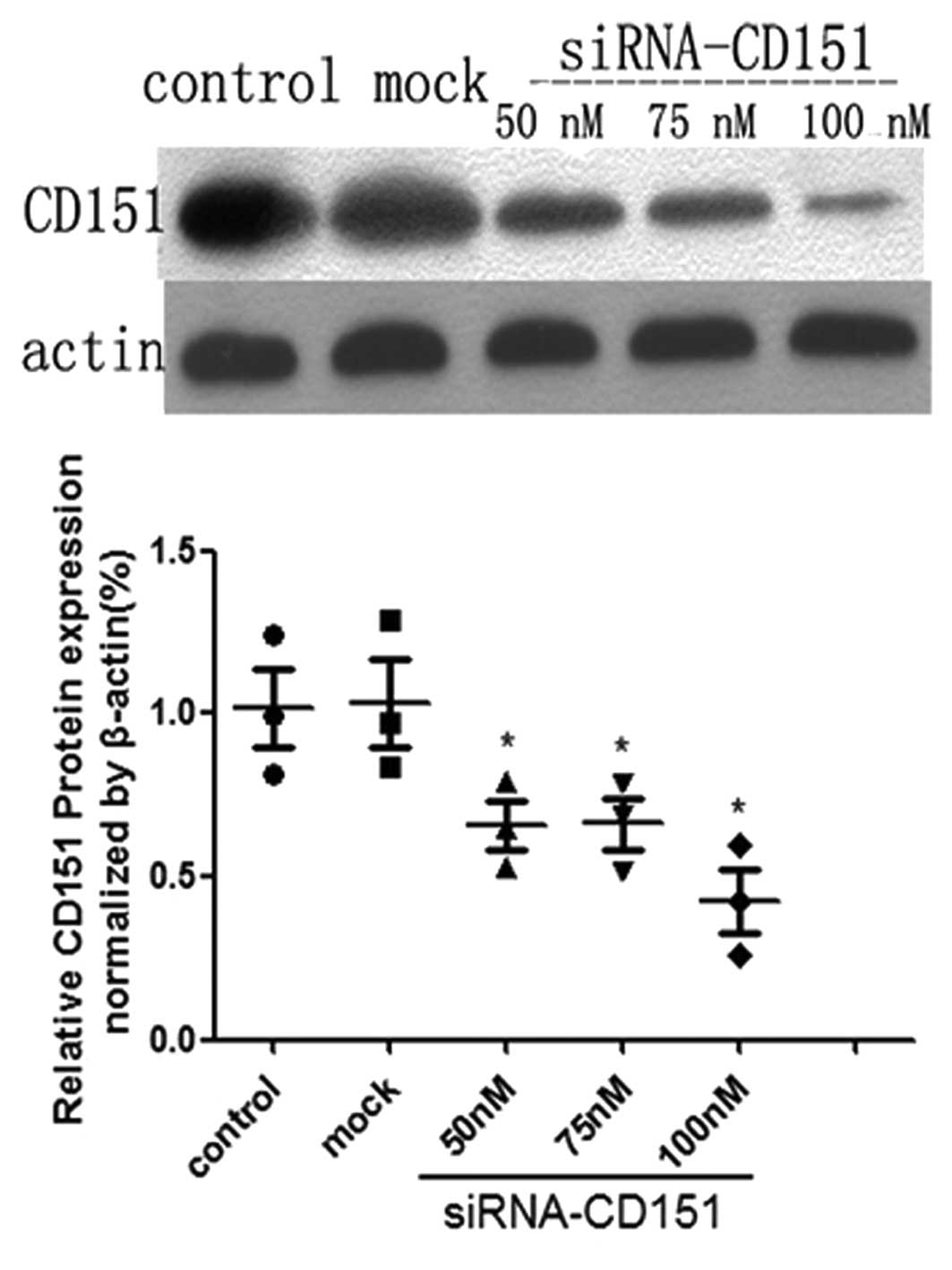
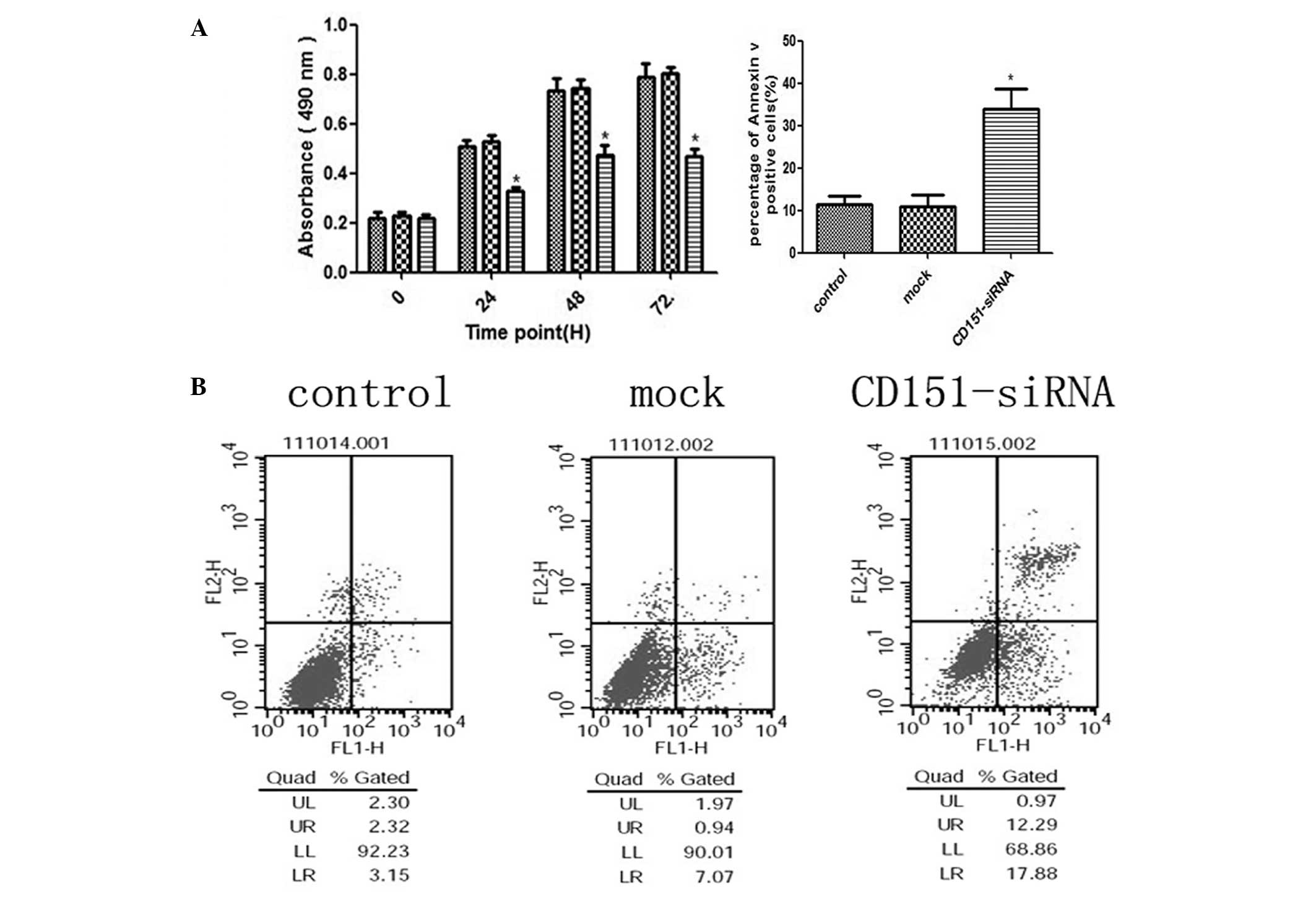
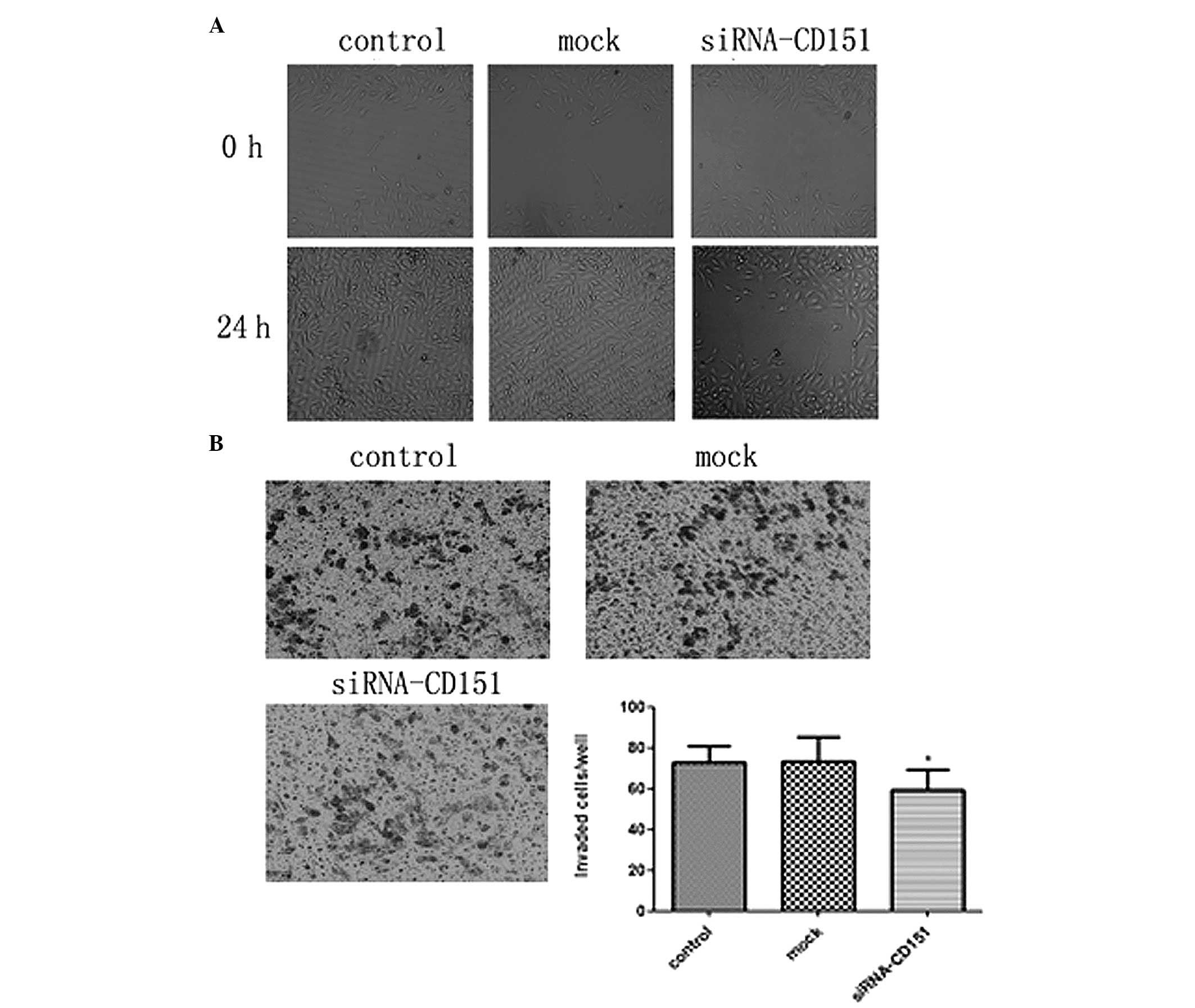
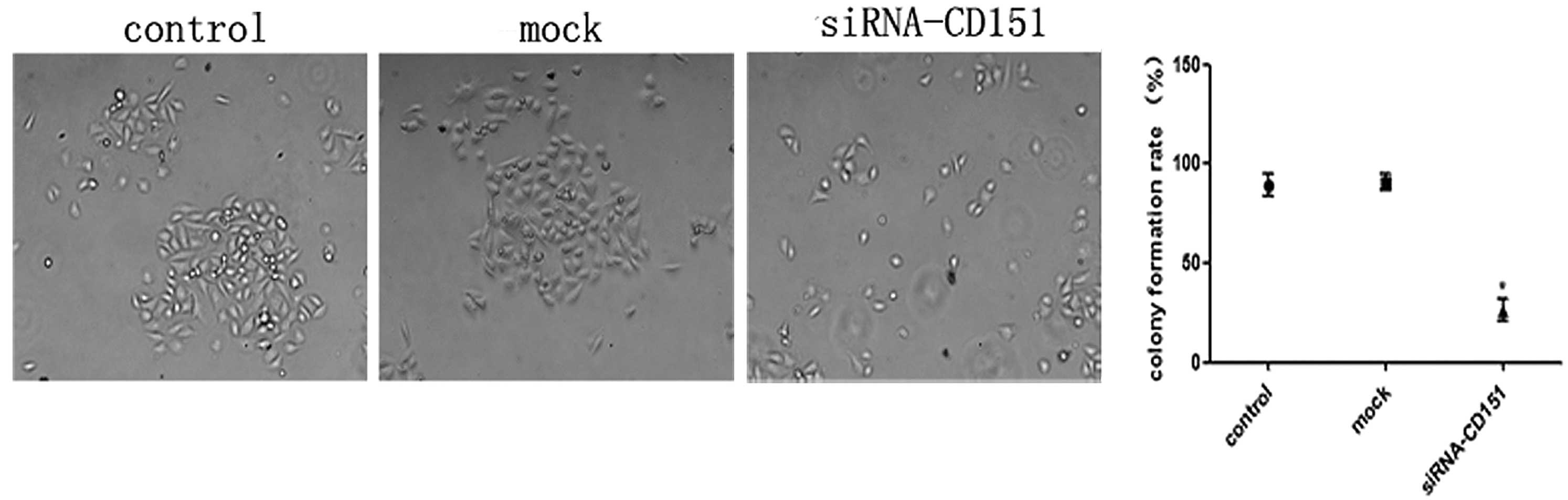
|
1
|
Bennett A and White J: Improving care and
quality of life for patients with lung cancer. Nurs Stand.
28:50–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oken MM, Hocking WG, Kvale PA, et al:
Screening by chest radiograph and lung cancer mortality: the
Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) randomized trial.
JAMA. 306:1865–1873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanagiri T, Baba T, So T, et al: Time
trends of surgical outcome in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5:825–829. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun X and Zheng Y: Retreatment with
icotinib in a patient with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Tumori.
99:e124–e126. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hashida H, Takabayashi A, Tokuhara T, et
al: Clinical significance of transmembrane 4 superfamily in colon
cancer. Br J Cancer. 89:158–167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kang BW, Lee D, Chung HY, et al:
Tetraspanin CD151 expression associated with prognosis for patients
with advanced gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
139:1835–1843. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang HX, Li Q, Sharma C, et al:
Tetraspanin protein contributions to cancer. Biochem Soc Trance.
39:547–552. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yue S, Mu W and Zöller M: Tspan8 and CD151
promote metastasis by distinct mechanisms. Eur J Cancer.
49:2934–2948. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Copeland BT, Bowman MJ and Ashman LK:
Genetic ablation of the tetraspanin CD151 reduces spontaneous
metastatic spread of prostate cancer in the TRAMP model. Mol Cancer
Res. 11:95–105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chernousov MA, Stahl RC and Carey DJ:
Tetraspanins are involved in Schwann cell-axon interaction. J
Neurosci Res. 91:1419–1428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Spring FA, Griffiths RE, Mankelow TJ, et
al: Tetraspanins CD81 and CD82 facilitate α4β1-mediated adhesion of
human erythroblasts to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. PLoS One.
8:e626542013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kwon MJ, Seo J, Kim YJ, et al: Prognostic
significance of CD151 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 81:109–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ang J, Lijovic M, Ashman LK, et al: CD151
protein expression predicts the clinical outcome of low-grade
primary prostate cancer better than histologic grading: a new
prognostic indicator? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
13:1717–1721. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee D, Suh YL, Park TI, et al: Prognostic
significance of tetraspanin CD151 in newly diagnosed glioblastomas.
J Surg Oncol. 107:646–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Haeuw JF, Goetsch L, Bailly C, et al:
Tetraspanin CD151 as a target for antibody-based cancer
immunotherapy. Biochem Soc Trans. 39:553–558. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Minner S, De Silva C, Rink M, et al:
Reduced CD151 expression is related to advanced tumour stage in
urothelial bladder cancer. Pathology. 44:448–452. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ang J, Fang BL, Ashman LK, et al: The
migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cell lines involves
CD151 expression. Onco Rep. 24:1593–1597. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Woegerbauer M, Thurnher D, Houben R, et
al: Expression of the tetraspanins CD9, CD37, CD63, and CD151 in
Merkel cell carcinoma: strong evidence for a posttranscriptional
fine-tuning of CD9 gene expression. Mod pathol. 23:751–762. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang W, Li P, Lin J, et al: CD151 promotes
proliferation and migration of PC3 cells via the formation of
CD151-integrin α3/α6 complex. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 32:383–388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gottumukkala SN, Dwarakanath CD and
Sudarsan S: Ribonucleic acid interference induced gene knockdown. J
Indian Soc Periodontol. 17:417–422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wilson RC and Doudna JA: Molecular
mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu Rev Biophys. 42:217–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujishima S, Shiomi T, Yamashita S, et al:
Production and activation of matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin
1) in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 134:1136–1142. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hong IK, Jin YJ, Byun HJ, et al:
Homophilic interactions of Tetraspanin CD151 up-regulate motility
and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression of human melanoma cells
through adhesion-dependent c-Jun activation signaling pathways. J
Biol Chem. 281:24279–24292. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ogorevc E, Kralj-Iglic V and Veranic P:
The role of extracellular vesicles in phenotypic cancer
transformation. Radiol Oncol. 47:197–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Olbryt M: Role of tumor microenvironment
in the formation and progression of skin melanoma. Postepy Hig Med
Dosw (Online). 67:413–432. 2013.(In Polish). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang HX, Li Q, Sharma C, et al:
Tetraspanin protein contributions to cancer. Biochem Soc Trans.
39:547–552. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Romanska HM and Berditchevski F:
Tetraspanins in human epithelial malignancies. J Pathol. 223:4–14.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Takeda Y, Kazarov AR, Butterfield CE, et
al: Deletion of tetraspanin Cd151 results in decreased pathologic
angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Blood. 109:1524–1532. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yañez-Mó M, Barreiro O, Gonzalo P, et al:
MT1-MMP collagenolytic activity is regulated through association
with tetraspanin CD151 in primary endothelial cells. Blood.
112:3217–3226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Devbhandari RP, Shi GM, Ke AW, et al:
Profiling of the tetraspanin CD151 web and conspiracy of
CD151/integrin β1 complex in the progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e249012011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Colin S, Guilmain W, Creoff E, et al: A
truncated form of CD9-partner 1 (CD9P-1), GS-168AT2, potently
inhibits in vivo tumour-induced angiogenesis and tumour growth. Br
J Cancer. 105:1002–1011. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Charrin S, Manié S, Billard M, et al:
Multiple levels of interactions within the tetraspanin web. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:107–112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|