|
1
|
Gelfand R, Vernet D, Bruhn K, Vadgama J
and Gonzalez-Cadavid NF: Long-term exposure of MCF-12A normal human
breast epithelial cells to ethanol induces epithelial mesenchymal
transition and oncogenic features. Int J Oncol. 48:2399–2414.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seitz HK, Pelucchi C, Bagnardi V and La
Vecchia C: Epidemiology and pathophysiology of alcohol and breast
cancer: Update 2012. Alcohol Alcohol. 47:204–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coronado GD, Beasley J and Livaudais J:
Alcohol consumption and the risk of breast cancer. Salud Publica
Mex. 53:440–447. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Pelucchi C, Tramacere I, Boffetta P, Negri
E and La Vecchia C: Alcohol consumption and cancer risk. Nutr
Cancer. 63:983–990. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
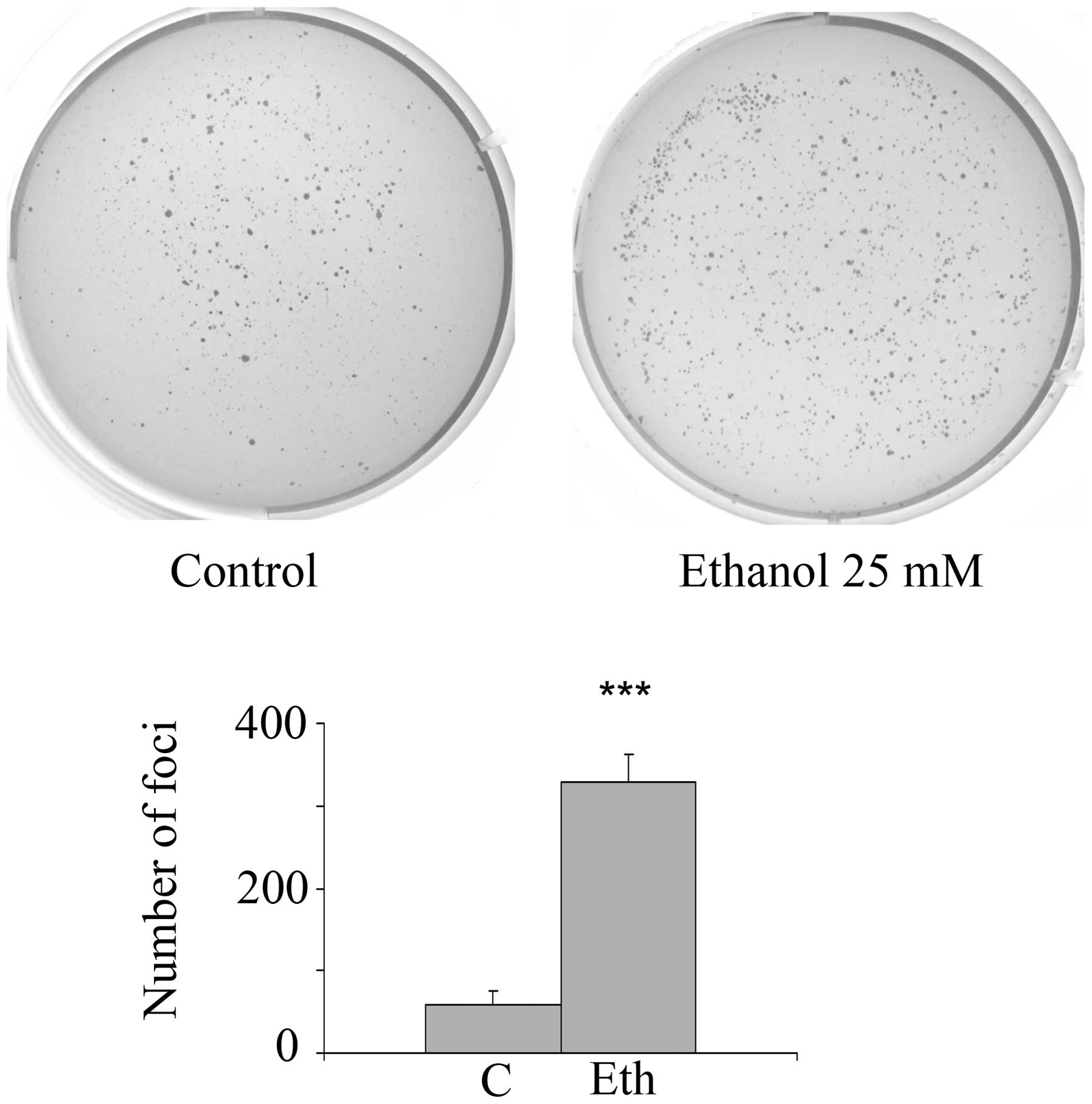
5
|
Chen WY, Rosner B, Hankinson SE, Colditz
GA and Willett WC: Moderate alcohol consumption during adult life,
drinking patterns, and breast cancer risk. JAMA. 306:1884–1890.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Narod SA: Alcohol and risk of breast
cancer. JAMA. 306:1920–1921. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saxena T, Lee E, Henderson KD, Clarke CA,
West D, Marshall SF, Deapen D, Bernstein L and Ursin G: Menopausal
hormone therapy and subsequent risk of specific invasive breast
cancer subtypes in the California Teachers Study. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 19:2366–2378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
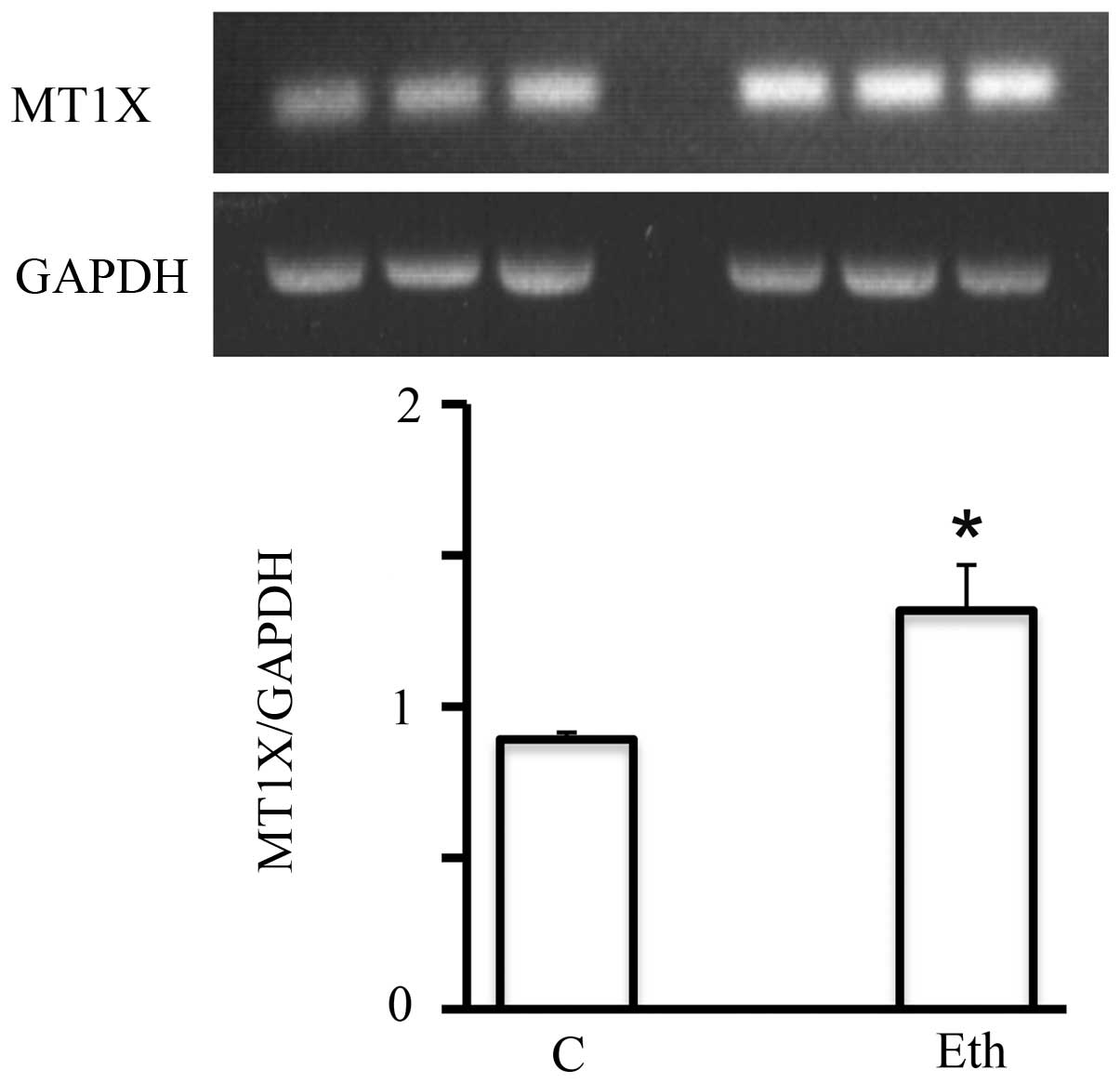
|
|
8
|
Allemani C, Berrino F, Krogh V, Sieri S,
Pupa SM, Tagliabue E, Tagliabue G and Sant M: Do pre-diagnostic
drinking habits influence breast cancer survival? Tumori.
97:142–148. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jelski W, Chrostek L, Szmitkowski M and
Markiewicz W: The activity of class I, II, III and IV alcohol
dehydrogenase isoenzymes and aldehyde dehydrogenase in breast
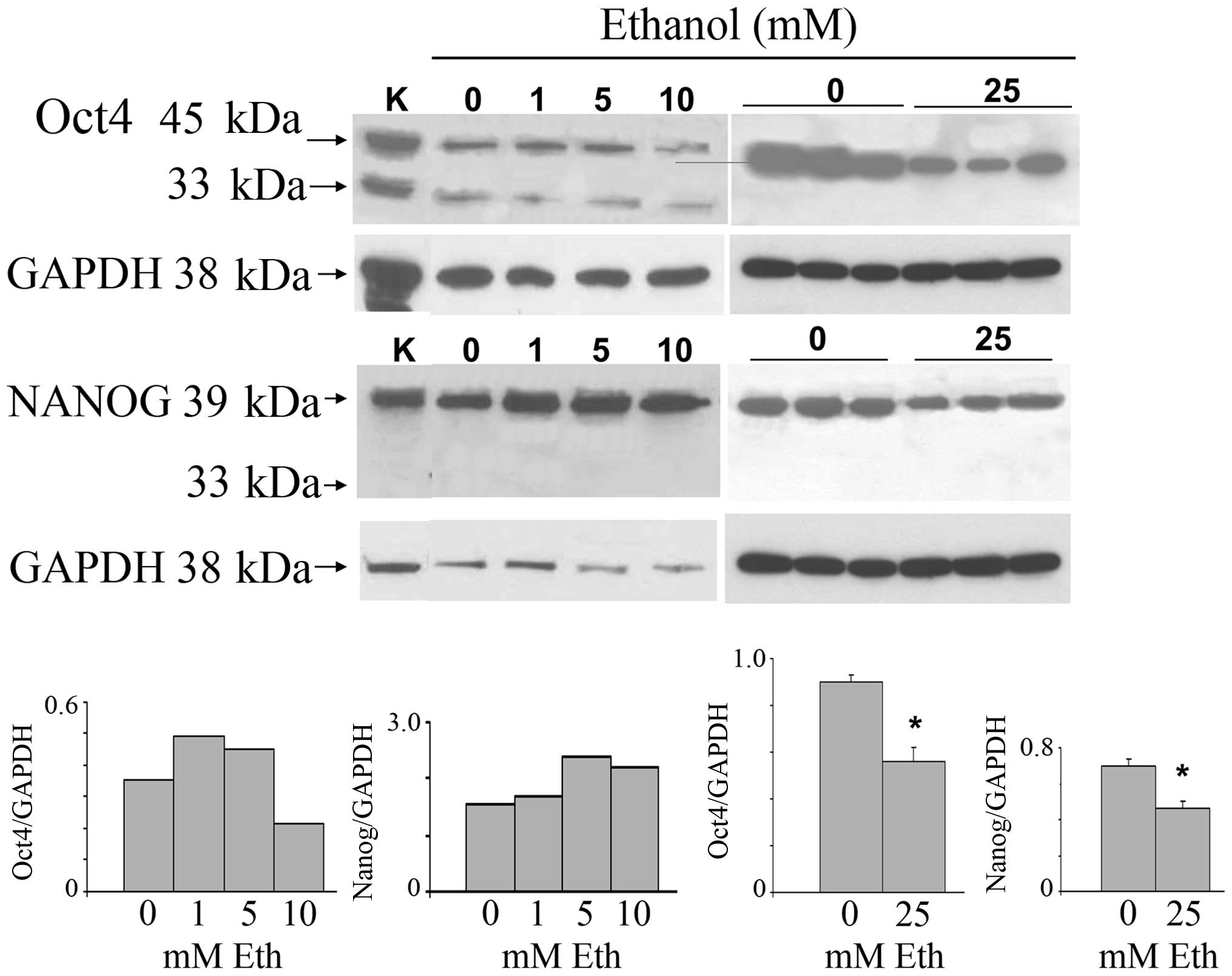
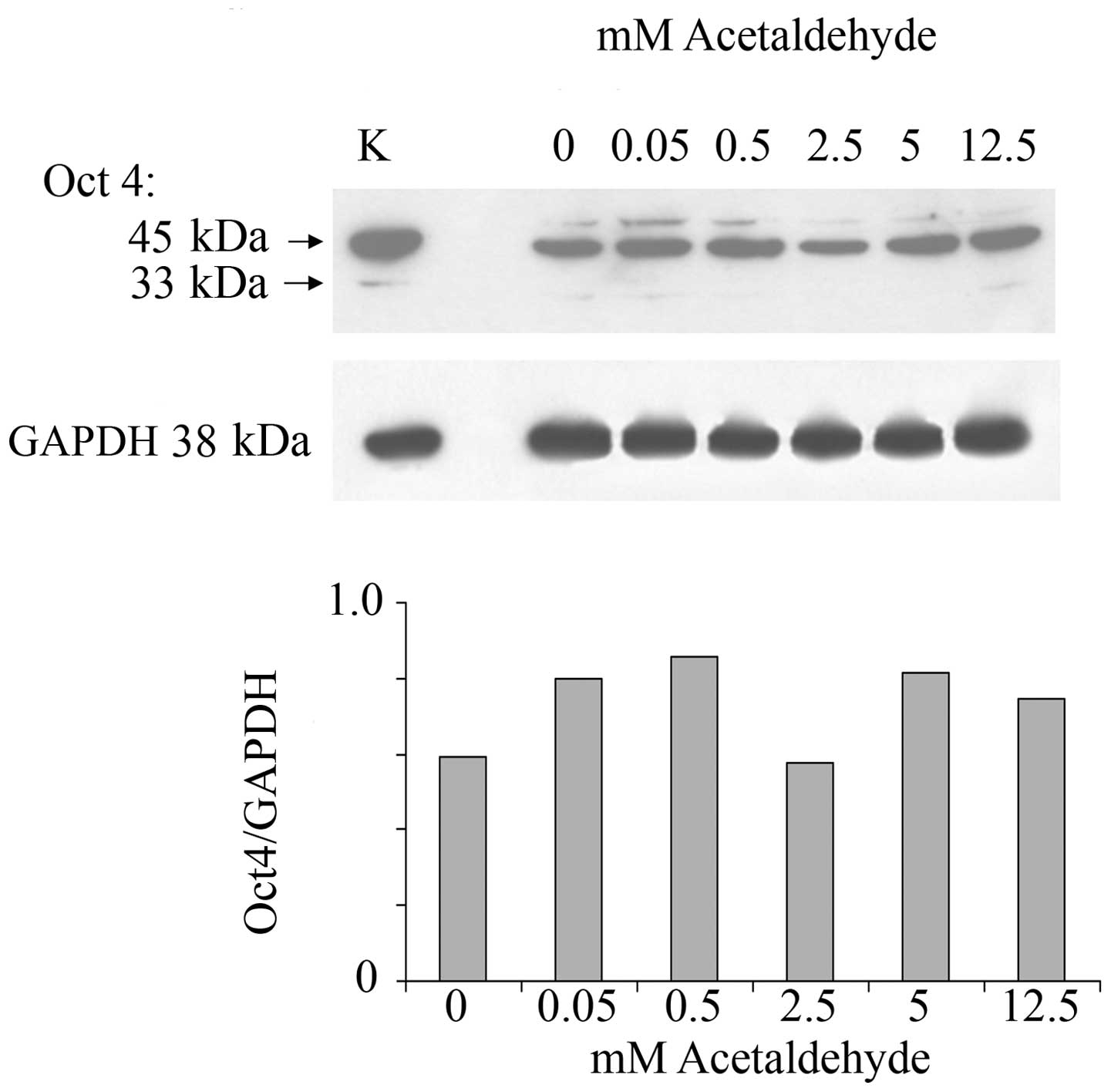
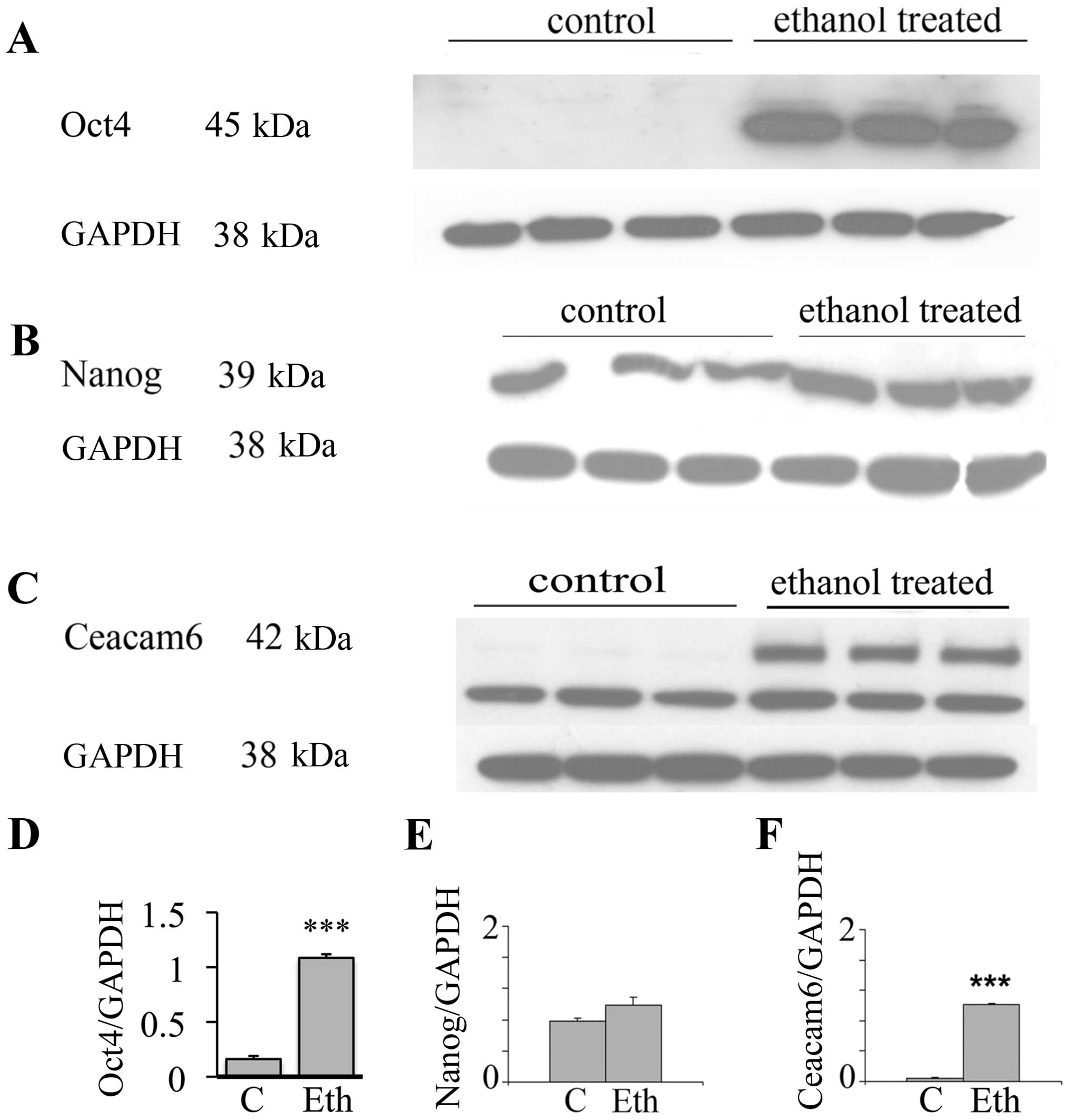
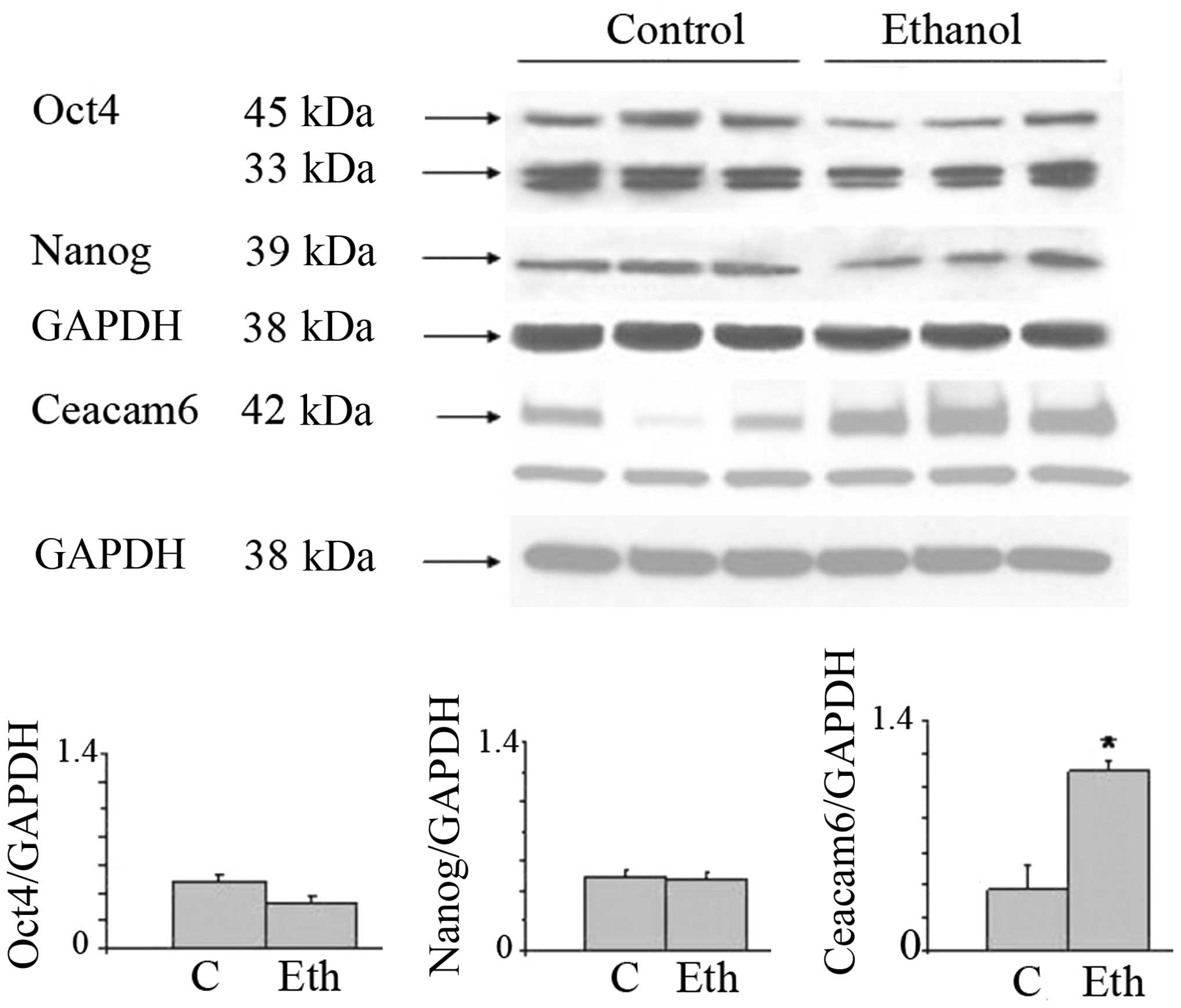
cancer. Clin Exp Med. 6:89–93. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seitz HK and Stickel F: Molecular
mechanisms of alcohol-mediated carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:599–612. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
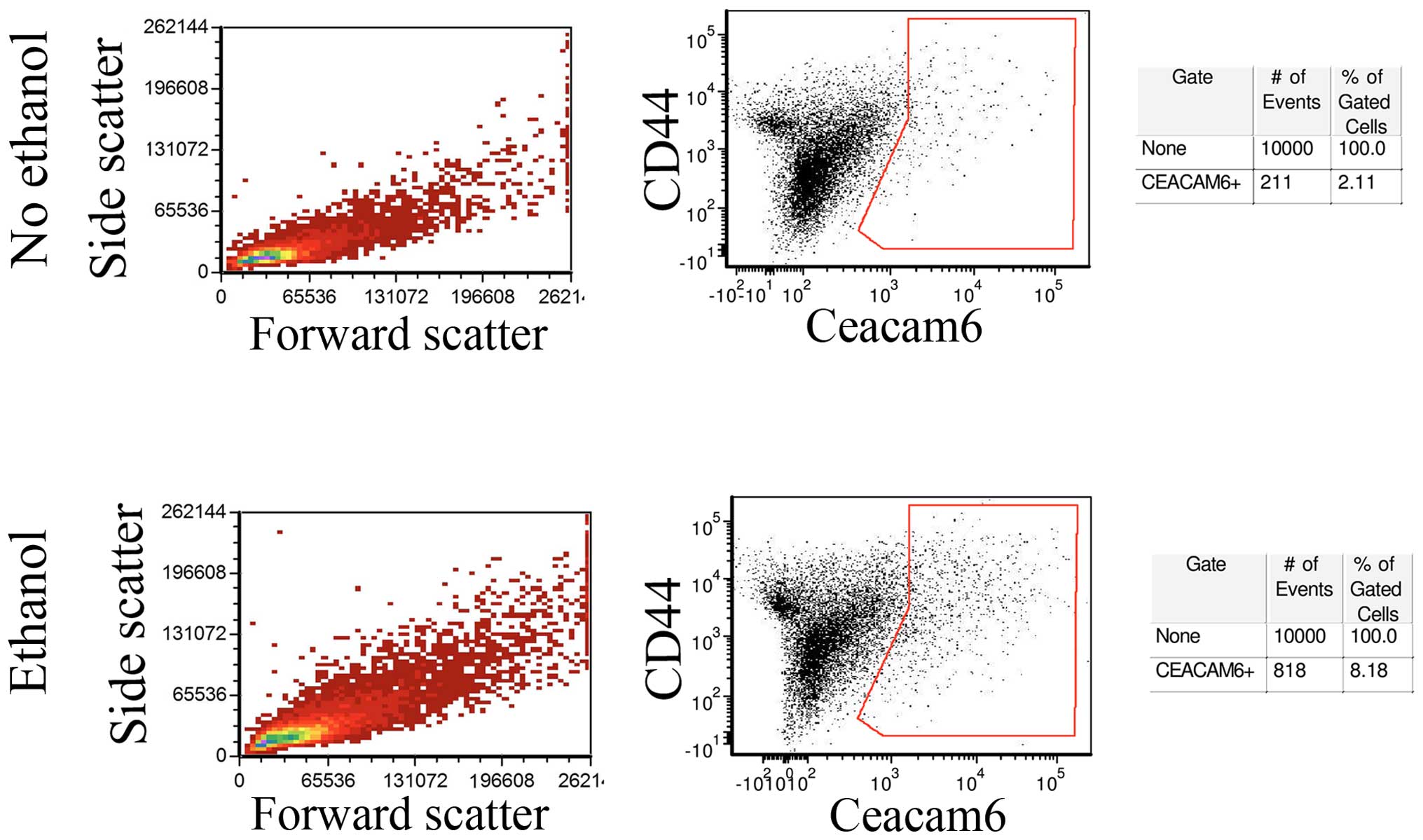
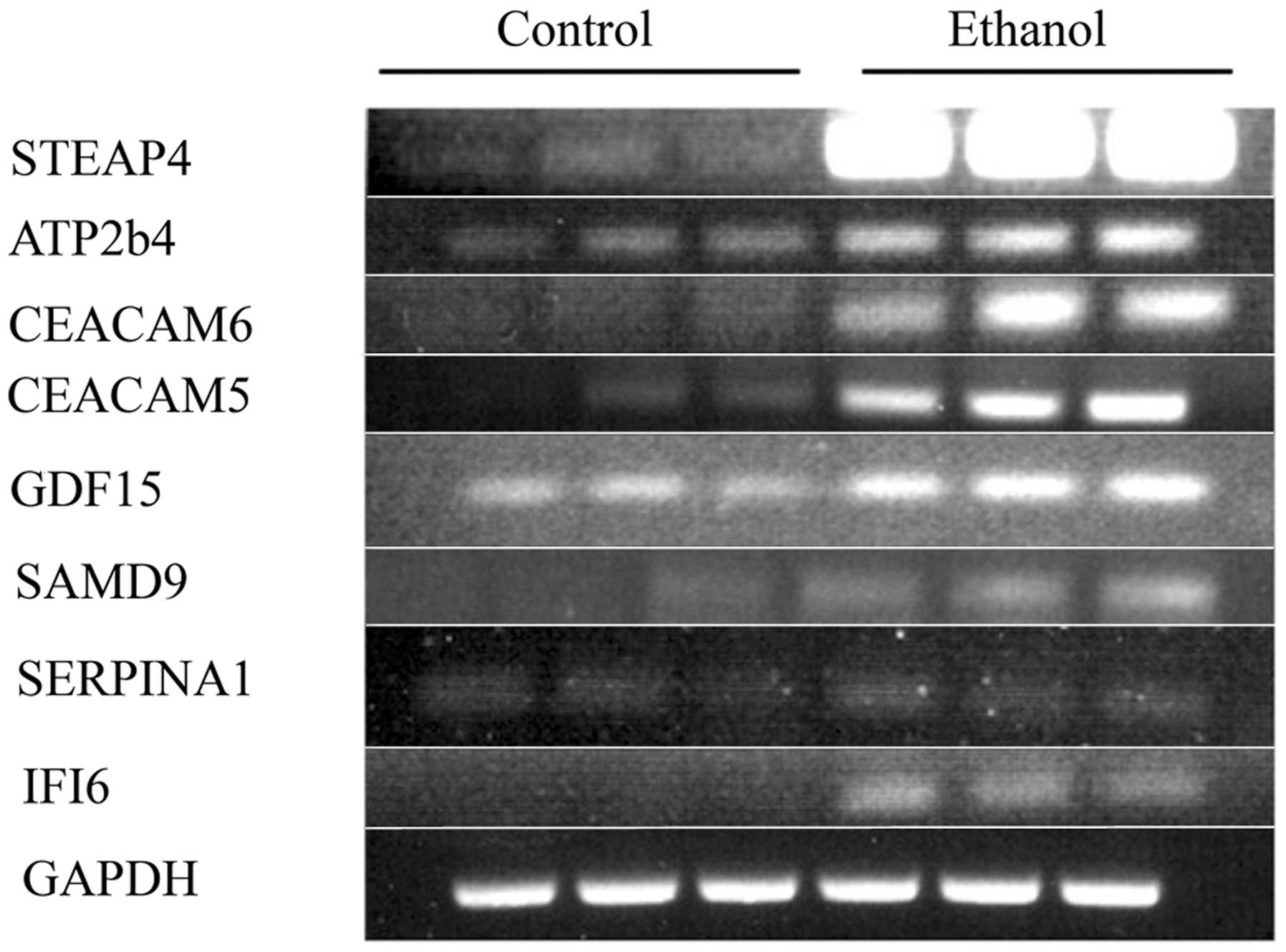
Hirano T: Alcohol consumption and
oxidative DNA damage. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 8:2895–2906.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balbo S, Meng L, Bliss RL, Jensen JA,
Hatsukami DK and Hecht SS: Time course of DNA adduct formation in
peripheral blood granulocytes and lymphocytes after drinking
alcohol. Mutagenesis. 27:485–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Seitz HK and Stickel F: Acetaldehyde as an
underestimated risk factor for cancer development: Role of genetics
in ethanol metabolism. Genes Nutr. 5:121–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Wong AW, Dunlap SM, Holcomb VB and Nunez
NP: Alcohol promotes mammary tumor development via the estrogen
pathway in estrogen receptor alpha-negative HER2/neu mice. Alcohol
Clin Exp Res. 36:577–587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Singletary KW, Frey RS and Yan W: Effect
of ethanol on proliferation and estrogen receptor-alpha expression
in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 165:131–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Etique N, Chardard D, Chesnel A, Merlin
JL, Flament S and Grillier-Vuissoz I: Ethanol stimulates
proliferation, ERalpha and aromatase expression in MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 13:149–155. 2004.
|
|
17
|
Etique N, Flament S, Lecomte J and
Grillier-Vuissoz I: Ethanol-induced ligand-independent activation
of ERalpha mediated by cyclic AMP/PKA signaling pathway: An in
vitro study on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
31:1509–1518. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Etique N, Grillier-Vuissoz I, Lecomte J
and Flament S: Crosstalk between adenosine receptor (A2A isoform)
and ERalpha mediates ethanol action in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 21:977–981. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Przylipiak A, Rabe T, Hafner J, Przylipiak
M and Runnebaum R: Influence of ethanol on in vitro growth of human
mammary carcinoma cell line MCF-7. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
258:137–140. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng Q, Gao B, Goldberg ID, Rosen EM and
Fan S: Stimulation of cell invasion and migration by alcohol in
breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 273:448–453. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo J and Miller MW: Ethanol enhances
erbB-mediated migration of human breast cancer cells in culture.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 63:61–69. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Izevbigie EB, Ekunwe SI, Jordan J and
Howard CB: Ethanol modulates the growth of human breast cancer
cells in vitro. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 227:260–265. 2002.
|
|
23
|
Etique N, Chardard D, Chesnel A, Flament S
and Grillier-Vuissoz I: Analysis of the effects of different
alcohols on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1030:78–85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Etique N, Grillier-Vuissoz I and Flament
S: Ethanol stimulates the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases 2
and 9 in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 15:603–608.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Verma M and Davidson EA: MUC1 upregulation
by ethanol. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 17:1–11. 1999.
|
|
26
|
Ma C, Lin H, Leonard SS, Shi X, Ye J and
Luo J: Overexpression of ErbB2 enhances ethanol-stimulated
intracellular signaling and invasion of human mammary epithelial
and breast cancer cells in vitro. Oncogene. 22:5281–5290. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aye MM, Ma C, Lin H, Bower KA, Wiggins RC
and Luo J: Ethanol-induced in vitro invasion of breast cancer
cells: The contribution of MMP-2 by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer.
112:738–746. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ke Z, Lin H, Fan Z, Cai TQ, Kaplan RA, Ma
C, Bower KA, Shi X and Luo J: MMP-2 mediates ethanol-induced
invasion of mammary epithelial cells over-expressing ErbB2. Int J
Cancer. 119:8–16. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cordes T, Diesing D, Becker S, Diedrich K,
Reichrath J and Friedrich M: Modulation of MAPK ERK1 and ERK2 in
VDR-positive and -negative breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer
Res. 26A:2749–2753. 2006.
|
|
30
|
Xu M, Bower KA, Wang S, Frank JA, Chen G,
Ding M, Wang S, Shi X, Ke Z and Luo J: Cyanidin-3-glucoside
inhibits ethanol-induced invasion of breast cancer cells
overexpressing ErbB2. Mol Cancer. 9:2852010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raouf A, Sun Y, Chatterjee S and Basak P:
The biology of human breast epithelial progenitors. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 23:606–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bruno RD and Smith GH: Role of epithelial
stem/progenitor cells in mammary cancer. Gene Expr. 15:133–140.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Korkaya H, Liu S and Wicha MS: Breast
cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor
microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 121:3804–3809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feifei N, Mingzhi Z, Yanyun Z, Huanle Z,
Fang R, Mingzhu H, Mingzhi C, Yafei S and Fengchun Z: MicroRNA
expression analysis of mammospheres cultured from human breast
cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1937–1944. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie G, Zhan J, Tian Y, Liu Y, Chen Z, Ren
C, Sun Q, Lian J, Chen L, Ruan J, et al: Mammosphere cells from
high-passage MCF7 cell line show variable loss of tumorigenicity
and radioresistance. Cancer Lett. 316:53–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nash R, Krishnamoorthy M, Jenkins A and
Csete M: Human embryonic stem cell model of ethanol-mediated early
developmental toxicity. Exp Neurol. 234:127–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Worley SL, Vaughn BJ, Terry AI, Gardiner
CS and DeKrey GK: Time- and dose-dependent effects of ethanol on
mouse embryonic stem cells. Reprod Toxicol. 57:157–164. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cortez MA, Welsh JW and Calin GA:
Circulating microRNAs as noninvasive biomarkers in breast cancer.
Recent Results Cancer Res. 195:151–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Krell J, Frampton AE, Jacob J, Castellano
L and Stebbing J: miRNAs in breast cancer: Ready for real time?
Pharmacogenomics. 13:709–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shore AN, Herschkowitz JI and Rosen JM:
Noncoding RNAs involved in mammary gland development and
tumorigenesis: There's a long way to go. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 17:43–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Valastyan S: Roles of microRNAs and other
non-coding RNAs in breast cancer metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 17:23–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guttilla IK, Adams BD and White BA: ERα,
microRNAs, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast
cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 23:73–82. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jain P and Alahari SK: Breast cancer stem
cells: A new challenge for breast cancer treatment. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 16:1824–1832. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Miranda RC, Pietrzykowski AZ, Tang Y,
Sathyan P, Mayfield D, Keshavarzian A, Sampson W and Hereld D:
MicroRNAs: Master regulators of ethanol abuse and toxicity? Alcohol
Clin Exp Res. 34:575–587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Meng F, Glaser SS, Francis H, Yang F, Han
Y, Stokes A, Staloch D, McCarra J, Liu J, Venter J, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of miR-34a expression in alcoholic liver
injury. Am J Pathol. 181:804–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Klinge CM: miRNAs and estrogen action.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 23:223–233. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guttilla IK, Phoenix KN, Hong X, Tirnauer
JS, Claffey KP and White BA: Prolonged mammosphere culture of MCF-7
cells induces an EMT and repression of the estrogen receptor by
microRNAs. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 132:75–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li X, Mertens-Talcott SU, Zhang S, Kim K,
Ball J and Safe S: MicroRNA-27a indirectly regulates estrogen
receptor {alpha} expression and hormone responsiveness in MCF-7
breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 151:2462–2473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Reed TE, Kalant H, Gibbins RJ, Kapur BM
and Rankin JG: Alcohol and acetaldehyde metabolism in Caucasians,
Chinese and Amerinds. Can Med Assoc J. 115:851–855. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tsang JY, Kwok YK, Chan KW, Ni YB, Chow
WN, Lau KF, Shao MM, Chan SK, Tan PH and Tse GM: Expression and
clinical significance of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell
adhesion molecule 6 in breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
142:311–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol
G, Vecchi M, Ronzoni S, Bernard L, Viale G, Pelicci PG and Di Fiore
PP: Biological and molecular heterogeneity of breast cancers
correlates with their cancer stem cell content. Cell. 140:62–73.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ono S, Ishizaki Y, Tokuda E, Tabata K,
Asami S and Suzuki T: Different patterns in the induction of
metallothionein mRNA synthesis among isoforms after acute ethanol
administration. Biol Trace Elem Res. 115:147–156. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pedersen MO, Larsen A, Stoltenberg M and
Penkowa M: The role of metallothionein in oncogenesis and cancer
prognosis. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 44:29–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ning MS, Kim AS, Prasad N, Levy SE, Zhang
H and Andl T: Characterization of the Merkel Cell Carcinoma
miRNome. J Skin Cancer. 2014:2895482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rojas F, Hernandez ME, Silva M, Li L,
Subramanian S, Wilson MJ and Liu P: The oncogenic response to
MiR-335 is associated with cell surface expression of membrane-type
1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) activity. PLoS One.
10:e01320262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lu Y, Yang H, Yuan L, Liu G, Zhang C, Hong
M, Liu Y, Zhou M, Chen F and Li X: Overexpression of miR-335
confers cell proliferation and tumour growth to colorectal
carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 412:235–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Saumet A, Vetter G, Bouttier M, Antoine E,
Roubert C, Orsetti B, Theillet C and Lecellier CH: Estrogen and
retinoic acid antagonistically regulate several microRNA genes to
control aerobic glycolysis in breast cancer cells. Mol Biosyst.
8:3242–3253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ruiz-Llorente L, Ardila-González S, Fanjul
LF, Martínez-Iglesias O and Aranda A: microRNAs 424 and 503 are
mediators of the anti-proliferative and anti-invasive action of the
thyroid hormone receptor beta. Oncotarget. 5:2918–2933. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang Z, Zhang H, Zhang P, Li J, Shan Z and
Teng W: Upregulation of miR-2861 and miR-451 expression in
papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. Med Oncol.
30:5772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Long C, Jiang L, Wei F, Ma C, Zhou H, Yang
S, Liu X and Liu Z: Integrated miRNA-mRNA analysis revealing the
potential roles of miRNAs in chordomas. PLoS One. 8:e666762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nakazawa K, Dashzeveg N and Yoshida K:
Tumor suppressor p53 induces miR-1915 processing to inhibit Bcl-2
in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. FEBS J. 281:2937–2944.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Boo L, Ho WY, Ali NM, Yeap SK, Ky H, Chan
KG, Yin WF, Satharasinghe DA, Liew WC, Tan SW, et al: MiRNA
transcriptome profiling of spheroid-enriched cells with cancer stem
cell properties in human breast MCF-7 cell line. Int J Biol Sci.
12:427–445. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yang B, Jing C, Wang J, Guo X, Chen Y, Xu
R, Peng L, Liu J and Li L: Identification of microRNAs associated
with lymphangiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:374–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Xu C, Zhang L, Li H, Liu Z, Duan L and Lu
C: MiRNA-1469 promotes lung cancer cells apoptosis through
targeting STAT5a. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1180–1189. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yu CC, Chen YW, Chiou GY, Tsai LL, Huang
PI, Chang CY, Tseng LM, Chiou SH, Yen SH, Chou MY, et al: MicroRNA
let-7a represses chemoresistance and tumourigenicity in head and
neck cancer via stem-like properties ablation. Oral Oncol.
47:202–210. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Molina-Pinelo S, Gutiérrez G, Pastor MD,
Hergueta M, Moreno-Bueno G, García-Carbonero R, Nogal A, Suárez R,
Salinas A, Pozo-Rodríguez F, et al: MicroRNA-dependent regulation
of transcription in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
9:e905242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ogony JW, Malahias E, Vadigepalli R and
Anni H: Ethanol alters the balance of Sox2, Oct4, and Nanog
expression in distinct subpopulations during differentiation of
embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 22:2196–2210. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zeineddine D, Hammoud AA, Mortada M and
Boeuf H: The Oct4 protein: More than a magic stemness marker. Am J
Stem Cells. 3:74–82. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu CG, Lu Y, Wang BB, Zhang YJ, Zhang RS,
Lu Y, Chen B, Xu H, Jin F and Lu P: Clinical implications of stem
cell gene Oct-4 expression in breast cancer. Ann Surg.
253:1165–1171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu C, Cao X, Zhang Y, Xu H, Zhang R, Wu
Y, Lu P and Jin F: Co-expression of Oct-4 and Nestin in human
breast cancers. Mol Biol Rep. 39:5875–5881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Leis O, Eguiara A, Lopez-Arribillaga E,
Alberdi MJ, Hernandez-Garcia S, Elorriaga K, Pandiella A, Rezola R
and Martin AG: Sox2 expression in breast tumours and activation in
breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 31:1354–1365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, Neubauer H,
Scheble V, Müller F, Schneider F, Petersen K, Wallwiener D, Kanz L,
et al: Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in
early-stage breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jung JW, Park SB, Lee SJ, Seo MS, Trosko
JE and Kang KS: Metformin represses self-renewal of the human
breast carcinoma stem cells via inhibition of estrogen
receptor-mediated OCT4 expression. PLoS One. 6:e280682011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hu J, Qin K, Zhang Y, Gong J, Li N, Lv D,
Xiang R and Tan X: Downregulation of transcription factor Oct4
induces an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via enhancement of
Ca2+ influx in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 411:786–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Trosko JE: From adult stem cells to cancer
stem cells: Oct-4 Gene, cell-cell communication, and hormones
during tumor promotion. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1089:36–58. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wu F, Zhang J, Wang P, Ye X, Jung K, Bone
KM, Pearson JD, Ingham RJ, McMullen TP, Ma Y, et al: Identification
of two novel phenotypically distinct breast cancer cell subsets
based on Sox2 transcription activity. Cell Signal. 24:1989–1998.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nagata T, Shimada Y, Sekine S, Hori R,
Matsui K, Okumura T, Sawada S, Fukuoka J and Tsukada K: Prognostic
significance of NANOG and KLF4 for breast cancer. Breast Cancer.
21:96–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Machida K, Tsukamoto H, Mkrtchyan H, Duan
L, Dynnyk A, Liu HM, Asahina K, Govindarajan S, Ray R, Ou JH, et
al: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates synergism between alcohol and HCV
in hepatic oncogenesis involving stem cell marker Nanog. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:1548–1553. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lewis-Wambi JS, Cunliffe HE, Kim HR,
Willis AL and Jordan VC: Overexpression of CEACAM6 promotes
migration and invasion of oestrogen-deprived breast cancer cells.
Eur J Cancer. 44:1770–1779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ihnen M, Kilic E, Köhler N, Löning T,
Witzel I, Hagel C, Höller S, Kersten JF, Müller V, Jänicke F, et
al: Protein expression analysis of ALCAM and CEACAM6 in breast
cancer metastases reveals significantly increased ALCAM expression
in metastases of the skin. J Clin Pathol. 64:146–152. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Maraqa L, Cummings M, Peter MB, Shaaban
AM, Horgan K, Hanby AM and Speirs V: Carcinoembryonic antigen cell
adhesion molecule 6 predicts breast cancer recurrence following
adjuvant tamoxifen. Clin Cancer Res. 14:405–411. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Blumenthal RD, Leon E, Hansen HJ and
Goldenberg DM: Expression patterns of CEACAM5 and CEACAM6 in
primary and metastatic cancers. BMC Cancer. 7:22007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Gomes IM, Maia CJ and Santos CR: STEAP
proteins: From structure to applications in cancer therapy. Mol
Cancer Res. 10:573–587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sano H, Wada S, Eguchi H, Osaki A, Saeki T
and Nishiyama M: Quantitative prediction of tumor response to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: Novel marker genes and
prediction model using the expression levels. Breast Cancer.
19:37–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Li CF, MacDonald JR, Wei RY, Ray J, Lau K,
Kandel C, Koffman R, Bell S, Scherer SW and Alman BA: Human sterile
alpha motif domain 9, a novel gene identified as down-regulated in
aggressive fibromatosis, is absent in the mouse. BMC Genomics.
8:922007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Stone A, Valdés-Mora F, Gee JM, Farrow L,
McClelland RA, Fiegl H, Dutkowski C, McCloy RA, Sutherland RL,
Musgrove EA, et al: Tamoxifen-induced epigenetic silencing of
oestrogen-regulated genes in anti-hormone resistant breast cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e404662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cimino D, Fuso L, Sfiligoi C, Biglia N,
Ponzone R, Maggiorotto F, Russo G, Cicatiello L, Weisz A, Taverna
D, et al: Identification of new genes associated with breast cancer
progression by gene expression analysis of predefined sets of
neoplastic tissues. Int J Cancer. 123:1327–1338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ito Y, Motoo Y, Yoshida H, Iovanna JL,
Takamura Y, Miya A, Kuma K and Miyauchi A: Decreased expression of
tumor protein p53-induced nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1) in breast
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 26B:4391–4395. 2006.
|
|
89
|
Sorbello V, Fuso L, Sfiligoi C, Scafoglio
C, Ponzone R, Biglia N, Weisz A, Sismondi P and De Bortoli M:
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of eight novel
estrogen-regulated genes in breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers.
18:123–129. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
He X, Dong DD, Yie SM, Yang H, Cao M, Ye
SR, Li K, Liu J and Chen J: HLA-G expression in human breast
cancer: Implications for diagnosis and prognosis, and effect on
allocytotoxic lymphocyte response after hormone treatment in vitro.
Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1459–1469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jia Y, Liu H, Zhuang Q, Xu S, Yang Z, Li
J, Lou J and Zhang W: Tumorigenicity of cancer stem-like cells
derived from hepatocarcinoma is regulated by microRNA-145. Oncol
Rep. 27:1865–1872. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yin R, Zhang S, Wu Y, Fan X, Jiang F,
Zhang Z, Feng D, Guo X and Xu L: MicroRNA-145 suppresses lung
adenocarcinoma-initiating cell proliferation by targeting OCT4.
Oncol Rep. 25:1747–1754. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson
JA and Kosik KS: MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and
represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell.
137:647–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39(Database): D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Cicatiello L, Mutarelli M, Grober OM,
Paris O, Ferraro L, Ravo M, Tarallo R, Luo S, Schroth GP, Seifert
M, et al: Estrogen receptor alpha controls a gene network in
luminal-like breast cancer cells comprising multiple transcription
factors and microRNAs. Am J Pathol. 176:2113–2130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ali HO, Arroyo AB, González-Conejero R,
Stavik B, Iversen N, Sandset PM, Martínez C and Skretting G: The
role of microRNA-27a/b and microRNA-494 in estrogen-mediated
downregulation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor α. J Thromb
Haemost. 14:1226–1237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lee YM, Lee JY, Ho CC, Hong QS, Yu SL,
Tzeng CR, Yang PC and Chen HW: miRNA-34b as a tumor suppressor in
estrogen-dependent growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer
Res. 13:R1162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Wang G, Collins NR,
Thomson MJ, Geistlinger TR, Carroll JS, Brown M, Hammond S, Srour
EF, Liu Y, et al: Estradiol-regulated microRNAs control estradiol
response in breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:4850–4861.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Tan S, Ding K, Li R, Zhang W, Li G, Kong
X, Qian P, Lobie PE and Zhu T: Identification of miR-26 as a key
mediator of estrogen stimulated cell proliferation by targeting
CHD1, GREB1 and KPNA2. Breast Cancer Res. 16:R402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Liao XH, Lu DL, Wang N, Liu LY, Wang Y, Li
YQ, Yan TB, Sun XG, Hu P and Zhang TC: Estrogen receptor α mediates
proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a
p21/PCNA/E2F1-dependent pathway. FEBS J. 281:927–942. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Zhang C, Zhao J and Deng H: 17β-estradiol
up-regulates miR-155 expression and reduces TP53INP1 expression in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 379:201–211. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Masuda M, Miki Y, Hata S, Takagi K,
Sakurai M, Ono K, Suzuki K, Yang Y, Abe E, Hirakawa H, et al: An
induction of microRNA, miR-7 through estrogen treatment in breast
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10(Suppl 1): S22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Manavalan TT, Teng Y, Litchfield LM,
Muluhngwi P, Al-Rayyan N and Klinge CM: Reduced expression of
miR-200 family members contributes to antiestrogen resistance in
LY2 human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e623342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Yu Y, Xiao CH, Tan LD, Wang QS, Li XQ and
Feng YM: Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells through
paracrine TGF-β signalling. Br J Cancer. 110:724–732. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Shibahara Y, Miki Y, Onodera Y, Hata S,
Chan MS, Yiu CC, Loo TY, Nakamura Y, Akahira J, Ishida T, et al:
Aromatase inhibitor treatment of breast cancer cells increases the
expression of let-7f, a microRNA targeting CYP19A1. J Pathol.
227:357–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yu X, Zhang X, Dhakal IB, Beggs M,
Kadlubar S and Luo D: Induction of cell proliferation and survival
genes by estradiol-repressed microRNAs in breast cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 12:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Cittelly DM, Das PM, Spoelstra NS,
Edgerton SM, Richer JK, Thor AD and Jones FE: Downregulation of
miR-342 is associated with tamoxifen resistant breast tumors. Mol
Cancer. 9:3172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Thornton JE and Gregory RI: How does Lin28
let-7 control development and disease? Trends Cell Biol.
22:474–482. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Quann K, Jing Y and Rigoutsos I:
Post-transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 through its coding
sequence by the miR-15/107 group of miRNAs. Front Genet. 6:2422015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Fu XM, Zhou YZ, Cheng Z, Liao XB and Zhou
XM: MicroRNAs: Novel players in aortic aneurysm. Biomed Res Int.
2015:8316412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Gambari R, Brognara E, Spandidos DA and
Fabbri E: Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor
miRNAs: New trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic
strategies in oncology (Review). Int J Oncol. 49:5–32.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wang H, Zhang P, Chen W, Feng D, Jia Y and
Xie LX: Evidence for serum miR-15a and miR-16 levels as biomarkers
that distinguish sepsis from systemic inflammatory response
syndrome in human subjects. Clin Chem Lab Med. 50:1423–1428. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
de Gonzalo-Calvo D, Davalos A, Montero A,
Garcia-Gonzalez A, Tyshkovska I, Gonzalez-Medina A, Soares SM,
Martínez-Camblor P, Casas-Agustench P, Rabadán M, et al:
Circulating inflammatory miRNA signature in response to different
doses of aerobic exercise. J Appl Physiol. 119:124–134. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Rodosthenous RS, Coull BA, Lu Q, Vokonas
PS, Schwartz JD and Baccarelli AA: Ambient particulate matter and
microRNAs in extracellular vesicles: A pilot study of older
individuals. Part Fibre Toxicol. 13:132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R,
Gaudio E, Santhanam R, Lovat F, Fadda P, Mao C, Nuovo GJ, et al:
MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic
inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E2110–E2116.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zhang L, Xu Y, Jin X, Wang Z, Wu Y, Zhao
D, Chen G, LiD, Wang X, Cao H, et al: A circulating miRNA signature
as a diagnostic biomarker for non-invasive early detection of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 154:423–434. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhang Y, Zhang D, Wang F, Xu D, Guo Y and
Cui W: Serum miRNAs panel (miR-16-2*, miR-195, miR-2861,
miR-497) as novel non-invasive biomarkers for detection of cervical
cancer. Sci Rep. 5:179422015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Zhao Q, Deng S, Wang G, Liu C, Meng L,
Qiao S, Shen L, Zhang Y, Lü J, Li W, et al: A direct quantification
method for measuring plasma MicroRNAs identified potential
biomarkers for detecting metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:21865–21874. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|