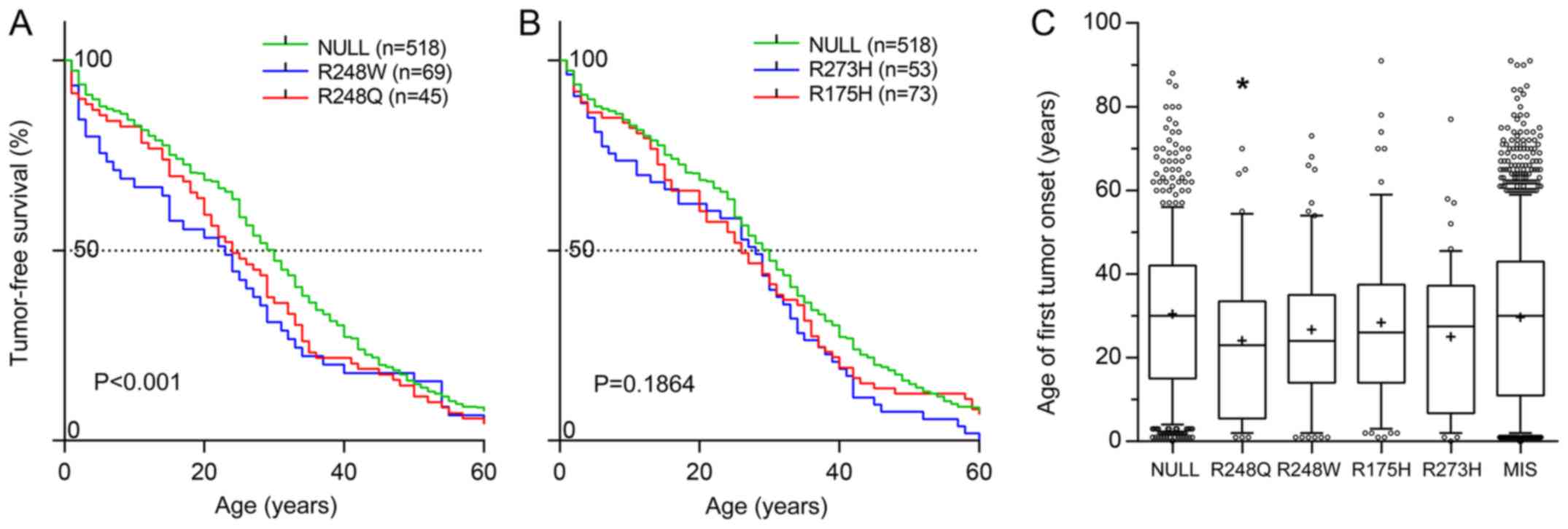
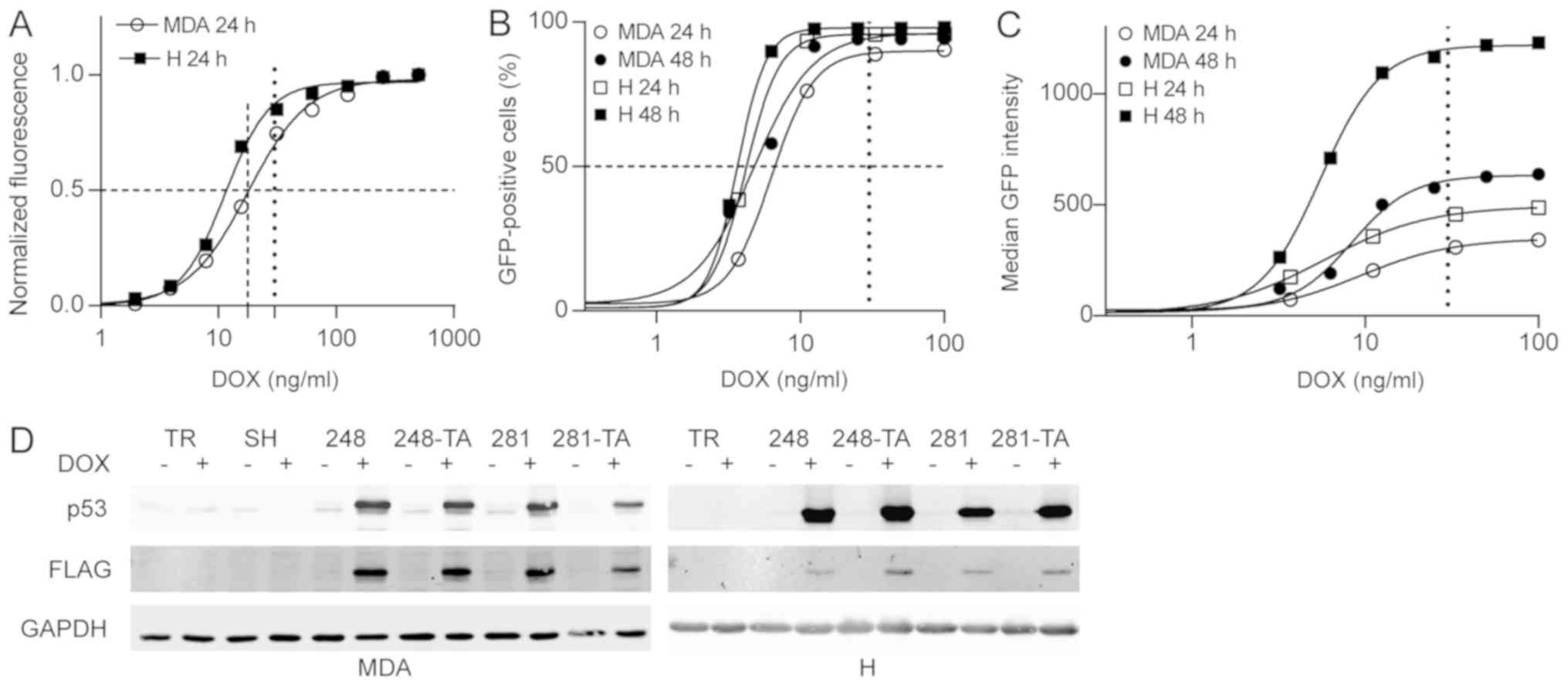
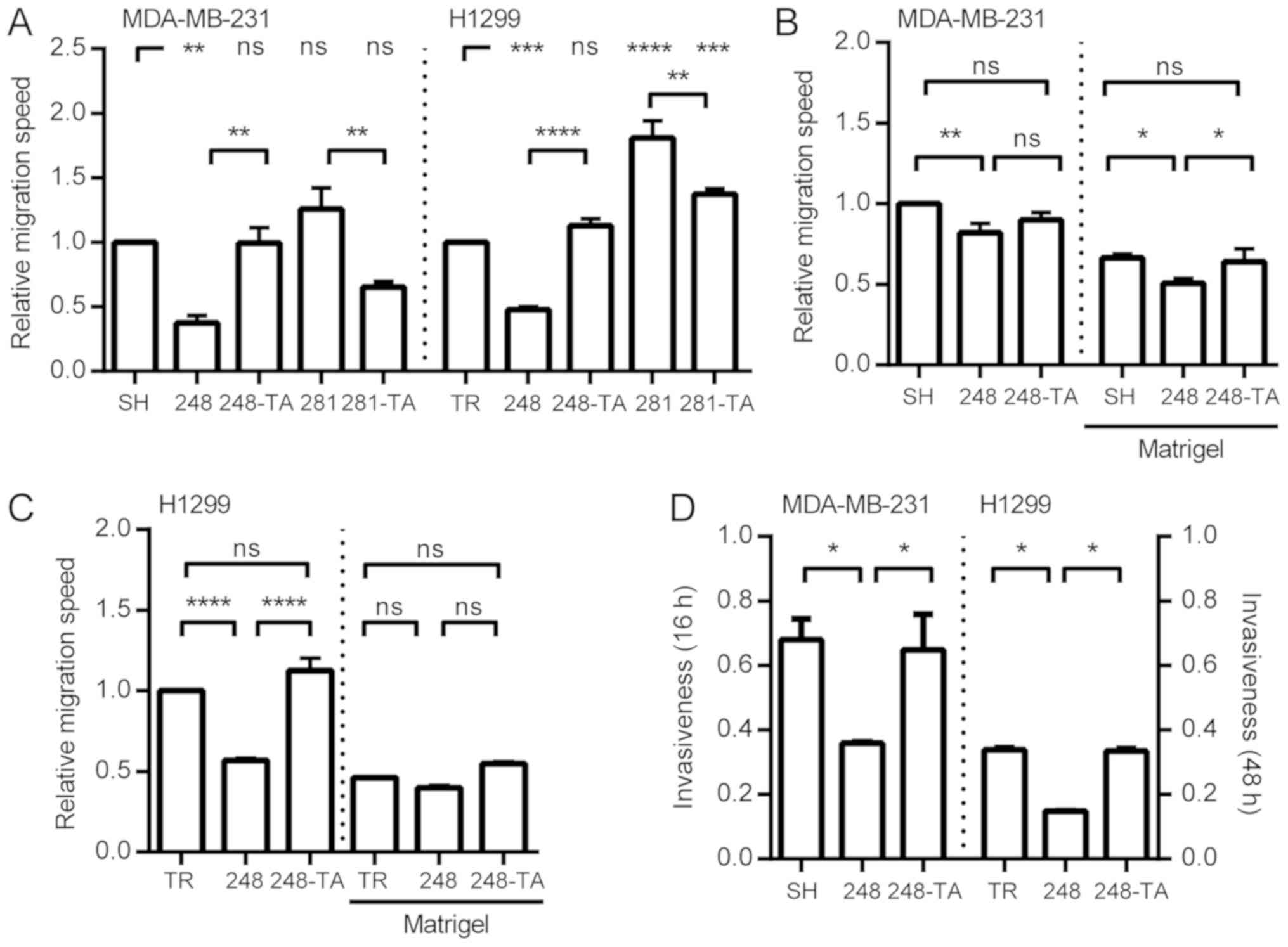
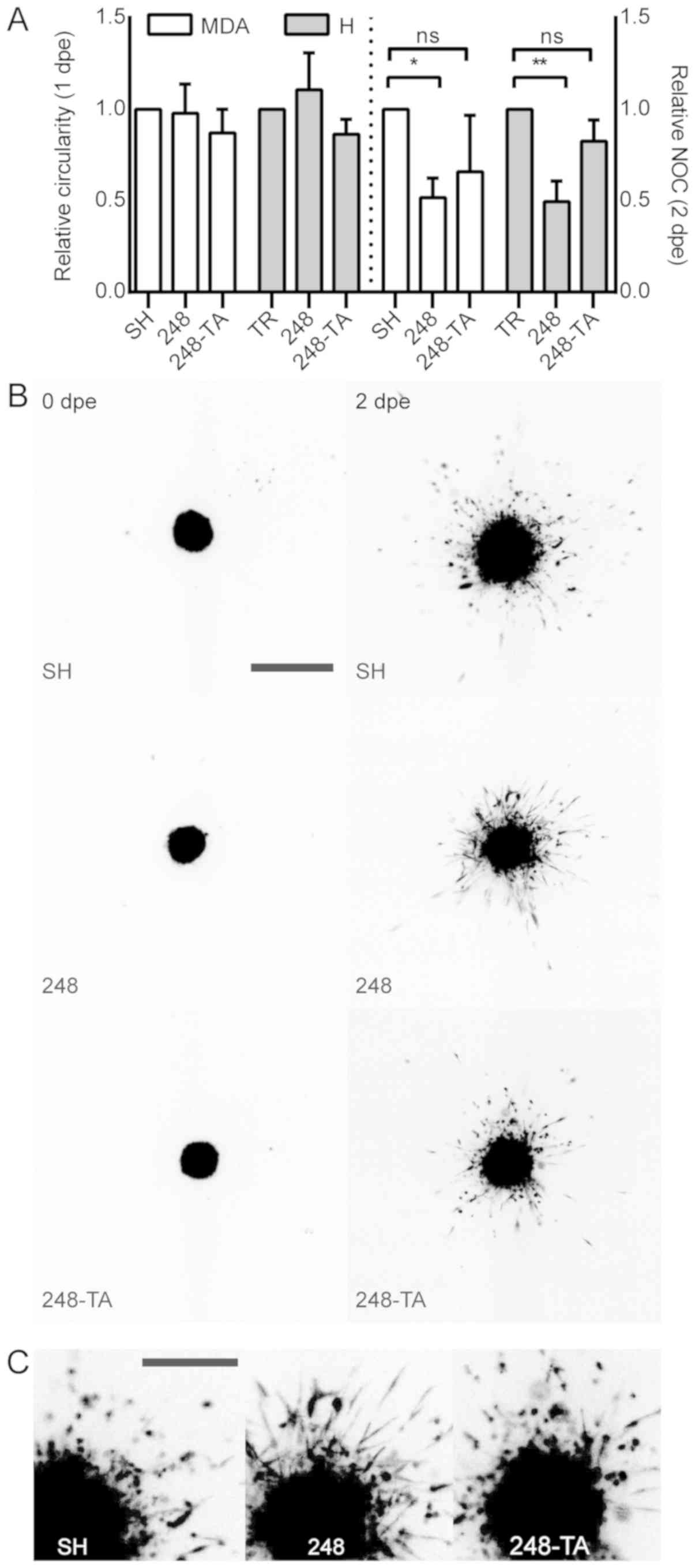
|
1
|
Lane DP: Cancer. p53, guardian of the
genome. Nature. 358:15–16. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL,
Hainaut P and Olivier M: TP53 mutations in human cancers:
Functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes.
Oncogene. 26:2157–2165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Halevy O, Michalovitz D and Oren M:
Different tumor-derived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological
activities. Science. 250:113–116. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Milner J and Medcalf EA: Cotranslation of
activated mutant p53 with wild-type drives the wild-type p53
protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 65:765–774. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan WM, Siu WY, Lau A and Poon RY: How
many mutant p53 molecules are needed to inactivate a tetramer? Mol
Cell Biol. 24:3536–3551. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Willis A, Jung EJ, Wakefield T and Chen X:
Mutant p53 exerts a dominant negative effect by preventing
wild-type p53 from binding to the promoter of its target genes.
Oncogene. 23:2330–2338. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dittmer D, Pati S, Zambetti G, Chu S,
Teresky AK, Moore M, Finlay C and Levine AJ: Gain of function
mutations in p53. Nat Genet. 4:42–46. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aschauer L and Muller PA: Novel targets
and interaction partners of mutant p53 Gain-Of-Function. Biochem
Soc Trans. 44:460–466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shetzer Y, Molchadsky A and Rotter V:
Oncogenic mutant p53 gain of function nourishes the vicious cycle
of tumor development and cancer stem-cell formation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Med. 6:202016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shetzer Y, Solomon H, Koifman G,
Molchadsky A, Horesh S and Rotter V: The paradigm of mutant
p53-expressing cancer stem cells and drug resistance.
Carcinogenesis. 35:1196–1208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pfister NT and Prives C: Transcriptional
regulation by wild-type and cancer-related mutant forms of p53.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 7:262017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu G, McDonnell TJ, Montes de Oca Luna R,
Kapoor M, Mims B, El-Naggar AK and Lozano G: High metastatic
potential in mice inheriting a targeted p53 missense mutation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4174–4179. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lang GA, Iwakuma T, Suh YA, Liu G, Rao VA,
Parant JM, Valentin-Vega YA, Terzian T, Caldwell LC, Strong LC, et
al: Gain of function of a p53 hot spot mutation in a mouse model of
Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cell. 119:861–872. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Olive KP, Tuveson DA, Ruhe ZC, Yin B,
Willis NA, Bronson RT, Crowley D and Jacks T: Mutant p53 gain of
function in two mouse models of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cell.
119:847–860. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu G, Parant JM, Lang G, Chau P,
Chavez-Reyes A, El-Naggar AK, Multani A, Chang S and Lozano G:
Chromosome stability, in the absence of apoptosis, is critical for
suppression of tumorigenesis in Trp53 mutant mice. Nat Genet.
36:63–68. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song H, Hollstein M and Xu Y: p53
gain-of-function cancer mutants induce genetic instability by
inactivating ATM. Nat Cell Biol. 9:573–580. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu DP, Song H and Xu Y: A common gain of
function of p53 cancer mutants in inducing genetic instability.
Oncogene. 29:949–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Hanel W, Marchenko N, Xu S, Yu SX, Weng W
and Moll U: Two hot spot mutant p53 mouse models display
differential gain of function in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ.
20:898–909. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gaiddon C, Lokshin M, Ahn J, Zhang T and
Prives C: A subset of tumor-derived mutant forms of p53
down-regulate p63 and p73 through a direct interaction with the p53
core domain. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1874–1887. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu J, Reumers J, Couceiro JR, De Smet F,
Gallardo R, Rudyak S, Cornelis A, Rozenski J, Zwolinska A, Marine
JC, et al: Gain of function of mutant p53 by coaggregation with
multiple tumor suppressors. Nat Chem Biol. 7:285–295. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wiech M, Olszewski MB, Tracz-Gaszewska Z,
Wawrzynow B, Zylicz M and Zylicz A: Molecular mechanism of mutant
p53 stabilization: The role of HSP70 and MDM2. PLoS One.
7:e514262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muller PA, Caswell PT, Doyle B, Iwanicki
MP, Tan EH, Karim S, Lukashchuk N, Gillespie DA, Ludwig RL,
Gosselin P, et al: Mutant p53 drives invasion by promoting integrin
recycling. Cell. 139:1327–1341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Adorno M, Cordenonsi M, Montagner M,
Dupont S, Wong C, Hann B, Solari A, Bobisse S, Rondina MB, Guzzardo
V, et al: A Mutant-p53/Smad complex opposes p63 to empower
TGFbeta-induced metastasis. Cell. 137:87–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weissmueller S, Manchado E, Saborowski M,
Morris JP IV, Wagenblast E, Davis CA, Moon SH, Pfister NT,
Tschaharganeh DF, Kitzing T, et al: Mutant p53 drives pancreatic
cancer metastasis through cell-autonomous PDGF receptor β
signaling. Cell. 157:382–394. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Subramanian M, Francis P, Bilke S, Li XL,
Hara T, Lu X, Jones MF, Walker RL, Zhu Y, Pineda M, et al: A mutant
p53/let-7i-axis-regulated gene network drives cell migration,
invasion and metastasis. Oncogene. 34:1094–1104. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Alam SK, Yadav VK, Bajaj S, Datta A, Dutta
SK, Bhattacharyya M, Bhattacharya S, Debnath S, Roy S, Boardman LA,
et al: DNA damage-induced ephrin-B2 reverse signaling promotes
chemo-resistance and drives EMT in colorectal carcinoma harboring
mutant p53. Cell Death Differ. 23:707–722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kollareddy M, Dimitrova E, Vallabhaneni
KC, Chan A, Le T, Chauhan KM, Carrero ZI, Ramakrishnan G, Watabe K,
Haupt Y, et al: Regulation of nucleotide metabolism by mutant p53
contributes to its gain-of-function activities. Nat Commun.
6:73892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arjonen A, Kaukonen R, Mattila E, Rouhi P,
Högnäs G, Sihto H, Miller BW, Morton JP, Bucher E, Taimen P, et al:
Mutant p53-associated myosin-X upregulation promotes breast cancer
invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 124:1069–1082. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Scian MJ, Stagliano KE, Ellis MA, Hassan
S, Bowman M, Miles MF, Deb SP and Deb S: Modulation of gene
expression by tumor-derived p53 mutants. Cancer Res. 64:7447–7454.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vaughan CA, Singh S, Grossman SR, Windle
B, Deb SP and Deb S: Gain-of-function p53 activates multiple
signaling pathways to induce oncogenicity in lung cancer cells. Mol
Oncol. 11:696–711. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kogan-Sakin I, Tabach Y, Buganim Y,
Molchadsky A, Solomon H, Madar S, Kamer I, Stambolsky P, Shelly A,
Goldfinger N, et al: Mutant p53(R175H) upregulates Twist1
expression and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
immortalized prostate cells. Cell Death Differ. 18:271–281. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Vaughan CA, Singh S, Windle B, Yeudall WA,
Frum R, Grossman SR, Deb SP and Deb S: Gain-of-Function Activity of
Mutant p53 in Lung Cancer through Up-Regulation of Receptor Protein
Tyrosine Kinase Axl. Genes Cancer. 3:491–502. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cavallaro S: CXCR4/CXCL12 in
non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis to the brain. Int J Mol Sci.
14:1713–1727. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hinton CV, Avraham S and Avraham HK: Role
of the CXCR4/CXCL12 signaling axis in breast cancer metastasis to
the brain. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:97–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL
and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human
breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through
elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yeudall WA, Vaughan CA, Miyazaki H,
Ramamoorthy M, Choi MY, Chapman CG, Wang H, Black E, Bulysheva AA,
Deb SP, et al: Gain-of-function mutant p53 upregulates CXC
chemokines and enhances cell migration. Carcinogenesis. 33:442–451.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Moskovits N, Kalinkovich A, Bar J, Lapidot
T and Oren M: p53 Attenuates cancer cell migration and invasion
through repression of SDF-1/CXCL12 expression in stromal
fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 66:10671–10676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Coradini D, Fornili M, Ambrogi F, Boracchi
P and Biganzoli E: TP53 mutation, epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, and stemlike features in breast cancer subtypes. J
Biomed Biotechnol. 2012.254085:2012.
|
|
41
|
Cordani M, Pacchiana R, Butera G, D’Orazi
G, Scarpa A and Donadelli M: Mutant p53 proteins alter cancer cell
secretome and tumour microenvironment: Involvement in cancer
invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 376:303–309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dong P, Tada M, Hamada J, Nakamura A,
Moriuchi T and Sakuragi N: p53 dominant-negative mutant R273H
promotes invasion and migration of human endometrial cancer HHUA
cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 24:471–483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kalo E, Buganim Y, Shapira KE, Besserglick
H, Goldfinger N, Weisz L, Stambolsky P, Henis YI and Rotter V:
Mutant p53 attenuates the SMAD-dependent transforming growth factor
beta1 (TGF-beta1) signaling pathway by repressing the expression of
TGF-beta receptor type II. Mol Cell Biol. 27:8228–8242. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Campeau E, Ruhl VE, Rodier F, Smith CL,
Rahmberg BL, Fuss JO, Campisi J, Yaswen P, Cooper PK and Kaufman
PD: A versatile viral system for expression and depletion of
proteins in mammalian cells. PLoS One. 4:e65292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press;
Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2001
|
|
46
|
Limame R, Wouters A, Pauwels B, Fransen E,
Peeters M, Lardon F, De Wever O and Pauwels P: Comparative analysis
of dynamic cell viability, migration and invasion assessments by
novel real-time technology and classic endpoint assays. PLoS One.
7:e465362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He S, Lamers GE, Beenakker JW, Cui C,
Ghotra VP, Danen EH, Meijer AH, Spaink HP and Snaar-Jagalska BE:
Neutrophil-mediated experimental metastasis is enhanced by VEGFR
inhibition in a zebrafish xenograft model. J Pathol. 227:431–445.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Petitjean A, Mathe E, Kato S, Ishioka C,
Tavtigian SV, Hainaut P and Olivier M: Impact of mutant p53
functional properties on TP53 mutation patterns and tumor
phenotype: Lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53
database. Hum Mutat. 28:622–629. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zehir A, Benayed R, Shah RH, Syed A,
Middha S, Kim HR, Srinivasan P, Gao J, Chakravarty D, Devlin SM, et
al: Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from
prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 p atients. Nat Med.
23:703–713. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lin J, Teresky AK and Levine AJ: Two
critical hydrophobic amino acids in the N-terminal domain of the
p53 protein are required for the gain of function phenotypes of
human p53 mutants. Oncogene. 10:2387–2390. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin J, Chen J, Elenbaas B and Levine AJ:
Several hydrophobic amino acids in the p53 amino-terminal domain
are required for transcriptional activation, binding to mdm-2 and
the adenovirus 5 E1B 55-kD protein. Genes Dev. 8:1235–1246. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Araki K, Ebata T, Guo AK, Tobiume K, Wolf
SJ and Kawauchi K: p53 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling to
suppress tumor progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:4077–4094. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bon G, Di Carlo SE, Folgiero V, Avetrani
P, Lazzari C, D’Orazi G, Brizzi MF, Sacchi A, Soddu S, Blandino G,
et al: Negative regulation of beta4 integrin transcription by
home-odomain-interacting protein kinase 2 and p53 impairs tumor
progression. Cancer Res. 69:5978–5986. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Janouskova H, Ray AM, Noulet F,
Lelong-Rebel I, Choulier L, Schaffner F, Lehmann M, Martin S,
Teisinger J and Dontenwill M: Activation of p53 pathway by
Nutlin-3a inhibits the expression of the therapeutic target α5
integrin in colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 336:307–318. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Guo AK, Hou YY, Hirata H, Yamauchi S, Yip
AK, Chiam KH, Tanaka N, Sawada Y and Kawauchi K: Loss of p53
enhances NF-κB-dependent lamellipodia formation. J Cell Physiol.
229:696–704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sulzmaier FJ, Jean C and Schlaepfer DD:
FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat
Rev Cancer. 14:598–610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Golubovskaya V, Kaur A and Cance W:
Cloning and characterization of the promoter region of human focal
adhesion kinase gene: Nuclear factor kappa B and p53 binding sites.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1678:111–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tulotta C, Stefanescu C, Beletkaia E,
Bussmann J, Tarbashevich K, Schmidt T and Snaar-Jagalska BE:
Inhibition of signaling between human CXCR4 and zebrafish ligands
by the small molecule IT1t impairs the formation of triple-negative
breast cancer early metastases in a zebrafish xenograft model. Dis
Model Mech. 9:141–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Stoletov K, Kato H, Zardouzian E, Kelber
J, Yang J, Shattil S and Klemke R: Visualizing extravasation
dynamics of metastatic tumor cells. J Cell Sci. 123:2332–2341.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li Y, Drabsch Y, Pujuguet P, Ren J, van
Laar T, Zhang L, van Dam H, Clément-Lacroix P and Ten Dijke P:
Genetic depletion and pharmacological targeting of αv integrin in
breast cancer cells impairs metastasis in zebrafish and mouse
xenograft models. Breast Cancer Res. 17:282015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Truong HH, Xiong J, Ghotra VP, Nirmala E,
Haazen L, Le Dévédec SE, Balcioğlu HE, He S, Snaar-Jagalska BE,
Vreugdenhil E, et al: β1 integrin inhibition elicits a
prometastatic switch through the TGFβ-miR-200-ZEB network in
E-cadherin-positive triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Signal.
7:ra152014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Wahlbuhl M,
Dimmler A, Bauer K, Sultan A, Hlubek F, Jung A, Strand D, Eger A,
et al: The transcriptional repressor ZEB1 promotes metastasis and
loss of cell polarity in cancer. Cancer Res. 68:537–544. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC,
Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D,
zur Hausen A, et al: The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity
by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol.
11:1487–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang P, Sun Y and Ma L: ZEB1: At the
crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and
therapy resistance. Cell Cycle. 14:481–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dong P, Karaayvaz M, Jia N, Kaneuchi M,
Hamada J, Watari H, Sudo S, Ju J and Sakuragi N: Mutant p53
gain-of-function induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
modulation of the miR-130b-ZEB1 axis. Oncogene. 32:3286–3295. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Jeong D, Park S, Kim H, Kim CJ, Ahn TS,
Bae SB, Kim HJ, Kim TH, Im J, Lee MS, et al: RhoA is associated
with invasion and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
48:714–722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
O’Connor K and Chen M: Dynamic functions
of RhoA in tumor cell migration and invasion. Small GTPases.
4:141–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Choi DS, Stark DJ, Raphael RM, Wen J, Su
J, Zhou X, Chang CC and Zu Y: SDF-1α stiffens myeloma bone marrow
mesenchymal stromal cells through the activation of
RhoA-ROCK-Myosin II. Int J Cancer. 136:E219–E229. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|