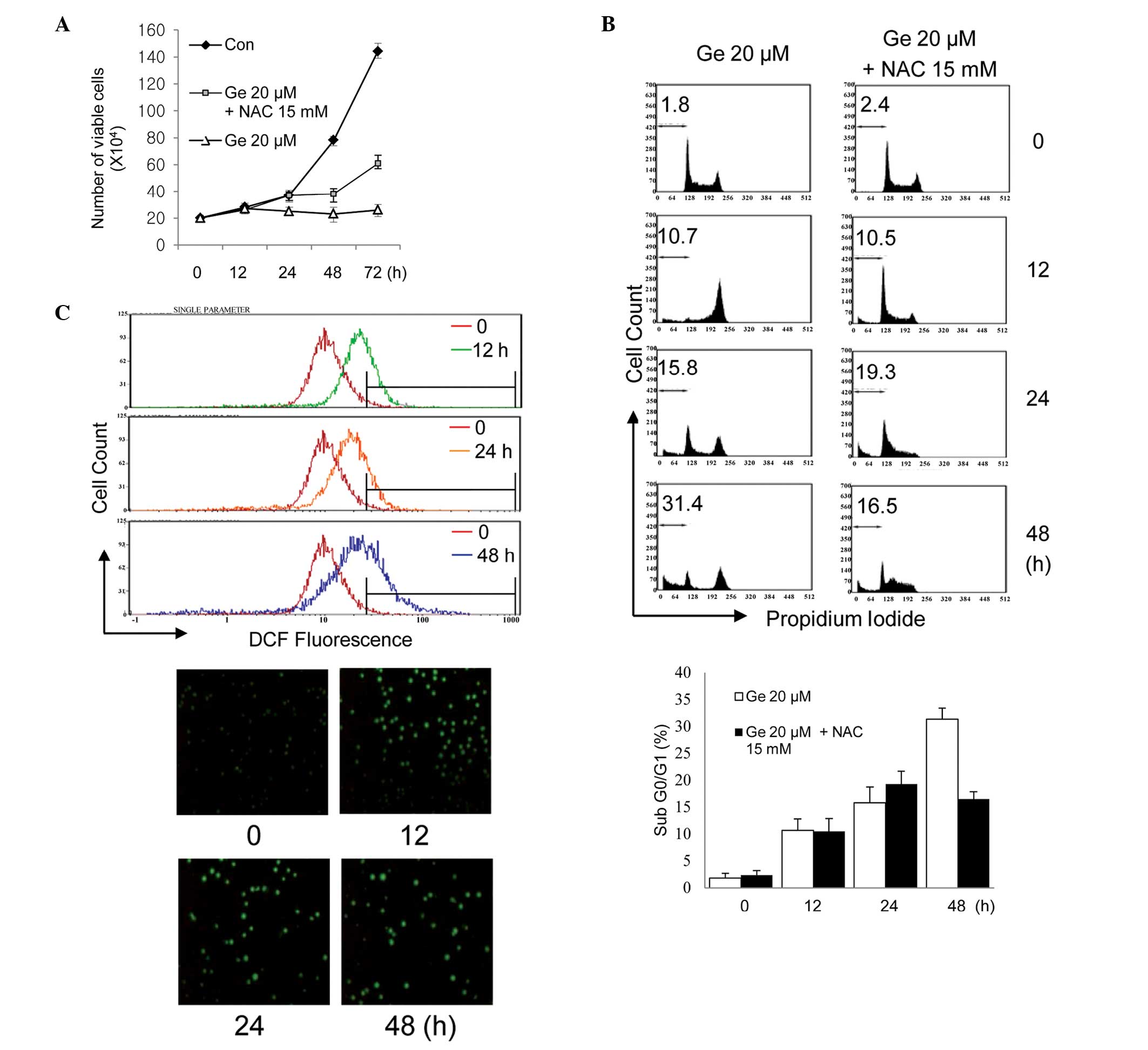
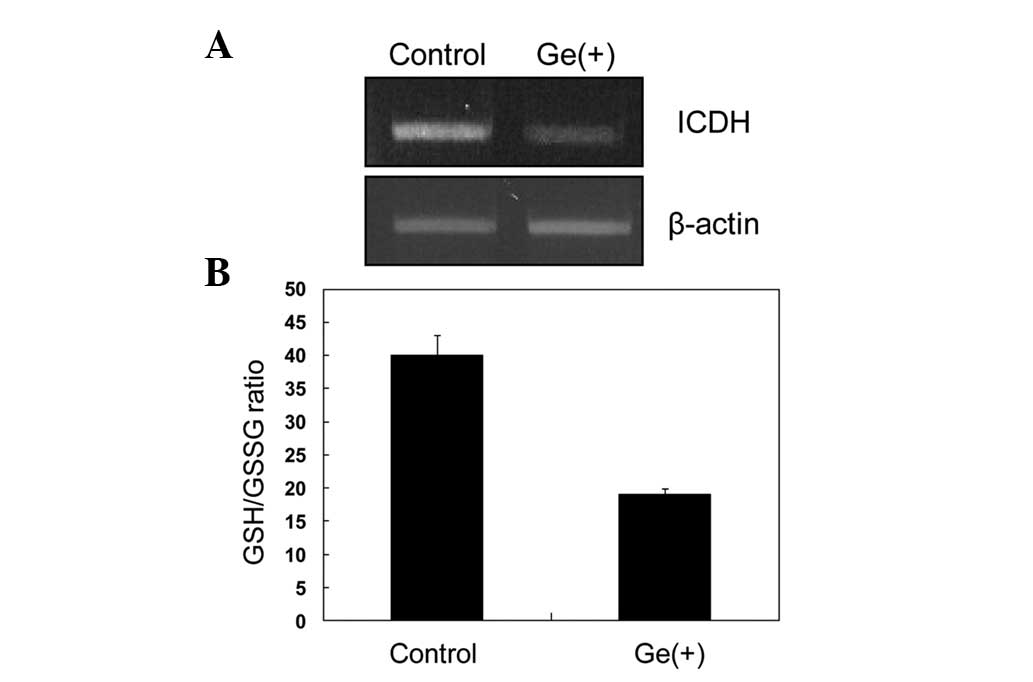
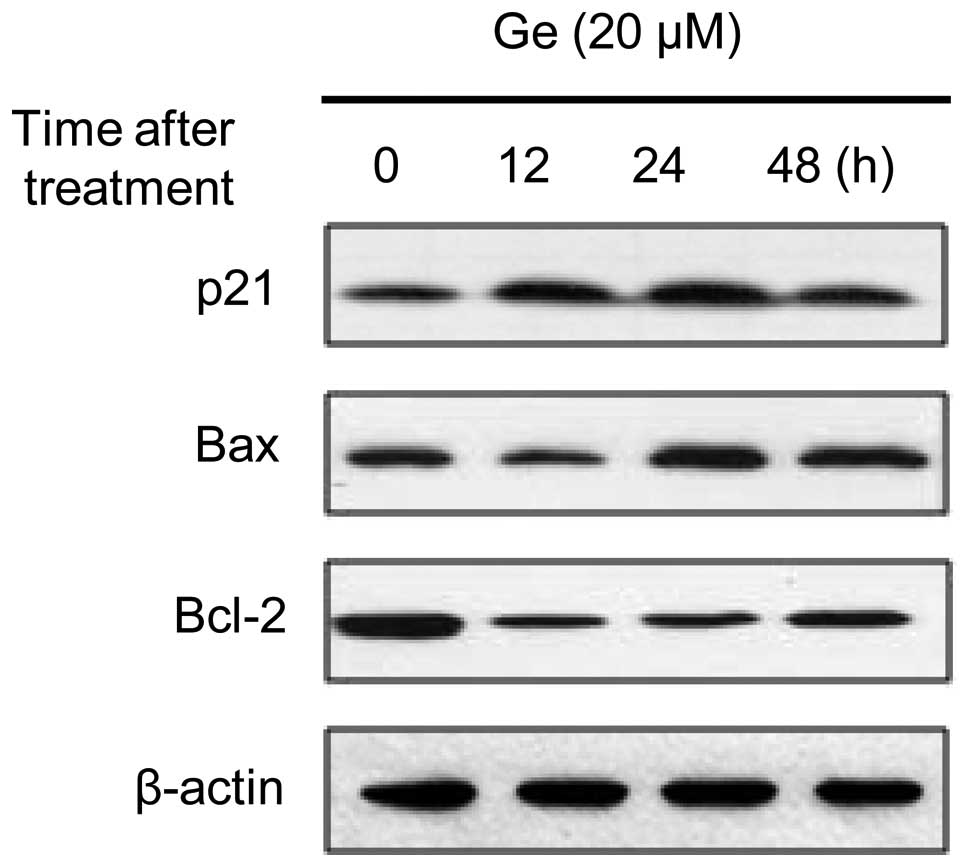
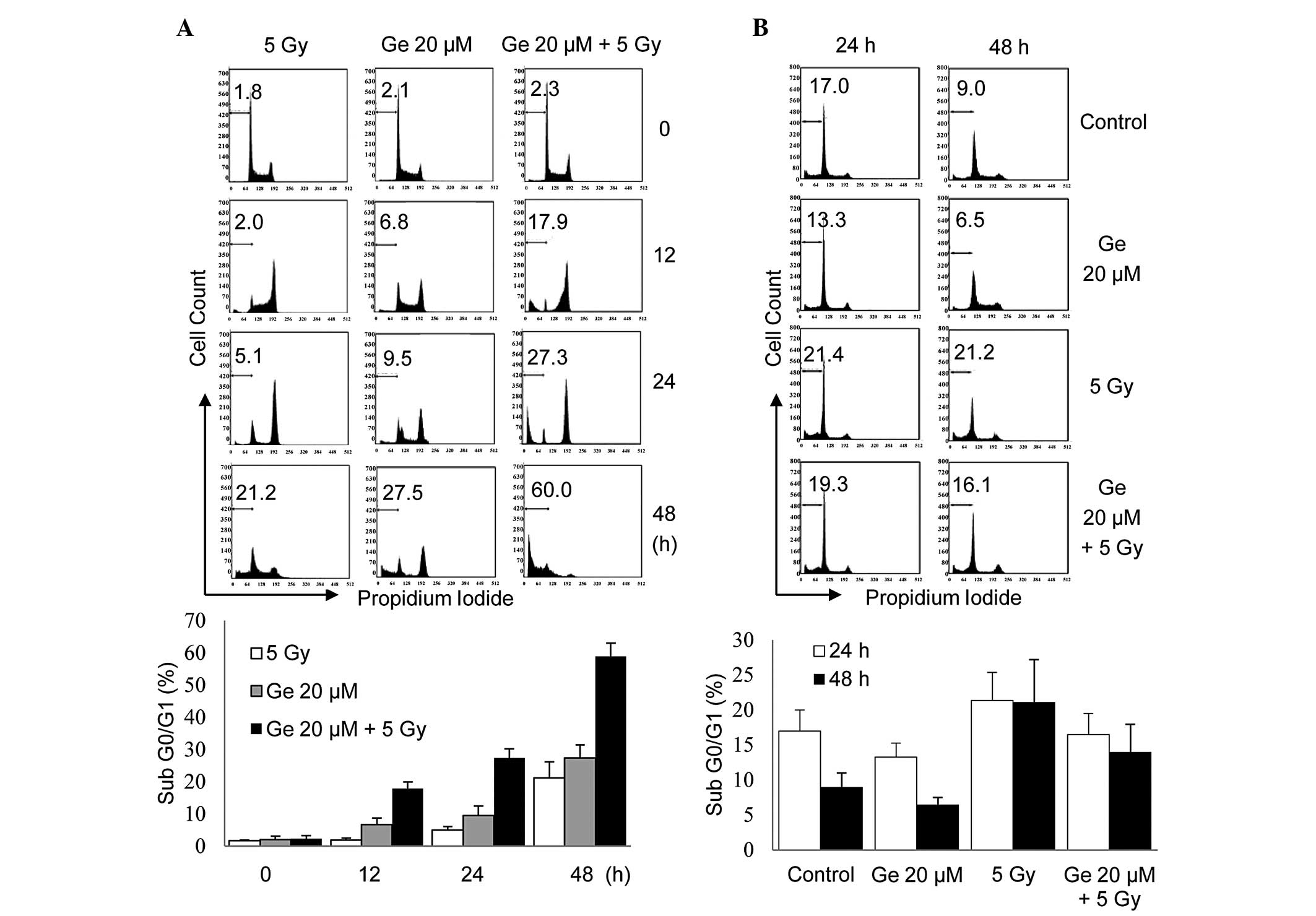
|
1
|
MacGregor JT: Genetic toxicology of
dietary flavonoids. Prog Clin Biol Res. 206:33–43. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soulinna EM, Buchsbaum RN and Racker E:
The effect of flavonoids on aerobic glycolysis and growth of tumor
cells. Cancer Res. 35:1865–1872. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Adlercreutz CH, Goldin BR, Gorbach SL, et
al: Soybean phytoestrogen intake and cancer risk. J Nutr.
125:757S–770S. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giovannucci E: Epidemiologic
characteristics of prostate cancer. Cancer. 75:1766–1777. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sarkar FH and Li Y: The role of
isoflavones in cancer chemoprevention. Front Biosci. 9:2714–2724.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pagliacci MC, Smacchia M, Migliorati G, et
al: Growth inhibitory effect of the natural phytoe-strogen
genistein in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Eur J Cancer.
30:1675–1682. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kyle E, Neckers L, Takimoto C, Curt G and
Bergan R: Genistein-induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells is
preceded by a specific decrease in focal adhesion kinase activity.
Mol Pharmacol. 51:193–200. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Spinnozi F, Pagliacci M, Migliorati G, et
al: The natural tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein produces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in Jurkat T-leukemia cells. Leuk Res.
18:431–439. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Upadhyay S, Bhuiyan M and Sarkar FH:
Induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 by
genistein. Oncogene. 18:3166–3172. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Bhuiyan M and Sarkar FH: Induction
of apoptosis and inhibition of c-erbB-2 in MDA-MB-435 cells by
genistein. Int J Oncol. 15:525–533. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alhasan SA, Pietrasczkiwicz H, Alonso MD,
Ensley J and Sarkar FH: Genistein-induced cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line.
Nutr Cancer. 34:12–19. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kumi-Diaka J, Sanderson NA and Hall A: The
mediating role of caspase-3 protease in the intracellular mechanism
of genistein-induced apoptosis in human prostatic carcinoma cell
lines, DU145 and LNCaP. Biol Cell. 92:595–604. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Davis N, Kucuk O and Sarkar FH: Genistein
inhibits NF-κB activation in prostate cancer cells. Nutr Cancer.
35:167–174. 1999.
|
|
14
|
Fotsis T, Pepper MS, Aktas E, et al:
Flavonoids, dietary-derived inhibitors of cell proliferation and in
vitro angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 57:2916–2921. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gradzka I, Buraczewska I, Kuduk-Jaworska
J, Romaniewska A and Szumiel I: Radiosensitizing properties of
novel hydroxydicarboxylatoplatinum (II) complexes with high or low
reactivity with thiols: two modes of action. Chem Biol Interact.
146:165–177. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Salti GI, Grewal S, Mehta RR, et al:
Genistein induces apoptosis and topoisomerase II-mediated DNA
breakage in colon cancer cells. Eur J Cancer. 36:796–802. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okura A, Arakawa H, Oka H, Yoshinari T and
Monnden Y: Effect of genistein on topoisomerase activity and on the
growth of (Val 12) Ha-ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 157:183–189. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davis JN, Singh B, Bhuiyan M and Sarkar
FH: Genistein-induced upregulation of p21WAF1,
downregulation of cyclin B, and induction of apoptosis in prostate
cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 32:123–131. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chan WH and Yu JS: Inhibition of UV
irradiation-induced oxidative stresses and apoptotic biochemical
changes in human epidermal carcinoma A431 cells by genistein. J
Cell Biochem. 78:73–84. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liang HW, Qiu SF, Shen J, et al: Genistein
attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal damage following transient
global cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett.
438:116–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu HJ and Chan WH: Genistein protects
methylglyoxal-induced oxidative DNA damage and cell injury in human
mononuclear cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 21:335–342. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Varbiro G, Veres B, Gallyas F Jr and
Sumegi B: Direct effect of Taxol on free radical formation and
mitochondrial permeability transition. Free Radic Biol Med.
31:548–558. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kinnula VL, Paakko P and Soini Y:
Antioxidant enzymes and redox regulating thiol proteins in
malignancies of human lung. FEBS Letters. 569:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nguyen TD, Maquart F and Monboisse J:
Ionizing radiations and collagen metabolism: from oxygen free
radicals to radio-induced late fibrosis. Radia Phys Chem.
72:381–386. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Meister A and Anderson ME: Glutathione.
Annu Rev Biochem. 52:711–760. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Singh KK: Mitochondria damage checkpoint,
aging, and cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1067:182–190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burhans WC and Hwintz NH: The cell cycle
is a redox cycle: linking phase-specific target to cell fate. Free
Radic Biol Med. 47:1282–1293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zielonka J, Gebicki J and Grynkiewicz G:
Radical scavenging properties of genistein. Free Radic Biol Med.
35:958–965. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wei H, Bowen R, Cai Q, Barnes S and Wang
Y: Antioxidant and antipromotional effects of the soybean
isoflavone genistein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 208:124–130. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Polkowski K and Mazurek AP: Biological
properties of genistein. A review of in vitro and in vivo data.
Acta Pol Pharm. 57:135–155. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Setchell KD and Cassidy A: Dietary
isoflavones: biological effects and relevance to human health. J
Nutr. 129:758S–767S. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schmidt F, Knobbe CB, Frank B, Wolburg H
and Weller M: The topoisomerase II inhibitor, genistein, induces
G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines.
Oncol Rep. 19:1061–1066. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Raffoul JJ, Che M, et al: Prostate
cancer treatment is enhanced by genistein in vitro and in vivo in a
syngeneic orthotopic tumor model. Radiat Res. 166:73–80. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shin JI, Shim JH, Kim KH, et al:
Sensitization of the apoptotic effect of gamma-irradiation in
genistein-pretreated CaSki cervical cancer cells. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 18:523–531. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matsukawa Y, Marui N, Sakai T, et al:
Genistein arrests cell cycle progression at G2-M. Cancer Res.
1328–1331. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cappelletti V, Fioravanti L, Miodini P and
Di Fronzo G: Genistein blocks breast cancer cells in the G(2)M
phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biochem. 79:594–600. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kumi-Diaka JK, Merchant K, Haces A, et al:
Genistein-selenium combination induces growth arrest in prostate
cancer cells. J Med Food. 13:842–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schafer FQ and Buettner GR: Redox
environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the
glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med.
30:1191–1212. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Szumiel I, Kapiszewska M, John A, et al:
Caffeine-inhibitable control of the radiation-induced G2 arrest in
L5178Y-S cells deficient in non-homologous end-joining. Radiat
Environ Biophys. 40:137–143. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Theron T, Binder A, Verheye-Dua F and
Boehm L: The role of G2-block abrogation, DNA double-strand break
repair and apoptosis in the radiosensitization of melanoma and
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by pentoxyfylline. Int J Radiat
Biol. 76:1197–1208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Abbott DW, Freeman ML and Holt JT:
Double-strand break repair deficiency and radiation sensitivity in
BRCA2 mutant cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 90:978–985. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|