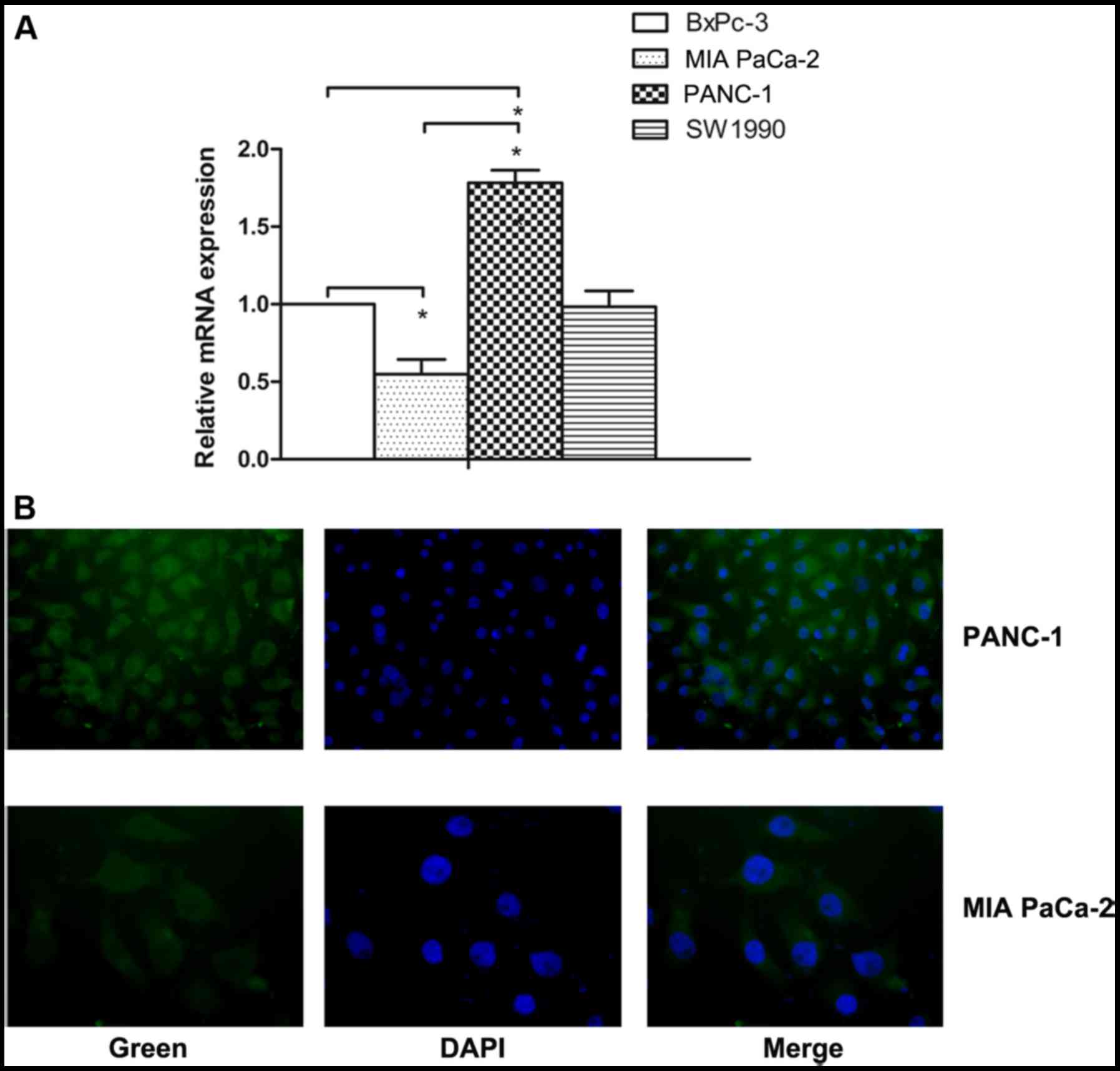
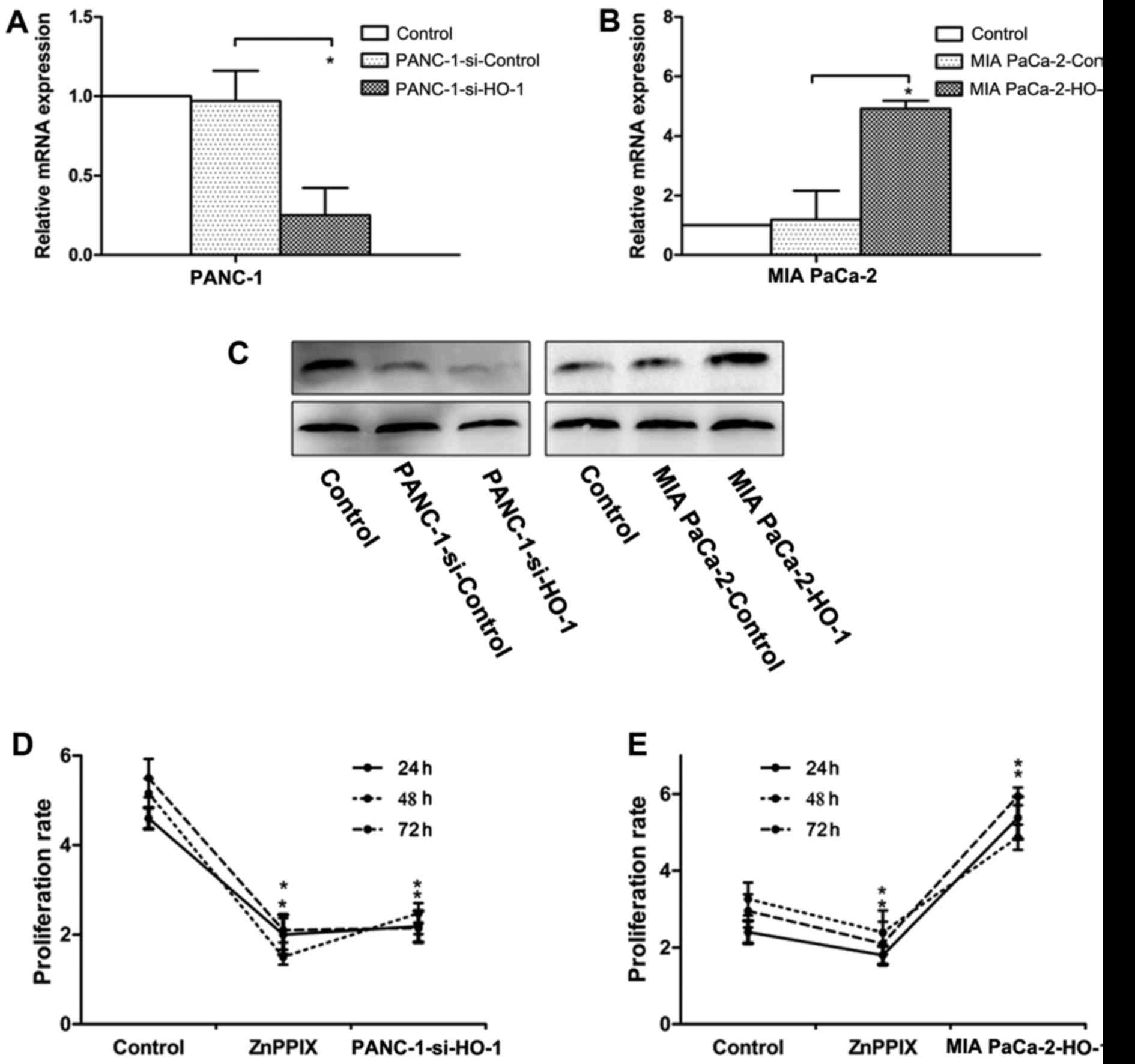
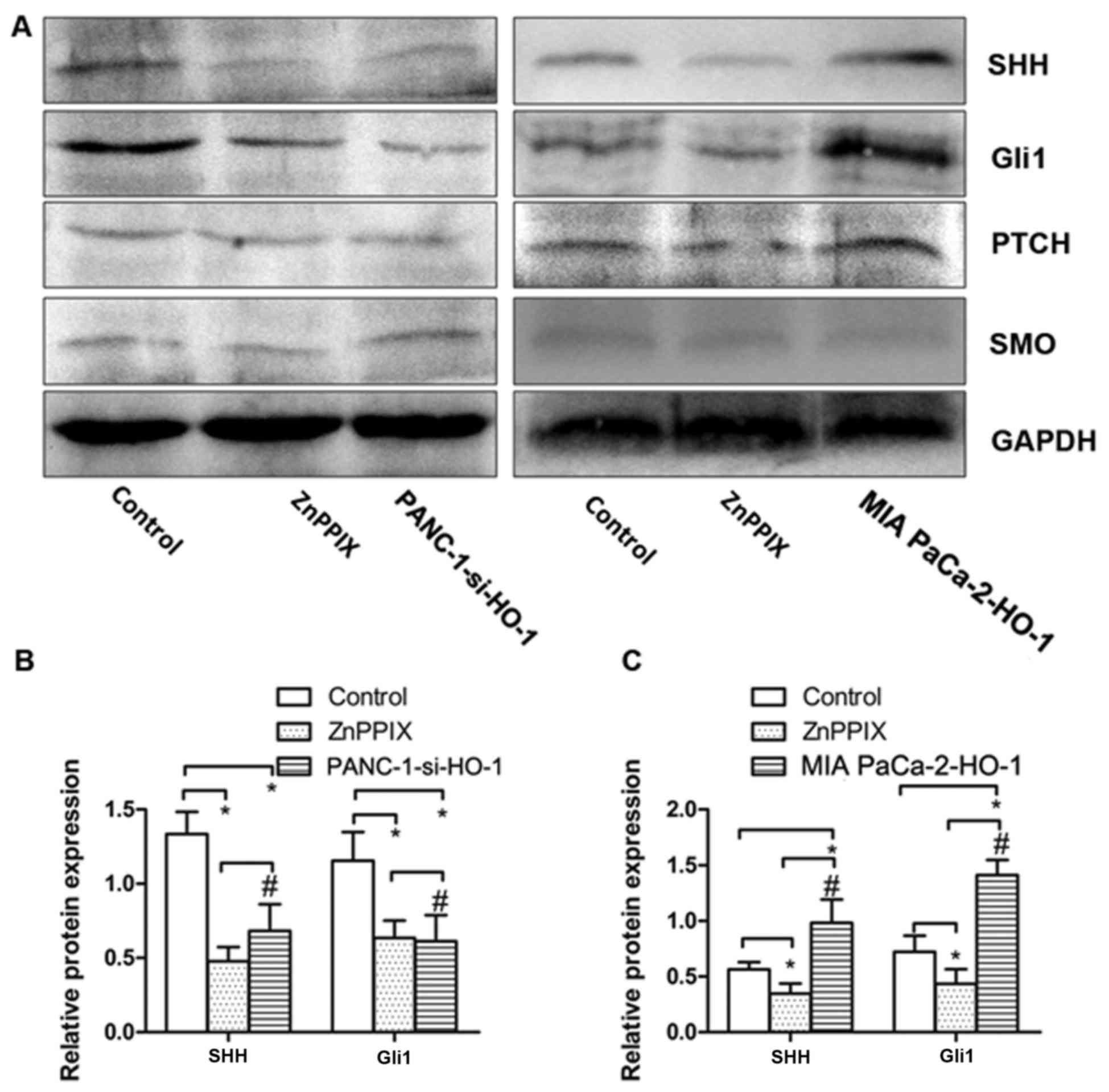
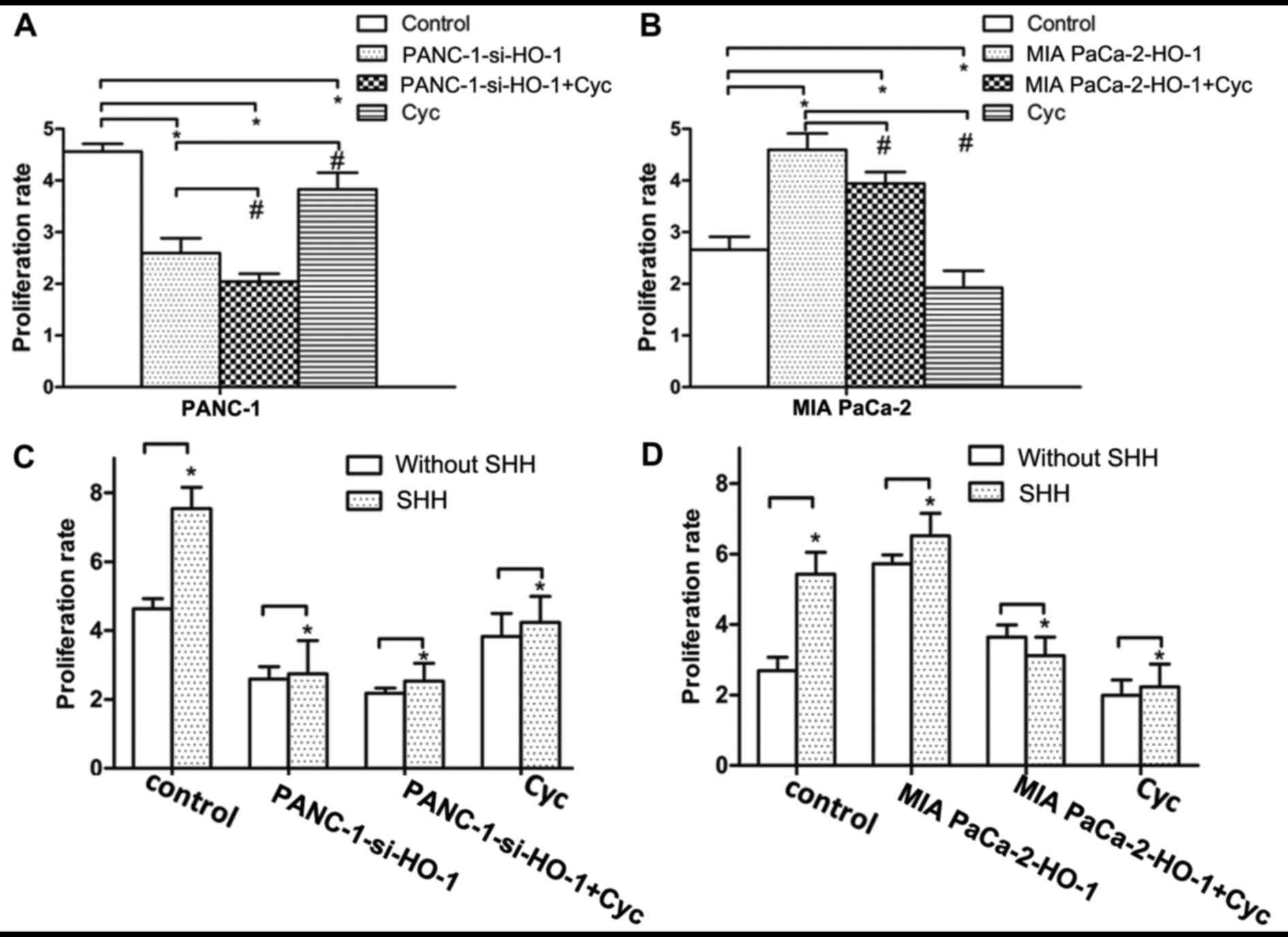
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu Q, Liao Q and Zhao Y: Chemotherapy and
tumor microenvi-ronment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int.
17:682017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Otterbein LE and Choi AM: Heme oxygenase:
Colors of defense against cellular stress. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 279:L1029–L1037. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nuhn P, Künzli BM, Hennig R, Mitkus T,
Ramanauskas T, Nobiling R, Meuer SC, Friess H and Berberat PO: Heme
oxygenase-1 and its metabolites affect pancreatic tumor growth in
vivo. Mol Cancer. 8:372009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Heeba GH, Hamza AA and Hassanin SO:
Induction of heme oxygenase-1 with hemin alleviates
cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity in male rats and enhances
its cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cell line. Toxicol Lett.
264:38–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jo EJ, Park SJ and Kim BC: Propyl gallate
sensitizes human lung cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis
by targeting heme oxygenase-1 for TRC8-mediated degradation. Eur J
Pharmacol. 788:321–327. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jang HJ, Hong EM, Kim M, Kim JH, Jang J,
Park SW, Byun HW, Koh DH, Choi MH, Kae SH, et al: Simvastatin
induces heme oxygenase-1 via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)
activation through ERK and PI3K/Akt pathway in colon cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:46219–46229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schwer CI, Guerrero AM, Humar M, Roesslein
M, Goebel U, Stoll P, Geiger KK, Pannen BH, Hoetzel A and Schmidt
R: Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits the proliferation of pancreatic
stellate cells by repression of the extracellular signal-regulated
kinase1/2 pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 327:863–871. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Berberat PO, Dambrauskas Z, Gulbinas A,
Giese T, Giese N, Künzli B, Autschbach F, Meuer S, Büchler MW and
Friess H: Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 increases responsiveness
of pancreatic cancer cells to anticancer treatment. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:3790–3798. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, Kim BH, Park JK,
Kim HK, Kim JS and Oh SC: Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes
metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and
MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Han L, Ma J, Duan W, Zhang L, Yu S, Xu Q,
Lei J, Li X, Wang Z, Wu Z, et al: Pancreatic stellate cells
contribute pancreatic cancer pain via activation of sHH signaling
pathway. Oncotarget. 7:18146–18158. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Jung IH, Jung DE, Park YN, Song SY and
Park SW: Aberrant Hedgehog ligands induce progressive pancreatic
fibrosis by paracrine activation of myofibroblasts and ductular
cells in transgenic zebrafish. PLoS One. 6:e279412011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shukla SK, Purohit V, Mehla K, Gunda V,
Chaika NV, Vernucci E, King RJ, Abrego J, Goode GD, Dasgupta A, et
al: MUC1 and HIF-1alpha signaling crosstalk induces anabolic
glucose metabolism to impart gemcitabine resistance to pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Cell. 32:3922017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jin X, Pan Y, Wang L, Ma T, Zhang L, Tang
AH, Billadeau DD, Wu H and Huang H: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
inhibits ERK activation and bypasses gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic cancer by blocking IQGAP1-MAPK interaction. Cancer Res.
77:4328–4341. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Ning Z, Li Y, Zhu X and Meng Z:
Bufalin suppresses cancer stem-like cells in gemcitabine-resistant
pancreatic cancer cells via Hedgehog signaling. Mol Med Rep.
14:1907–1914. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim EJ, Sahai V, Abel EV, Griffith KA,
Greenson JK, Takebe N, Khan GN, Blau JL, Craig R, Balis UG, et al:
Pilot clinical trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449
(vismodegib) in combination with gemcitabine in patients with
metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5937–5945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cao Z, Geng B, Xu S, Xuan W, Nie L, Shen
W, Liang Y and Guan R: BnHO1, a haem oxygenase-1 gene from Brassica
napus, is required for salinity and osmotic stress-induced lateral
root formation. J Exp Bot. 62:4675–4689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen R, Lai LA, Sullivan Y, Wong M, Wang
L, Riddell J, Jung L, Pillarisetty VG, Brentnall TA and Pan S:
Disrupting glutamine metabolic pathways to sensitize
gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 7:79502017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sunamura M, Duda DG, Ghattas MH, Lozonschi
L, Motoi F, Yamauchi J, Matsuno S, Shibahara S and Abraham NG: Heme
oxygenase-1 accelerates tumor angiogenesis of human pancreatic
cancer. Angiogenesis. 6:15–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jakstaite A, Maziukiene A, Silkuniene G,
Kmieliute K, Gulbinas A and Dambrauskas Z: HuR mediated
post-transcriptional regulation as a new potential adjuvant
therapeutic target in chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:13004–13019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bai Y, Bai Y, Dong J, Li Q, Jin Y, Chen B
and Zhou M: Hedgehog signaling in pancreatic fibrosis and cancer.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e29962016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee RT, Zhao Z and Ingham PW: Hedgehog
signalling. Development. 143:367–372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tadros S, Shukla SK, King RJ, Gunda V,
Vernucci E, Abrego J, Chaika NV, Yu F, Lazenby AJ, Berim L, et al:
De novo lipid synthesis facilitates gemcitabine resistance through
endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.
77:5503–5517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pishvaian MJ and Brody JR: Therapeutic
implications of molecular subtyping for pancreatic cancer. Oncology
(Williston Park). 31:159–166. 1682017.
|
|
26
|
Adamska A, Domenichini A and Falasca M:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Current and evolving therapies.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Borowa-Mazgaj B: Pancreatic
cancer-mechanisms of chemoresistance. Postepy Hig Med Dosw.
70:169–179. 2016.In Polish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Güngör C, Hofmann BT, Wolters-Eisfeld G
and Bockhorn M: Pancreatic cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 171:849–858.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Catenacci DV, Junttila MR, Karrison T,
Bahary N, Horiba MN, Nattam SR, Marsh R, Wallace J, Kozloff M,
Rajdev L, et al: Randomized phase Ib/II study of gemcitabine plus
placebo or vismodegib, a hedgehog pathway inhibitor, in patients
with metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 33:4284–4292.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cao J, Peterson SJ, Sodhi K, Vanella L,
Barbagallo I, Rodella LF, Schwartzman ML, Abraham NG and Kappas A:
Heme oxygenase gene targeting to adipocytes attenuates adiposity
and vascular dysfunction in mice fed a high-fat diet. Hypertension.
60:467–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Felley-Bosco E, Opitz I and Meerang M:
Hedgehog signaling in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Genes
(Basel). 6:500–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wendling-Keim DS, Wanie L, von Schweinitz
D, Grantzow R and Kappler R: Transcriptional activation of Hedgehog
pathway components in aggressive haemangioma. Exp Dermatol.
26:934–939. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang H, Cotton JL, Wang Y, Rajurkar M,
Zhu LJ, Lewis BC and Mao J: Specific requirement of Gli
transcription factors in Hedgehog-mediated intestinal development.
J Biol Chem. 288:17589–17596. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Frank J, Lornejad-Schäfer MR, Schöffl H,
Flaccus A, Lambert C and Biesalski HK: Inhibition of heme
oxygenase-1 increases responsiveness of melanoma cells to ALA-based
photodynamic therapy. Int J Oncol. 31:1539–1545. 2007.
|