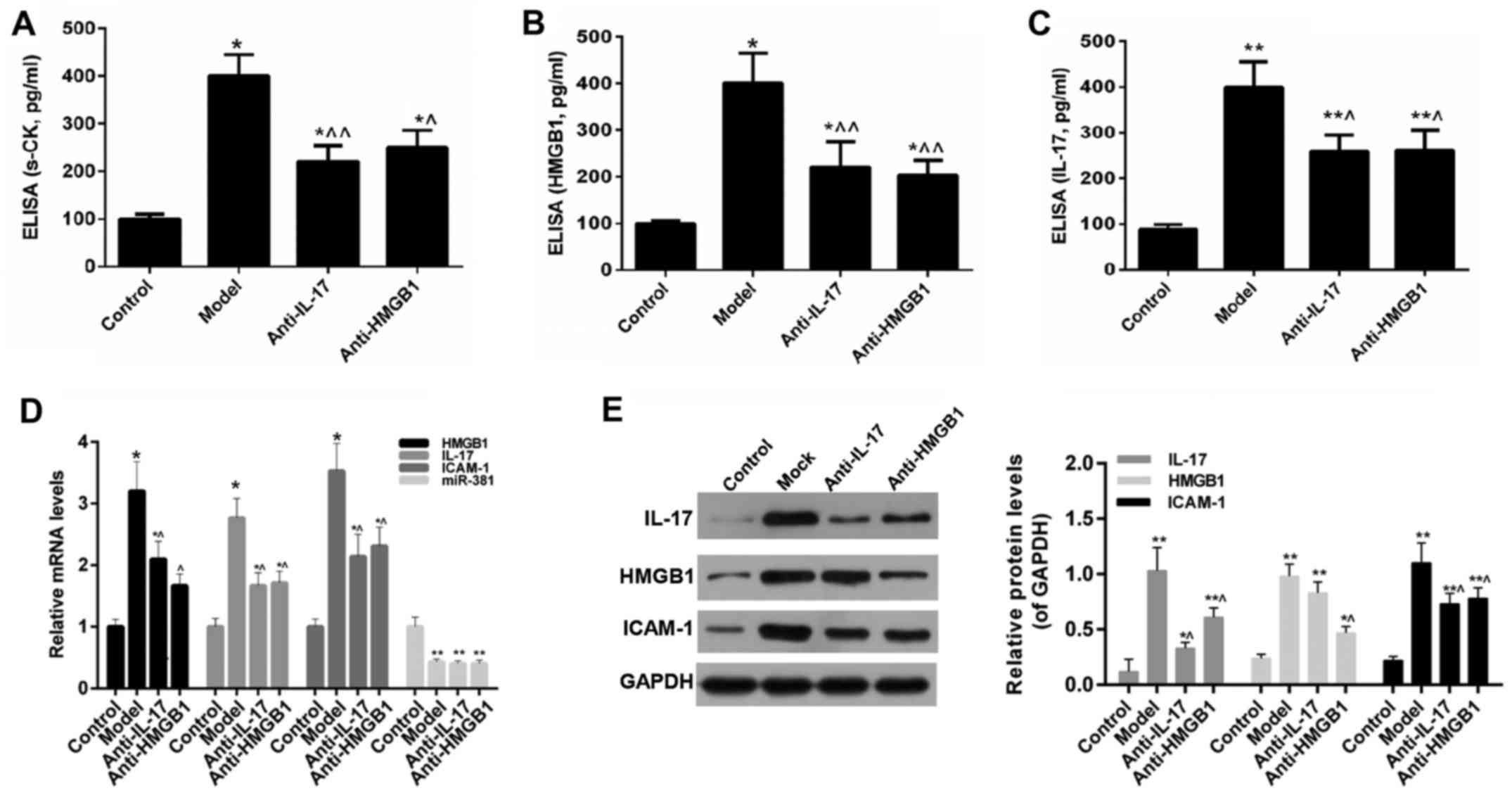
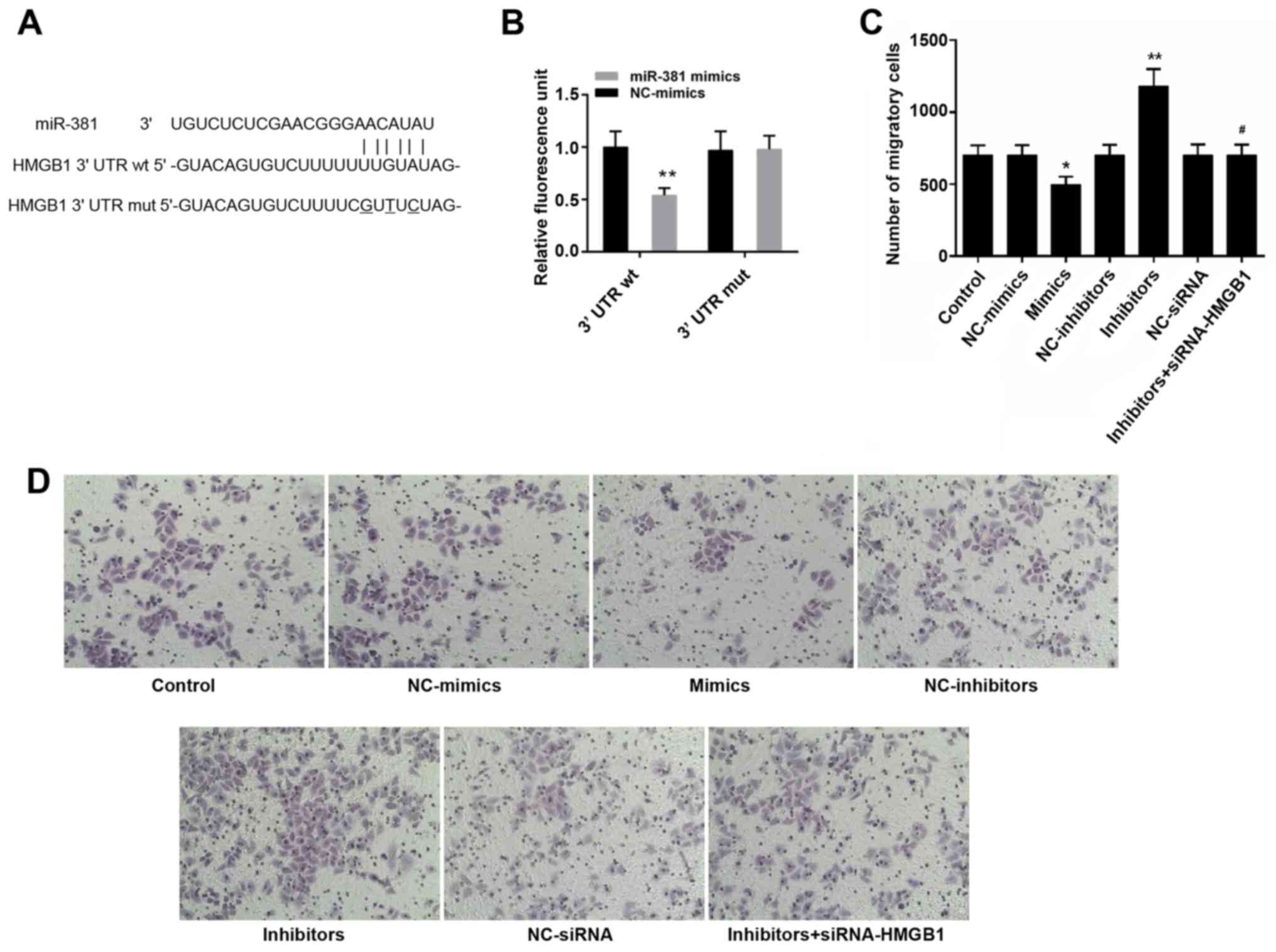
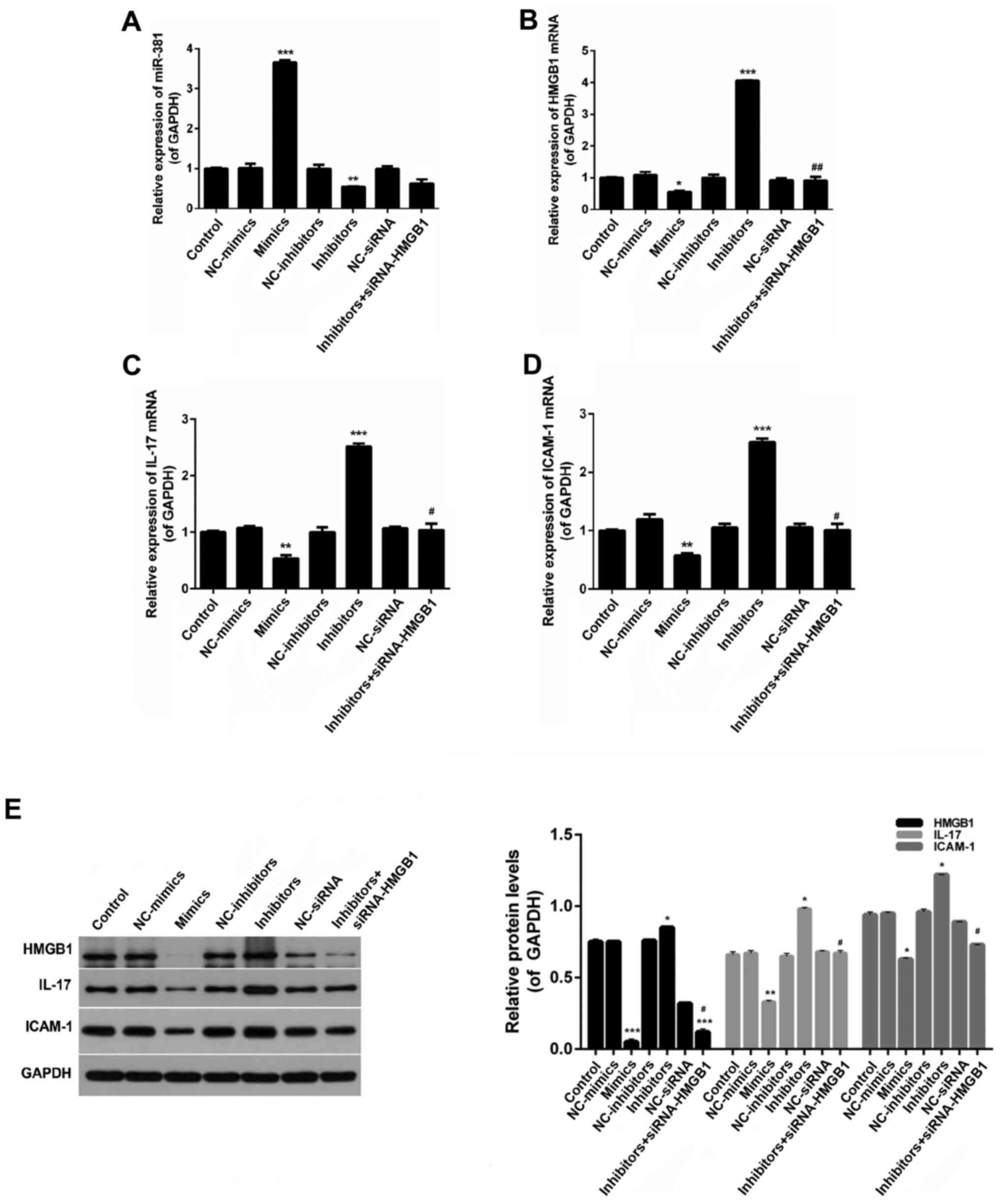
|
1
|
Maoz CR, Langevitz P, Livneh A, Blumstein
Z, Sadeh M, Bank I, Gur H and Ehrenfeld M: High incidence of
malignancies in patients with dermatomyositis and polymyositis: An
11-year analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 27:319–324. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang J, Guo G, Chen G, Wu B, Lu L and Bao
L: Meta-analysis of the association of dermatomyositis and
polymyositis with cancer. Br J Dermatol. 169:838–847. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hill CL, Zhang Y, Sigurgeirsson B, Pukkala
E, Mellemkjaer L, Airio A, Evans SR and Felson DT: Frequency of
specific cancer types in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: A
population-based study. Lancet. 357:96–100. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rayavarapu S, Coley W and Nagaraju K: An
update on pathogenic mechanisms of inflammatory myopathies. Curr
Opin Rheumatol. 23:579–584. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fasth AE, Dastmalchi M, Rahbar A,
Salomonsson S, Pandya JM, Lindroos E, Nennesmo I, Malmberg KJ,
Soderberg-Naucler C, Trollmo C, et al: T cell infiltrates in the
muscles of patients with dermatomyositis and polymyositis are
dominated by CD28null T cells. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md
: 1950). 183:4792–4799. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Henriques-Pons A and Nagaraju K: Nonimmune
mechanisms of muscle damage in myositis: Role of the endoplasmic
reticulum stress response and autophagy in the disease
pathogenesis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 21:581–587. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Salajegheh M, Kong SW, Pinkus JL, Walsh
RJ, Liao A, Nazareno R, Amato AA, Krastins B, Morehouse C, Higgs
BW, et al: Interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) conjugates
proteins in dermatomyositis muscle with perifascicular atrophy. Ann
Neurol. 67:53–63. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Walsh RJ, Kong SW, Yao Y, Jallal B, Kiener
PA, Pinkus JL, Beggs AH, Amato AA and Greenberg SA: Type I
interferon-inducible gene expression in blood is present and
reflects disease activity in dermatomyositis and polymyositis.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:3784–3792. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wenzel J, Scheler M, Bieber T and Tüting
T: Evidence for a role of type I interferons in the pathogenesis of
dermatomyositis. Br J Dermatol. 153:462–463; author reply 463–464.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scovell WM: High mobility group protein 1:
A collaborator in nucleosome dynamics and estrogen-responsive gene
expression. World J Biol Chem. 7:206–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Musumeci D, Roviello GN and Montesarchio
D: An overview on HMGB1 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents
in HMGB1-related pathologies. Pharmacol Ther. 141:347–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang Q, Liu X, Yao Z, Mao S, Wei Q and
Chang Y: Penehyclidine hydrochloride inhibits the release of
high-mobility group box 1 in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264.7
cells and cecal ligation and puncture-induced septic mice. J Surg
Res. 186:310–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Harris HE, Andersson U and Pisetsky DS:
HMGB1: A multifunctional alarmin driving autoimmune and
inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:195–202. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lotze MT and Tracey KJ: High-mobility
group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:331–342. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pisetsky DS, Erlandsson-Harris H and
Andersson U: High-mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1): An alarmin
mediating the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res
Ther. 10:2092008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Müller S, Scaffidi P, Degryse B, Bonaldi
T, Ronfani L, Agresti A, Beltrame M and Bianchi ME: New EMBO
members' review: The double life of HMGB1 chromatin protein:
architectural factor and extracellular signal. EMBO J.
20:4337–4340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moestrup SK and Møller HJ: CD163: A
regulated hemoglobin scavenger receptor with a role in the
anti-inflammatory response. Ann Med. 36:347–354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Niimoto T, Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Okuhara
A, Izumi B, Deie M, Suzuki O, Adachi N and Ochi M: MicroRNA-146a
expresses in interleukin-17 producing T cells in rheumatoid
arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 11:2092010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hirota K, Hashimoto M, Yoshitomi H, Tanaka
S, Nomura T, Yamaguchi T, Iwakura Y, Sakaguchi N and Sakaguchi S: T
cell self-reactivity forms a cytokine milieu for spontaneous
development of IL-17+ Th cells that cause autoimmune
arthritis. J Exp Med. 204:41–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee YK, Mukasa R, Hatton RD and Weaver CT:
Developmental plasticity of Th17 and Treg cells. Curr Opin Immunol.
21:274–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Crispin JC, Oukka M, Bayliss G, Cohen RA,
Van Beek CA, Stillman IE, Kyttaris VC, Juang YT and Tsokos GC:
Expanded double negative T cells in patients with systemic lupus
erythe-matosus produce IL-17 and infiltrate the kidneys. J Immunol.
181:8761–8766. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pickens SR, Volin MV, Mandelin AM 2nd,
Kolls JK, Pope RM and Shahrara S: IL-17 contributes to angiogenesis
in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 184:3233–3241. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM,
Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA and
Cua DJ: IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces
autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 201:233–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tzartos JS, Friese MA, Craner MJ, Palace
J, Newcombe J, Esiri MM and Fugger L: Interleukin-17 production in
central nervous system-infiltrating T cells and glial cells is
associated with active disease in multiple sclerosis. Am J Pathol.
172:146–155. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Gao Q, Jiang Y, Ma T, Zhu F, Gao F, Zhang
P, Guo C, Wang Q, Wang X, Ma C, et al: A critical function of Th17
proinflam-matory cells in the development of atherosclerotic plaque
in mice. J Immunol. 185:5820–5827. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smith E, Prasad KM, Butcher M, Dobrian A,
Kolls JK, Ley K and Galkina E: Blockade of interleukin-17A results
in reduced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Circulation. 121:1746–1755. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Othumpangat S, Noti JD, McMillen CM and
Beezhold DH: ICAM-1 regulates the survival of influenza virus in
lung epithelial cells during the early stages of infection.
Virology. 487:85–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Gabr MA, Jing L, Helbling AR, Sinclair SM,
Allen KD, Shamji MF, Richardson WJ, Fitch RD, Setton LA and Chen J:
Interleukin-17 synergizes with IFNgamma or TNFalpha to promote
inflammatory mediator release and intercellular adhesion molecule-1
(ICAM-1) expression in human interver-tebral disc cells. J Orthop
Res. 29:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Plaisance-Bonstaff K and Renne R: Viral
miRNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 721:43–66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang J, Zhang SY, Gao YM, Liu YF, Liu YB,
Zhao ZG and Yang K: MicroRNAs as oncogenes or tumour suppressors in
oesophageal cancer: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Cell Prolif. 47:277–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, You T and Jing J: MiR-125b inhibits
cell biological progression of Ewing's sarcoma by suppressing the
PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 47:152–160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li M, Yu M, Liu C, Zhu H, He X, Peng S and
Hua J: miR-34c works downstream of p53 leading to dairy goat male
germline stem-cell (mGSCs) apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 46:223–231.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J and Jiang Y: MicroRNA
dysregulation in uveal melanoma: A new player enters the game.
Oncotarget. 6:4562–4568. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu Z, Asahchop EL, Branton WG, Gelman BB,
Power C and Hobman TC: MicroRNAs upregulated during HIV infection
target peroxisome biogenesis factors: Implications for virus
biology, disease mechanisms and neuropathology. PLoS Pathog.
13:e10063602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cao Q, Liu F, Ji K, Liu N, He Y, Zhang W
and Wang L: MicroRNA-381 inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer
by targeting TMEM16A expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:292017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hou C, Meng F, Zhang Z, Kang Y, Chen W,
Huang G, Fu M, Sheng P, Zhang Z and Liao W: The role of
MicroRNA-381 in chondrogenesis and interleukin-1-beta induced
chondrocyte responses. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1753–1766. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang X, Goncalves R and Mosser DM: The
isolation and characterization of murine macrophages. Curr Protoc
Immunol Chapter 14. Unit. 14:12008.
|
|
38
|
Arahata K and Engel AG: Monoclonal
antibody analysis of mono-nuclear cells in myopathies. I:
Quantitation of subsets according to diagnosis and sites of
accumulation and demonstration and counts of muscle fibers invaded
by T cells. Ann Neurol. 16:193–208. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Engel AG and Arahata K: Monoclonal
antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. II:
Phenotypes of autoinvasive cells in polymyositis and inclusion body
myositis. Ann Neurol. 16:209–215. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goebels N, Michaelis D, Engelhardt M,
Huber S, Bender A, Pongratz D, Johnson MA, Wekerle H, Tschopp J,
Jenne D, et al: Differential expression of perforin in
muscle-infiltrating T cells in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J
Clin Invest. 97:2905–2910. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zong M and Lundberg IE: Pathogenesis,
classification and treatment of inflammatory myopathies. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 7:297–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Notarnicola A, Lapadula G, Natuzzi D,
Lundberg IE and Iannone F: Correlation between serum levels of
IL-15 and IL-17 in patients with idiopathic inflammatory
myopathies. Scand J Rheumatol. 44:224–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yin Y, Li F, Shi J, Li S, Cai J and Jiang
Y: MiR-146a regulates inflammatory infiltration by macrophages in
polymyositis/derma-tomyositis by targeting TRAF6 and affecting
IL-17/ICAM-1 pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:486–498. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Miossec P: Interleukin-17 in fashion, at
last: Ten years after its description, its cellular source has been
identified. Arthritis Rheum. 56:2111–2115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kenna TJ and Brown MA: The role of
IL-17-secreting mast cells in inflammatory joint disease. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 9:375–379. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Baeten DL and Kuchroo VK: How Cytokine
networks fuel inflammation: Interleukin-17 and a tale of two
autoimmune diseases. Nat Med. 19:824–825. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sallum AM, Kiss MH, Silva CA, Wakamatsu A,
Vianna MA, Sachetti S and Marie SK: Difference in adhesion molecule
expression (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) in juvenile and adult
dermatomyositis, polymyositis and inclusion body myositis.
Autoimmun Rev. 5:93–100. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Szodoray P, Alex P, Knowlton N, Centola M,
Dozmorov I, Csipo I, Nagy AT, Constantin T, Ponyi A, Nakken B, et
al: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, signified by distinctive
peripheral cytokines, chemokines and the TNF family members B-cell
activating factor and a proliferation inducing ligand. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 49:1867–1877. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Tournadre A, Porcherot M, Chérin P, Marie
I, Hachulla E and Miossec P: Th1 and Th17 balance in inflammatory
myopathies: Interaction with dendritic cells and possible link with
response to high-dose immunoglobulins. Cytokine. 46:297–301. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yin Y, Li F, Shi J, Li S, Cai J and Jiang
Y: MiR-146a regulates inflammatory infiltration by macrophages in
polymyositis/derma-tomyositis by targeting TRAF6 and affecting
IL-17/ICAM-1 Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:486–498. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Tang Q, Li J, Zhu H, Li P, Zou Z and Xiao
Y: Hmgb1-IL-23-IL-17-IL-6-Stat3 axis promotes tumor growth in
murine models of melanoma. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:7138592013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|