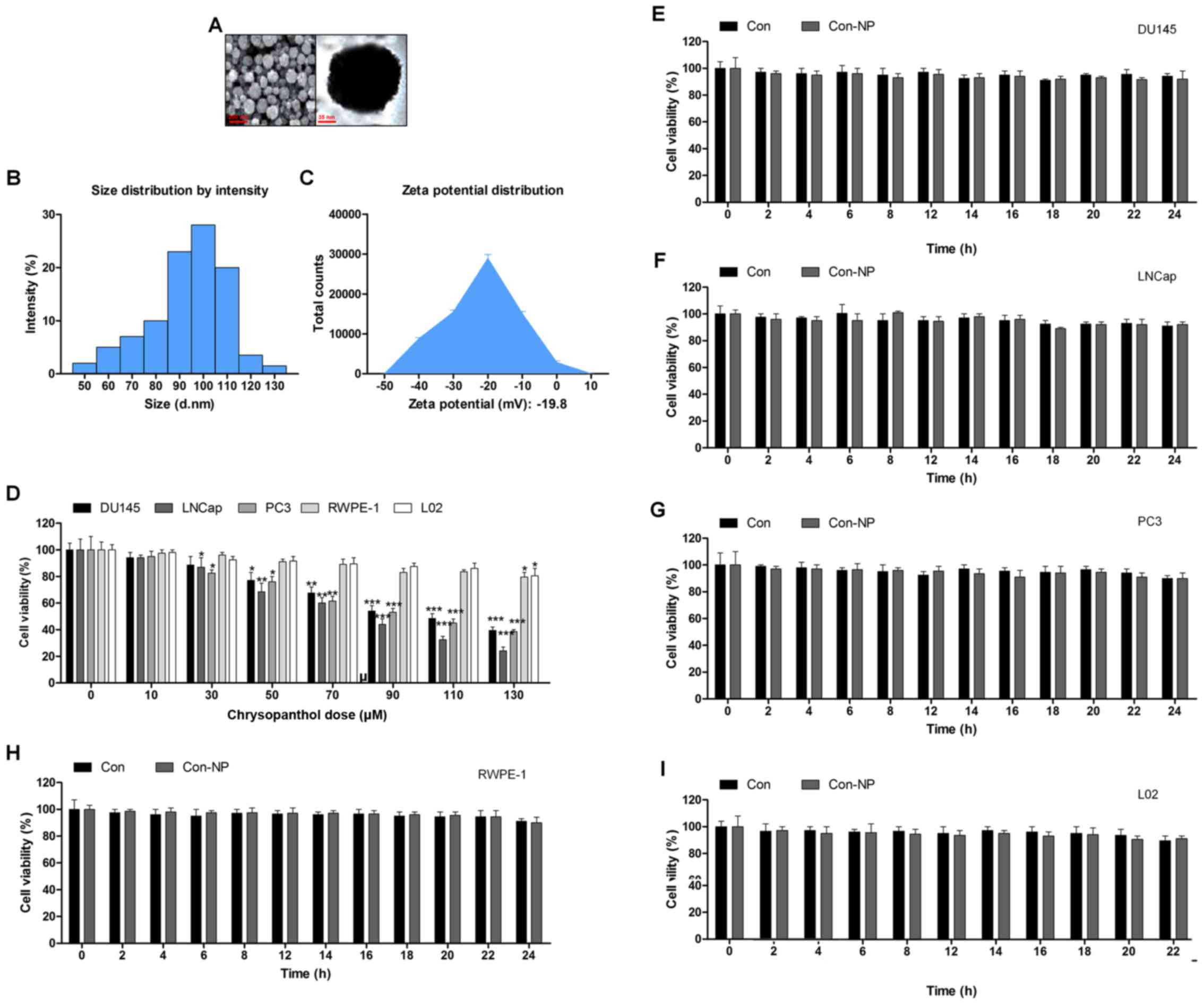
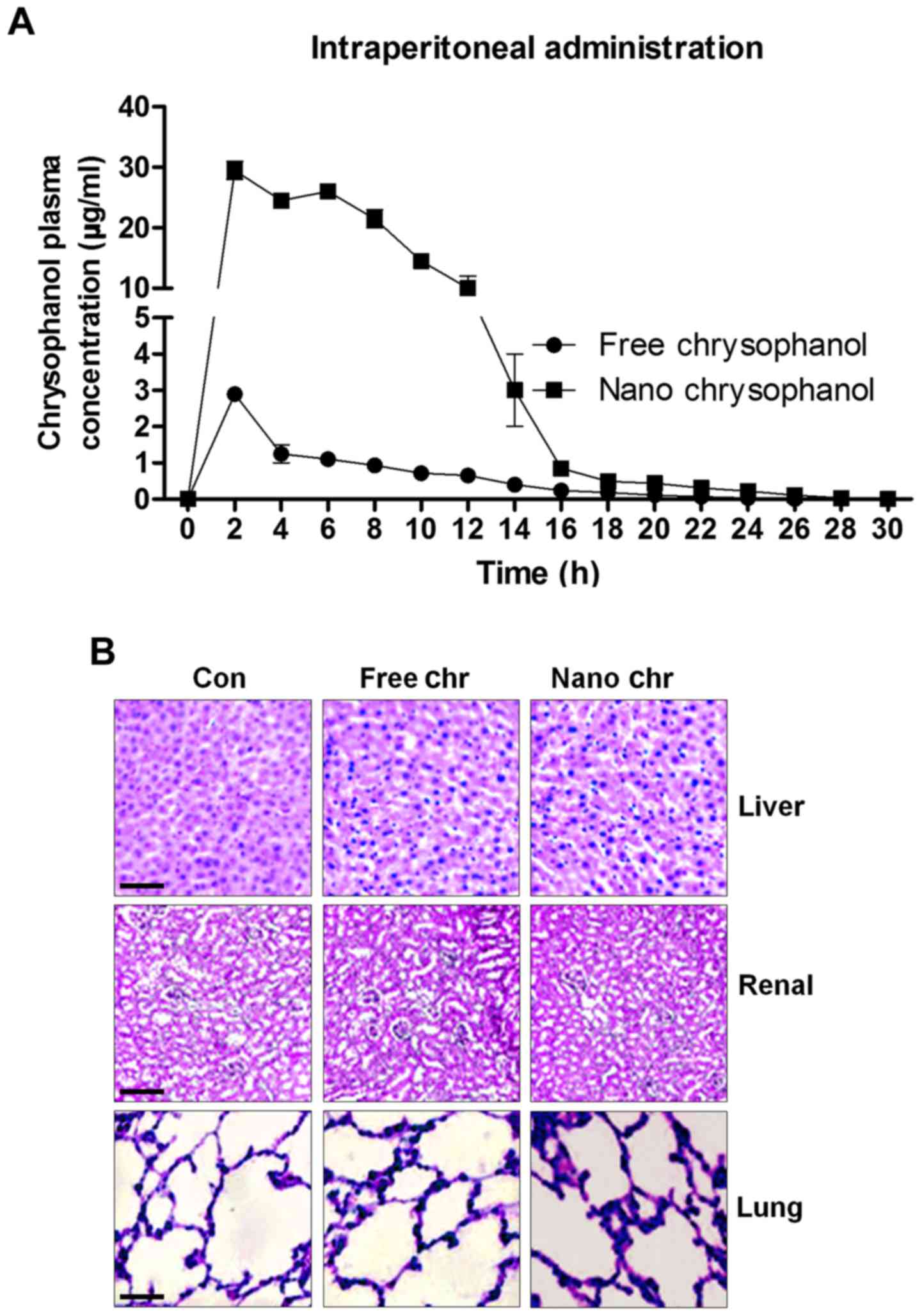
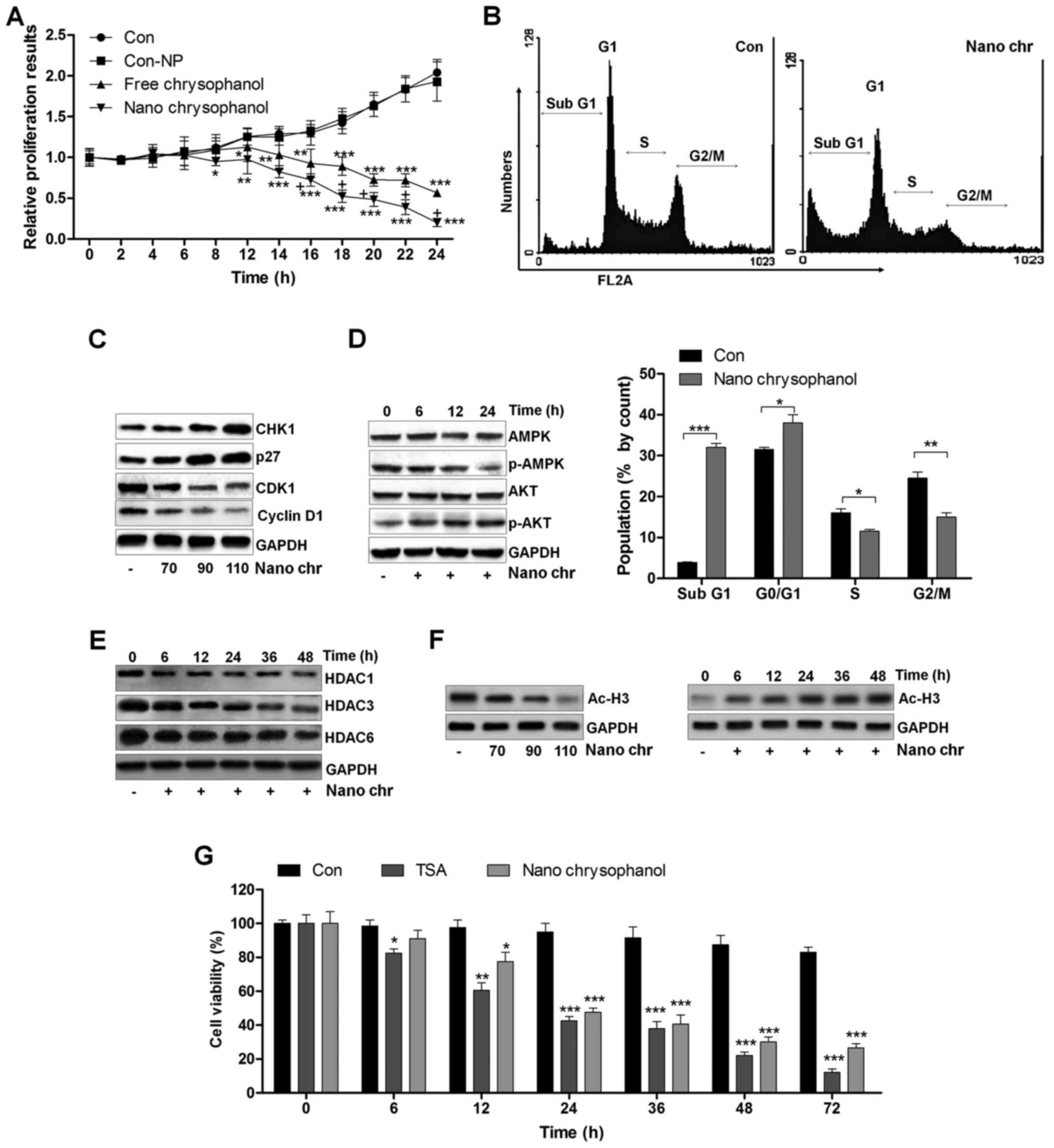
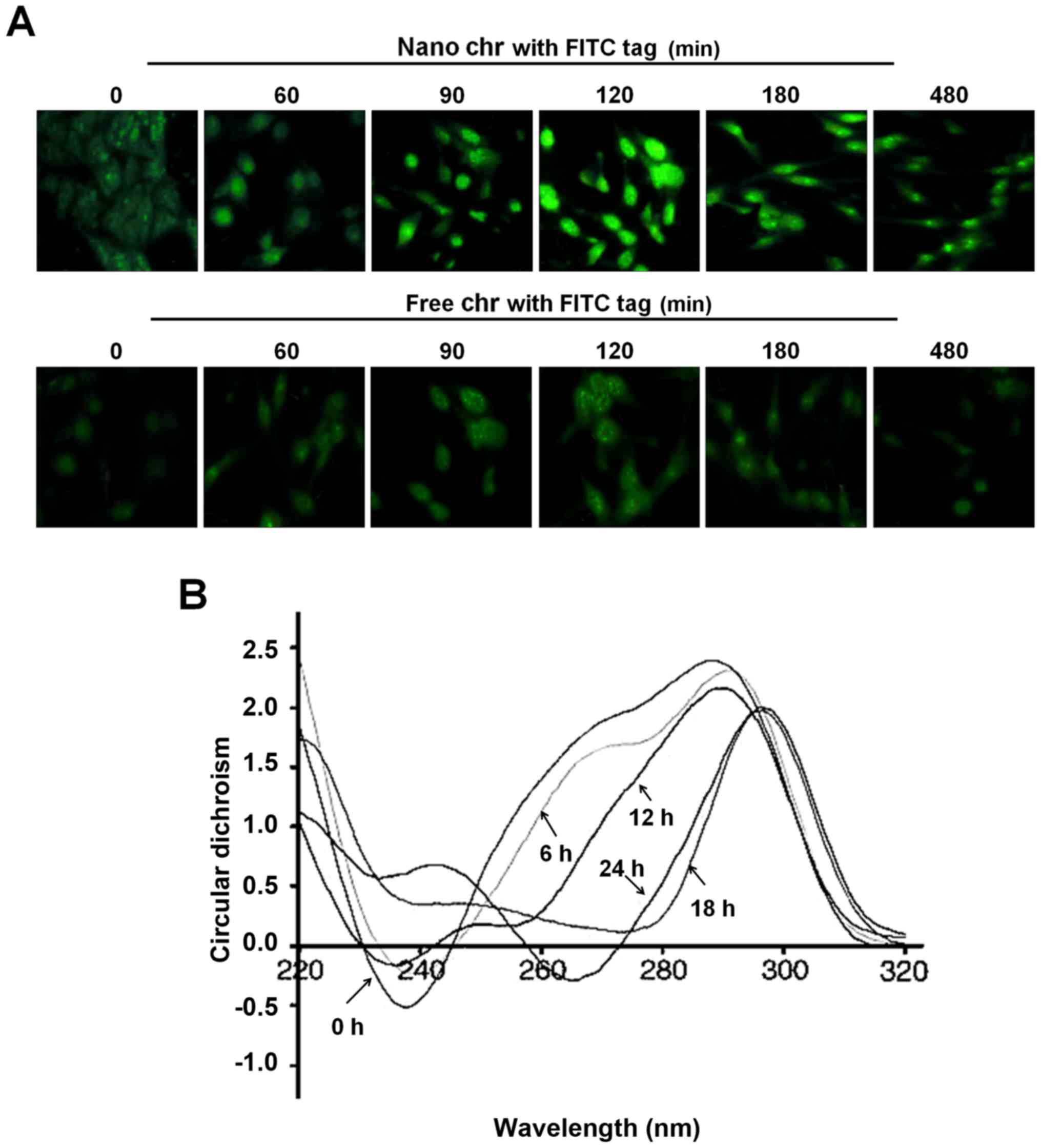
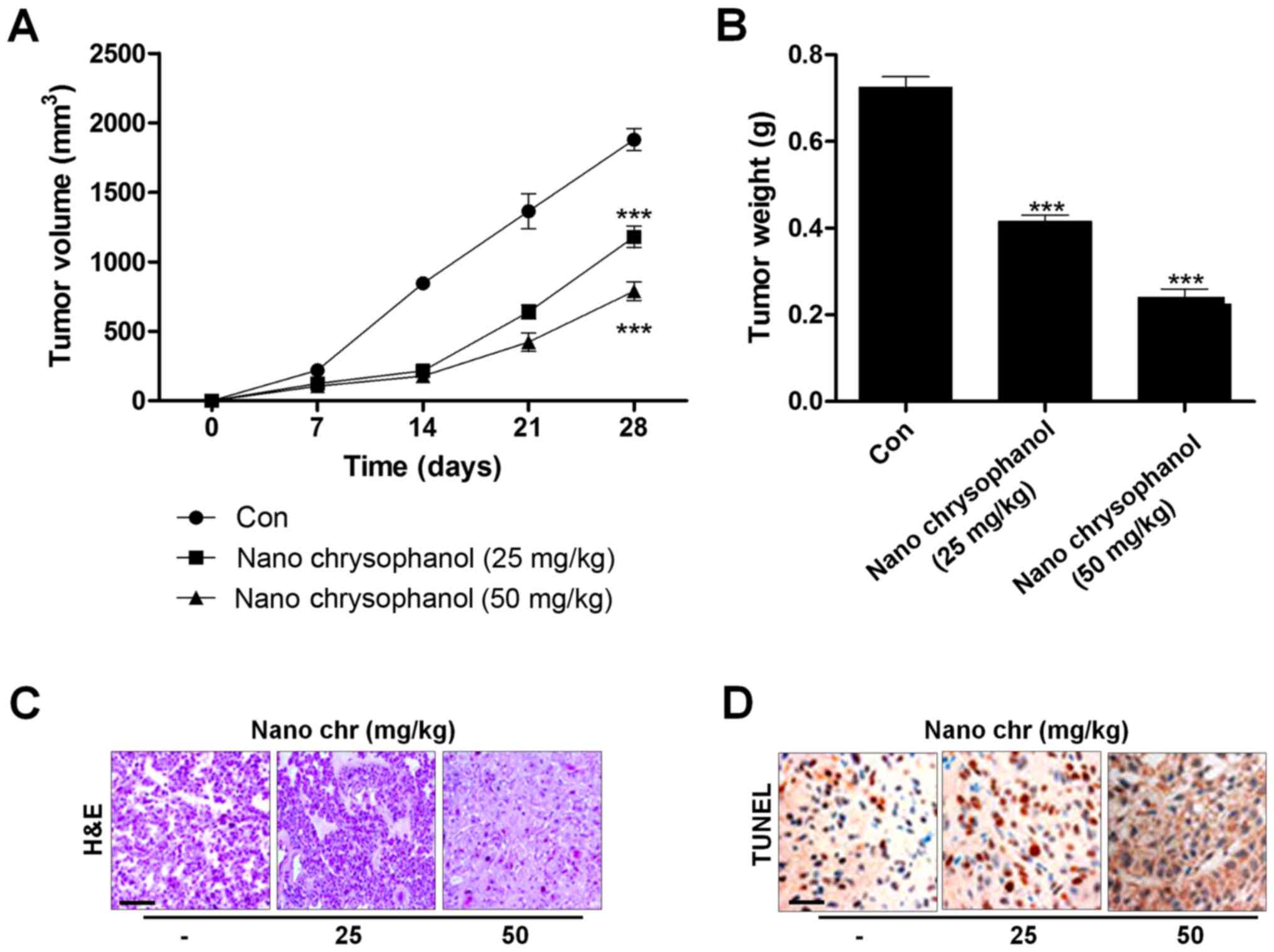
|
1
|
Øverbye A, Skotland T, Koehler CJ, Thiede
B, Seierstad T, Berge V, Sandvig K and Llorente A: Identification
of prostate cancer biomarkers in urinary exosomes. Oncotarget.
6:30357–30376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tanno T, Rabel A, Alleyne M, Lee YT, Dahut
WL, Gulley JL and Miller JL: Hepcidin, anaemia, and prostate
cancer. BJU Int. 107:678–679. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu T, Wu LY, Kazak M and Berkman CE:
Cell-Surface labeling and internalization by a fluorescent
inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Prostate.
68:955–964. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tagawa ST, Beltran H, Vallabhajosula S,
Goldsmith SJ, Osborne J, Matulich D, Petrillo K, Parmar S, Nanus DM
and Bander NH: Anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen-based
radioimmunotherapy for prostate cancer. Cancer. 116(Suppl):
1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho SY, Gage KL, Mease RC,
Senthamizhchelvan S, Holt DP, Jeffrey-Kwanisai A, Endres CJ,
Dannals RF, Sgouros G, Lodge M, et al: Biodistribution, tumor
detection, and radiation dosimetry of 18F-DCFBC, a
low-molecular-weight inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane
antigen, in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. J Nucl Med.
53:1883–1891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
López-Lázaro M: Distribution and
biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:31–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Webb KM and DiRuggiero J: Role of
Mn2+ and compatible solutes in the radiation resistance
of thermophilic bacteria and archaea. Archaea. 2012:8457562012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Huang AC, Hsia TC, Chou
ST, Kuo CL, Lu HF, Lee TH, Wood WG and Chung JG: Chrysophanol
induces necrosis through the production of ROS and alteration of
ATP levels in J5 human liver cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
54:967–976. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Darzynkiewicz Z, Carter SP, Kapuscinski J
and Watanabe KA: Effect of derivatives of chrysophanol, a new type
of potential antitumor agents of anthraquinone family, on growth
and cell cycle of L1210 leukemic cells. Cancer Lett. 46:181–187.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeng X, Tao W, Mei L, Huang L, Tan C and
Feng SS: Cholic acid-functionalized nanoparticles of star-shaped
PLGA-vitamin E TPGS copolymer for docetaxel delivery to cervical
cancer. Biomaterials. 34:6058–6067. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thamake SI, Raut SL, Gryczynski Z, Ranjan
AP and Vishwanatha JK: Alendronate coated poly-lactic-co-glycolic
acid (PLGA) nanoparticles for active targeting of metastatic breast
cancer. Biomaterials. 33:7164–7173. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hrkach J, Von Hoff D, Mukkaram Ali M,
Andrianova E, Auer J, Campbell T, De Witt D, Figa M, Figueiredo M,
Horhota A, et al: Preclinical development and clinical translation
of a PSMA-targeted docetaxel nanoparticle with a differentiated
pharmacological profile. Sci Transl Med. 4:128ra392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ganju A, Yallapu MM, Khan S, Behrman SW,
Chauhan SC and Jaggi M: Nanoways to overcome docetaxel resistance
in prostate cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 17:13–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X: Gold nanoparticles: Recent
advances in the biomedical applications. Cell Biochem Biophys.
72:771–775. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang CC, Wu SM, Li HW and Chang HT:
Biomedical applications of DNA-conjugated gold nanoparticles.
ChemBioChem. 17:1052–1062. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Simon LC, Stout RW and Sabliov C:
Bioavailability of orally delivered alpha-tocopherol by poly
(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) nanoparticles and chitosan covered
PLGA nanoparticles in F344 rats. Nanobiomedicine. 3:82016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lin TsT, Gao DY, Liu YC, Sung YC, Wan D,
Liu JY, Chiang T, Wang L and Chen Y: Development and
characterization of sorafenib-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for the
systemic treatment of liver fibrosis. J Control Release. 221:62–70.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gu W and Roeder RG: Activation of p53
sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal
domain. Cell. 90:595–606. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Horikoshi M: Histone acetylation: From
code to web and router via intrinsically disordered regions. Curr
Pharm Des. 19:5019–5042. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sachweh MC, Drummond CJ, Higgins M,
Campbell J and Laín S: Incompatible effects of p53 and HDAC
inhibition on p21 expression and cell cycle progression. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e5332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu T, Kuljaca S, Tee A and Marshall GM:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Multifunctional anticancer agents.
Cancer Treat Rev. 32:157–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang XJ and Seto E: The Rpd3/Hda1 family
of lysine deacetylases: From bacteria and yeast to mice and men.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:206–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weichert W, Röske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T,
Ebert MP, Pross M, Dietel M, Denkert C and Röcken C: Association of
patterns of class I histone deacetylase expression with patient
prognosis in gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 9:139–148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
West AC and Johnstone RW: New and emerging
HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J Clin Invest. 124:30–39.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi
Y, Ito A, Nixon A, Yoshida M, Wang XF and Yao TP: HDAC6 is a
microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature. 417:455–458. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zuo Q, Wu W, Li X, Zhao L and Chen W:
HDAC6 and SIRT2 promote bladder cancer cell migration and invasion
by targeting cortactin. Oncol Rep. 27:819–824. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Park SY, Jun JA, Jeong KJ, Heo HJ, Sohn
JS, Lee HY, Park CG and Kang J: Histone deacetylases 1, 6 and 8 are
critical for invasion in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 25:1677–1681.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aldana-Masangkay GI and Sakamoto KM: The
role of HDAC6 in cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:8758242011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Haggarty SJ, Koeller KM, Wong JC,
Grozinger CM and Schreiber SL: Domain-selective small-molecule
inhibitor of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6)-mediated tubulin
deacetylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4389–4394. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Henderson C, Mizzau M, Paroni G, Maestro
R, Schneider C and Brancolini C: Role of caspases, Bid, and p53 in
the apoptotic response triggered by histone deacetylase inhibitors
trichostatin-A (TSA) and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). J
Biol Chem. 278:12579–12589. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML,
Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV and Mann M: Lysine acetylation
targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular
functions. Science. 325:834–840. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kloster MM, Naderi EH, Haaland I, Gjertsen
BT, Blomhoff HK and Naderi S: cAMP signalling inhibits p53
acetylation and apoptosis via HDAC and SIRT deacetylases. Int J
Oncol. 42:1815–1821. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang X and Wang X: Cytochrome c-mediated
apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:87–106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE,
Didelot C and Kroemer G: Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from
mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 13:1423–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Prensner JR, Zhao S, Erho N, Schipper M,
Iyer MK, Dhanasekaran SM, Magi-Galluzzi C, Mehra R, Sahu A,
Siddiqui J, et al: RNA biomarkers associated with metastatic
progression in prostate cancer: A multi-institutional
high-throughput analysis of SChLAP1. Lancet Oncol. 15:1469–1480.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Severi G, Morris HA, MacInnis RJ, English
DR, Tilley W, Hopper JL, Boyle P and Giles GG: Circulating steroid
hormones and the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 15:86–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ni CH, Yu CS, Lu HF, Yang JS, Huang HY,
Chen PY, Wu SH, Ip SW, Chiang SY, Lin JG, et al:
Chrysophanol-induced cell death (necrosis) in human lung cancer
A549 cells is mediated through increasing reactive oxygen species
and decreasing the level of mitochondrial membrane potential.
Environ Toxicol. 29:740–749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hong JY, Chung HJ, Bae SY, Trung TN, Bae K
and Lee SK: Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by
physcion, an anthraquinone isolated from rhubarb (rhizomes of Rheum
tanguticum), in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. J Cancer
Prev. 19:273–278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ozenver N, Saeed M, Guvenalp Z, et al:
Chrysophanol-and nepodin-8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from Rumex
acetosella, the cytotoxicity towards drug sensitive and multi-drug
resistant T leukaemia cancer cells. Planta Med. 81:3882016.
|
|
40
|
Gradishar WJ, Tjulandin S, Davidson N,
Shaw H, Desai N, Bhar P, Hawkins M and O'Shaughnessy J: Phase III
trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with
polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:7794–7803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Y, Tan B and Wu Y: Mesoporous
Co3O4 nanowire arrays for lithium ion
batteries with high capacity and rate capability. Nano Lett.
8:265–270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Park SY, Chae SY, Park JO, Lee KJ and Park
G: Gold-conjugated resveratrol nanoparticles attenuate the invasion
and MMP-9 and COX-2 expression in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
35:3248–3256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X and Rotello
VM: Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem
Rev. 112:2739–2779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi J, Chan C, Pang Y, Ye W, Tian F, Lyu
J, Zhang Y and Yang M: A fluorescence resonance energy transfer
(FRET) biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and gold
nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of mecA gene sequence of
Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron. 67:595–600. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zeng L, Wu GZ, Goh KJ, Lee YM, Ng CC, You
AB, Wang J, Jia D, Hao A, Yu Q, et al: Saturated fatty acids
modulate cell response to DNA damage: Implication for their role in
tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 3:e23292008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fahrer J and Kaina B: O6-methylguanine-DNA
methyltransferase in the defense against N-nitroso compounds and
colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:2435–2442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Casagrande F and Darbon JM: Effects of
structurally related flavonoids on cell cycle progression of human
melanoma cells: Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases CDK2 and
CDK1. Biochem Pharmacol. 61:1205–1215. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hansel DE, Dhara S, Huang RC, Ashfaq R,
Deasel M, Shimada Y, Bernstein HS, Harmon J, Brock M, Forastiere A,
et al: CDC2/CDK1 expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma and
precursor lesions serves as a diagnostic and cancer progression
marker and potential novel drug target. Am J Surg Pathol.
29:390–399. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu Z and Hunter T: Ubiquitylation and
proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2)
CDK inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 9:2342–2352. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pandey M, Kaur P, Shukla S, Abbas A, Fu P
and Gupta S: Plant flavone apigenin inhibits HDAC and remodels
chromatin to induce growth arrest and apoptosis in human prostate
cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo study. Mol Carcinog. 51:952–962.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Schäfer C, Göder A, Beyer M, Kiweler N,
Mahendrarajah N, Rauch A, Nikolova T, Stojanovic N, Wieczorek M,
Reich TR, et al: Class I histone deacetylases regulate p53/NF-κB
crosstalk in cancer cells. Cell Signal. 29:218–225. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ververis K, Hiong A, Karagiannis TC and
Licciardi PV: Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs):
Multitargeted anticancer agents. Biologics. 7:47–60.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Varricchio L, Dell'Aversana C, Nebbioso A,
Migliaccio G, Altucci L, Mai A, Grazzini G, Bieker JJ and
Migliaccio AR: Identification of NuRSERY, a new functional HDAC
complex composed by HDAC5, GATA1, EKLF and pERK present in human
erythroid cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 50:112–122. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yuan H, Li AJ, Ma SL, Cui LJ, Wu B, Yin L
and Wu MC: Inhibition of autophagy significantly enhances
combination therapy with sorafenib and HDAC inhibitors for human
hepatoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:4953–4962. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao Y, Chaiswing L, Velez JM,
Batinic-Haberle I, Colburn NH, Oberley TD and St Clair DK : p53
translocation to mitochondria precedes its nuclear translocation
and targets mitochondrial oxidative defense protein-manganese
superoxide dismutase. Cancer Res. 65:3745–3750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Erster S, Mihara M, Kim RH, Petrenko O and
Moll UM: In vivo mitochondrial p53 translocation triggers a rapid
first wave of cell death in response to DNA damage that can precede
p53 target gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 24:6728–6741. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Proietti S, Cucina A, Dobrowolny G,
D'Anselmi F, Dinicola S, Masiello MG, Pasqualato A, Palombo A,
Morini V, Reiter RJ, et al: Melatonin down-regulates MDM2 gene
expression and enhances p53 acetylation in MCF-7 cells. J Pineal
Res. 57:120–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ono W, Hayashi Y, Yokoyama W, Kuroda T,
Kishimoto H, Ito I, Kimura K, Akaogi K, Waku T and Yanagisawa J:
The nucleolar protein Myb-binding protein 1A (MYBBP1A) enhances p53
tetramerization and acetylation in response to nucleolar
disruption. J Biol Chem. 289:4928–4940. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL and
Mignotte B: The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 942:157–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pradelli LA, Bénéteau M and Ricci JE:
Mitochondrial control of caspase-dependent and -independent cell
death. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1589–1597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shi Y: caspase activation: Revisiting the
induced proximity model. Cell. 117:855–858. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Isabelle M, Moreel X, Gagné JP, Rouleau M,
Ethier C, Gagné P, Hendzel MJ and Poirier GG: Investigation of
PARP-1, PARP-2, and PARG interactomes by affinity-purification mass
spectrometry. Proteome Sci. 8:222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li W, Saud SM, Young MR, Chen G and Hua B:
Targeting AMPK for cancer prevention and treatment. Oncotarget.
6:7365–7378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Oakhill JS, Scott JW and Kemp BE: AMPK
functions as an adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 23:125–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Benbrook DM and Masamha CP: The
pro-survival function of Akt kinase can be overridden or altered to
contribute to induction of apoptosis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
11:586–599. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Unger C, Popescu R, Giessrigl B, Rarova L,
Herbacek I, Seelinger M, Diaz R, Wallnöfer B, Fritzer-Szekeres M,
Szekeres T, et al: An apolar extract of Critonia morifolia inhibits
c-Myc, cyclin D1, Cdc25A, Cdc25B, Cdc25C and Akt and induces
apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 40:2131–2139. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Polivka J Jr and Janku F: Molecular
targets for cancer therapy in the I3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|