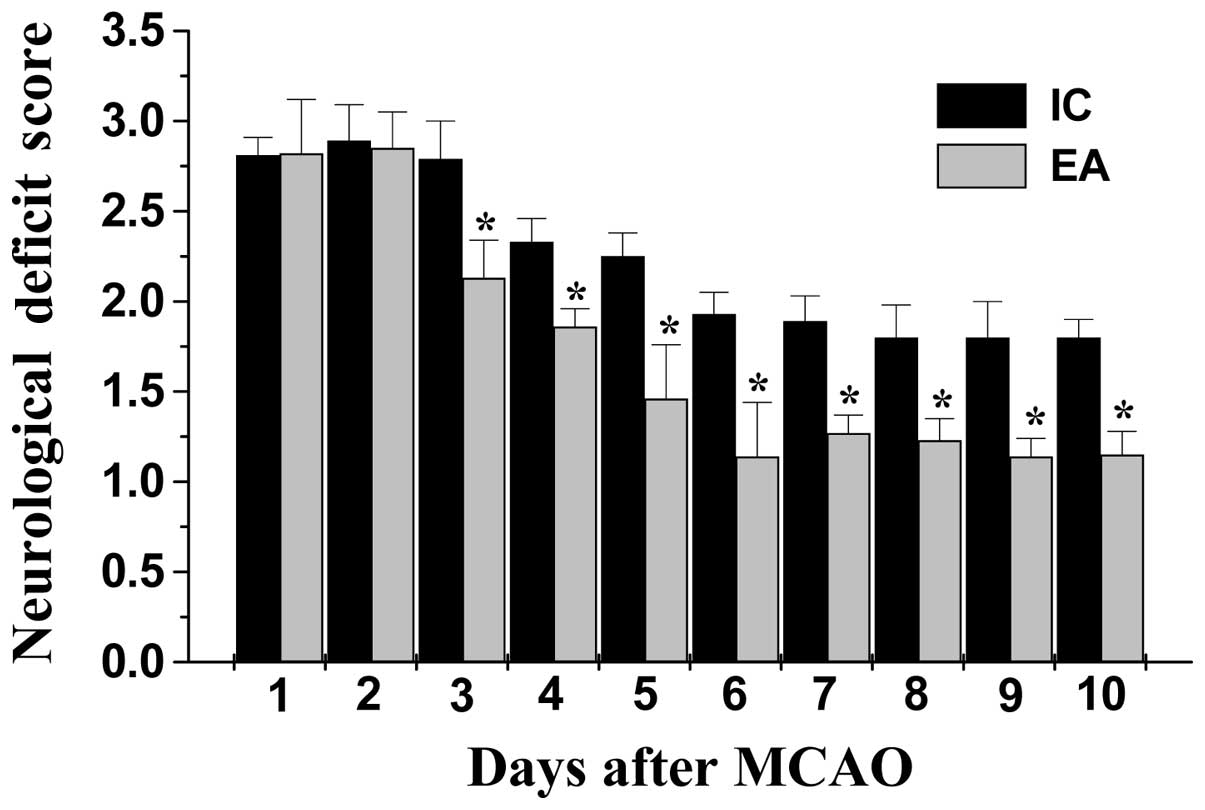
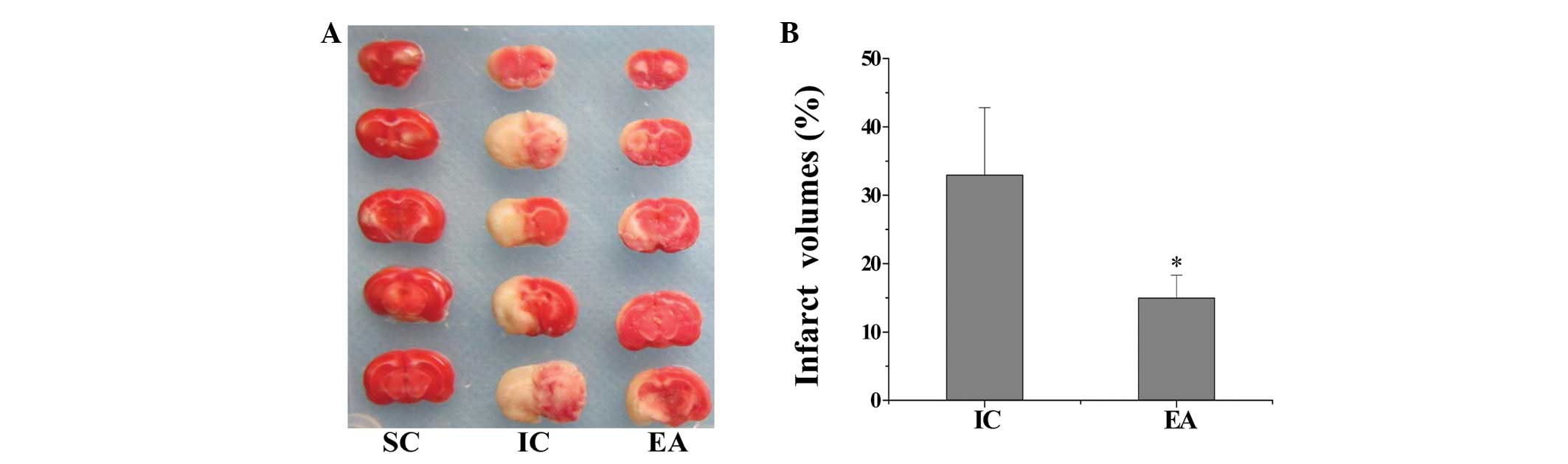
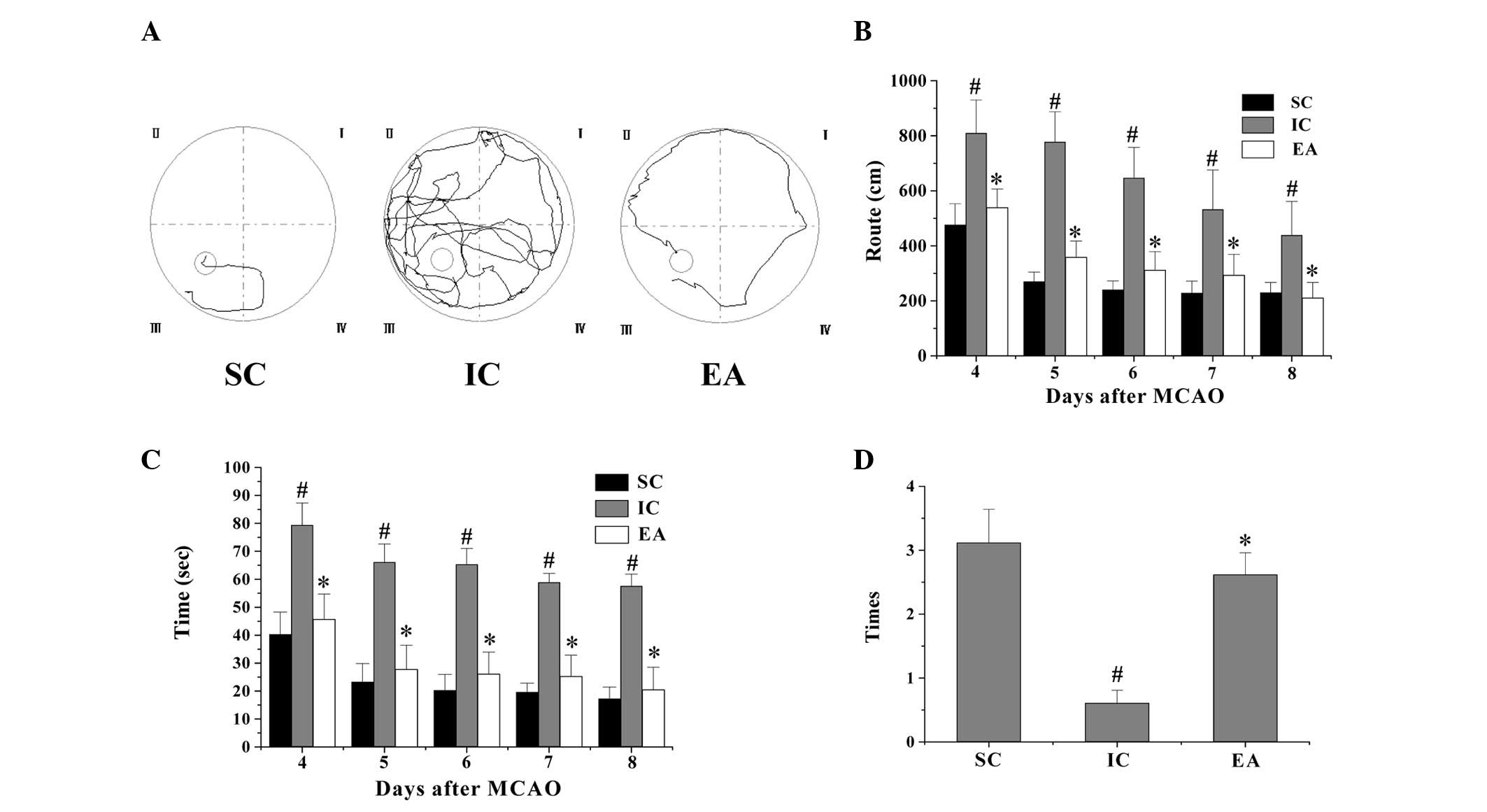
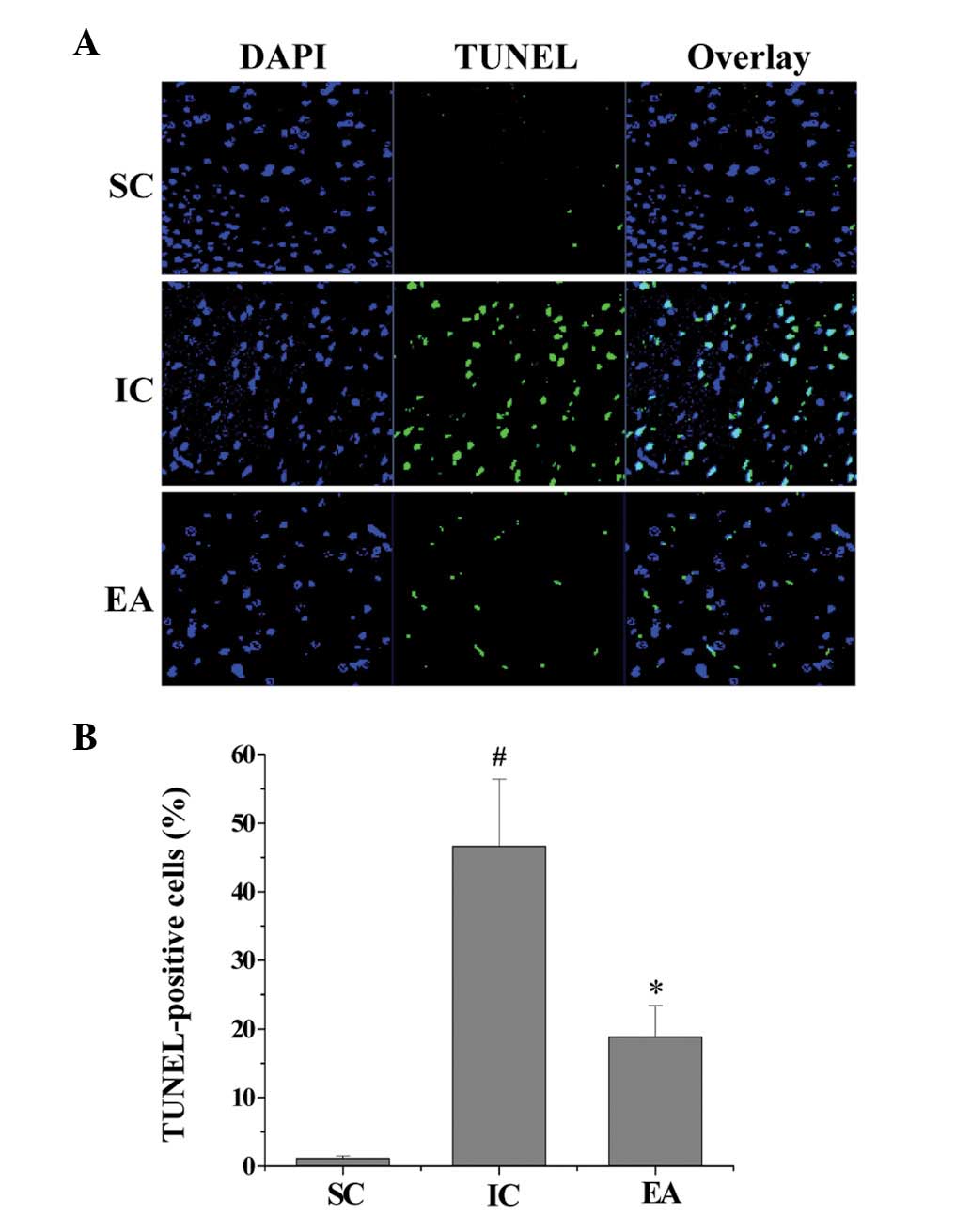
|
1
|
Jokinen H, Kalska H, Mäntylä R, et al:
Cognitive profile of subcortical ischaemic vascular disease. J
Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 77:28–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lindeboom J and Weinstein H:
Neuropsychology of cognitive ageing, minimal cognitive impairment,
Alzheimer's disease, and vascular cognitive impairment. Eur J
Pharmacol. 490:83–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nyenhuis DL, Gorelick PB, Geenen EJ, et
al: The pattern of neuropsychological deficits in Vascular
Cognitive Impairment-No Dementia (Vascular CIND). Clin
Neuropsychol. 18:41–49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sachdev PS, Brodaty H, Valenzuela MJ, et
al: The neuropsychological profile of vascular cognitive impairment
in stroke and TIA patients. Neurology. 62:912–919. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mok V, Chang C, Wong A, et al:
Neuroimaging determinants of cognitive performances in stroke
associated with small vessel disease. J Neuroimaging. 15:129–137.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mok VC, Wong A, Lam WW, et al: Cognitive
impairment and functional outcome after stroke associated with
small vessel disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 75:560–566.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haring HP: Cognitive impairment after
stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 15:79–84. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Alvarez-Sabín J and Román GC: Citicoline
in vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia after
stroke. Stroke. 42(Suppl 1): S40–S43. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hachinski V and Munoz D: Vascular factors
in cognitive impairment - where are we now? Ann NY Acad Sci.
903:1–5. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Stern Y, et al:
Cognitive impairment after stroke: frequency, patterns, and
relationship to functional abilities. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 57:202–207. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Desmond DW, Moroney JT, Paik MC, et al:
Frequency and clinical determinants of dementia after ischemic
stroke. Neurology. 54:1124–1131. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mattson MP: Apoptosis in neurodegenerative
disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:120–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nakka VP, Gusain A, Mehta SL and Raghubir
R: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in cerebral ischemia: multiple
neuroprotective opportunities. Mol Neurobiol. 37:7–38. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Broughton BR, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–e339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-of-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Borner C: Bcl-2 family members:
integrators of survival and death. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1644:71–72. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baeuerle PA and Baltimore D: NF-kappa B:
ten years after. Cell. 87:13–20. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taglialatela G, Robinson R and Perez-Polo
JR: Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) activity
induces nerve growth factor-resistant apoptosis in PC12 cells. J
Neurosci Res. 47:155–162. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Middleton G, Hamanoue M, Enokido Y, et al:
Cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation promotes the
survival of developing neurons. J Cell Biol. 148:325–332. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goodman Y and Mattson MP: Ceramide
protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative
insults, and amyloid beta-peptide toxicity. J Neurochem.
66:869–872. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mattson MP, Goodman Y, Luo H, et al:
Activation of NF-kappaB protects hippocampal neurons against
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: evidence for induction of
manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of peroxynitrite
production and protein tyrosine nitration. J Neurosci Res.
49:681–697. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Grilli M, Pizzi M, Memo M and Spano P:
Neuroprotection by aspirin and sodium salicylate through blockade
of NF-kappaB activation. Science. 274:1383–1385. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Won SJ, Ko HW, Kim EY, et al: Nuclear
factor kappa B-mediated kainite neurotoxicity in the rat and
hamster hippocampus. Neuroscience. 94:83–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van der Kooij MA, Nijboer CH, Ohl F, et
al: NF-kappaB inhibition after neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia
improves long-term motor and cognitive outcome in rats. Neurobiol
Dis. 38:266–272. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu JN: A short history of acupuncture. J
Altern Complement Med. 2:19–21. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hu HH, Chung C, Liu TJ, et al: A
randomized controlled trial on the treatment for acute partial
ischemic stroke with acupuncture. Neuroepidemiology. 12:106–113.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jansen G, Lundeberg T, Kjartansson J and
Samuelson UE: Acupuncture and sensory neuropeptides increase
cutaneous blood flow in rats. Neurosci Lett. 97:305–309. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Johansson K, Lindgren I, Widner H, et al:
Can sensory stimulation improve the functional outcome in stroke
patients? Neurology. 43:2189–2192. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Magnusson M, Johansson K and Johansson BB:
Sensory stimulation promotes normalization of postural control
after stroke. Stroke. 25:1176–1180. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao L, Zhang H, Zheng Z, et al:
Electroacupuncture on the head points for improving gnosia in
patients with vascular dementia. J Tradit Chin Med. 29:29–34. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen LP, Wang FW, Zuo F, et al: Clinical
research on comprehensive treatment of senile vascular dementia. J
Tradit Chin Med. 31:178–181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen AZ, Lin ZC, Lan L, et al:
Electroacupuncture at the Quchi and Zusanli acu points exerts
neuroprotective role in cerebral ischemia- reperfusion injured rats
via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 30:791–796.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang GZ, Liu AL and Zhou YB: Panax
ginseng ginsenoside-Rg2 protects memory impairment
via-anti-apoptosis in a rat model with vascular dementia. J
Ethnopharmacol. 115:440–448. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sarnico I, Lanzillotta A and Benarese M:
NF-kappaB dimers in the regulation of neuronal survival. Int Rev
Neurobiol. 85:351–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Freudenthal R, Romano A and Routtenberg A:
Transcription factor NF-kappaB activation after in vivo perforant
path LTP in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampus. 14:677–683. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang W, Potrovita I, Tarabin V, et al:
Neuronal activation of NF-kB contributes to cell death in cerebral
ischemia. J Cerebral Blood F Met. 25:30–34. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kumar A, Takada Y, Boriek AM and Aggarwal
BB: Nuclear factor-kB: its role in health and disease. J Mol Med
(Berl). 82:434–448. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|