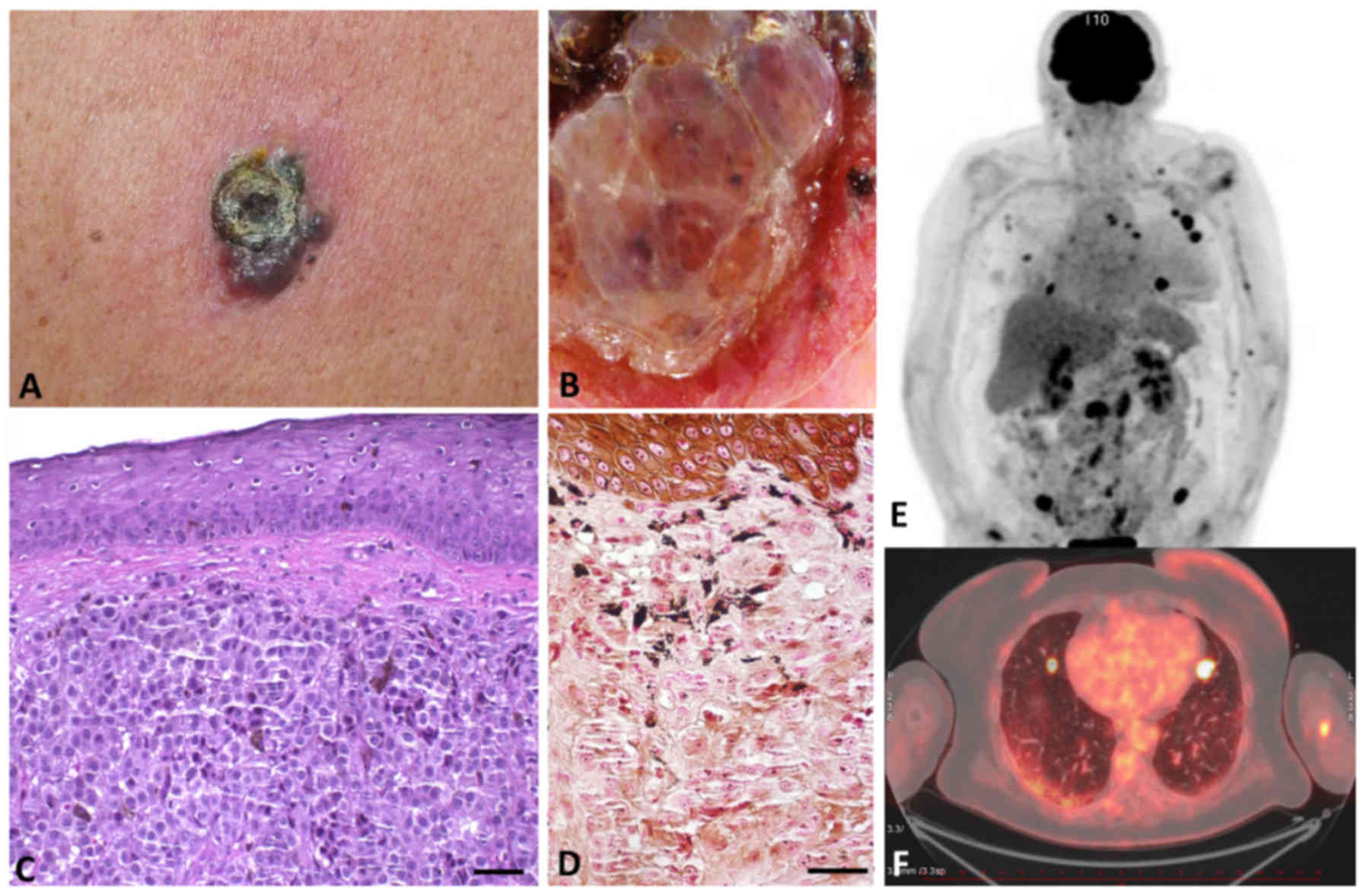
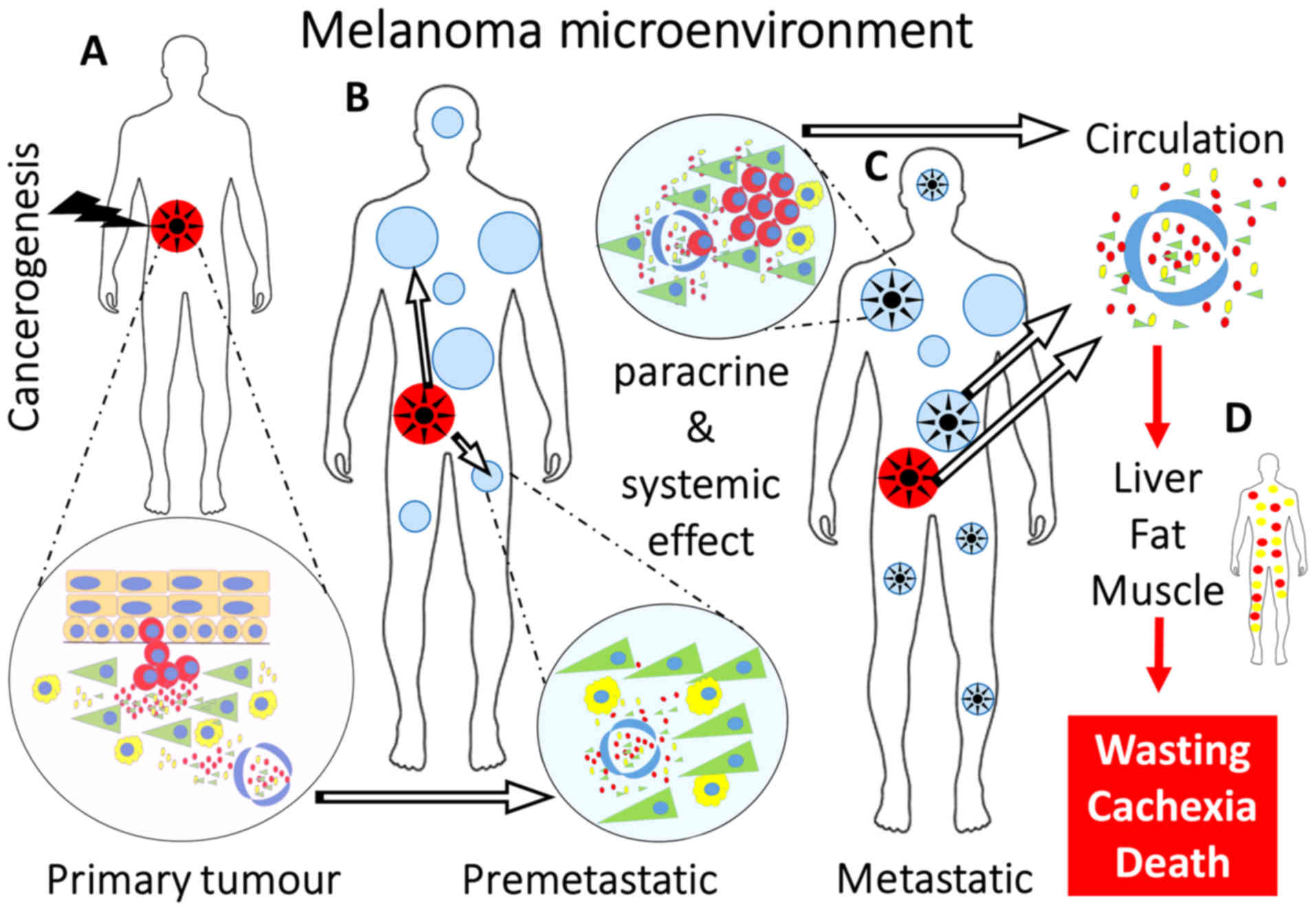
|
1
|
Sacchetto L, Zanetti R, Comber H,
Bouchardy C, Brewster DH, Broganelli P, Chirlaque MD, Coza D,
Galceran J, Gavin A, et al: Trends in incidence of thick, thin and
in situ melanoma in Europe. Eur J Cancer. 92:108–118. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rabbie R, Ferguson P, Molina-Aguilar C,
Adams DJ and Robles-Espinoza CD: Melanoma subtypes: Genomic
profiles, prognostic molecular markers and therapeutic
possibilities. J Pathol. 247:539–551. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Lorentzen HF: Targeted therapy for
malignant melanoma. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 46:116–121. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet. 133:571–573. 1889.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Faries MB, Thompson JF, Cochran AJ,
Andtbacka RH, Mozzillo N, Zager JS, Jahkola T, Bowles TL, Testori
A, Beitsch PD, et al: Completion dissection or observation for
sentinel-node metastasis in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 376:2211–2222.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nathanson SD: Insights into the mechanisms
of lymph node metastasis. Cancer. 98:413–423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barth A, Wanek LA and Morton DL:
Prognostic factors in 1,521 melanoma patients with distant
metastases. J Am Coll Surg. 181:193–201. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Damsky WE Jr and Bosenberg M: Mouse
melanoma models and cell lines. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
23:853–859. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abdel-Ghany M, Cheng HC, Elble RC and
Pauli BU: The breast cancer ß 4 integrin and endothelial human
CLCA2 mediate lung metastasis. J Biol Chem. 276:25438–25446. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tawbi HA, Boutros C, Kok D, Robert C and
McArthur G: New era in the management of melanoma brain metastases.
Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 38:741–750. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Menter DG, Herrmann JL and Nicolson GL:
The role of trophic factors and autocrine/paracrine growth factors
in brain metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 13:67–88. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balch CM, Houghton AN, Sober AJ and Soong
S: Cutaneous Melanoma, 4th Edition. Dermatologic Surg. 31:1715.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Murakami T, Cardones AR and Hwang ST:
Chemokine receptors and melanoma metastasis. J Dermatol Sci.
36:71–78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martinez-Rodriguez M, Thompson AK and
Monteagudo C: High CCL27 immunoreactivity in 'supratumoral'
epidermis correlates with better prognosis in patients with
cutaneous malignant melanoma. J Clin Pathol. 70:15–19. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ben-Baruch A: Organ selectivity in
metastasis: Regulation by chemokines and their receptors. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:345–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Marcoval J, Ferreres JR, Martrn C, Gomez
S, Penrn RM, Ochoa de Olza M and Fabra À: Patterns of Visceral
Metastasis in Cutaneous Melanoma: A Descriptive Study. Actas
Dermosifiliog. 104:593–597. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Adler NR, Wolfe R, Kelly JW, Haydon A,
McArthur GA, McLean CA and Mar VJ: Tumour mutation status and sites
of metastasis in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Br J Cancer.
117:1026–1035. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Holt JB, Sangueza OP, Levine EA, Shen P,
Bergman S, Geisinger KR and Creager AJ: Nodal melanocytic nevi in
sentinel lymph nodes. Correlation with melanoma-associated
cutaneous nevi. Am J Clin Pathol. 121:58–63. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ji Y, Hao H, Reynolds K, McMahon M and
Zhou CJ: Wnt signaling in neural crest ontogenesis and oncogenesis.
Cells. 8:11732019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Lim J, Thiery JP, Kassem Y, Kalcheim C,
Moens CB, Burden SJ and Granato M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions: Insights from development. Development. 139:3471–3486.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mayor R and Theveneau E: The neural crest.
Development. 140:2247–2251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hall BK: The neural crest and neural crest
cells: Discovery and significance for theories of embryonic
organization. J Biosci. 33:781–793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mort RL, Jackson IJ and Patton EE: The
melanocyte lineage in development and disease. Development.
142:620–632. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Duband JL, Monier F, Delannet M and
Newgreen D: Epithelium-mesenchyme transition during neural crest
development. Acta Anat (Basel). 154:63–78. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vega-Lopez GA, Cerrizuela S and Aybar MJ:
Trunk neural crest cells: Formation, migration and beyond. Int J
Dev Biol. 61:5–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Larribère L and Utikal J: Stem
cell-derived models of neural crest are essential to understand
melanoma progression and therapy resistance. Front Mol Neurosci.
12:1112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gallik KL, Treffy RW, Nacke LM, Ahsan K,
Rocha M, Green-Saxena A and Saxena A: Neural crest and cancer:
Divergent travelers on similar paths. Mech Dev. 148:89–99. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sieber-Blum M and Grim M: The adult hair
follicle: Cradle for pluripotent neural crest stem cells. Birth
Defects Res C Embryo Today. 72:162–172. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Person F, Wilczak W, Hube-Magg C,
Burdelski C, Moller-Koop C, Simon R, Noriega M, Sauter G, Steurer
S, Burdak-Rothkamm S, et al: Prevalence of pIII-tubulin (TUBB3)
expression in human normal tissues and cancers. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177121662017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Stasiak M, Boncela J, Perreau C, Karamanou
K, Chatron-Colliet A, Proult I, Przygodzka P, Chakravarti S,
Maquart FX, Kowalska MA, et al: Lumican inhibits SNAIL-induced
melanoma cell migration specifically by blocking MMP-14 activity.
PLoS One. 11:e01502262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang X, Liang R, Liu C, Liu JA, Cheung
MPL, Liu X, Man OY, Guan XY, Lung HL and Cheung M: SOX9 is a
dose-dependent metastatic fate determinant in melanoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee H, Torres FX, McLean SA, Chen R and
Lee MW: Immunophenotypic heterogeneity of primary sinonasal
melanoma with aberrant expression of neuroendocrine markers and
calponin. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 19:48–53. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tudrej KB, Czepielewska E and
Kozlowska-Wojciechowska M: SOX10-MITF pathway activity in melanoma
cells. Arch Med Sci. 13:1493–1503. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwakami Y, Yokoyama S, Watanabe K and
Hayakawa Y: STAM-binding protein regulates melanoma metastasis
through SLUG stabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
507:484–488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goding CR and Arnheiter H: MITF-the first
25 years. Genes Dev. 33:983–1007. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Campbell K, Kumarapeli AR, Gokden N, Cox
RM, Hutchins L and Gardner JM: Metastatic melanoma with
dedifferentiation and extensive rhabdomyosarcomatous heterologous
component. J Cutan Pathol. 45:360–364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krejci E and Grim M: Isolation and
characterization of neural crest stem cells from adult human hair
follicles. Folia Biol (Praha). 56:149–157. 2010.
|
|
38
|
Marzagalli M, Raimondi M, Fontana F,
Montagnani Marelli M, Moretti RM and Limonta P: Cellular and
molecular biology of cancer stem cells in melanoma: Possible
therapeutic implications. Semin Cancer Biol. 59:221–235. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kasemeier-Kulesa JC, Teddy JM, Postovit
LM, Seftor EA, Seftor REB, Hendrix MJC and Kulesa PM: Reprogramming
multipotent tumor cells with the embryonic neural crest
microenvironment. Dev Dyn. 237:2657–2666. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kaufman CK, Mosimann C, Fan ZP, Yang S,
Thomas AJ, Ablain J, Tan JL, Fogley RD, van Rooijen E, Hagedorn EJ,
et al: A zebrafish melanoma model reveals emergence of neural crest
identity during melanoma initiation. Science. 351:aad21972016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Agnoletto C, Corrà F, Minotti L,
Baldassari F, Crudele F, Cook WJJ, Di Leva G, d'Adamo AP, Gasparini
P and Volinia S: Heterogeneity in circulating tumor cells: The
relevance of the stem-cell subset. Cancers (Basel). 11:112019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gkountela S and Aceto N: Stem-like
features of cancer cells on their way to metastasis. Biol Direct.
11:332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Empringham B, Chiang KY and Krueger J:
Collection of hematopoietic stem cells and immune effector cells in
small children. Transfus Apheresis Sci. 57:614–618. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Feehan J, Nurgali K, Apostolopoulos V, Al
Saedi A and Duque G: Circulating osteogenic precursor cells:
Building bone from blood. EBioMedicine. 39:603–611. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Ratajczak MZ, Bujko K, Mack A, Kucia M and
Ratajczak J: Cancer from the perspective of stem cells and
misappropriated tissue regeneration mechanisms. Leukemia.
32:2519–2526. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lacina L, Plzak J, Kodet O, Szabo P,
Chovanec M, Dvorankova B and Smetana K Jr: Cancer microenvironment:
What can we learn from the stem cell niche. Int J Mol Sci.
16:24094–24110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hill BS, Pelagalli A, Passaro N and
Zannetti A: Tumor-educated mesenchymal stem cells promote
pro-metastatic phenotype. Oncotarget. 8:73296–73311. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Plzak J, Boucek J, Bandurova V, Kolar M,
Hradilova M, Szabo P, Lacina L, Chovanec M and Smetana K Jr: The
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment as a
potential target for cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 11:112019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lacina L, Kodet O, Dvorankova B, Szabo P
and Smetana K Jr: Ecology of melanoma cell. Histol Histopathol.
33:247–254. 2018.
|
|
50
|
Preisner F, Leimer U, Sandmann S, Zoernig
I, Germann G and Koellensperger E: Impact of human adipose
tissue-derived stem cells on malignant melanoma cells in an in
vitro co-culture model. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 14:125–140. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Dvorankova B, Smetana K Jr, Rihova B,
Kucera J, Mateu R and Szabo P: Cancer-associated fibroblasts are
not formed from cancer cells by epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in nu/nu mice. Histochem Cell Biol. 143:463–469. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Inada M, Takita M, Yokoyama S, Watanabe K,
Tominari T, Matsumoto C, Hirata M, Maru Y, Maruyama T, Sugimoto Y,
et al: Direct melanoma cell contact induces stromal cell autocrine
prostaglandin E2-EP4 receptor signaling that drives tumor growth,
angiogenesis, and metastasis. J Biol Chem. 290:29781–29793. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ziani L, Safta-Saadoun TB, Gourbeix J,
Cavalcanti A, Robert C, Favre G, Chouaib S and Thiery J:
Melanoma-associated fibroblasts decrease tumor cell susceptibility
to NK cell-mediated killing through matrix-metalloproteinases
secretion. Oncotarget. 8:19780–19794. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kodet O, Lacina L, Krejci E, Dvorankova B,
Grim M, Stork J, Kodetova D, Vlcek C, Sachova J, Kolar M, et al:
Melanoma cells influence the differentiation pattern of human
epidermal keratinocytes. Mol Cancer. 14:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Van Kilsdonk JWJ, Bergers M, Van Kempen
LCLT, Schalkwijk J and Swart GWM: Keratinocytes drive melanoma
invasion in a reconstructed skin model. Melanoma Res. 20:372–380.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ciolczyk-Wierzbicka D and Laidler P: The
inhibition of invasion of human melanoma cells through N-cadherin
knock-down. Med Oncol. 35:422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chung H, Jung H, Jho EH, Multhaupt HAB,
Couchman JR and Oh ES: Keratinocytes negatively regulate the
N-cadherin levels of melanoma cells via contact-mediated calcium
regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:615–620. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nikkola J, Vihinen P, Vlaykova T,
Hahka-Kemppinen M, Heino J and Pyrhonen S: Integrin chains |31 and
alphav as prognostic factors in human metastatic melanoma. Melanoma
Res. 14:29–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Van Belle PA, Elenitsas R, Satyamoorthy K,
Wolfe JT, Guerry D IV, Schuchter L, Van Belle TJ, Albelda S, Tahin
P, Herlyn M, et al: Progression-related expression of |33 integrin
in melanomas and nevi. Hum Pathol. 30:562–567. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li G, Satyamoorthy K, Meier F, Berking C,
Bogenrieder T and Herlyn M: Function and regulation of
melanoma-stromal fibroblast interactions: When seeds meet soil.
Oncogene. 22:3162–3171. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Brandner JM and Haass NK: Melanoma's
connections to the tumour microenvironment. Pathology. 45:443–452.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Peitsch WK, Doerflinger Y, Fischer-Colbrie
R, Huck V, Bauer AT, Utikal J, Goerdt S and Schneider SW:
Desmoglein 2 depletion leads to increased migration and
upregulation of the chemoattractant secretoneurin in melanoma
cells. PLoS One. 9:e894912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tan LY, Mintoff C, Johan MZ, Ebert BW,
Fedele C, Zhang YF, Szeto P, Sheppard KE, McArthur GA, Foster-Smith
E, et al: Desmoglein 2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry in melanoma
and is associated with poor clinical outcome. Oncotarget.
7:46492–46508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Klemke M, Weschenfelder T, Konstandin MH
and Samstag Y: High affinity interaction of integrin a4pi (VLA-4)
and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) enhances migration
of human melanoma cells across activated endothelial cell layers. J
Cell Physiol. 212:368–374. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lacaria L, Lange JR, Goldmann WH, Rico F
and Alonso JL: av|33 integrin expression increases elasticity in
human melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 525:836–840.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bedogni B: Notch signaling in melanoma:
Interacting pathways and stromal influences that enhance Notch
targeting. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27:162–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Jobe NP, Rosel D, Dvorankova B, Kodet O,
Lacina L, Mateu R, Smetana K and Brabek J: Simultaneous blocking of
IL-6 and IL-8 is sufficient to fully inhibit CAF-induced human
melanoma cell invasiveness. Histochem Cell Biol. 146:205–217. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jobe NP, Zivicova V, Mifkova A, Rosel D,
Dvorankova B, Kodet O, Strnad H, Kolar M, Sedo A, Smetana K Jr, et
al: Fibroblasts potentiate melanoma cells in vitro invasiveness
induced by UV-irradiated keratinocytes. Histochem Cell Biol.
149:503–516. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Strnadova K, Sandera V, Dvorankova B,
Kodet O, Duskova M, Smetana K and Lacina L: Skin aging: The dermal
perspective. Clin Dermatol. 37:326–335. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Payne AS and Cornelius LA: The role of
chemokines in melanoma tumor growth and metastasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 118:915–922. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Gebhardt C, Averbeck M, Viertel A, Kauer
F, Saalbach A, Anderegg U and Simon JC: Ultraviolet-B irradiation
enhances melanoma cell motility via induction of autocrine
interleukin 8 secretion. Exp Dermatol. 16:636–643. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Araki K, Shimura T, Yajima T, Tsutsumi S,
Suzuki H, Okada K, Kobayashi T, Raz A and Kuwano H: Phosphoglucose
isomerase/autocrine motility factor promotes melanoma cell
migration through ERK activation dependent on autocrine production
of interleukin-8. J Biol Chem. 284:32305–32311. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kemp DM, Pidich A, Larijani M, Jonas R,
Lash E, Sato T, Terai M, De Pizzol M, Allegretti M, Igoucheva O, et
al: Ladarixin, a dual CXCR1/2 inhibitor, attenuates experimental
melanomas harboring different molecular defects by affecting
malignant cells and tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget.
8:14428–14442. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Brennecke S, Deichmann M, Naeher H and
Kurzen H: Decline in angiogenic factors, such as interleukin-8,
indicates response to chemotherapy of metastatic melanoma. Melanoma
Res. 15:515–522. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Gabellini C, Trisciuoglio D, Desideri M,
Candiloro A, Ragazzoni Y, Orlandi A, Zupi G and Del Bufalo D:
Functional activity of CXCL8 receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, on human
malignant melanoma progression. Eur J Cancer. 45:2618–2627. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Nürnberg W, Tobias D, Otto F, Henz BM and
Schadendorf D: Expression of interleukin-8 detected by in situ
hybridization correlates with worse prognosis in primary cutaneous
melanoma. J Pathol. 189:546–551. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ortega-Bernal D, La Rosa CHG,
Arechaga-Ocampo E, Alvarez-Avitia MA, Moreno NS and Rangel-Escareno
C: A meta-analysis of transcriptome datasets characterizes
malignant transformation from melanocytes and nevi to melanoma.
Oncol Lett. 16:1899–1911. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Adamski V, Mentlein R, Lucius R, Synowitz
M, Held-Feindt J and Hattermann K: The chemokine receptor CXCR6
evokes reverse signaling via the transmembrane chemokine CXCL16.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
da Silva WC, Oshiro TM, de Sa DC, Franco
DDGS, Festa Neto C and Pontillo A: Genotyping and differential
expression analysis of inflammasome genes in sporadic malignant
melanoma reveal novel contribution of CARD8, IL1B and IL18 in
melanoma susceptibility and progression. Cancer Genet. 209:474–480.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lacina L, Brabek J, Kral V, Kodet O and
Smetana K Jr: Interleukin-6: A molecule with complex biological
impact in cancer. Histol Histopathol. 34:125–136. 2019.
|
|
81
|
Armstrong CA, Murray N, Kennedy M, Koppula
SV, Tara D and Ansel JC: Melanoma-derived interleukin 6 inhibits in
vivo melanoma growth. J Invest Dermatol. 102:278–284. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lu C and Kerbel RS: Interleukin-6
undergoes transition from paracrine growth inhibitor to autocrine
stimulator during human melanoma progression. J Cell Biol.
120:1281–1288. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Elias EG, Hasskamp JH and Sharma BK:
Cytokines and growth factors expressed by human cutaneous melanoma.
Cancers (Basel). 2:794–808. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Linnskog R, Jönsson G, Axelsson L, Prasad
CP and Andersson T: Interleukin-6 drives melanoma cell motility
through p38a-MAPK-dependent up-regulation of WNT5A expression. Mol
Oncol. 8:1365–1378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Karst AM, Gao K, Nelson CC and Li G:
Nuclear factor kappa B subunit p50 promotes melanoma angiogenesis
by upregulating interleukin-6 expression. Int J Cancer.
124:494–501. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Nagai H, Oniki S, Fujiwara S, Xu M,
Mizoguchi I, Yoshimoto T and Nishigori C: Antitumor activities of
interleukin-27 on melanoma. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug
Targets. 10:41–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Shinozaki Y, Wang S, Miyazaki Y, Miyazaki
K, Yamada H, Yoshikai Y, Hara H and Yoshida H: Tumor-specific
cytotoxic T cell generation and dendritic cell function are
differentially regulated by interleukin 27 during development of
anti-tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 124:1372–1378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Chiba Y, Mizoguchi I, Mitobe K, Higuchi K,
Nagai H, Nishigori C, Mizuguchi J and Yoshimoto T: IL-27 enhances
the expression of TRAIL and TLR3 in human melanomas and inhibits
their tumor growth in cooperation with a TLR3 agonist poly(I:C)
partly in a TRAIL-dependent manner. PLoS One. 8:e761592013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bisevac JP, Stanojevic I, Mijuskovic Z,
Banovic T, Djukic M and Vojvodic D: High interleukin 27 production
is associated with early clinical stage and localized disease in
patients with melanoma. J Med Biochem. 35:443–450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Onoue K, Kusubashi H, Sato Y, Wakitani S
and Takagi M: Quantitative correlation between production rate of
melanoma inhibitory activity and aggrecan gene expression level
during differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells to chondrocytes
and redifferentiation of chondrocytes. J Biosci Bioeng.
111:594–596. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Decarlo K, Yang S, Emley A, Wajapeyee N,
Green M and Mahalingam M: Oncogenic BRAF-positive dysplastic nevi
and the tumor suppressor IGFBP7 - challenging the concept of
dysplastic nevi as precursor lesions? Hum Pathol. 41:886–894. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yotsumoto F, Yagi H, Suzuki SO, Oki E,
Tsujioka H, Hachisuga T, Sonoda K, Kawarabayashi T, Mekada E and
Miyamoto S: Validation of HB-EGF and amphiregulin as targets for
human cancer therapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 365:555–561.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Marchetti D and Nicolson GL: Neurotrophin
stimulation of human melanoma cell invasion: Selected enhancement
of heparanase activity and heparanase degradation of specific
heparan sulfate subpopulations. Adv Enzyme Regul. 37:111–134. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Antunes LCM, Cartell A, de Farias CB,
Bakos RM, Roesler R and Schwartsmann G: Tropomyosin-related kinase
receptor and neurotrophin expression in cutaneous melanoma is
associated with a poor prognosis and decreased survival. Oncology.
97:26–37. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Li JR, Wang JQ, Gong Q, Fang RH and Guo
YL: MicroRNA-328 inhibits proliferation of human melanoma cells by
targeting TGFp2. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:1575–1579. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Hutchenreuther J, Vincent K, Norley C,
Racanelli M, Gruber SB, Johnson TM, Fullen DR, Raskin L, Perbal B,
Holdsworth DW, et al: Activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts
is required for tumor neovascularization in a murine model of
melanoma. Matrix Biol. 74:52–61. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Straussman R, Morikawa T, Shee K,
Barzily-Rokni M, Qian ZR, Du J, Davis A, Mongare MM, Gould J,
Frederick DT, et al: Tumour micro-environment elicits innate
resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature.
487:500–504. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Capparelli C, Rosenbaum S, Berger AC and
Aplin AE: Fibroblast-derived neuregulin 1 promotes compensatory
ErbB3 receptor signaling in mutant BRAF melanoma. J Biol Chem.
290:24267–24277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ruivo CF, Adem B, Silva M and Melo SA: The
biology of cancer exosomes: Insights and new perspectives. Cancer
Res. 77:6480–6488. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hood JL: Melanoma exosome induction of
endothelial cell GM-CSF in pre-metastatic lymph nodes may result in
different M1 and M2 macrophage mediated angiogenic processes. Med
Hypotheses. 94:118–122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Xiao D, Barry S, Kmetz D, Egger M, Pan J,
Rai SN, Qu J, McMasters KM and Hao H: Melanoma cell-derived
exosomes promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary
melanocytes through paracrine/autocrine signaling in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 376:318–327. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Gowda R, Robertson BM, Iyer S, Barry J,
Dinavahi SS and Robertson GP: The role of exosomes in metastasis
and progression of melanoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 85:1019752020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gajos-Michniewicz A and Czyz M: Role of
mirnas in melanoma metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 11:112019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Clayton A, Mitchell JP, Court J, Mason MD
and Tabi Z: Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair
lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 67:7458–7466.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Gerloff D, Lützkendorf J, Moritz RKC,
Wersig T, Mader K, Müller LP and Sunderkotter C: Melanoma-derived
exosomal mir-125b-5p educates tumor associated macrophages (TAMs)
by targeting lysosomal acid lipase A (LIPA). Cancers (Basel).
12:122020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Bardi GT, Smith MA and Hood JL: Melanoma
exosomes promote mixed M1 and M2 macrophage polarization. Cytokine.
105:63–72. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Gershenwald JE and Scolyer RA: Melanoma
Staging: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition and
Beyond. Ann Surg Oncol. 25:2105–2110. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Michielin O, van Akkooi ACJ, Ascierto PA,
Dummer R and Keilholz U; ESMO Guidelines Committee: Electronic
address: simpleclinicalguidelines@esmo.org:
Cutaneous melanoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 30:1884–1901. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Riechers A and Bosserhoff AK: Melanoma
inhibitory activity in melanoma diagnostics and therapy - a small
protein is looming large. Exp Dermatol. 23:12–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Forgber M, Trefzer U, Sterry W and Walden
P: Proteome serological determination of tumor-associated antigens
in melanoma. PLoS One. 4:e51992009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Muqaku B, Eisinger M, Meier SM, Tahir A,
Pukrop T, Haferkamp S, Slany A, Reichle A and Gerner C: Multi-omics
analysis of serum samples demonstrates reprogramming of organ
functions via systemic calcium mobilization and platelet activation
in metastatic melanoma. Mol Cell Proteomics. 16:86–99. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
112
|
Weber JS, Sznol M, Sullivan RJ, Blackmon
S, Boland G, Kluger HM, Halaban R, Bacchiocchi A, Ascierto PA,
Capone M, et al: A serum protein signature associated with outcome
after anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res.
6:79–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Hoejberg L, Bastholt L, Johansen JS,
Christensen IJ, Gehl J and Schmidt H: Serum interleukin-6 as a
prognostic biomarker in patients with metastatic melanoma. Melanoma
Res. 22:287–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Correa D, Somoza RA, Lin P, Schiemann WP
and Caplan AI: Mesenchymal stem cells regulate melanoma cancer
cells extravasation to bone and liver at their perivascular niche.
Int J Cancer. 138:417–427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
115
|
Gandalovicova A, Rosel D, Fernandes M,
Vesely P, Heneberg P, Cermak V, Petruzelka L, Kumar S, Sanz-Moreno
V and Brabek J: Migrastatics-anti-metastatic and anti-invasion
Drugs: Promises and challenges. Trends Cancer. 3:391–406. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Herman H, Fazakas C, Hasko J, Molnar K,
Mészaros A, Nyul-Toth A, Szabo G, Erdélyi F, Ardelean A, Hermenean
A, et al: Paracellular and transcellular migration of metastatic
cells through the cerebral endothelium. J Cell Mol Med.
23:2619–2631. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Kucera R, Topolcan O, Treskova I,
Kinkorova J, Windrichova J, Fuchsova R, Svobodova S, Treska V,
Babuska V, Novak J, et al: Evaluation of IL-2, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10
in malignant melanoma diagnostics. Anticancer Res. 35:3537–3541.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Sanmamed MF, Carranza-Rua O, Alfaro C,
Onate C, Martin-Algarra S, Perez G, Landazuri SF, Gonzalez A, Gross
S, Rodriguez I, et al: Serum interleukin-8 reflects tumor burden
and treatment response across malignancies of multiple tissue
origins. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5697–5707. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kucera J, Strnadova K, Dvorankova B,
Lacina L, Krajsova I, Stork J, Kovarova H, Skalmkova HK, Vodicka P,
Motlik J, et al: Serum proteomic analysis of melanoma patients with
immunohistochemical profiling of primary melanomas and cultured
cells: Pilot study. Oncol Rep. 42:1793–1804. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Pelletier F, Bermont L, Puzenat E, Blanc
D, Cairey-Remonnay S, Mougin C, Laurent R, Humbert P and Aubin F:
Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor in cutaneous
malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 152:685–689. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ugurel S, Rappl G, Tilgen W and Reinhold
U: Increased serum concentration of angiogenic factors in malignant
melanoma patients correlates with tumor progression and survival. J
Clin Oncol. 19:577–583. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Krasagakis K, Tholke D, Farthmann B,
Eberle J, Mansmann U and Orfanos CE: Elevated plasma levels of
transforming growth factor (TGF)-pi and TGF-|32 in patients with
disseminated malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer. 77:1492–1494. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tuccitto A, Tazzari M, Beretta V, Rini F,
Miranda C, Greco A, Santinami M, Patuzzo R, Vergani B, Villa A, et
al: Immunomodulatory factors control the fate of melanoma tumor
initiating cells. Stem Cells. 34:2449–2460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Tung KH, Ernstoff MS, Allen C and Shu S: A
Review of exosomes and their role in the tumor microenvironment and
host-tumor 'macroenvironment'. J Immunol Sci. 3:4–8. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
125
|
Shu S, Yang Y, Allen CL, Maguire O,
Minderman H, Sen A, Ciesielski MJ, Collins KA, Bush PJ, Singh P, et
al: Metabolic reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts by melanoma
exosome microRNA favours a pre-metastatic microenvironment. Sci
Rep. 8:129052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Kodet O, Dvorankova B, Bendlova B,
Sykorova V, Krajsova I, Stork J, Kucera J, Szabo P, Strnad H, Kolar
M, et al: Microenvironment driven resistance to B Raf inhibition in
a melanoma patient is accompanied by broad changes of gene
methylation and expression in distal fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med.
41:2687–2703. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Jouve N, Bachelier R, Despoix N, Blin MG,
Matinzadeh MK, Poitevin S, Aurrand-Lions M, Fallague K, Bardin N,
Blot-Chabaud M, et al: CD146 mediates vEGF-induced melanoma cell
extravasation through FAK activation. Int J Cancer. 137:50–60.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Hamilla SM, Stroka KM and Aranda-Espinoza
H: VE-cadherin-independent cancer cell incorporation into the
vascular endothelium precedes transmigration. PLoS One.
9:e1097482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Kim KJ, Kwon SH, Yun JH, Jeong HS, Kim HR,
Lee EH, Ye SK and Cho CH: STAT3 activation in endothelial cells is
important for tumor metastasis via increased cell adhesion molecule
expression. Oncogene. 36:5445–5459. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Borgenström M, Wärri A, Hiilesvuo K,
Käkönen R, Käkönen S, Nissinen L, Pihlavisto M, Marjamäki A,
Vlodavsky I, Naggi A, et al: O-sulfated bacterial polysaccharides
with low anticoagulant activity inhibit metastasis. Semin Thromb
Hemost. 33:547–556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Dange MC, Srinivasan N, More SK, Bane SM,
Upadhya A, Ingle AD, Gude RP, Mukhopadhyaya R and Kalraiya RD:
Galectin-3 expressed on different lung compartments promotes organ
specific metastasis by facilitating arrest, extravasation and organ
colonization via high affinity ligands on melanoma cells. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 31:661–673. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Desch A, Strozyk EA, Bauer AT, Huck V,
Niemeyer V, Wieland T and Schneider SW: Highly invasive melanoma
cells activate the vascular endothelium via an MMP-2/integrin
αvβ5-induced secretion of VEGF-A. Am J Pathol. 181:693–705. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Tsukamoto H, Fujieda K, Miyashita A,
Fukushima S, Ikeda T, Kubo Y, Senju S, Ihn H, Nishimura Y and
Oshiumi H: Combined blockade of IL6 and PD-1/PD-L1 signaling
abrogates mutual regulation of their immunosuppressive effects in
the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 78:5011–5022. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Anker MS, Holcomb R, Muscaritoli M, von
Haehling S, Haverkamp W, Jatoi A, Morley JE, Strasser F, Landmesser
U, Coats AJS, et al: Orphan disease status of cancer cachexia in
the USA and in the European Union: A systematic review. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 10:22–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Loumaye A and Thissen JP: Biomarkers of
cancer cachexia. Clin Biochem. 50:1281–1288. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Weidle UH, Klostermann S, Eggle D and
Krüger A: Interleukin 6/interleukin 6 receptor interaction and its
role as a therapeutic target for treatment of cachexia and cancer.
Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 7:287–302. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Zimmers TA, Fishel ML and Bonetto A: STAT3
in the systemic inflammation of cancer cachexia. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 54:28–41. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Cehreli R, Yavuzsen T, Ates H, Akman T,
Ellidokuz H and Oztop I: Can inflammatory and nutritional serum
markers predict chemotherapy outcomes and survival in advanced
stage nonsmall cell lung cancer patients? BioMed Res Int.
2019:16480722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Johannes CM and Musser ML: Anorexia and
the cancer patient. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 49:837–854.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Pisetsky DS, Trace SE, Brownley KA, Hamer
RM, Zucker NL, Roux-Lombard P, Dayer JM and Bulik CM: The
expression of cytokines and chemokines in the blood of patients
with severe weight loss from anorexia nervosa: An exploratory
study. Cytokine. 69:110–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Rochfort KD and Cummins PM: The
blood-brain barrier endothelium. A target for pro-inflammatory
cytokines. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:702–706. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Dwarkasing JT, Witkamp RF, Boekschoten MV,
Ter Laak MC, Heins MS and van Norren K: Increased hypothalamic
serotonin turnover in inflammation-induced anorexia. BMC Neurosci.
17:262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Liu WJ, Wang XD, Wu W and Huang X:
Relationship between depression and blood cytokine levels in lung
cancer patients. Med Sci (Paris). 34(Focus issue F1): 113–115.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Lu YR, Rao YB, Mou YJ, Chen Y, Lou HF,
Zhang Y, Zhang DX, Xie HY, Hu LW and Fang P: High concentrations of
serum interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in patients with bipolar
disorder. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e144192019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Ju RJ, Stehbens SJ and Haass NK: The role
of melanoma cell-stroma interaction in cell motility, invasion, and
metastasis. Front Med (Lausanne). 5:3072018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Johnson DE, O'Keefe RA and Grandis JR:
Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 15:234–248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Donnelly D III, Aung PP and Jour G: The
'-OMICS' facet of melanoma: Heterogeneity of genomic, proteomic and
metabolomic biomarkers. Semin Cancer Biol. 59:165–174. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|