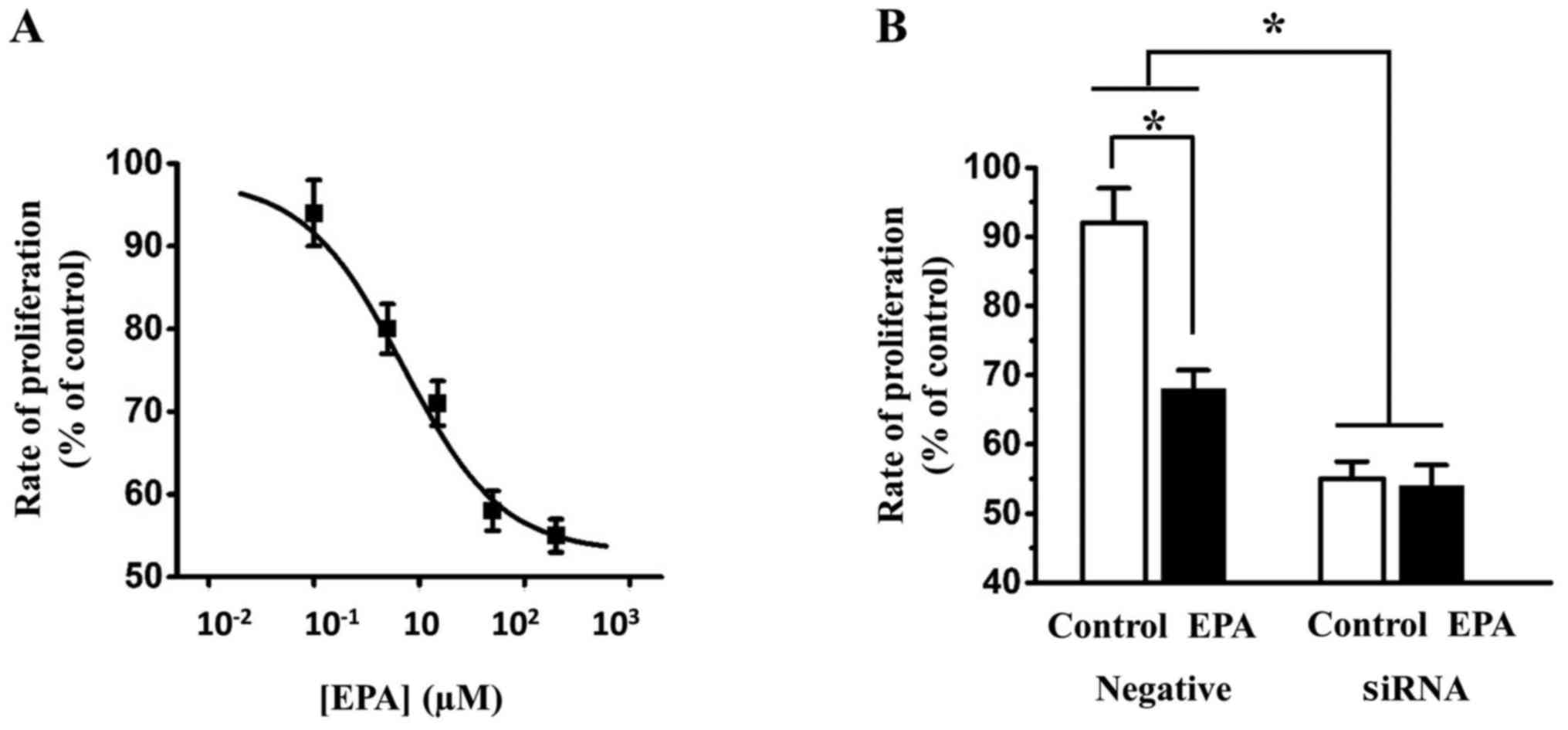
|
1
|
Smith RA, Andrews KS, Brooks D, Fedewa SA,
Manassaram-Baptiste D, Saslow D, Brawley OW and Wender RC: Cancer
screening in the United States, 2017: A review of current American
Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening.
CA Cancer J Clin. 67:100–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jelovac D and Armstrong DK: Recent
progress in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer. CA
Cancer J Clin. 61:183–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen M, Yao S, Cao Q, Xia M, Liu J and He
M: The prognostic value of Ki67 in ovarian high-grade serous
carcinoma: An 11-year cohort study of Chinese patients. Oncotarget.
8:107877–107885. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Asher V, Khan R, Warren A, Shaw R,
Schalkwyk GV, Bali A and Sowter HM: The Eag potassium channel as a
new prognostic marker in ovarian cancer. Diagn Pathol. 5:782010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu FH and Catterall WA: Overview of the
voltage-gated sodium channel family. Genome Biol. 4:2072003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu M, Yang KC and Dudley SC Jr: Cardiac
sodium channel mutations: Why so many phenotypes? Nat Rev Cardiol.
11:607–615. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fraser SP, Diss JK, Lloyd LJ, Pani F,
Chioni AM, George AJ and Djamgoz MB: T-lymphocyte invasiveness:
Control by voltage-gated Na+ channel activity. FEBS
Lett. 569:191–194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shan B, Dong M, Tang H, Wang N, Zhang J,
Yan C, Jiao X, Zhang H and Wang C: Voltage-gated sodium channels
were differentially expressed in human normal prostate, benign
prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
8:345–350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fraser SP, Diss JK, Chioni AM, Mycielska
ME, Pan H, Yamaci RF, Pani F, Siwy Z, Krasowska M, Grzywna Z, et
al: Voltage-gated sodium channel expression and potentiation of
human breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5381–5389.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
House CD, Vaske CJ, Schwartz AM, Obias V,
Frank B, Luu T, Sarvazyan N, Irby R, Strausberg RL, Hales TG, et
al: Voltage-gated Na+ channel SCN5A is a key regulator
of a gene transcriptional network that controls colon cancer
invasion. Cancer Res. 70:6957–6967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Frede J, Fraser SP, Oskay-Özcelik G, Hong
Y, Ioana Braicu E, Sehouli J, Gabra H and Djamgoz MB: Ovarian
cancer: Ion channel and aquaporin expression as novel targets of
clinical potential. Eur J Cancer. 49:2331–2344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao R, Shen Y, Cai J, Lei M and Wang Z:
Expression of voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit in human
ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 23:1293–1299. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brinton EA and Mason RP: Prescription
omega-3 fatty acid products containing highly purified
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Lipids Health Dis. 16:232017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li GR, Sun HY, Zhang XH, Cheng LC, Chiu
SW, Tse HF and Lau CP: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit
transient outward and ultra-rapid delayed rectifier K+
currents and Na+ current in human atrial myocytes.
Cardiovasc Res. 81:286–293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wan XH, Fu X and Ababaikeli G:
Docosahexaenoic acid induces growth suppression on epithelial
ovarian cancer cells more effectively than eicosapentaenoic acid.
Nutr Cancer. 68:320–327. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pathak MM, Tran T, Hong L, Joós B, Morris
CE and Tombola F: The Hv1 proton channel responds to mechanical
stimuli. J Gen Physiol. 148:405–418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong L and Tombola F: Allostery: A lipid
two-step. Nat Chem Biol. 12:202–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leifert WR, McMurchie EJ and Saint DA:
Inhibition of cardiac sodium currents in adult rat myocytes by n-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Physiol. 520:671–679. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alkhalil A, Hong L, Nguitragool W and
Desai SA: Voltage-dependent inactivation of the plasmodial surface
anion channel via a cleavable cytoplasmic component. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1818:367–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Hong L, Wang G and Guan Y: Involvement of
volume-regulated Cl- current in myocardial hypertrophy. Chinese
Pharmacological Bulletin. 23:990–993. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Hong L, Singh V, Wulff H and Tombola F:
Interrogation of the intersubunit interface of the open Hv1 proton
channel with a probe of allosteric coupling. Sci Rep. 5:140772015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim IH, Hevezi P, Varga C, Pathak MM, Hong
L, Ta D, Tran CT, Zlotnik A, Soltesz I and Tombola F: Evidence for
functional diversity between the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1
and its closest related protein HVRP1. PLoS One. 9:e1059262014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zimmer T, Haufe V and Blechschmidt S:
Voltage-gated sodium channels in the mammalian heart. Glob Cardiol
Sci Pract. 2014:449–463. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao YF, Ke Q, Wang SY, Auktor K, Yang Y,
Wang GK, Morgan JP and Leaf A: Single point mutations affect fatty
acid block of human myocardial sodium channel alpha subunit
Na+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:3606–3611.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xiao YF, Ma L, Wang SY, Josephson ME, Wang
GK, Morgan JP and Leaf A: Potent block of inactivation-deficient
Na+ channels by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 290:C362–C370. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Besson P, Driffort V, Bon É, Gradek F,
Chevalier S and Roger S: How do voltage-gated sodium channels
enhance migration and invasiveness in cancer cells? Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1848:2493–2501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pappalardo G, Almeida A and Ravasco P:
Eicosapentaenoic acid in cancer improves body composition and
modulates metabolism. Nutrition. 31:549–555. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sharma A, Belna J, Espat J, Rodriguez G,
Cannon VT and Hurteau JA: Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on
components of the transforming growth factor beta-1 pathway:
implication for dietary modification and prevention in ovarian
cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 200:516.e1–6. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sharma A, Belna J, Logan J, Espat J and
Hurteau JA: The effects of Omega-3 fatty acids on growth regulation
of epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines. Gynecol Oncol. 99:58–64.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Attwell D, Cohen I, Eisner D, Ohba M and
Ojeda C: The steady state TTX-sensitive ('window') sodium current
in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Pflugers Arch. 379:137–142. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frenz CT, Hansen A, Dupuis ND, Shultz N,
Levinson SR, Finger TE and Dionne VE: NaV1.5 sodium channel window
currents contribute to spontaneous firing in olfactory sensory
neurons. J Neurophysiol. 112:1091–1104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moreau A, Krahn AD, Gosselin-Badaroudine
P, Klein GJ, Christé G, Vincent Y, Boutjdir M and Chahine M: Sodium
overload due to a persistent current that attenuates the
arrhythmogenic potential of a novel LQT3 mutation. Front Pharmacol.
4:1262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Janssen LJ: T-type and L-type
Ca2+ currents in canine bronchial smooth muscle:
Characterization and physiological roles. Am J Physiol.
272:C1757–C1765. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brackenbury WJ, Chioni AM, Diss JK and
Djamgoz MB: The neonatal splice variant of Nav1.5 potentiates in
vitro invasive behaviour of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 101:149–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Baptista-Hon DT, Robertson FM, Robertson
GB, Owen SJ, Rogers GW, Lydon EL, Lee NH and Hales TG: Potent
inhibition by ropivacaine of metastatic colon cancer SW620 cell
invasion and NaV1.5 channel function. Br J Anaesth. 113(Suppl 1):
i39–i48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gillet L, Roger S, Besson P, Lecaille F,
Gore J, Bougnoux P, Lalmanach G and Le Guennec JY: Voltage-gated
sodium channel activity promotes cysteine cathepsin-dependent
invasiveness and colony growth of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
284:8680–8691. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xing D, Wang J, Ou S, Wang Y, Qiu B, Ding
D, Guo F and Gao Q: Expression of neonatal Nav1.5 in human brain
astrocytoma and its effect on proliferation, invasion and apoptosis
of astrocytoma cells. Oncol Rep. 31:2692–2700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nelson M, Yang M, Millican-Slater R and
Brackenbury WJ: Nav1.5 regulates breast tumor growth and metastatic
dissemi-nation in vivo. Oncotarget. 6:32914–32929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ozkucur N, Monsees TK, Perike S, Do HQ and
Funk RH: Local calcium elevation and cell elongation initiate
guided motility in electrically stimulated osteoblast-like cells.
PLoS One. 4:e61312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Perike S, Özkucur N, Sharma P, Staroske W,
Bläsche R, Barth K and Funk RH: Phospho-NHE3 forms membrane patches
and interacts with beta-actin to sense and maintain constant
direction during cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 324:13–29. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ozkucur N, Perike S, Sharma P and Funk RH:
Persistent directional cell migration requires ion transport
proteins as direction sensors and membrane potential differences in
order to maintain directedness. BMC Cell Biol. 12:42011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Roger S, Gillet L, Le Guennec JY and
Besson P: Voltage-gated sodium channels and cancer: Is excitability
their primary role? Front Pharmacol. 6:1522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang M and Brackenbury WJ: Membrane
potential and cancer progression. Front Physiol. 4:1852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Redmann K, Müller V, Tanneberger S and
Kalkoff W: The membrane potential of primary ovarian tumor cells in
vitro and its dependence on the cell cycle. Acta Biol Med Ger.
28:853–856. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Brisson L, Driffort V, Benoist L, Poet M,
Counillon L, Antelmi E, Rubino R, Besson P, Labbal F, Chevalier S,
et al: NaV1.5 Na+ channels allosterically regulate the
NHE-1 exchanger and promote the activity of breast cancer cell
invadopodia. J Cell Sci. 126:4835–4842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|