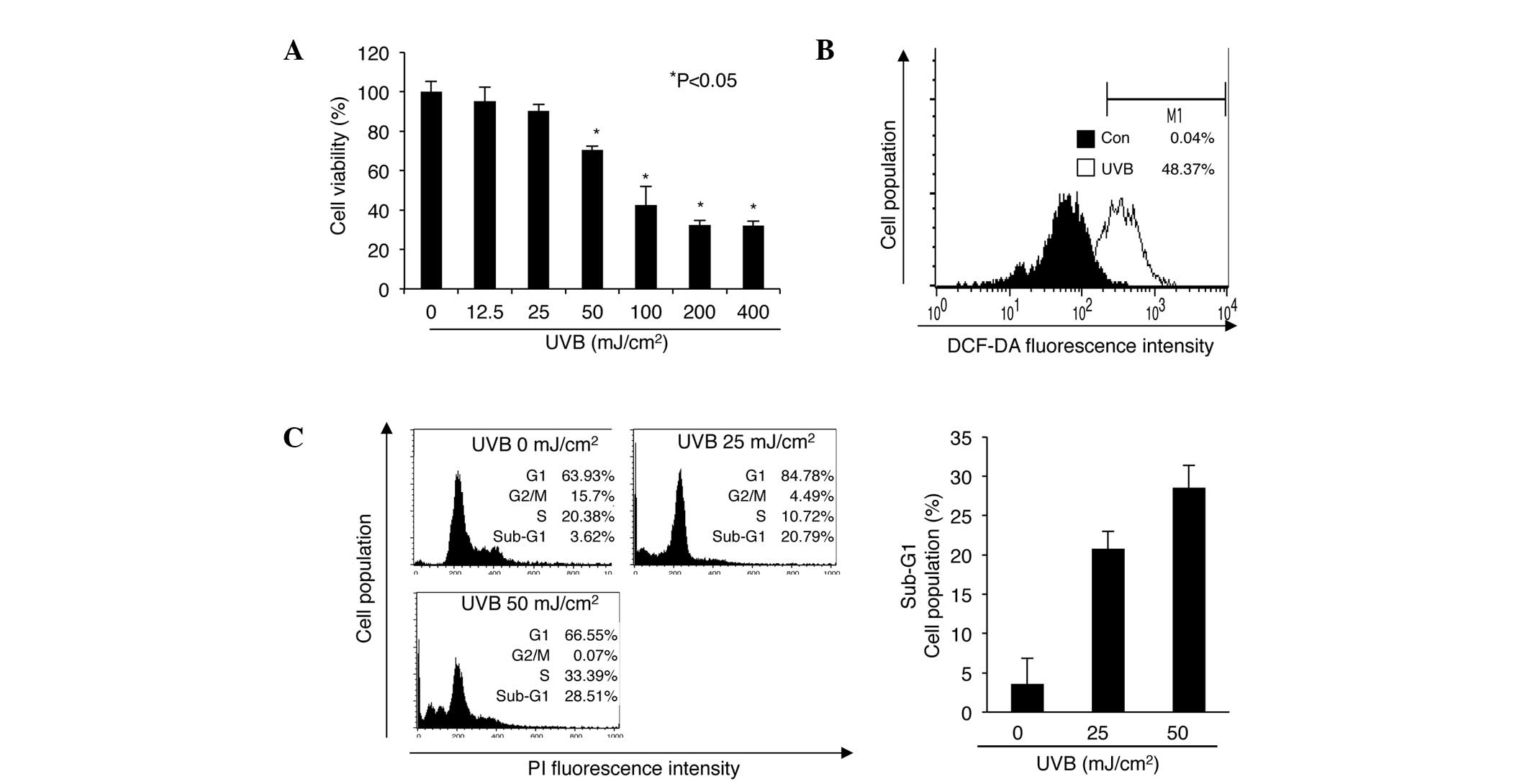
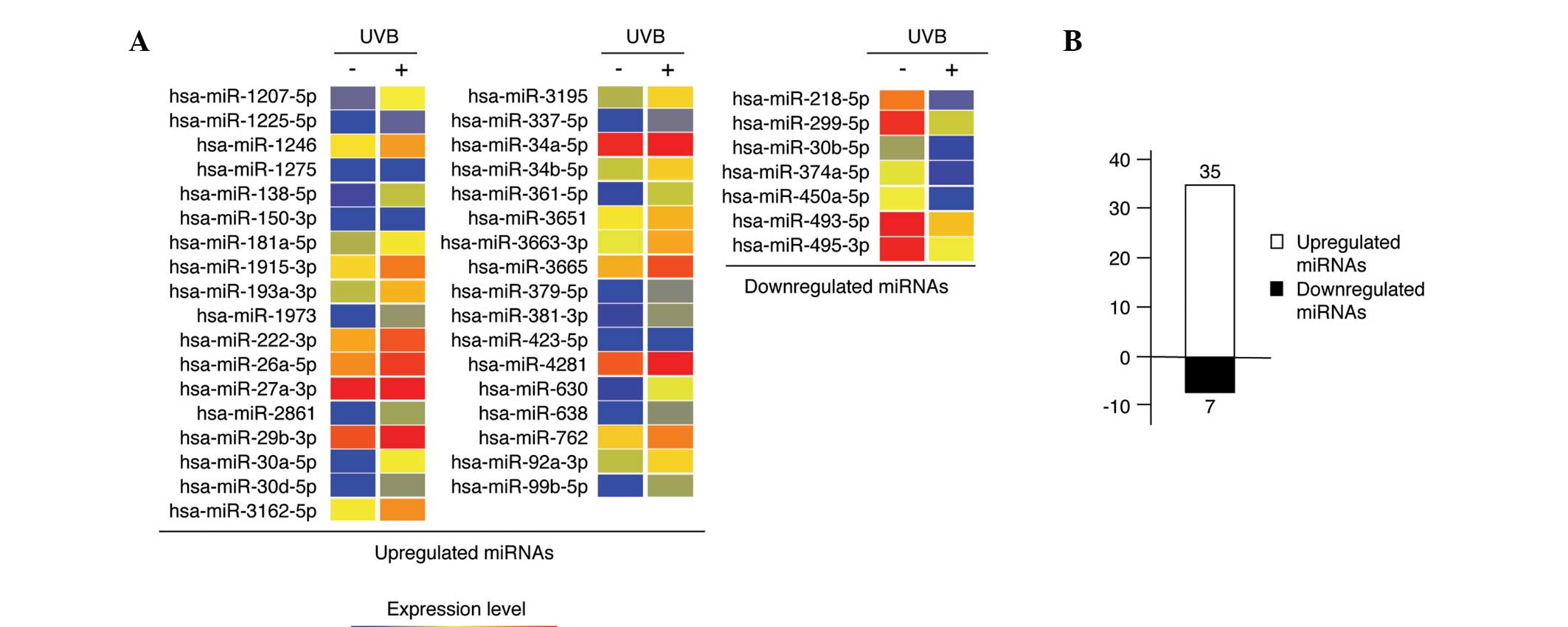
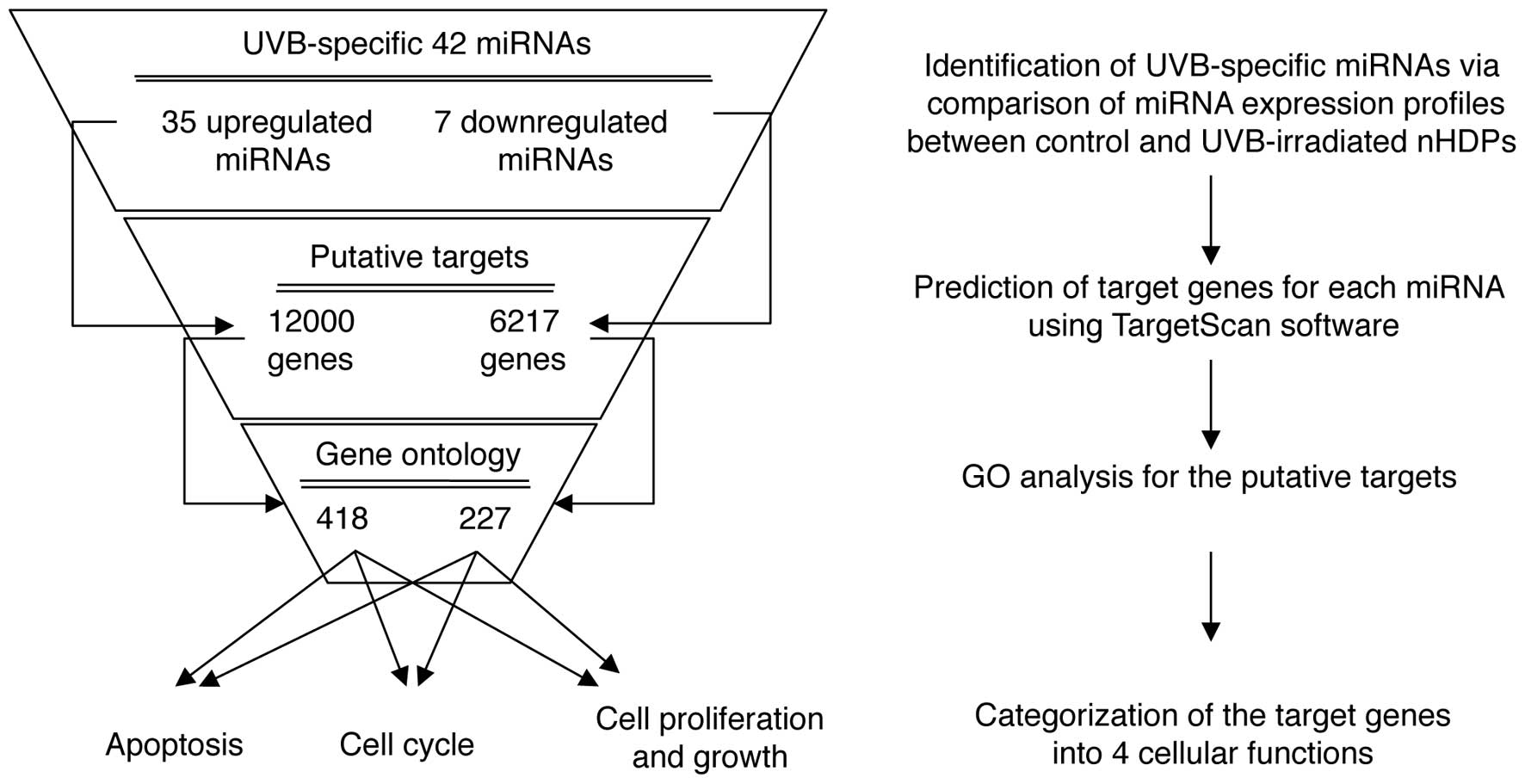
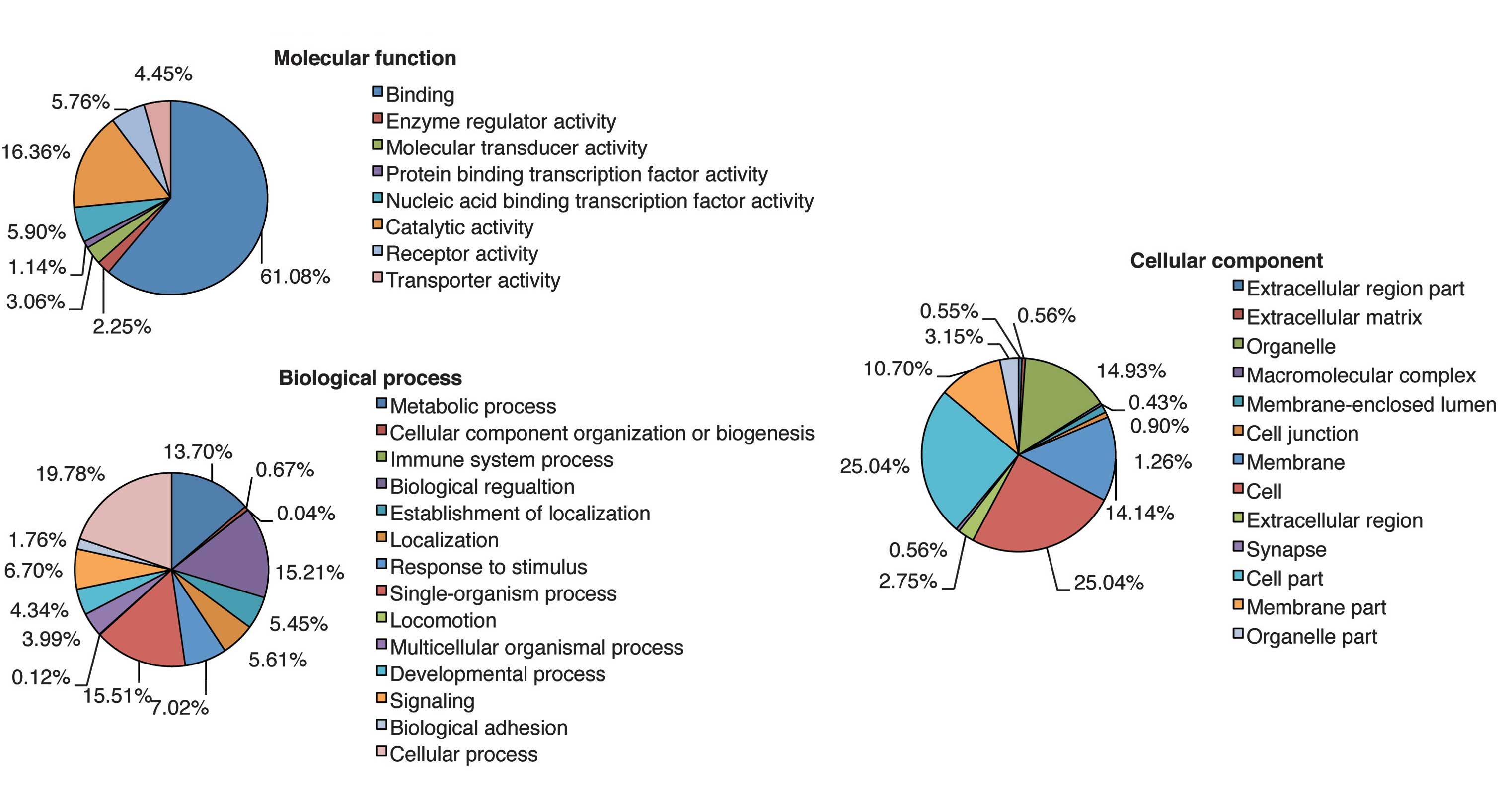
|
1
|
Schreiber MM, Moon TE and Bozzo PD:
Chronic solar ultraviolet damage associated with malignant melanoma
of the skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 10:755–759. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Helfrich YR, Sachs DL and Voorhees JJ:
Overview of skin aging and photoaging. Dermatol Nurs. 20:177–184.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muller HK and Woods GM: Ultraviolet
radiation effects on the proteome of skin cells. Adv Exp Med Biol.
990:111–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee YK, Cha HJ, Hong M, Yoon Y, Lee H and
An S: Role of NF-κB-p53 crosstalk in ultraviolet A-induced cell
death and G1 arrest in human dermal fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res.
304:73–79. 2012.
|
|
5
|
Xu H, Yan Y, Li L, Peng S, Qu T and Wang
B: Ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis of human skin fibroblasts
involves activation of caspase-8 and -3 with increased expression
of vimentin. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 26:198–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trüeb RM: Is androgenetic alopecia a
photoaggravated dermatosis? Dermatology. 207:343–348. 2003.
|
|
7
|
Lu Z, Fischer TW, Hasse S, et al:
Profiling the response of human hair follicles to ultraviolet
radiation. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1790–1804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cha HJ, Shin S, Yoo H, et al:
Identification of ionizing radiation-responsive microRNAs in the
IM9 human B lymphoblastic cell line. Int J Oncol. 34:1661–1668.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wan G, Mathur R, Hu X, Zhang X and Lu X:
miRNA response to DNA damage. Trends Biochem Sci. 36:478–484. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tan G, Shi Y and Wu ZH: MicroRNA-22
promotes cell survival upon UV radiation by repressing PTEN.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:546–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pothof J, Verkaik NS, van IJcken W, et al:
MicroRNA-mediated gene silencing modulates the UV-induced
DNA-damage response. EMBO J. 28:2090–2099. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dynoodt P, Mestdagh P, Van Peer G, et al:
Identification of miR-145 as a key regulator of the pigmentary
process. J Invest Dermatol. 133:201–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu Z, He J, Jia X, et al: MicroRNA-25
functions in regulation of pigmentation by targeting the
transcription factor MITF in Alpaca (Lama pacos) skin
melanocytes. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 38:200–209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan G, Niu J, Shi Y, Ouyang H and Wu ZH:
NF-κB-dependent microRNA-125b up-regulation promotes cell survival
by targeting p38α upon ultraviolet radiation. J Biol Chem.
287:33036–33047. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Zhou BR, Xu Y and Luo D: Effect of UVB
irradiation on microRNA expression in mouse epidermis. Oncol Lett.
3:560–564. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou BR, Xu Y, Permatasari F, et al:
Characterization of the miRNA profile in UVB-irradiated normal
human keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 21:317–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YJ, Cha HJ, Nam KH, Yoon Y, Lee H and
An S: Centella asiatica extracts modulate hydrogen
peroxide-induced senescence in human dermal fibroblasts. Exp
Dermatol. 20:998–1003. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Smith ML, Ford JM, Hollander MC, et al:
p53-mediated DNA repair responses to UV radiation: studies of mouse
cells lacking p53, p21, and/or gadd45 genes. Mol Cell Biol.
20:3705–3714. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meek DW: The p53 response to DNA damage.
DNA Repair (Amst). 3:1049–1056. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lewis DA, Yi Q, Travers JB and Spandau DF:
UVB-induced senescence in human keratinocytes requires a functional
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and p53. Mol Biol Cell.
19:1346–1353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
El-Abaseri TB, Putta S and Hansen LA:
Ultraviolet irradiation induces keratinocyte proliferation and
epidermal hyperplasia through the activation of the epidermal
growth factor receptor. Carcinogenesis. 27:225–231. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Takasawa R, Nakamura H, Mori T and Tanuma
S: Differential apoptotic pathways in human keratinocyte HaCaT
cells exposed to UVB and UVC. Apoptosis. 10:1121–1130. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chainiaux F, Magalhaes JP, Eliaers F,
Remacle J and Toussaint O: UVB-induced premature senescence of
human diploid skin fibroblasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
34:1331–1339. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bossi O, Gartsbein M, Leitges M, Kuroki T,
Grossman S and Tennenbaum T: UV irradiation increases ROS
production via PKCdelta signaling in primary murine fibroblasts. J
Cell Biochem. 105:194–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Wlaschek M,
Brenneisen P, Schauen M, Blaudschun R and Wenk J: UV-induced
reactive oxygen species in photocarcinogenesis and photoaging. Biol
Chem. 378:1247–1257. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pustisek N and Situm M: UV-radiation,
apoptosis and skin. Coll Antropol. 35(Suppl 2): 339–341. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Schneider MR: MicroRNAs as novel players
in skin development, homeostasis and disease. Br J Dermatol.
166:22–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Baraniskin A, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,
Maghnouj A, et al: MiR-30a-5p suppresses tumor growth in colon
carcinoma by targeting DTL. Carcinogenesis. 33:732–739. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu H and Gatti RA: MicroRNAs: new players
in the DNA damage response. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:151–158. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kato M, Paranjape T, Müller RU, et al: The
mir-34 microRNA is required for the DNA damage response in vivo in
C. elegans and in vitro in human breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 28:2419–2424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamauchi T, Adachi S, Yasuda I, et al:
Ultra-violet irradiation induces apoptosis via mitochondrial
pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 39:1375–1380.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang X: The expanding role of mitochondria
in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|