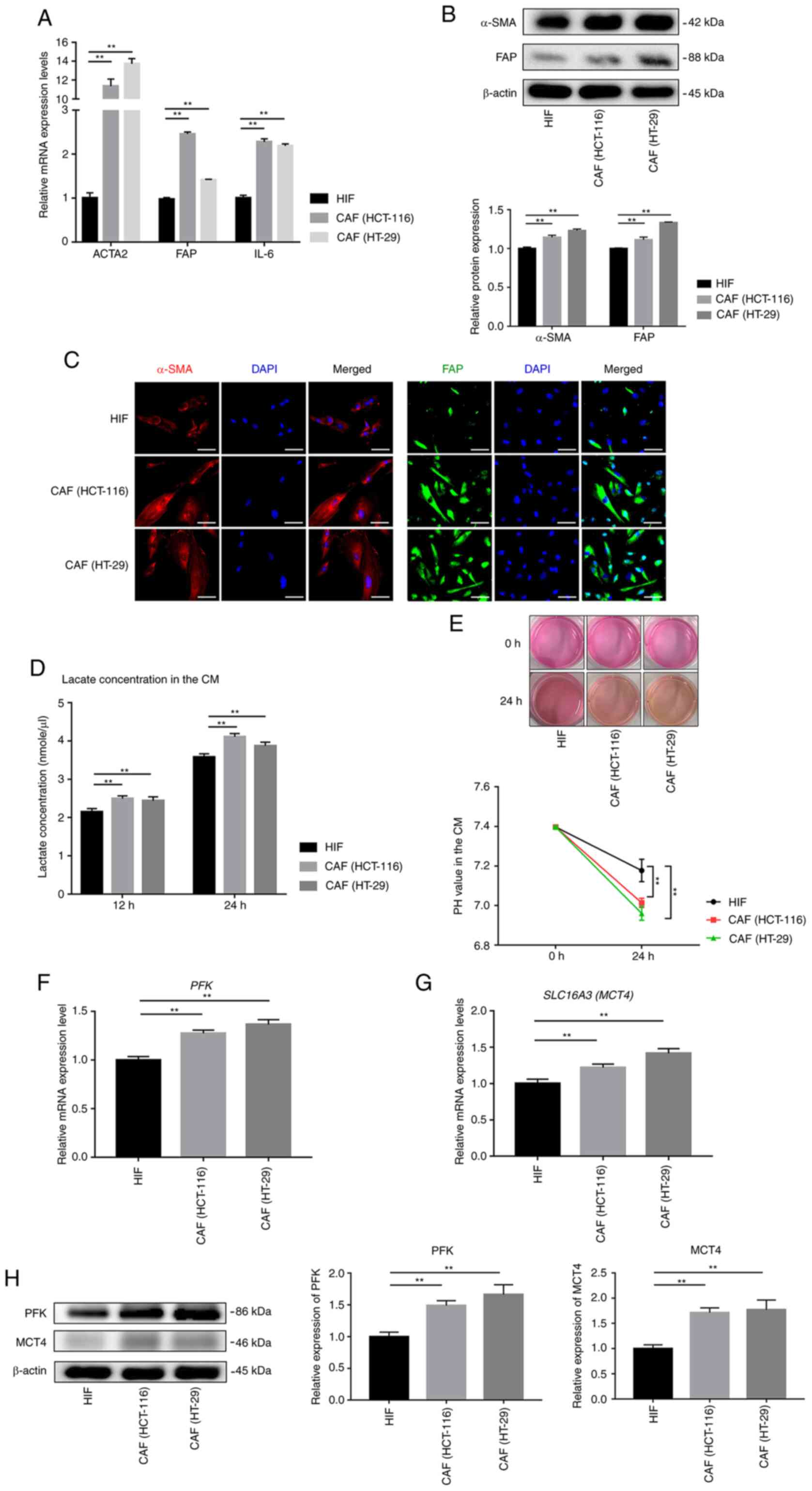
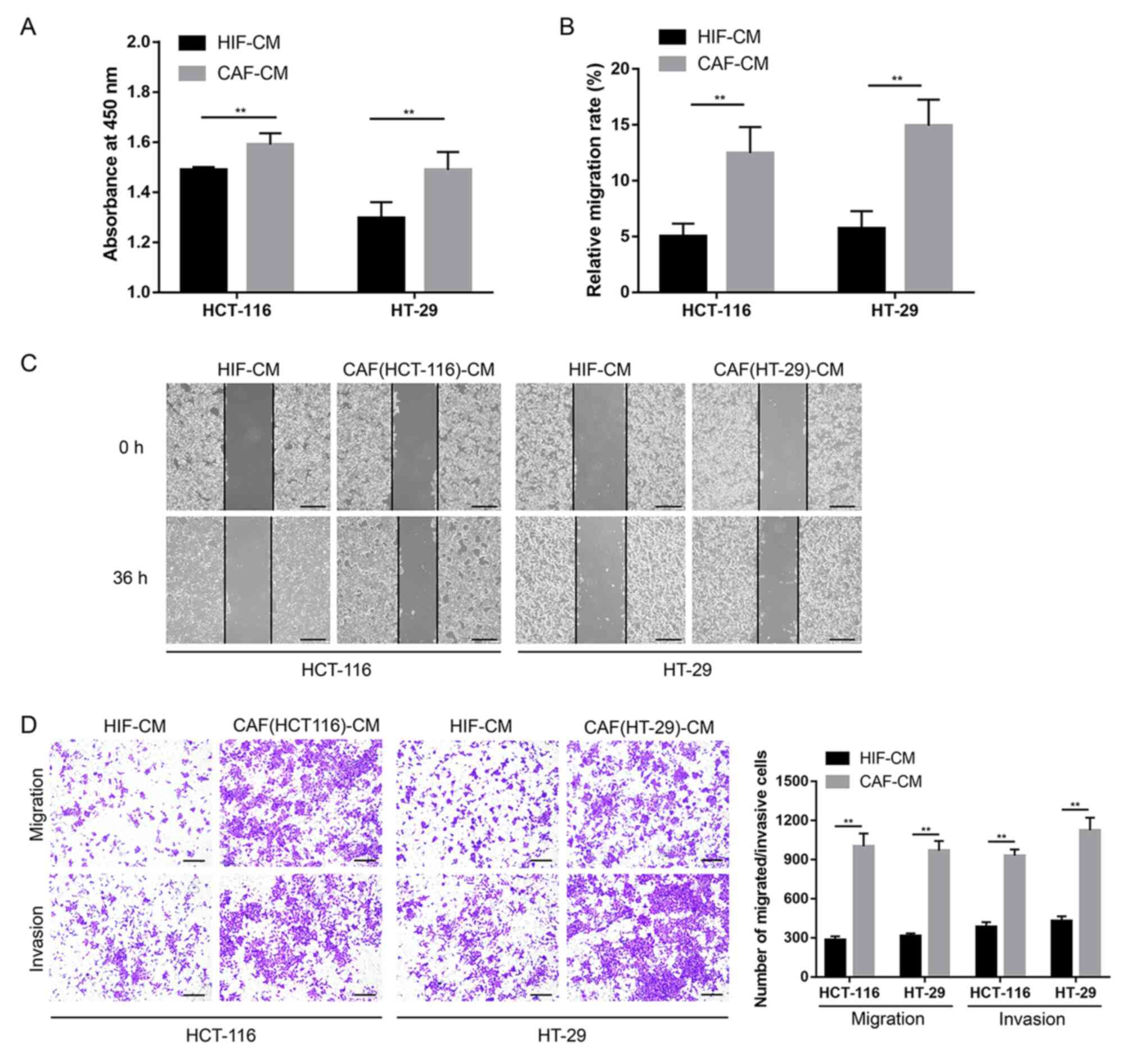
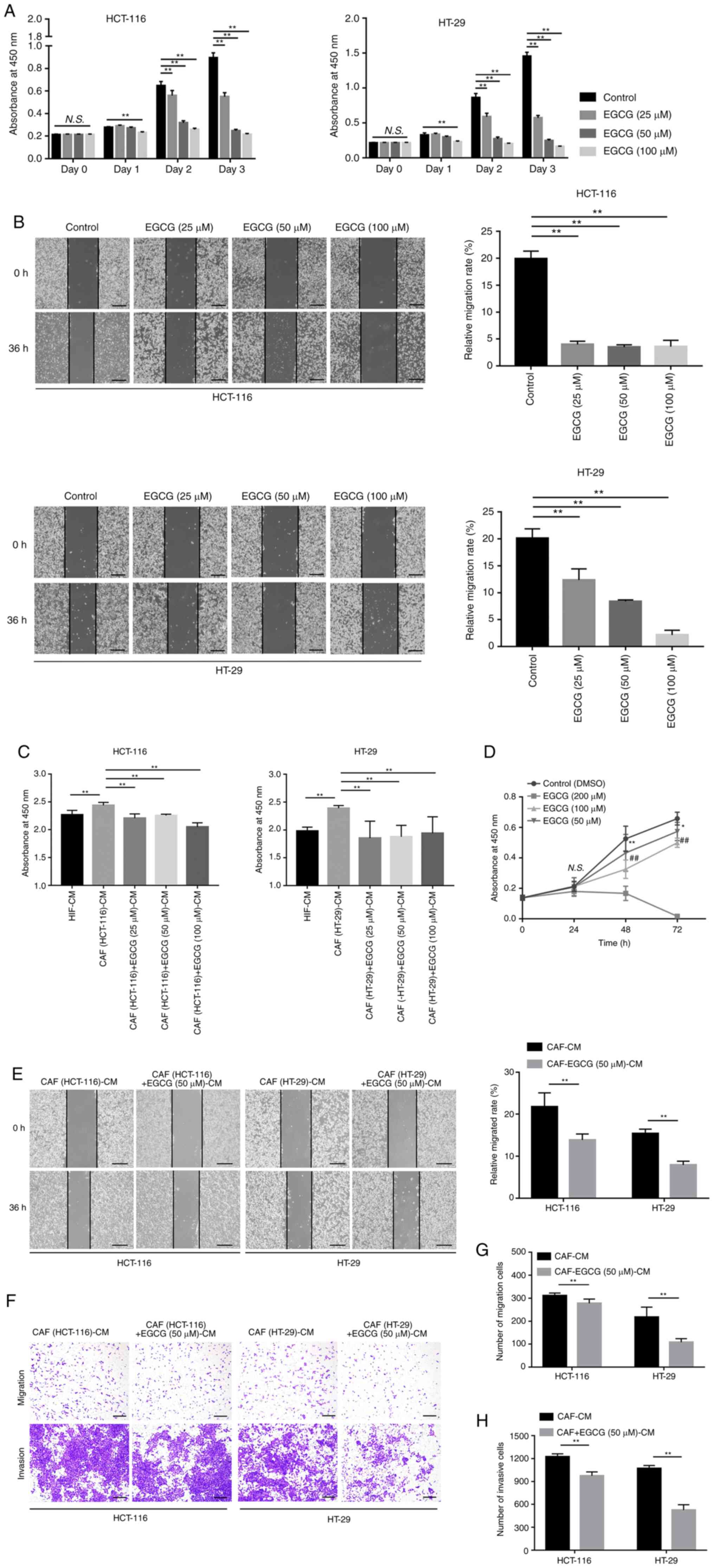
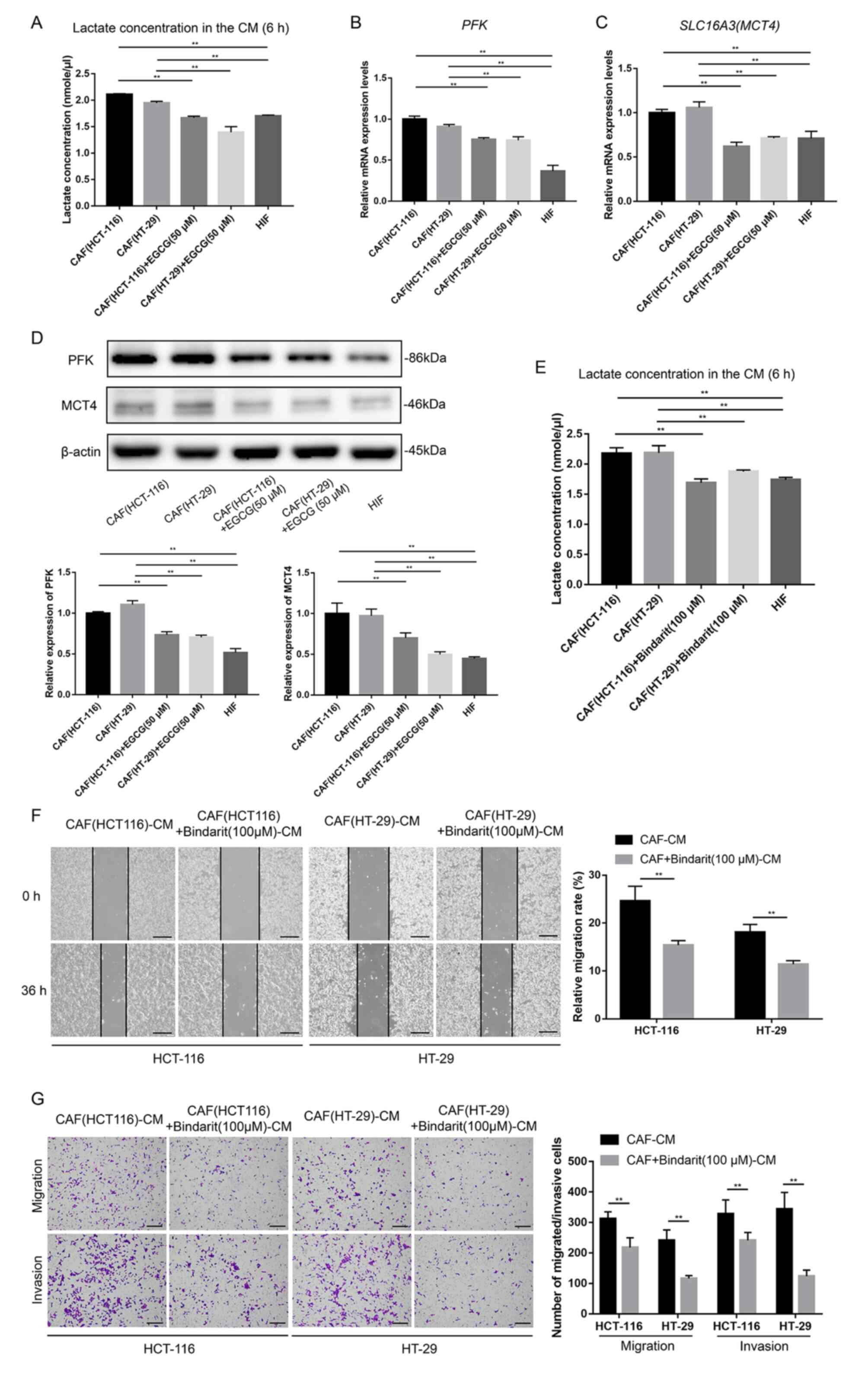
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A,
Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, Cercek A, Smith RA and Jemal
A: Colorectal Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin.
70:145–164. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gentric G and Mechta-Grigoriou F: Tumor
cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts: An updated metabolic
perspective. Cancers (Basel). 13:3992021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Eisenberg L, Eisenberg-Bord M,
Eisenberg-Lerner A and Sagi-Eisenberg R: Metabolic alterations in
the tumor microenvironment and their role in oncogenesis. Cancer
Lett. 484:65–71. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pavlides S, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Frank PG, Casimiro
MC, Wang C, Fortina P, Addya S, et al: The reverse Warburg effect:
Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor
stroma. Cell Cycle. 8:3984–4001. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Becker LM, O'Connell JT, Vo AP, Cain MP,
Tampe D, Bizarro L, Sugimoto H, McGow AK, Asara JM, Lovisa S, et
al: Epigenetic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts
deregulates glucose metabolism and facilitates progression of
breast cancer. Cell Rep. 31:1077012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jung JG and Le A: Targeting metabolic
cross talk between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1311:205–214. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lisanti MP and
Sotgia F: Catabolic cancer-associated fibroblasts transfer energy
and biomass to anabolic cancer cells, fueling tumor growth. Semin
Cancer Biol. 25:47–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu Y, Liu S, Yin S, Niu W, Xiong W, Tan M,
Li G and Zhou M: The reverse Warburg effect is likely to be an
Achilles' heel of cancer that can be exploited for cancer therapy.
Oncotarget. 8:57813–57825. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Peiris-Pagés M,
Pestell RG, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Cancer metabolism: A
therapeutic perspective. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:11–31. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Benny S, Mishra R, Manojkumar MK and
Aneesh TP: From Warburg effect to reverse Warburg effect; the new
horizons of anti-cancer therapy. Med Hypotheses. 144:1102162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Keller F, Bruch R, Schneider R,
Meier-Hubberten J, Hafner M and Rudolf R: A scaffold-free 3-D
co-culture mimics the major features of the reverse Warburg effect
in vitro. Cells. 9:19002020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jankun J, Selman SH, Swiercz R and
Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Why drinking green tea could prevent cancer.
Nature. 387:5611997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aggarwal V, Tuli HS, Tania M, Srivastava
S, Ritzer EE, Pandey A, Aggarwal D, Barwal TS, Jain A, Kaur G, et
al: Molecular mechanisms of action of epigallocatechin gallate in
cancer: Recent trends and advancement. Semin Cancer Biol May.
24:2020Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shen X, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, Li J,
Xie YA and Luo X: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits cell growth,
induces apoptosis and causes S phase arrest in hepatocellular
carcinoma by suppressing the AKT pathway. Int J Oncol. 44:791–796.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo KW, Xia J, Cheng BH, Gao HC, Fu LW and
Luo XL: Tea polyphenol EGCG inhibited colorectal-cancer-cell
proliferation and migration via downregulation of STAT3.
Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 9:59–70. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wei R, Mao L, Xu P, Zheng X, Hackman RM,
Mackenzie GG and Wang Y: Suppressing glucose metabolism with
epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces breast cancer cell growth
in preclinical models. Food Funct. 9:5682–5696. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Xie Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, Huang X,
Shen X and Luo X: (-)-Epigallocatechingallate induces apoptosis in
B lymphoma cells via caspase-dependent pathway and Bcl-2 family
protein modulation. Int J Oncol. 46:1507–1515. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Chow HH, Cai Y, Hakim IA, Crowell JA,
Shahi F, Brooks CA, Dorr RT, Hara Y and Alberts DS:
Pharmacokinetics and safety of green tea polyphenols after
multiple-dose administration of epigallocatechin gallate and
polyphenon E in healthy individuals. Clin Cancer Res. 9:3312–3319.
2003.
|
|
21
|
Kuo PL and Lin CC: Green tea constituent
(-)-epigallocate-chin-3-gallate inhibits Hep G2 cell proliferation
and induces apoptosis through p53-dependent and Fas-mediated
pathways. J Biomed Sci. 10:219–227. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gupta S, Hastak K, Afaq F, Ahmad N and
Mukhtar H: Essential role of caspases in
epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated inhibition of nuclear factor
kappa B and induction of apoptosis. Oncogene. 23:2507–2522. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li S, Xia Y, Chen K, Li J, Liu T, Wang F,
Lu J, Zhou Y and Guo C: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates
apoptosis and autophagy in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by
inhibiting BNIP3. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:631–647. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li S, Wu L, Feng J, Li J, Liu T, Zhang R,
Xu S, Cheng K, Zhou Y, Zhou S, et al: In vitro and in vivo study of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis in aerobic glycolytic
hepatocellular carcinoma cells involving inhibition of
phosphofructokinase activity. Sci Rep. 6:284792016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen S, Morine Y, Tokuda K, Yamada S,
Saito Y, Nishi M, Ikemoto T and Shimada M: Cancer-associated
fibroblast-induced M2-polarized macrophages promote hepatocellular
carcinoma progression via the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
pathway. Int J Oncol. 59:592021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fiori ME, Di Franco S, Villanova L, Bianca
P, Stassi G and De Maria R: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as
abettors of tumor progression at the crossroads of EMT and therapy
resistance. Mol Cancer. 18:702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim J and DeBerardinis RJ: Mechanisms and
implications of metabolic heterogeneity in cancer. Cell Metab.
30:434–446. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Salem AF, Whitaker-Menezes D, Lin Z,
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Tanowitz HB, Al-Zoubi MS, Howell A, Pestell
RG, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Two-compartment tumor metabolism:
Autophagy in the tumor microenvironment and oxidative mitochondrial
metabolism (OXPHOS) in cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 11:2545–2556.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Witkiewicz AK, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Dasgupta A, Philp NJ, Lin Z, Gandara R, Sneddon S,
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Using the 'reverse
Warburg effect' to identify high-risk breast cancer patients:
Stromal MCT4 predicts poor clinical outcome in triple-negative
breast cancers. Cell Cycle. 11:1108–1117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pavlides S, Vera I, Gandara R, Sneddon S,
Pestell RG, Mercier I, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Howell A, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Warburg meets autophagy:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts accelerate tumor growth and
metastasis via oxidative stress, mitophagy, and aerobic glycolysis.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1264–1284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Gonzalez CD, Alvarez S, Ropolo A,
Rosenzvit C, Bagnes MF and Vaccaro MI: Autophagy, Warburg, and
Warburg reverse effects in human cancer. BioMed Res Int.
2014:9267292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wilde L, Roche M, Domingo-Vidal M, Tanson
K, Philp N, Curry J and Martinez-Outschoorn U: Metabolic coupling
and the Reverse Warburg Effect in cancer: Implications for novel
biomarker and anticancer agent development. Semin Oncol.
44:198–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cruz-Bermúdez A, Laza-Briviesca R,
Vicente-Blanco RJ, García-Grande A, Coronado MJ, Laine-Menéndez S,
Alfaro C, Sanchez JC, Franco F, Calvo V, et al: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts modify lung cancer metabolism involving ROS and TGF-β
signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 130:163–173. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shao S, Qin T, Qian W, Yue Y, Xiao Y, Li
X, Zhang D, Wang Z, Ma Q and Lei J: Positive feedback in Cav-1-ROS
signaling in PSCs mediates metabolic coupling between PSCs and
tumour cells. J Cell Mol Med. 24:9397–9408. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Z, Gao Z, Rajthala S, Sapkota D,
Dongre H, Parajuli H, Suliman S, Das R, Li L, Bindoff LA, et al:
Metabolic reprogramming of normal oral fibroblasts correlated with
increased glycolytic metabolism of oral squamous cell carcinoma and
precedes their activation into carcinoma associated fibroblasts.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:1115–1133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang X, Dong Y, Zhao M, Ding L, Yang X,
Jing Y, Song Y, Chen S, Hu Q and Ni Y: ITGB2-mediated metabolic
switch in CAFs promotes OSCC proliferation by oxidation of NADH in
mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system. Theranostics.
10:12044–12059. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sung JS, Kang CW, Kang S, Jang Y, Chae YC,
Kim BG and Cho NH: ITGB4-mediated metabolic reprogramming of
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene. 39:664–676. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ippolito L, Morandi A, Taddei ML, Parri M,
Comito G, Iscaro A, Raspollini MR, Magherini F, Rapizzi E,
Masquelier J, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote prostate
cancer malignancy via metabolic rewiring and mitochondrial
transfer. Oncogene. 38:5339–5355. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu X, Zhou X, Xu S, Liao C, Chen X, Li B,
Peng J, Li D and Yang L: Extracellular vesicle packaged
LMP1-activated fibroblasts promote tumor progression via autophagy
and stroma-tumor metabolism coupling. Cancer Lett. 478:93–106.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Deng L, Jiang N, Zeng J, Wang Y and Cui H:
The versatile roles of cancer-associated fibroblasts in colorectal
cancer and therapeutic implications. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7332702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu
J, Zhang B, Meng Q, Yu X and Shi S: Crosstalk between
cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor
microenvironment: New findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer.
20:1312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kobayashi H, Enomoto A, Woods SL, Burt AD,
Takahashi M and Worthley DL: Cancer-associated fibroblasts in
gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:282–295.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tan HX, Gong WZ, Zhou K, Xiao ZG, Hou FT,
Huang T, Zhang L, Dong HY, Zhang WL, Liu Y, et al: CXCR4/TGF-β1
mediated hepatic stellate cells differentiation into
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and promoted liver metastasis of
colon cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 21:258–268. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wu YH, Huang YF, Chang TH, Chen CC, Wu PY,
Huang SC and Chou CY: COL11A1 activates cancer-associated
fibroblasts by modulating TGF-β3 through the NF-κB/IGFBP2 axis in
ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 40:4503–4519. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Park CR, Lee JS, Son CG and Lee NH: A
survey of herbal medicines as tumor microenvironment-modulating
agents. Phytother Res. 35:78–94. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn
UE, Lin Z, Ertel A, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Birbe RC, Howell
A, Pavlides S, Gandara R, et al: Evidence for a stromal-epithelial
'lactate shuttle' in human tumors: MCT4 is a marker of oxidative
stress in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 10:1772–1783.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fiaschi T, Marini A, Giannoni E, Taddei
ML, Gandellini P, De Donatis A, Lanciotti M, Serni S, Cirri P and
Chiarugi P: Reciprocal metabolic reprogramming through lactate
shuttle coordinately influences tumor-stroma interplay. Cancer Res.
72:5130–5140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun K, Tang S, Hou Y, Xi L, Chen Y, Yin J,
Peng M, Zhao M, Cui X and Liu M: Oxidized ATM-mediated glycolysis
enhancement in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to
tumor invasion through lactate as metabolic coupling. EBioMedicine.
41:370–383. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Futagi Y, Kobayashi M, Narumi K, Furugen A
and Iseki K: Identification of a selective inhibitor of human
monocarboxylate transporter 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
495:427–432. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hui S, Ghergurovich JM, Morscher RJ, Jang
C, Teng X, Lu W, Esparza LA, Reya T, Le Zhan Yanxiang, Guo J, et
al: Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate. Nature.
551:115–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim BG, Sung JS, Jang Y, Cha YJ, Kang S,
Han HH, Lee JH and Cho NH: Compression-induced expression of
glycolysis genes in CAFs correlates with EMT and angiogenesis gene
expression in breast cancer. Commun Biol. 2:3132019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|