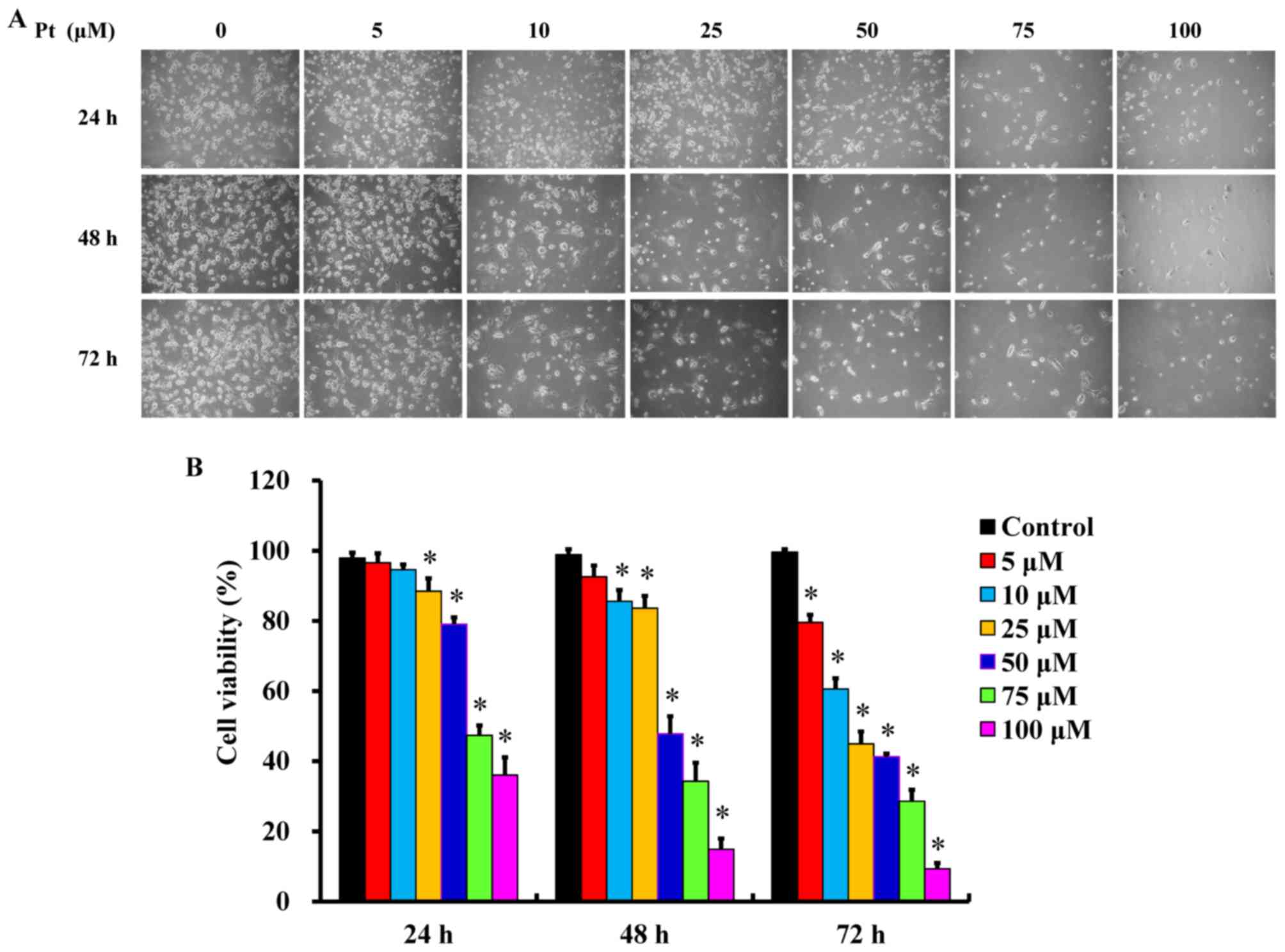
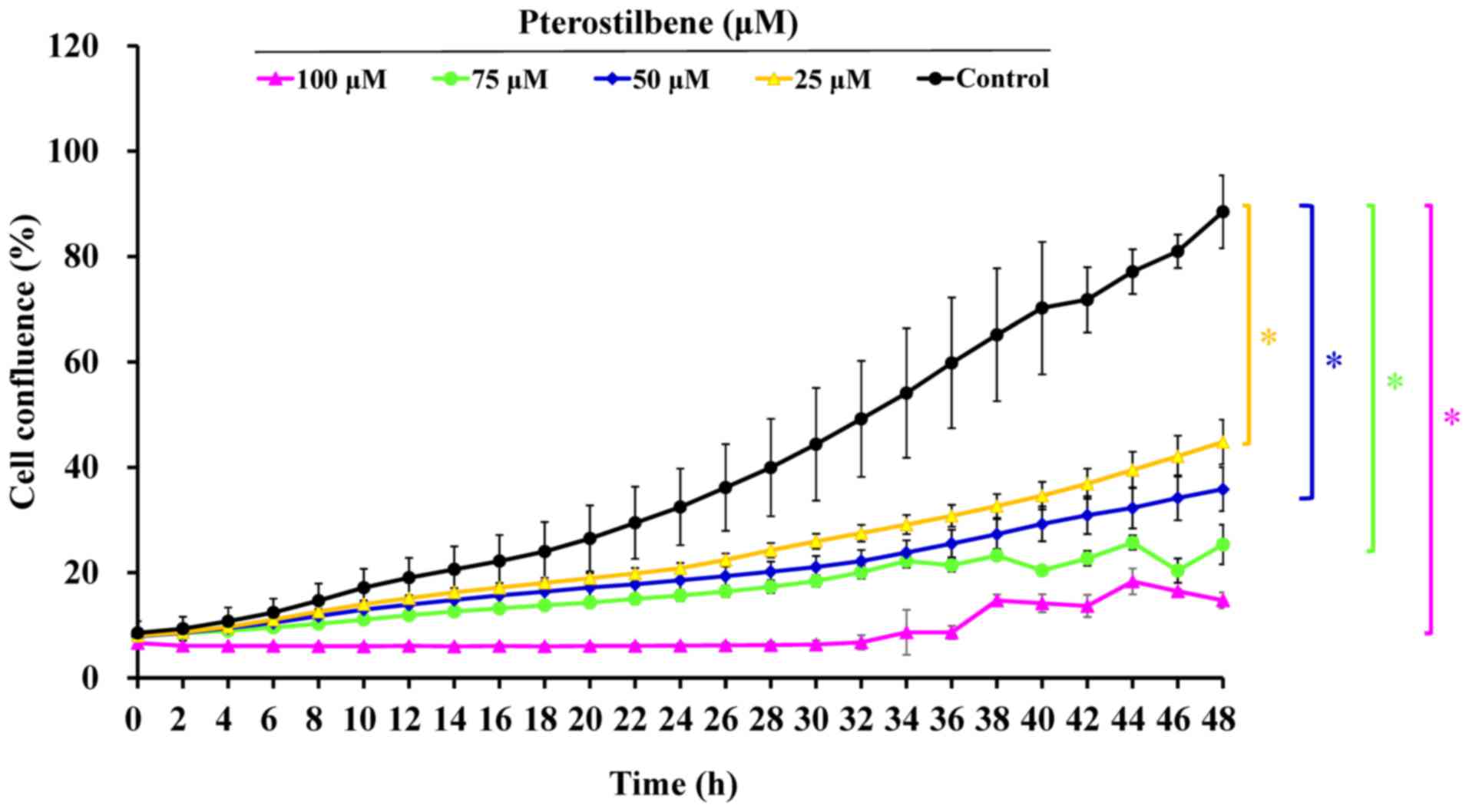
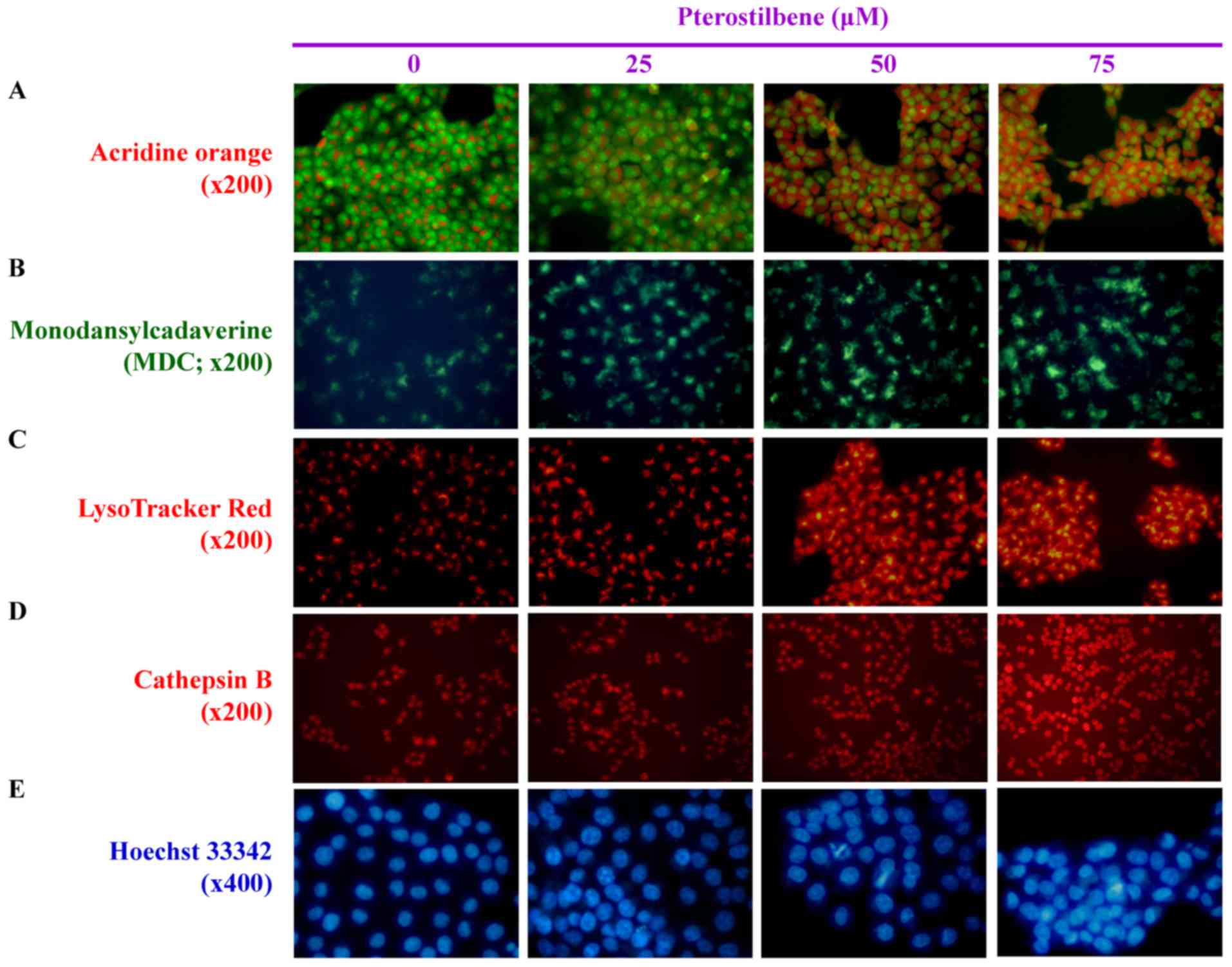
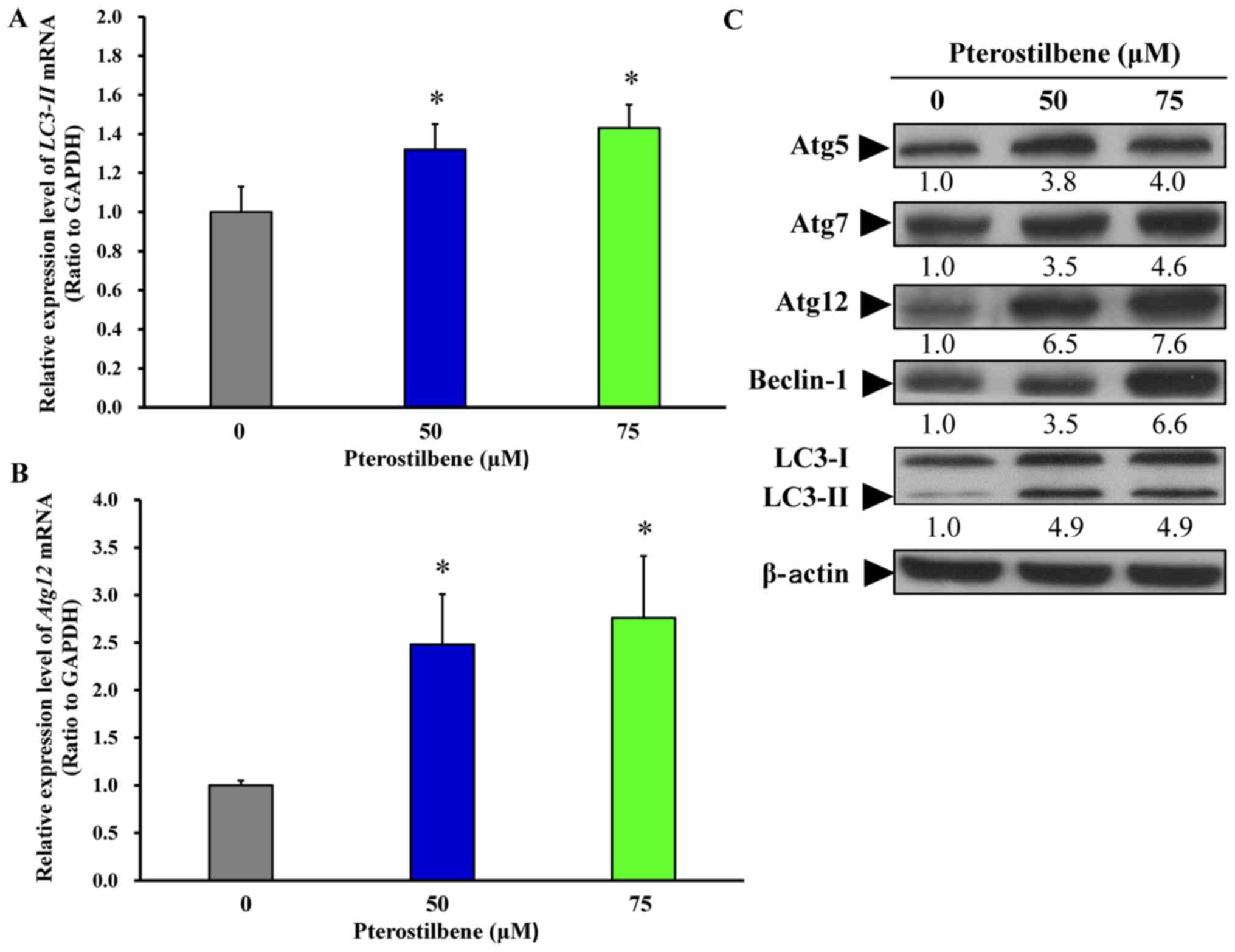
|
1
|
Tsai SC, Huang SF, Chiang JH, Chen YF,
Huang CC, Tsai MH, Tsai FJ, Kao MC and Yang JS: The differential
regulation of microRNAs is associated with oral cancer. Oncol Rep.
38:1613–1620. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kawakita D, Lee YA, Li Q, Chen Y, Chen CJ,
Hsu WL, Lou PJ, Zhu C, Pan J, Shen H, et al: Impact of oral hygiene
on head and neck cancer risk in a Chinese population. Head Neck.
39:2549–2557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ministry of Health and Welfare: Republic
of China (Taiwan). https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-3425-33347-2.html.
2017
|
|
4
|
Chiang SL, Velmurugan BK, Chung CM, Lin
SH, Wang ZH, Hua CH, Tsai MH, Kuo TM, Yeh KT, Chang PY, et al:
Preventive effect of celecoxib use against cancer progression and
occurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:62352017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Macha MA, Rachagani S, Qazi AK, Jahan R,
Gupta S, Patel A, Seshacharyulu P, Lin C, Li S, Wang S, et al:
Afatinib radiosensitizes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
cells by targeting cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 8:20961–20973.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rapidis A, Sarlis N, Lefebvre JL and Kies
M: Docetaxel in the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the
head and neck. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 4:865–886. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bauman J, Langer C, Quon H, Algazy K, Lin
A, Desai A, Mutale F and Weiss J: Induction chemotherapy with
cetuximab, carboplatin and paclitaxel for the treatment of locally
advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Exp Ther
Med. 5:1247–1253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Torres-Bugarín O, Ventura-Aguilar A,
Zamora-Perez A, Gómez-Meda BC, Ramos-Ibarra ML, Morgan-Villela G,
Gutiérrez-Franco A and Zúñiga-González G: Evaluation of cisplatin +
5-FU, carboplatin + 5-FU, and ifosfamide + epirubicine regimens
using the micronuclei test and nuclear abnormalities in the buccal
mucosa. Mutat Res. 539:177–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Passiglia F, Listì A, Castiglia M, Perez
A, Rizzo S, Bazan V and Russo A: EGFR inhibition in NSCLC: New
findings…. and opened questions? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
112:126–135. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska
K, Longacre M, Snyder N and Sarkar S: Drug resistance in cancer: An
overview. Cancers (Basel). 6:1769–1792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zahreddine H and Borden KL: Mechanisms and
insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front Pharmacol. 4:282013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang YY, Chen YK, Hsu YL, Chiu WC, Tsai
CH, Hu SC, Hsieh PW and Yuan SF: Synthetic β-nitrostyrene
derivative CYT-Rx20 as inhibitor of oral cancer cell proliferation
and tumor growth through glutathione suppression and reactive
oxygen species induction. Head Neck. 39:1055–1064. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McCormack D and McFadden D: A review of
pterostilbene antioxidant activity and disease modification. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2013:5754822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dvorakova M and Landa P: Anti-inflammatory
activity of natural stilbenoids: A review. Pharmacol Res.
124:126–145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McCormack D and McFadden D: Pterostilbene
and cancer: Current review. J Surg Res. 173:e53–e61. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xue EX, Lin JP, Zhang Y, Sheng SR, Liu HX,
Zhou YL and Xu H: Pterostilbene inhibits inflammation and ROS
production in chondrocytes by activating Nrf2 pathway. Oncotarget.
8:41988–42000. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhakkiyalakshmi E, Sireesh D,
Sakthivadivel M, Sivasubramanian S, Gunasekaran P and Ramkumar KM:
Antihyperlipidemic and anti-peroxidative role of pterostilbene via
Nrf2 signaling in experimental diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol. 777:9–16.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wakimoto R, Ono M, Takeshima M, Higuchi T
and Nakano S: Differential anticancer activity of pterostilbene
against three subtypes of human breast cancer cells. Anticancer
Res. 37:6153–6159. 2017.
|
|
19
|
Nikhil K, Sharan S, Chakraborty A,
Bodipati N, Krishna Peddinti R and Roy P: Role of isothiocyanate
conjugate of pterostilbene on the inhibition of MCF-7 cell
proliferation and tumor growth in Ehrlich ascitic cell induced
tumor bearing mice. Exp Cell Res. 320:311–328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kostin SF, McDonald DE and McFadden DW:
Inhibitory effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
pterostilbene on pancreatic cancer growth in vitro. J Surg Res.
177:255–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mannal PW, Alosi JA, Schneider JG,
McDonald DE and McFadden DW: Pterostilbene inhibits pancreatic
cancer in vitro. J Gastrointest Surg. 14:873–879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma Z, Yang Y, Di S, Feng X, Liu D, Jiang
S, Hu W, Qin Z, Li Y, Lv J, et al: Pterostilbene exerts anticancer
activity on non-small-cell lung cancer via activating endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Sci Rep. 7:80912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang YJ, Lin JF, Cheng LH, Chang WT, Kao
YH, Chang MM, Wang BJ and Cheng HC: Pterostilbene prevents AKT-ERK
axis-mediated polymerization of surface fibronectin on suspended
lung cancer cells independently of apoptosis and suppresses
metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 10:722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schneider JG, Alosi JA, McDonald DE and
McFadden DW: Pterostilbene inhibits lung cancer through induction
of apoptosis. J Surg Res. 161:18–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nikhil K, Sharan S, Chakraborty A and Roy
P: Pterostilbene-isothiocyanate conjugate suppresses growth of
prostate cancer cells irrespective of androgen receptor status.
PLoS One. 9:e933352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin VC, Tsai YC, Lin JN, Fan LL, Pan MH,
Ho CT, Wu JY and Way TD: Activation of AMPK by pterostilbene
suppresses lipogenesis and cell-cycle progression in p53 positive
and negative human prostate cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
60:6399–6407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun Y, Wu X, Cai X, Song M, Zheng J, Pan
C, Qiu P, Zhang L, Zhou S, Tang Z, et al: Identification of
pinostilbene as a major colonic metabolite of pterostilbene and its
inhibitory effects on colon cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
60:1924–1932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tolba MF and Abdel-Rahman SZ:
Pterostilbine, an active component of blueberries, sensitizes colon
cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil cytotoxicity. Sci Rep. 5:152392015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mena S, Rodríguez ML, Ponsoda X, Estrela
JM, Jäättela M and Ortega AL: Pterostilbene-induced tumor
cytotoxicity: A lysosomal membrane permeabilization-dependent
mechanism. PLoS One. 7:e445242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen RJ, Ho CT and Wang YJ: Pterostilbene
induces autophagy and apoptosis in sensitive and chemoresistant
human bladder cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1819–1832. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pan MH, Chang YH, Badmaev V, Nagabhushanam
K and Ho CT: Pterostilbene induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest
in human gastric carcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem. 55:7777–7785.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ko CP, Lin CW, Chen MK, Yang SF, Chiou HL
and Hsieh MJ: Pterostilbene induce autophagy on human oral cancer
cells through modulation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway. Oral Oncol. 51:593–601. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bundela S, Sharma A and Bisen PS:
Potential compounds for oral cancer treatment: Resveratrol,
nimbolide, lovastatin, bortezomib, vorinostat, berberine,
pterostilbene, deguelin, andrographolide, and colchicine. PLoS One.
10:e01417192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin CW, Chou YE, Chiou HL, Chen MK, Yang
WE, Hsieh MJ and Yang SF: Pterostilbene suppresses oral cancer cell
invasion by inhibiting MMP-2 expression. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
18:1109–1120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo L, Tan K, Wang H and Zhang X:
Pterostilbene inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma through
p53/SOD2/ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Oncol Rep.
36:3233–3240. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lombardi G, Vannini S, Blasi F,
Marcotullio MC, Dominici L, Villarini M, Cossignani L and Moretti
M: In vitro safety/protection assessment of resveratrol and
pterostilbene in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). Nat Prod
Commun. 10:1403–1408. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang G, Xiao W, Xu Z, Yu D, Li B, Zhang
Y, Sun X, Xie Y, Chang S, Gao L, et al: Pterostilbene induces cell
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in T-cell leukemia/lymphoma by
suppressing the ERK1/2 pathway. BioMed Res Int. 2017:98720732017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Siedlecka-Kroplewska K, Jozwik A,
Boguslawski W, Wozniak M, Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak A, Spodnik JH,
Rychlowski M and Kmiec Z: Pterostilbene induces accumulation of
autophagic vacuoles followed by cell death in HL60 human leukemia
cells. J Physiol Pharmacol. 64:545–556. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Siedlecka-Kroplewska K, Jozwik A,
Kaszubowska L, Kowalczyk A and Boguslawski W: Pterostilbene induces
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MOLT4 human leukemia cells.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:574–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roslie H, Chan KM, Rajab NF, Velu SS,
Kadir SA, Bunyamin I, Weber JF, Thomas NF, Majeed AB, Myatt G, et
al: 3,5-Dibenzyloxy-4′-hydroxystilbene induces early caspase-9
activation during apoptosis in human K562 chronic myelogenous
leukemia cells. J Toxicol Sci. 37:13–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Y, Ding L, Wang X, Zhang J, Han W,
Feng L, Sun J, Jin H and Wang XJ: Pterostilbene simultaneously
induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and cyto-protective autophagy
in breast cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 4:44–51. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chakraborty A, Bodipati N, Demonacos MK,
Peddinti R, Ghosh K and Roy P: Long term induction by pterostilbene
results in autophagy and cellular differentiation in MCF-7 cells
via ROS dependent pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 355:25–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gosepath EM, Eckstein N, Hamacher A,
Servan K, von Jonquieres G, Lage H, Györffy B, Royer HD and Kassack
MU: Acquired cisplatin resistance in the head-neck cancer cell line
Cal27 is associated with decreased DKK1 expression and can
partially be reversed by overexpression of DKK1. Int J Cancer.
123:2013–2019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chang PY, Peng SF, Lee CY, Lu CC, Tsai SC,
Shieh TM, Wu TS, Tu MG, Chen MY and Yang JS: Curcumin-loaded
nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through regulation of the
function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in cisplatin-resistant
CAR human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:1141–1150. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu CC, Huang BR, Liao PJ and Yen GC:
Ursolic acid triggers nonprogrammed death (necrosis) in human
glioblastoma multiforme DBTRG-05MG cells through MPT pore opening
and ATP decline. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:2146–2156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, Lu HF, Yeh HF,
Li KH, Chen PY, Chung JG and Yang JS: Kaempferol induced apoptosis
via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathway
in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun JM, Yang LN, Xu H, Chang B, Wang HY
and Yang G: Inhibition of Aurora A promotes chemosensitivity via
inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cervical cancer cells.
Am J Cancer Res. 5:1133–1145. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gelles JD and Chipuk JE: Robust
high-throughput kinetic analysis of apoptosis with real-time
high-content live-cell imaging. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24932016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee MR, Lin C, Lu CC, Kuo SC, Tsao JW,
Juan YN, Chiu HY, Lee FY, Yang JS and Tsai FJ: YC-1 induces
G0/G1phase arrest and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in
cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer CAR cells. Biomedicine
(Taipei). 7:122017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hsieh MT, Chen HP, Lu CC, Chiang JH, Wu
TS, Kuo DH, Huang LJ, Kuo SC and Yang JS: The novel pterostilbene
derivative ANK-199 induces autophagic cell death through regulating
PI3 kinase class III/beclin 1/Atg related proteins in cisplatin
resistant CAR human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 45:782–794.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chang CH, Lee CY, Lu CC, Tsai FJ, Hsu YM,
Tsao JW, Juan YN, Chiu HY, Yang JS and Wang CC: Resveratrol-induced
autophagy and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer
CAR cells: A key role of AMPK and Akt/mTOR signaling. Int J Oncol.
50:873–882. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Lu CC, Hour MJ, Chang
SJ, Lee TH and Chung JG: Newly synthesized quinazolinone HMJ-38
suppresses angiogenetic responses and triggers human umbilical vein
endothelial cell apoptosis through p53-modulated Fas/death receptor
signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 269:150–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ma YS, Weng SW, Lin MW, Lu CC, Chiang JH,
Yang JS, Lai KC, Lin JP, Tang NY, Lin JG, et al: Antitumor effects
of emodin on LS1034 human colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo:
Roles of apoptotic cell death and LS1034 tumor xenografts model.
Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1271–1278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, Hour MJ, Lin
KL, Lee TH and Chung JG: Cell death caused by quinazolinone HMJ-38
challenge in oral carcinoma CAL 27 cells: Dissections of
endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and tumor
xenografts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1840.2310–2320. 2014.
|
|
56
|
Tsai HY, Ho CT and Chen YK: Biological
actions and molecular effects of resveratrol, pterostilbene, and
3′-hydroxypterostilbene. J Food Drug Anal. 25:134–147. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Traversi G, Fiore M, Leone S, Basso E, Di
Muzio E, Polticelli F, Degrassi F and Cozzi R: Resveratrol and its
methoxy-derivatives as modulators of DNA damage induced by ionising
radiation. Mutagenesis. 31:433–441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lin HS, Yue BD and Ho PC: Determination of
pterostilbene in rat plasma by a simple HPLC-UV method and its
application in pre-clinical pharmacokinetic study. Biomed
Chromatogr. 23:1308–1315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lin HS and Ho PC: Preclinical
pharmacokinetic evaluation of resveratrol trimethyl ether in
sprague-dawley rats: The impacts of aqueous solubility, dose
escalation, food and repeated dosing on oral bioavailability. J
Pharm Sci. 100:4491–4500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yeo SC, Ho PC and Lin HS: Pharmacokinetics
of pterostilbene in Sprague-Dawley rats: The impacts of aqueous
solubility, fasting, dose escalation, and dosing route on
bioavailability. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:1015–1025. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Asensi M, Medina I, Ortega A, Carretero J,
Baño MC, Obrador E and Estrela JM: Inhibition of cancer growth by
resveratrol is related to its low bioavailability. Free Radic Biol
Med. 33:387–398. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu Y, Wang L, Wu Y, Lv C, Li X, Cao X,
Yang M, Feng D and Luo Z: Pterostilbene exerts antitumor activity
against human osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Toxicology. 304:120–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yang JS, Lu CC, Kuo SC, Hsu YM, Tsai SC,
Chen SY, Chen YT, Lin YJ, Huang YC, Chen CJ, et al: Autophagy and
its link to type II diabetes mellitus. Biomedicine (Taipei).
7:82017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hsiao PC, Chou YE, Tan P, Lee WJ, Yang SF,
Chow JM, Chen HY, Lin CH, Lee LM and Chien MH: Pterostilbene
simultaneously induced G0/G1-phase arrest and MAPK-mediated
mitochondrial-derived apoptosis in human acute myeloid leukemia
cell lines. PLoS One. 9:e1053422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Davoudi Z, Akbarzadeh A, Rahmatiyamchi M,
Movassaghpour AA, Alipour M, Nejati-Koshki K, Sadeghi Z,
Dariushnejad H and Zarghami N: Molecular target therapy of AKT and
NF-kB signaling pathways and multidrug resistance by specific cell
penetrating inhibitor peptides in HL-60 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:4353–4358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yuan CH, Horng CT, Lee CF, Chiang NN, Tsai
FJ, Lu CC, Chiang JH, Hsu YM, Yang JS and Chen FA: Epigallocatechin
gallate sensitizes cisplatin-resistant oral cancer CAR cell
apoptosis and autophagy through stimulating AKT/STAT3 pathway and
suppressing multidrug resistance 1 signaling. Environ Toxicol.
32:845–855. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|