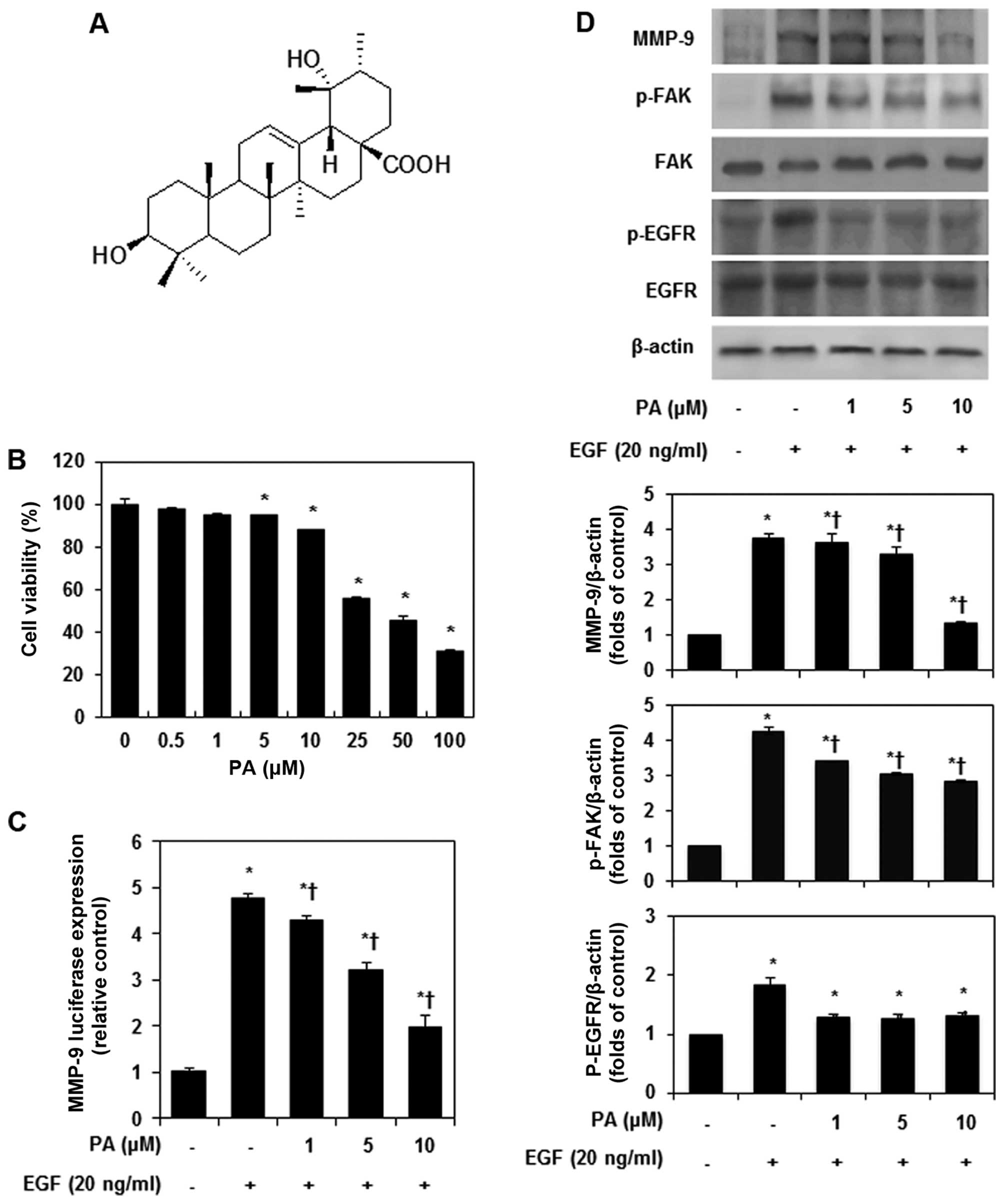
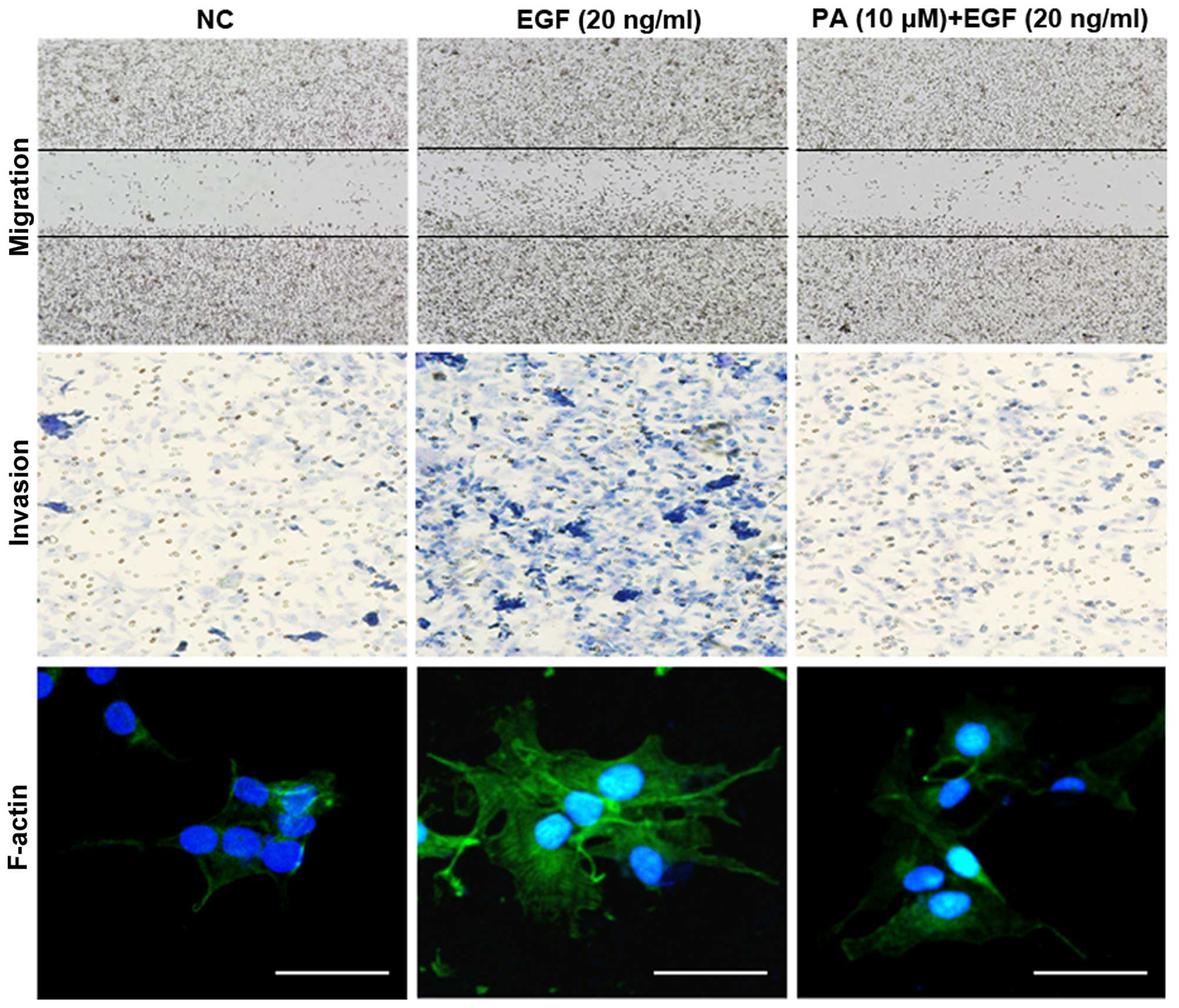
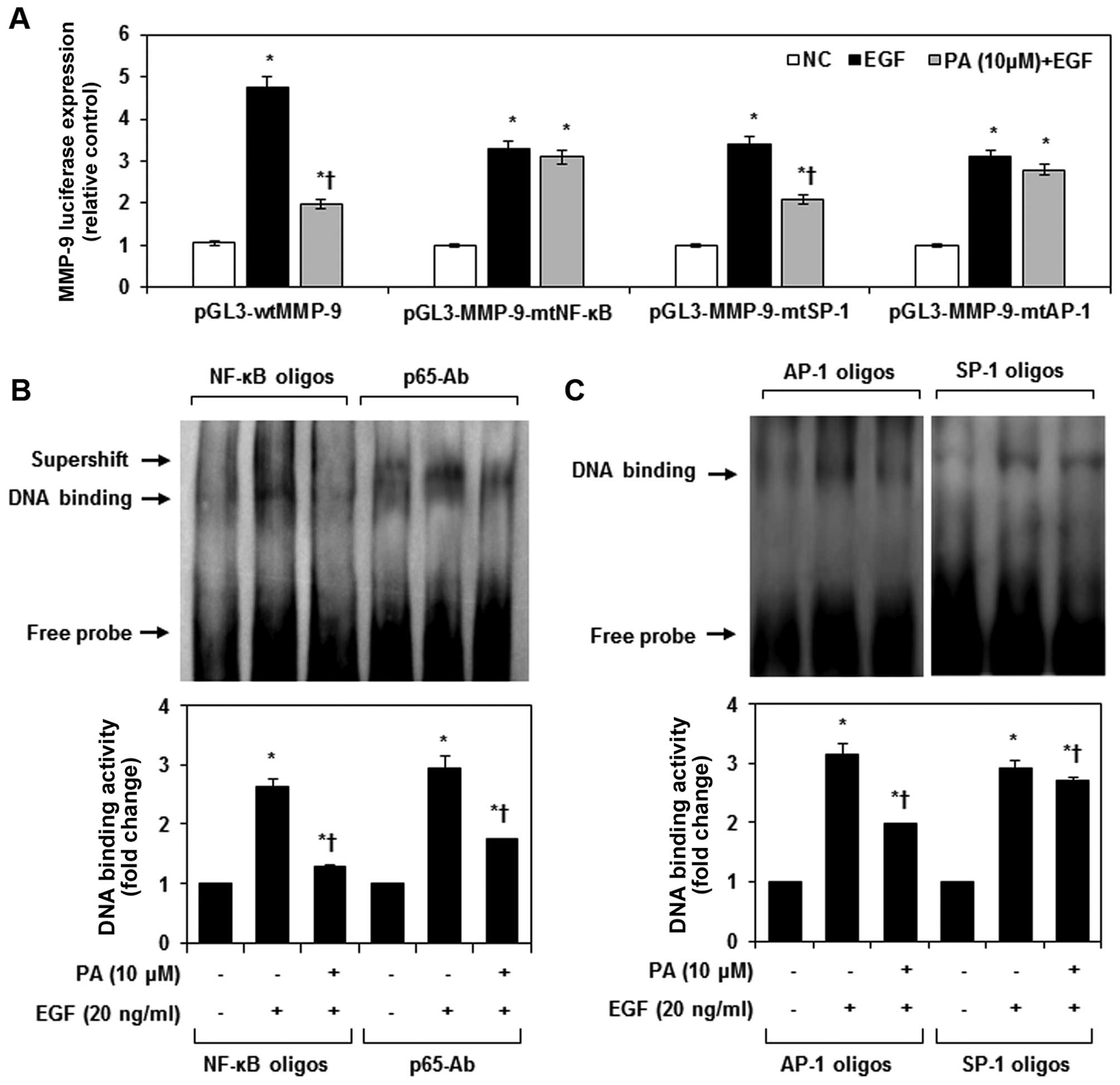
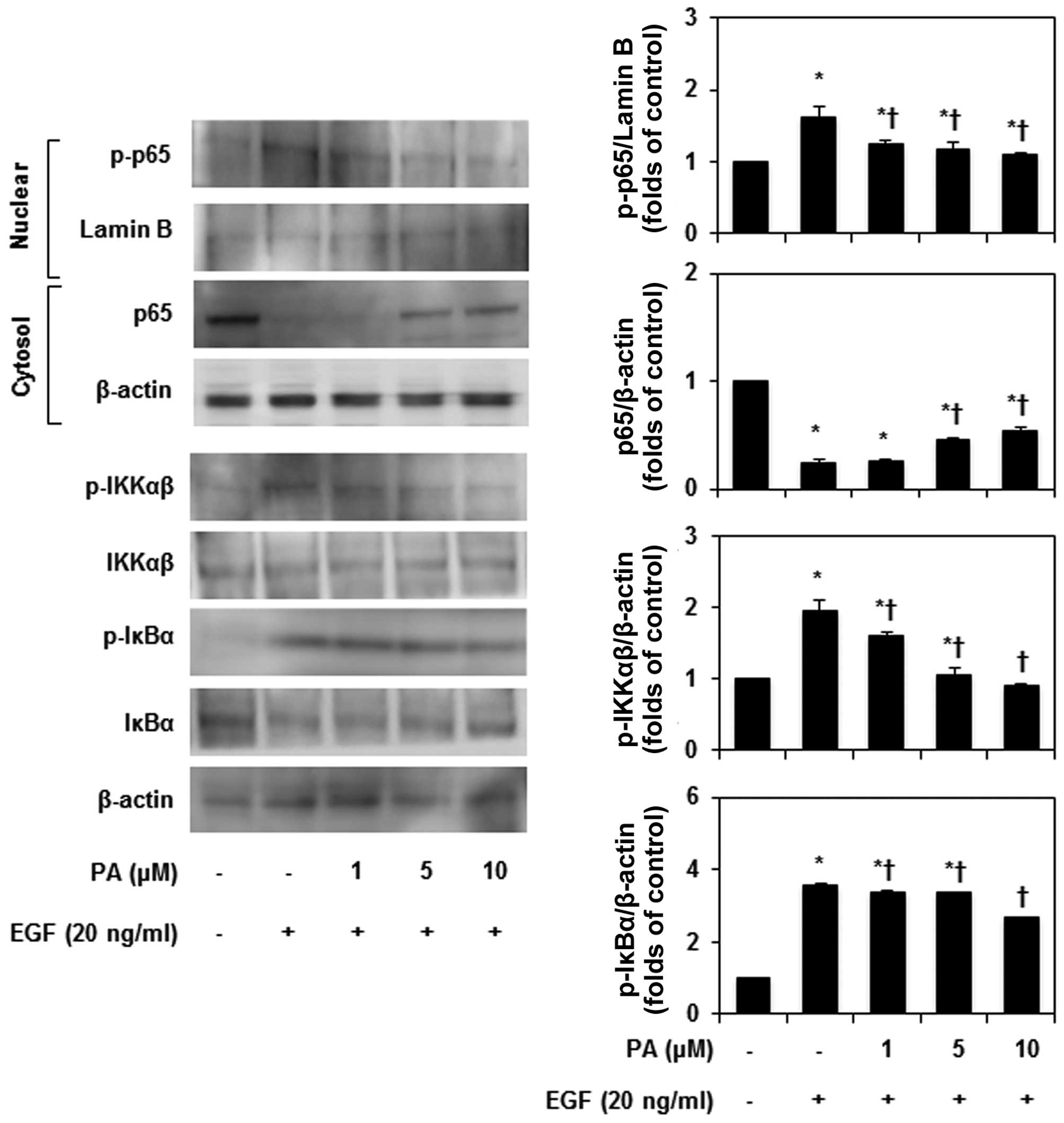
|
1
|
Hu Z, Xu R, Liu J, Zhang Y, Du J, Li W,
Zhang W, Li Y, Zhu Y and Gu L: GEP100 regulates epidermal growth
factor-induced MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell invasion through the
activation of Arf6/ERK/uPAR signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res.
319:1932–1941. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee YC, Lee LM, Yang CH, Lin AM, Huang YC,
Hsu CC, Chen MS, Chi CW, Yin PH, Kuo CD, et al: Norcantharidin
suppresses cell growth and migration with enhanced anticancer
activity of gefitinib and cisplatin in human non-small cell lung
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 29:237–243. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Saxena R, Chandra V, Manohar M, Hajela K,
Debnath U, Prabhakar YS, Saini KS, Konwar R, Kumar S, Megu K, et
al: Chemotherapeutic potential of
2-[piperidinoethoxyphenyl]-3-phenyl-2H-benzo(b)pyran in estrogen
receptor-negative breast cancer cells: Action via prevention of
EGFR activation and combined inhibition of PI-3-K/Akt/FOXO and
MEK/Erk/AP-1 pathways. PLoS One. 8:e662462013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jeong YJ, Choi Y, Shin JM, Cho HJ, Kang
JH, Park KK, Choe JY, Bae YS, Han SM, Kim CH, et al: Melittin
suppresses EGF-induced cell motility and invasion by inhibiting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 68:218–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chun J and Kim YS: Platycodin D inhibits
migration, invasion, and growth of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
cells via suppression of EGFR-mediated Akt and MAPK pathways. Chem
Biol Interact. 205:212–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho HJ, Kang JH, Kwak JY, Lee TS, Lee IS,
Park NG, Nakajima H, Magae J and Chang YC: Ascofuranone suppresses
PMA-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene activation through the
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK- and Ap1-dependent mechanisms. Carcinogenesis.
28:1104–1110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Ling Y, Chen Y, Li CL, Feng F, You
QD, Lu N and Guo QL: Flavonoid baicalein suppresses adhesion,
migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 297:42–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E,
Evans J, Brunton VG and Frame MC: The role of focal-adhesion kinase
in cancer - a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:505–515. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee WJ, Chen WK, Wang CJ, Lin WL and Tseng
TH: Apigenin inhibits HGF-promoted invasive growth and metastasis
involving blocking PI3K/Akt pathway and beta 4 integrin function in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
226:178–191. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hwang YP, Yun HJ, Choi JH, Han EH, Kim HG,
Song GY, Kwon KI, Jeong TC and Jeong HG: Suppression of EGF-induced
tumor cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by
capsaicin via the inhibition of EGFR-mediated FAK/Akt, PKC/Raf/ERK,
p38 MAPK, and AP-1 signaling. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:594–605. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin JM, Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Park KK, Chung
IK, Lee IK, Kwak JY, Chang HW, Kim CH, Moon SK, et al: Melittin
suppresses HIF-1α/VEGF expression through inhibition of ERK and
mTOR/p70S6K pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
8:e693802013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Magae J, Lee IK, Park KG
and Chang YC: Ascofuranone suppresses EGF-induced HIF-1α protein
synthesis by inhibition of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
273:542–550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee MK, Lee KY, Jeon HY, Sung SH and Kim
YC: Antifibrotic activity of triterpenoids from the aerial parts of
Euscaphis japonica on hepatic stellate cells. J Enzyme Inhib Med
Chem. 24:1276–1279. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HH, Lin CT and Yang LL:
Neuroprotection and free radical scavenging effects of Osmanthus
fragrans. J Biomed Sci. 14:819–827. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fernandes J, Weinlich R, Castilho RO,
Amarante-Mendes GP and Gattass CR: Pomolic acid may overcome
multidrug resistance mediated by overexpression of anti-apoptotic
Bcl-2 proteins. Cancer Lett. 245:315–320. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yoo KH, Park JH, Lee DK, Fu YY, Baek NI
and Chung IS: Pomolic acid induces apoptosis in SK-OV-3 human
ovarian adenocarcinoma cells through the mitochondrial-mediated
intrinsic and death receptor-induced extrinsic pathways. Oncol
Lett. 5:386–390. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Yoshida M, Fuchigami M, Nagao T, Okabe H,
Matsunaga K, Takata J, Karube Y, Tsuchihashi R, Kinjo J, Mihashi K,
et al: Antiproliferative constituents from Umbelliferae plants VII.
Active triterpenes and rosmarinic acid from Centella asiatica. Biol
Pharm Bull. 28:173–175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim B, Kim JH and Park B: Pomolic acid
inhibits invasion of breast cancer cells through the suppression of
CXC chemokine receptor type 4 expression. J Cell Biochem.
117:1296–1307. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim B and Park B: Baohuoside I suppresses
invasion of cervical and breast cancer cells through the
downregulation of CXCR4 chemokine receptor expression.
Biochemistry. 53:7562–7569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park JH, Lee KY, Park B and Yoon J:
Suppression of Th2 chemokines by crocin via blocking of
ERK-MAPK/NF-κB/STAT1 signalling pathways in TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated
human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 24:634–636. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park JH and Yoon J: Schizandrin inhibits
fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in transforming
growth factor-β1-stimulated AML12 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
25:276–284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nabeshima K, Inoue T, Shimao Y and
Sameshima T: Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion: Role for
cell migration. Pathol Int. 52:255–264. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marchesin V, Montagnac G and Chavrier P:
ARF6 promotes the formation of Rac1 and WAVE-dependent ventral
F-actin rosettes in breast cancer cells in response to epidermal
growth factor. PLoS One. 10:e01217472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cho HJ, Jeong YJ, Park KK, Park YY, Chung
IK, Lee KG, Yeo JH, Han SM, Bae YS and Chang YC: Bee venom
suppresses PMA-mediated MMP-9 gene activation via JNK/p38 and
NF-kappaB-dependent mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol. 127:662–668.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sandur SK, Deorukhkar A, Pandey MK, Pabón
AM, Shentu S, Guha S, Aggarwal BB and Krishnan S: Curcumin
modulates the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by
suppressing constitutive and inducible NF-kappaB activity. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:534–542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rothhut B, Ghoneim C, Antonicelli F and
Soula-Rothhut M: Epidermal growth factor stimulates matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression and invasion in human follicular
thyroid carcinoma cells through Focal adhesion kinase. Biochimie.
89:613–624. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hsieh CY, Tsai PC, Tseng CH, Chen YL,
Chang LS and Lin SR: Inhibition of EGF/EGFR activation with
naphtho[1,2-b]furan-4,5-dione blocks migration and invasion of
MDA-MB-231 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dan HC, Cooper MJ, Cogswell PC, Duncan JA,
Ting JP and Baldwin AS: Akt-dependent regulation of NF-{kappa}B is
controlled by mTOR and Raptor in association with IKK. Genes Dev.
22:1490–1500. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Friedl P, Locker J, Sahai E and Segall JE:
Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol.
14:777–783. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gialeli Ch, Theocharis AD, Kletsas D,
Tzanakakis GN and Karamanos NK: Expression of matrix macromolecules
and functional properties of EGF-responsive colon cancer cells are
inhibited by panitumumab. Invest New Drugs. 31:516–524. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sen T and Chatterjee A:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) downregulates EGF-induced MMP-9
in breast cancer cells: Involvement of integrin receptor α5β1 in
the process. Eur J Nutr. 50:465–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Han H, Du B, Pan X, Liu J, Zhao Q, Lian X,
Qian M and Liu M: CADPE inhibits PMA-stimulated gastric carcinoma
cell invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by
FAK/MEK/ERK-mediated AP-1 activation. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1477–1488.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen JS, Wang Q, Fu XH, Huang XH, Chen XL,
Cao LQ, Chen LZ, Tan HX, Li W, Bi J, et al: Involvement of
PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in invasion and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Association with MMP-9. Hepatol Res.
39:177–186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu L, Li F, Cardelli JA, Martin KA,
Blenis J and Huang S: Rapamycin inhibits cell motility by
suppression of mTOR-mediated S6K1 and 4E-BP1 pathways. Oncogene.
25:7029–7040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Berven LA, Willard FS and Crouch MF: Role
of the p70(S6K) pathway in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and
cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 296:183–195. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|