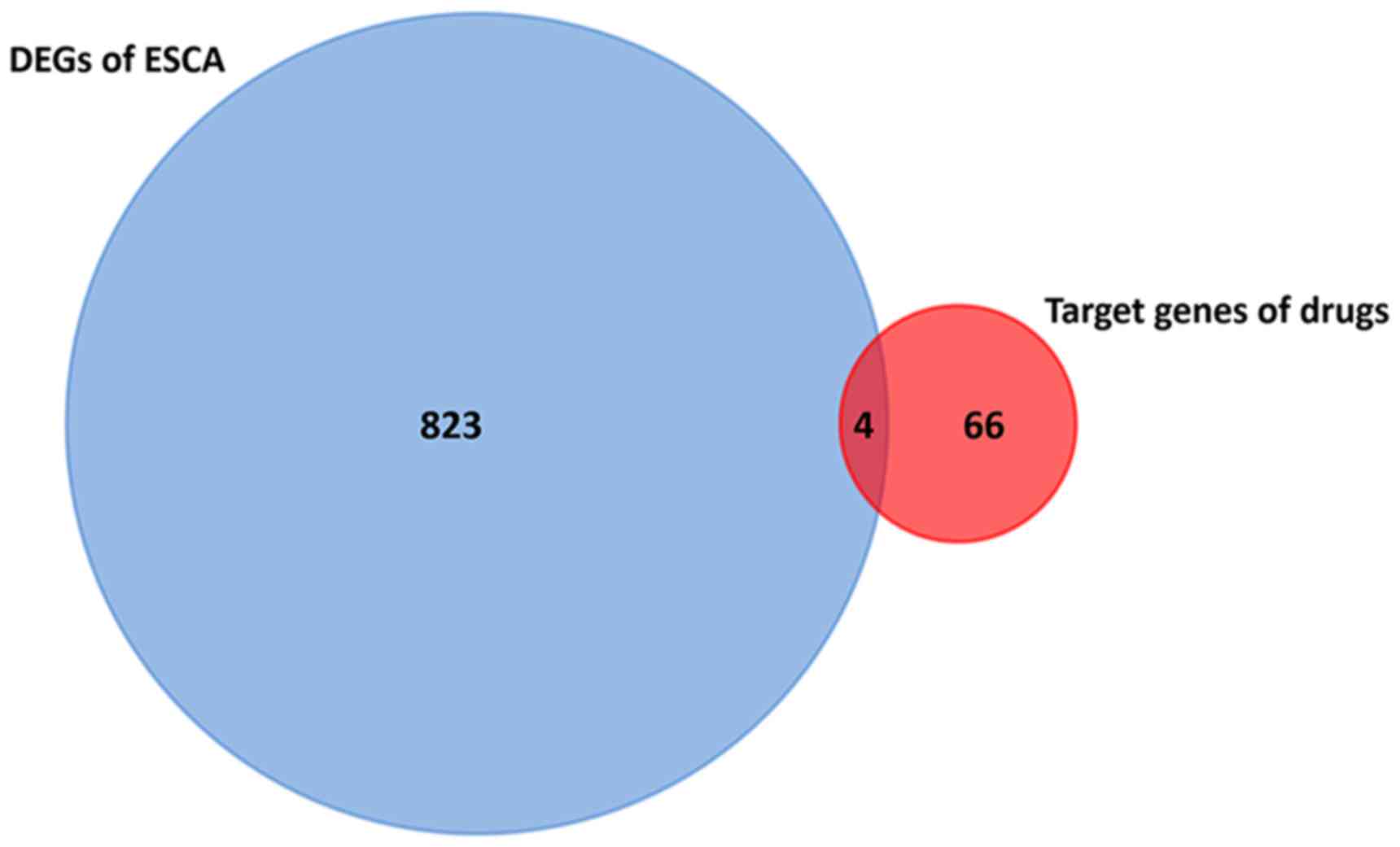
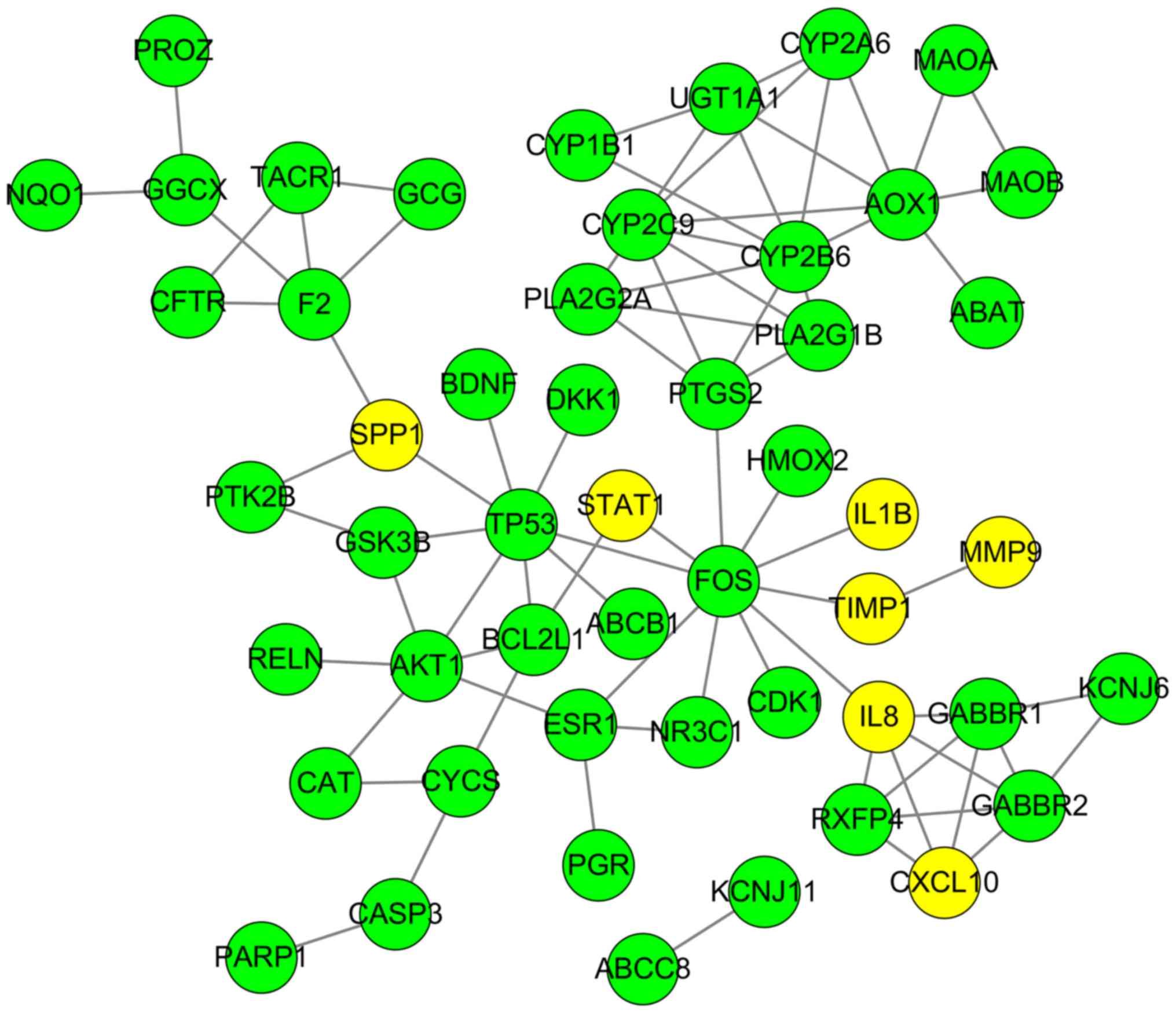
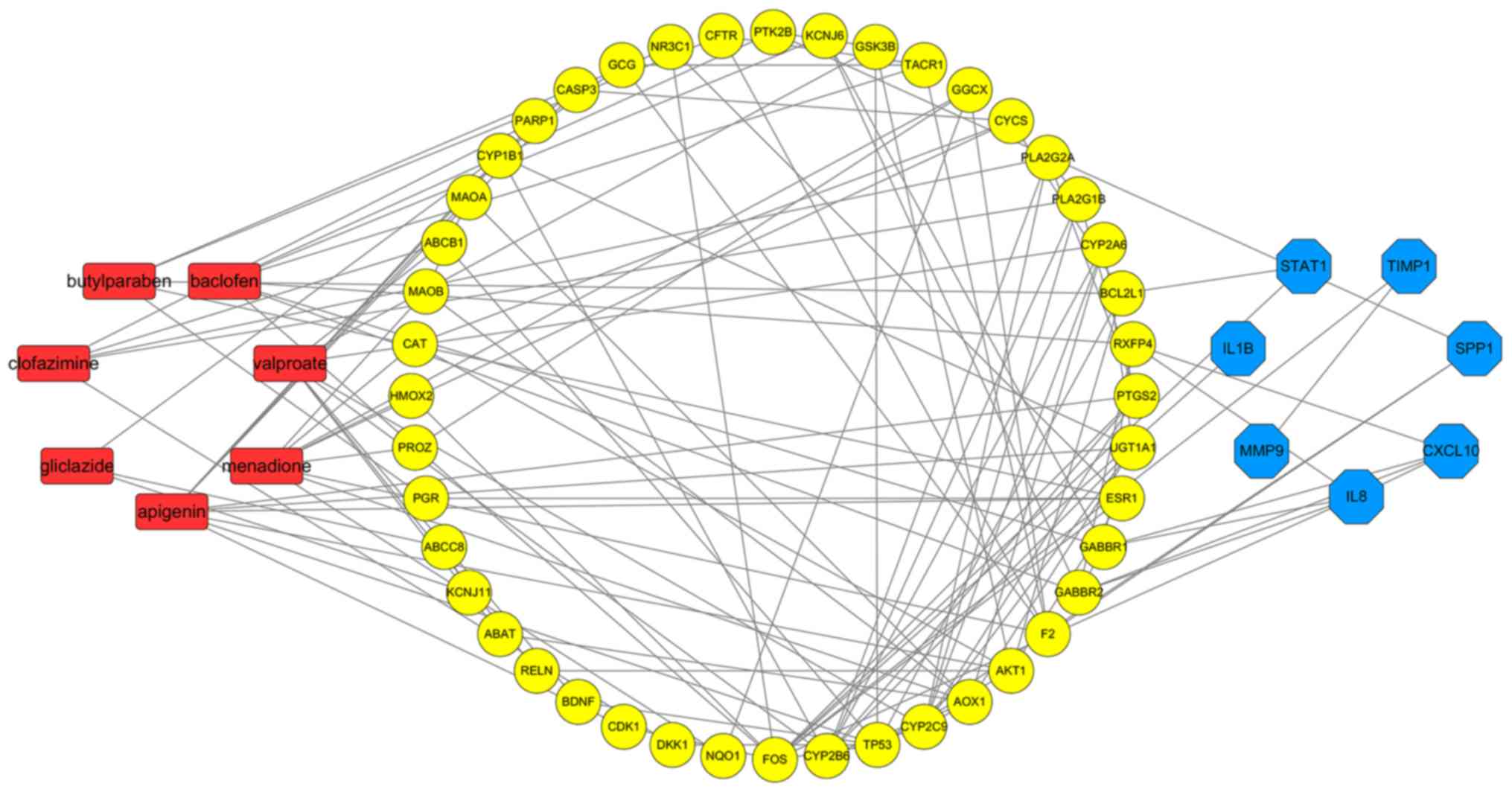
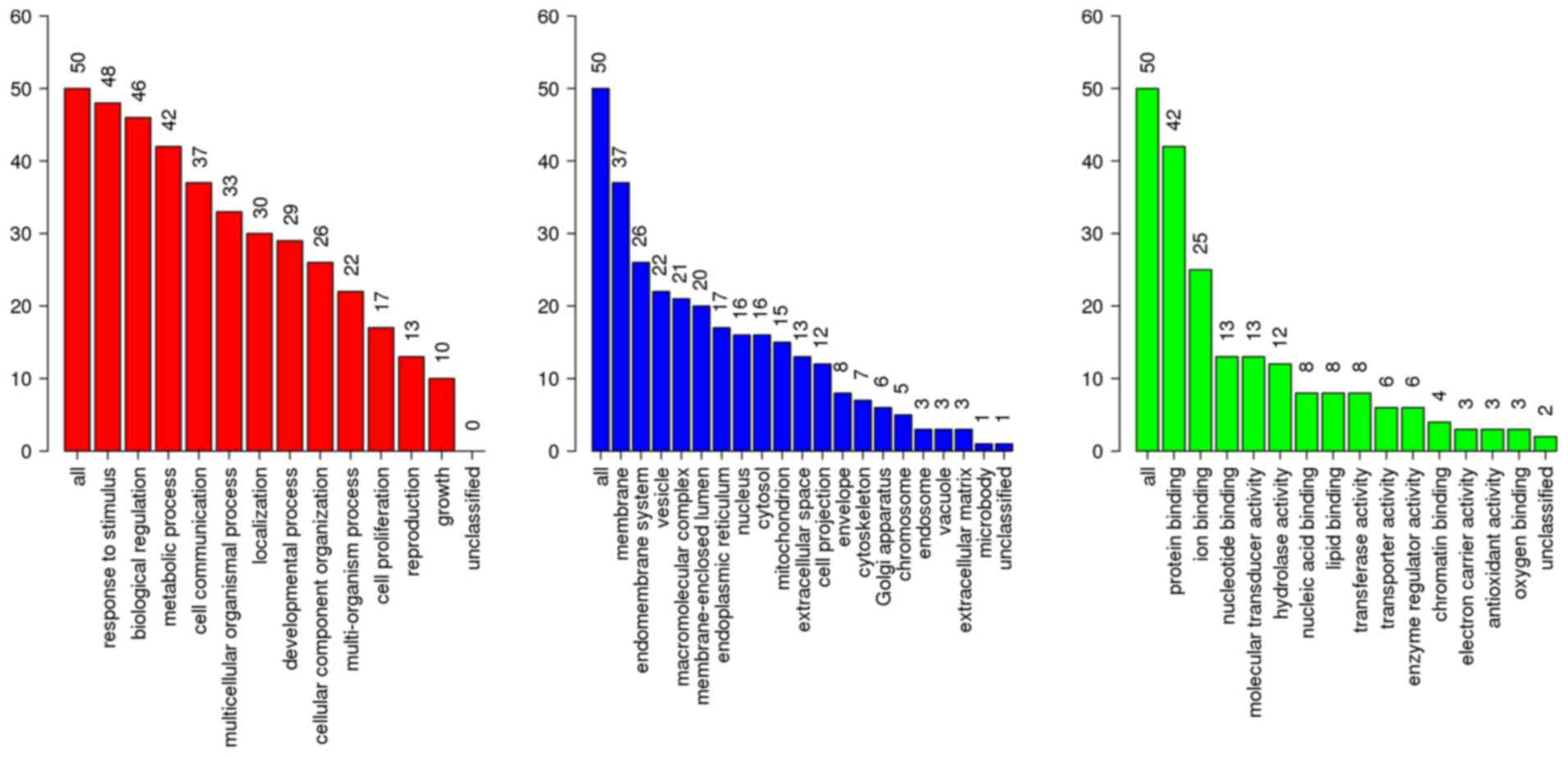
|
1
|
Ma K, Cao B and Guo M: The detective,
prognostic, and predictive value of DNA methylation in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Epigenetics. 8:432016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erkizan HV, Johnson K, Ghimbovschi S,
Karkera D, Trachiotis G, Adib H, Hoffman EP and Wadleigh RG:
African-American esophageal squamous cell carcinoma expression
profile reveals dysregulation of stress response and detox
networks. BMC Cancer. 17:4262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang S, Zhang Q, Su Y and Pan L:
Network-based differential analysis to identify molecular features
of tumorigenesis for esophageal squamous carcinoma. Molecules.
23:232018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang XX, Ma M, Sang MX, Wang XX, Song H,
Liu ZK and Zhu SC: Radiosensitization of esophageal carcinoma cells
by knockdown of RNF2 expression. Int J Oncol. 48:1985–1996. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma Z, Cai H and Cui Y: Progress in the
treatment of esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177113132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vellayappan BA, Soon YY, Ku GY, Leong CN,
Lu JJ and Tey JC: Chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy plus
surgery for esophageal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
8:CD0105112017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen GZ, Zhu HC, Dai WS, Zeng XN, Luo JH
and Sun XC: The mechanisms of radioresistance in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma and current strategies in radiosensitivity.
J Thorac Dis. 9:849–859. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Recio-Boiles A and Babiker HM: Cancer,
Esophageal. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure
Island, FL: 2018
|
|
10
|
Sasaki Y and Kato K: Chemoradiotherapy for
esophageal squamous cell cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:805–810.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harada K, Mizrak Kaya D, Baba H and Ajani
JA: Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Thorac Dis. 10:699–702. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai Z, Lv H, Cao W, Zhou C, Liu Q, Li H
and Zhou F: Targeting strategies of adenovirus mediated gene
therapy and virotherapy for prostate cancer (Review). Mol Med Rep.
16:6443–6458. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grisham RN and Iyer G: Low-grade serous
ovarian cancer: Current treatment paradigms and future directions.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 19:542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Le Grazie M, Biagini MR, Tarocchi M,
Polvani S and Galli A: Chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma:
The present and the future. World J Hepatol. 9:907–920. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mayank and Jaitak V: Drug target
strategies in breast cancer treatment: Recent developments.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 14:1414–1427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Michels S and Wolf J: Stratified treatment
in lung cancer. Oncol Res Treat. 39:760–766. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia Y, Xiao Z, Gongsun X, Xin Z, Shang B,
Chen G, Wang Z and Jiang W: CEP55 promotes the proliferation,
migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via
the PI3K/Akt pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 11:4221–4232. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Niyaz M, Abdurahman A, Turghun A and Awut
I: CEP3 and CEP17 DNA probe potential in the genetic diagnosis and
prognostic prediction of esophageal squamous cell cancer. Exp Ther
Med. 11:1375–1380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Zhou Y, Liu Q, Xu J and Ma Y:
Prognostic value of SOX2, Cyclin D1, P53, and ki-67 in patients
with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther.
11:5171–5181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lin S, Liu K, Zhang Y, Jiang M, Lu R,
Folts CJ, Gao X, Noble MD, Zhao T, Zhou Z, et al: Pharmacological
targeting of p38 MAP-Kinase 6 (MAP2K6) inhibits the growth of
esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cell Signal. 51:222–232. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
MacGregor TP, Carter R, Gillies RS,
Findlay JM, Kartsonaki C, Castro-Giner F, Sahgal N, Wang LM, Chetty
R, Maynard ND, et al: Translational study identifies XPF and MUS81
as predictive biomarkers for oxaliplatin-based peri-operative
chemotherapy in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep.
8:72652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang ZW, Jia YX, Zhang WJ, Song LJ, Gao
M, Li MJ, Zhao RH, Li J, Zhong YL, Sun QZ, et al:
LncRNA-TUSC7/miR-224 affected chemotherapy resistance of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma by competitively regulating DESC1. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 37:562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu B, Wang C, Chen P, Cheng B and Cheng
Y: RACKI induces chemotherapy resistance in esophageal carcinoma by
upregulating the PI3K/AKT pathway and Bcl-2 expression. OncoTargets
Ther. 11:211–220. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu X, Li W, Xia Z, Xie L, Ma X, Liang Q,
Liu L, Wang J, Zhou X, Yang Y, et al: Targeting MCL-1 sensitizes
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced
apoptosis. BMC Cancer. 17:4492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pang Y, Liu J, Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang B,
Zhang J, Du N, Xu C, Liang R, Ren H, et al: Nano Let 7b
sensitization of eliminating esophageal cancer stem like cells is
dependent on blockade of Wnt activation of symmetric division. Int
J Oncol. 51:1077–1088. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW,
Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, Lerner J, Brunet JP, Subramanian A, Ross KN, et
al: The Connectivity Map: Using gene-expression signatures to
connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science.
313:1929–1935. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin P, Xiong DD, Dang YW, Yang H, He Y,
Wen DY, Qin XG and Chen G: The anticipating value of PLK1 for
diagnosis, progress and prognosis and its prospective mechanism in
gastric cancer: A comprehensive investigation based on
high-throughput data and immunohistochemical validation.
Oncotarget. 8:92497–92521. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dang YW, Lin P, Liu LM, He RQ, Zhang LJ,
Peng ZG, Li XJ and Chen G: In silico analysis of the potential
mechanism of telocinobufagin on breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Pathol
Res Pract. 214:631–643. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He RQ, Yang X, Liang L, Chen G and Ma J:
MicroRNA-124-3p expression and its prospective functional pathways
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A quantitative polymerase chain
reaction, gene expression omnibus and bioinformatics study. Oncol
Lett. 15:5517–5532. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li HM, Yang H, Wen DY, Luo YH, Liang CY,
Pan DH, Ma W, Chen G, He Y and Chen JQ: Overexpression of LncRNA
HOTAIR is associated with poor prognosis in thyroid carcinoma: A
study based on TCGA and GEO data. Horm Metab Res. 49:388–399. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao L, Li SH, Tian YX, Zhu QQ, Chen G,
Pang YY and Hu XH: Role of downregulated miR-133a-3p expression in
bladder cancer: A bioinformatics study. OncoTargets Ther.
10:3667–3683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
He RQ, Wu PR, Xiang XL, Yang X, Liang HW,
Qiu XH, Yang LH, Peng ZG and Chen G: Downregulated miR-23b-3p
expression acts as a predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma
progression: A study based on public data and RT-qPCR verification.
Int J Mol Med. 41:2813–2831. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liang L, Wei DM, Li JJ, Luo DZ, Chen G,
Dang YW and Cai XY: Prognostic microRNAs and their potential
molecular mechanism in pancreatic cancer: A study based on The
Cancer Genome Atlas and bioinformatics investigation. Mol Med Rep.
17:939–951. 2018.
|
|
35
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hsin KY, Ghosh S and Kitano H: Combining
machine learning systems and multiple docking simulation packages
to improve docking prediction reliability for network pharmacology.
PLoS One. 8:e839222013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hsin KY, Matsuoka Y, Asai Y, Kamiyoshi K,
Watanabe T, Kawaoka Y and Kitano H: systemsDock: A web server for
network pharmacology-based prediction and analysis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44(W1): W507–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang J, Li M, Wang Y and Liu X:
Integrating subpathway analysis to identify candidate agents for
hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 9:1221–1230. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zador Z, King AT and Geifman N: New drug
candidates for treatment of atypical meningiomas: An integrated
approach using gene expression signatures for drug repurposing.
PLoS One. 13:e01947012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu G, Hu X, Gao L and Feng Z:
Personalized drug analysis in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
patients. Med Sci Monit. 23:2159–2167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nelson N, Szekeres K, Iclozan C, Rivera
IO, McGill A, Johnson G, Nwogu O and Ghansah T: Apigenin: Selective
CK2 inhibitor increases Ikaros expression and improves T cell
homeostasis and function in murine pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 12.
pp. e01701972017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pal MK, Jaiswar SP, Dwivedi A, Goyal S,
Dwivedi VN, Pathak AK, Kumar V, Sankhwar PL and Ray RS: Synergistic
effect of graphene oxide coated nanotised apigenin with paclitaxel
(GO-NA/PTX): A ROS dependent mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in
ovarian cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 17:1721–1732.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shan S, Shi J, Yang P, Jia B, Wu H, Zhang
X and Li Z: Apigenin restrains colon cancer cell proliferation via
targeted blocking of pyruvate kinase M2-dependent glycolysis. J
Agric Food Chem. 65:8136–8144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vrhovac Madunić I, Madunić J, Antunović M,
Paradžik M, Garaj-Vrhovac V, Breljak D, Marijanović I and Gajski G:
Apigenin, a dietary flavonoid, induces apoptosis, DNA damage, and
oxidative stress in human breast cancer MCF-7 and MDA MB-231 cells.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 391:537–550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhou Z, Tang M, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Lu R and
Lu J: Apigenin inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion
by targeting Akt in the A549 human lung cancer cell line.
Anticancer Drugs. 28:446–456. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhu H, Jin H, Pi J, Bai H, Yang F, Wu C,
Jiang J and Cai J: Apigenin induced apoptosis in esophageal
carcinoma cells by destruction membrane structures. Scanning.
38:322–328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yan X, Qi M, Li P, Zhan Y and Shao H:
Apigenin in cancer therapy: Anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of
action. Cell Biosci. 7:502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sung B, Chung HY and Kim ND: Role of
apigenin in cancer prevention via the induction of apoptosis and
autophagy. J Cancer Prev. 21:216–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Pérez-Arredondo A, Cázares-Ramírez E,
Carrillo-Mora P, Martínez-Vargas M, Cárdenas-Rodríguez N,
Coballase-Urrutia E, Alemón-Medina R, Sampieri A III, Navarro L and
Carmona-Aparicio L: Baclofen in the therapeutic of sequele of
traumatic brain injury: Spasticity. Clin Neuropharmacol.
39:311–319. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ertzgaard P, Campo C and Calabrese A:
Efficacy and safety of oral baclofen in the management of
spasticity: A rationale for intrathecal baclofen. J Rehabil Med.
49:193–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sharma V, De A, Lamoria S and Lamba BM:
Baclofen-responsive hiccups after esophageal stenting for
malignancy-related dysphagia. Proc Bayl Univ Med Cent. 29:1502016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yomiya K, Matsuo N, Tomiyasu S, Yoshimoto
T, Tamaki T, Suzuki T and Matoba M: Baclofen as an adjuvant
analgesic for cancer pain. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 26:112–118.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Koval AV, Vlasov P, Shichkova P,
Khunderyakova S, Markov Y, Panchenko J, Volodina A, Kondrashov FA
and Katanaev VL: Anti-leprosy drug clofazimine inhibits growth of
triple-negative breast cancer cells via inhibition of canonical Wnt
signaling. Biochem Pharmacol. 87:571–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Durusu IZ, Hüsnügil HH, Ataş H, Biber A,
Gerekçi S, Güleç EA and Özen C: Anti-cancer effect of clofazimine
as a single agent and in combination with cisplatin on U266
multiple myeloma cell line. Leuk Res. 55:33–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee MH, Cho Y, Kim DH, Woo HJ, Yang JY,
Kwon HJ, Yeon MJ, Park M, Kim SH, Moon C, et al: Menadione induces
G2/M arrest in gastric cancer cells by downregulation of CDC25C and
proteasome mediated degradation of CDK1 and cyclin B1. Am J Transl
Res. 8:5246–5255. 2016.
|
|
56
|
Prasad CV, Nayak VL, Ramakrishna S and
Mallavadhani UV: Novel menadione hybrids: Synthesis, anticancer
activity, and cell-based studies. Chem Biol Drug Des. 91:220–233.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Delwar ZM, Siden A, Cruz MH and Yakisich
JS: Menadione : Sodium orthovanadate combination eliminates and
inhibits migration of detached cancer cells. ISRN Pharmacol.
2012.307102:2012.
|
|
58
|
Yamada A, Osada S, Tanahashi T, Matsui S,
Sasaki Y, Tanaka Y, Okumura N, Matsuhashi N, Takahashi T, Yamaguchi
K, et al: Novel therapy for locally advanced triple-negative breast
cancer. Int J Oncol. 47:1266–1272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Teixeira J, Amorim R, Santos K, Soares P,
Datta S, Cortopassi GA, Serafim TL, Sardão VA, Garrido J, Borges F,
et al: Disruption of mitochondrial function as mechanism for
anti-cancer activity of a novel mitochondriotropic menadione
derivative. Toxicology. 393:123–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wróbel AM and Gregoraszczuk EL: Action of
methyl-, propyl- and butylparaben on GPR30 gene and protein
expression, cAMP levels and activation of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt
signaling pathways in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and MCF-10A
non-transformed breast epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 238:110–116.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Leiter LA, Shestakova MV and Satman I:
Effectiveness of gliclazide MR 60 mg in the management of type 2
diabetes: Analyses from the EASYDia trial. Diabetol Metab Syndr.
10:302018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Mikov M, Danic M, Pavlovic N, Stanimirov
B, Goločorbin-Kon S, Stankov K and Al-Salami H: Potential
applications of gliclazide in treating type 1 diabetes mellitus:
Formulation with bile acids and probiotics. Eur J Drug Metab
Pharmacokinet. 43:269–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Sliwinska A, Rogalska A, Szwed M,
Kasznicki J, Jozwiak Z and Drzewoski J: Gliclazide may have an
antiapoptotic effect related to its antioxidant properties in human
normal and cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 39:5253–5267. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Sliwinska A, Sliwinski T, Kasznicki J and
Drzewoski J: Effect of gliclazide on nucleotide excision repair
(NER) and non-homologous DNA end joining (NHEJ) in normal and
cancer cells. J Physiol Pharmacol. 61:347–353. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Caponigro F, Di Gennaro E, Ionna F, Longo
F, Aversa C, Pavone E, Maglione MG, Di Marzo M, Muto P, Cavalcanti
E, et al: Phase II clinical study of valproic acid plus cisplatin
and cetuximab in recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell
carcinoma of Head and Neck-V-CHANCE trial. BMC Cancer. 16:9182016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Scialdone A, Hasni MS, Damm JK,
Lennartsson A, Gullberg U and Drott K: The HDAC inhibitor valproate
induces a bivalent status of the CD20 promoter in CLL patients
suggesting distinct epigenetic regulation of CD20 expression in CLL
in vivo. Oncotarget. 8:37409–37422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sha S, Zhai Y, Lin C, Wang H, Chang Q,
Song S, Ren M and Liu G: A combination of valproic acid sodium
salt, CHIR99021, E-616452, tranylcypromine, and 3-Deazaneplanocin A
causes stem cell-like characteristics in cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:53302–53312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wei M, Mao S, Lu G, Li L, Lan X, Huang Z,
Chen Y, Zhao M, Zhao Y and Xia Q: Valproic acid sensitizes
metformin-resistant human renal cell carcinoma cells by
upregulating H3 acetylation and EMT reversal. BMC Cancer.
18:4342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xu X, Huang M and Zou X: Docking-based
inverse virtual screening: Methods, applications, and challenges.
Biophys Rep. 4:1–16. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Abdolmaleki A, Ghasemi JB and Ghasemi F:
Computer aided drug design for multi-target drug design: SAR/QSAR,
molecular docking and pharmacophore methods. Curr Drug Targets.
18:556–575. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Bartuzi D, Kaczor AA, Targowska-Duda KM
and Matosiuk D: Recent advances and applications of molecular
docking to G protein-coupled receptors. Molecules. 22:222017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
de Ruyck J, Brysbaert G, Blossey R and
Lensink MF: Molecular docking as a popular tool in drug design, an
in silico travel. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 9:1–11. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Rosano C, Ponassi M, Santolla MF, Pisano
A, Felli L, Vivacqua A, Maggiolini M and Lappano R: Macromolecular
modelling and docking simulations for the discovery of selective
GPER ligands. AAPS J. 18:41–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Scotti L, Mendonca Junior FJ, Ishiki HM,
Ribeiro FF, Singla RK, Barbosa Filho JM, Da Silva MS and Scotti MT:
Docking studies for multi-target drugs. Curr Drug Targets.
18:592–604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Zhang Y, Molavi O, Su M and Lai R: The
clinical and biological significance of STAT1 in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:7912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Yun H, Lai R and Su M:
Correlation of STAT1 with apoptosis and cell-cycle markers in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e1139282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Klimczak-Bitner AA, Kordek R, Bitner J,
Musiał J and Szemraj J: Expression of MMP9, SERPINE1 and miR-134 as
prognostic factors in esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:4133–4138.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shin WS, Hong Y, Lee HW and Lee ST:
Catalytically defective receptor protein tyrosine kinase PTK7
enhances invasive phenotype by inducing MMP-9 through activation of
AP-1 and NF-κB in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Oncotarget. 7:73242–73256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Juchniewicz A, Kowalczuk O, Milewski R,
Laudański W, Dzięgielewski P, Kozłowski M and Nikliński J: MMP-10,
MMP-7, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA expression in esophageal cancer. Acta
Biochim Pol. 64:295–299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kozłowski M, Laudański W, Mroczko B,
Szmitkowski M, Milewski R and Łapuć G: Serum tissue inhibitor of
metallo-proteinase 1 (TIMP-1) and vascular endothelial growth
factor A (VEGF-A) are associated with prognosis in esophageal
cancer patients. Adv Med Sci. 58:227–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Zheng L, Yin J, Wang L, Wang X, Shi Y,
Shao A, Tang W, Ding G, Liu C, Chen S, et al: Interleukin 1B
rs16944 G>A polymorphism was associated with a decreased risk of
esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. Clin Biochem.
46:1469–1473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shrivastava MS, Hussain Z, Giricz O,
Shenoy N, Polineni R, Maitra A and Verma A: Targeting chemokine
pathways in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cell Cycle. 13:3320–3327.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|