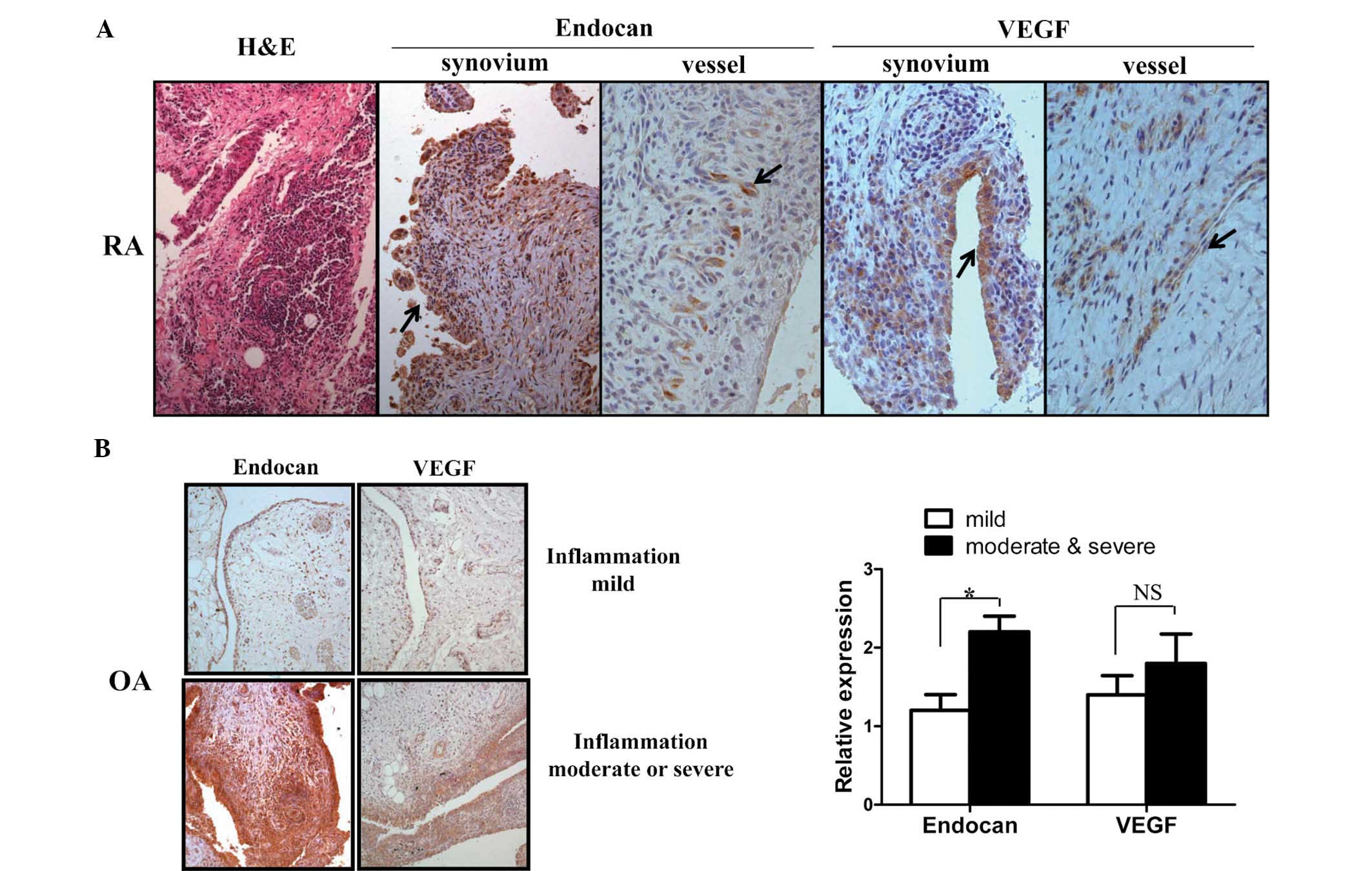
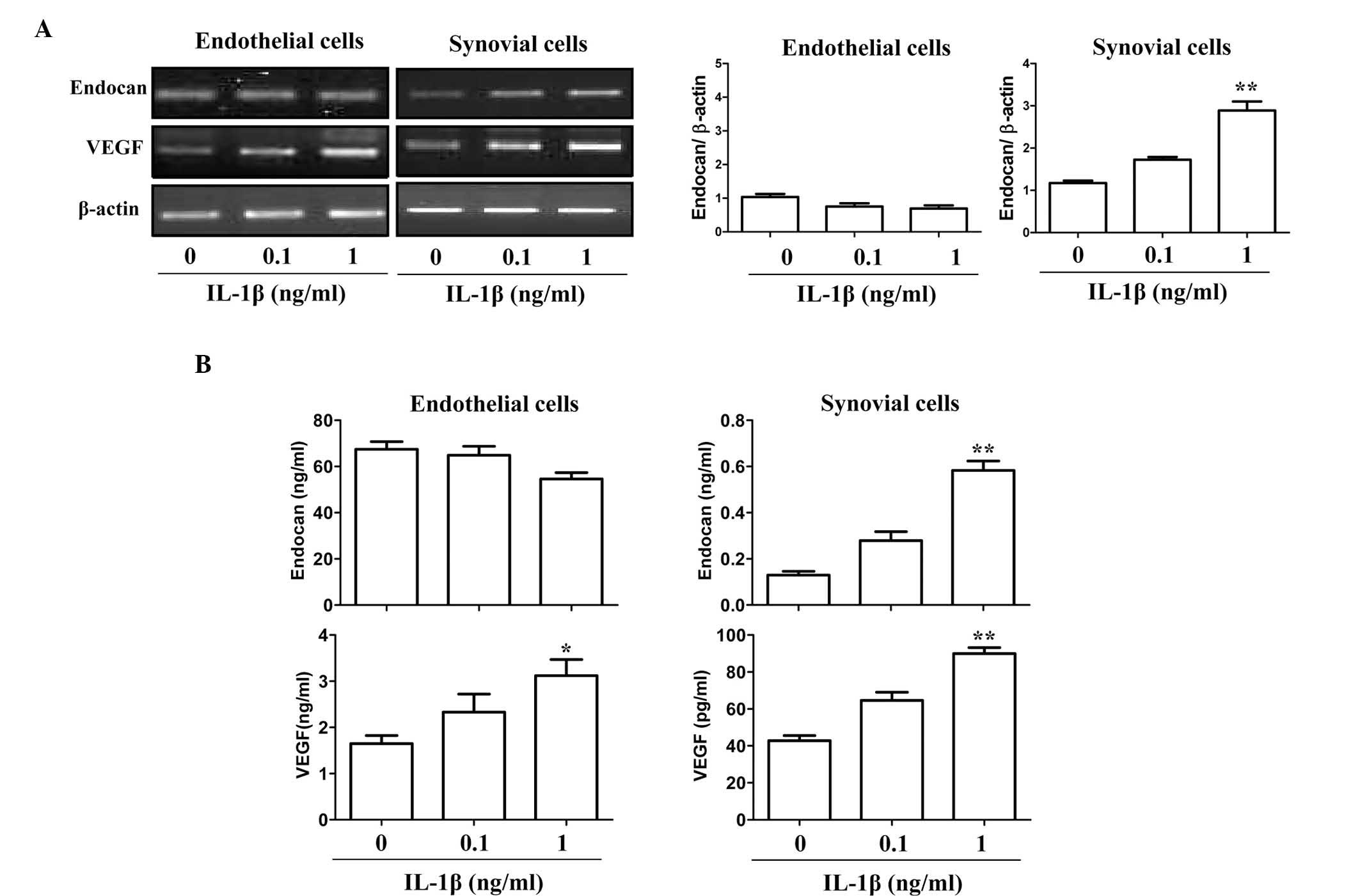
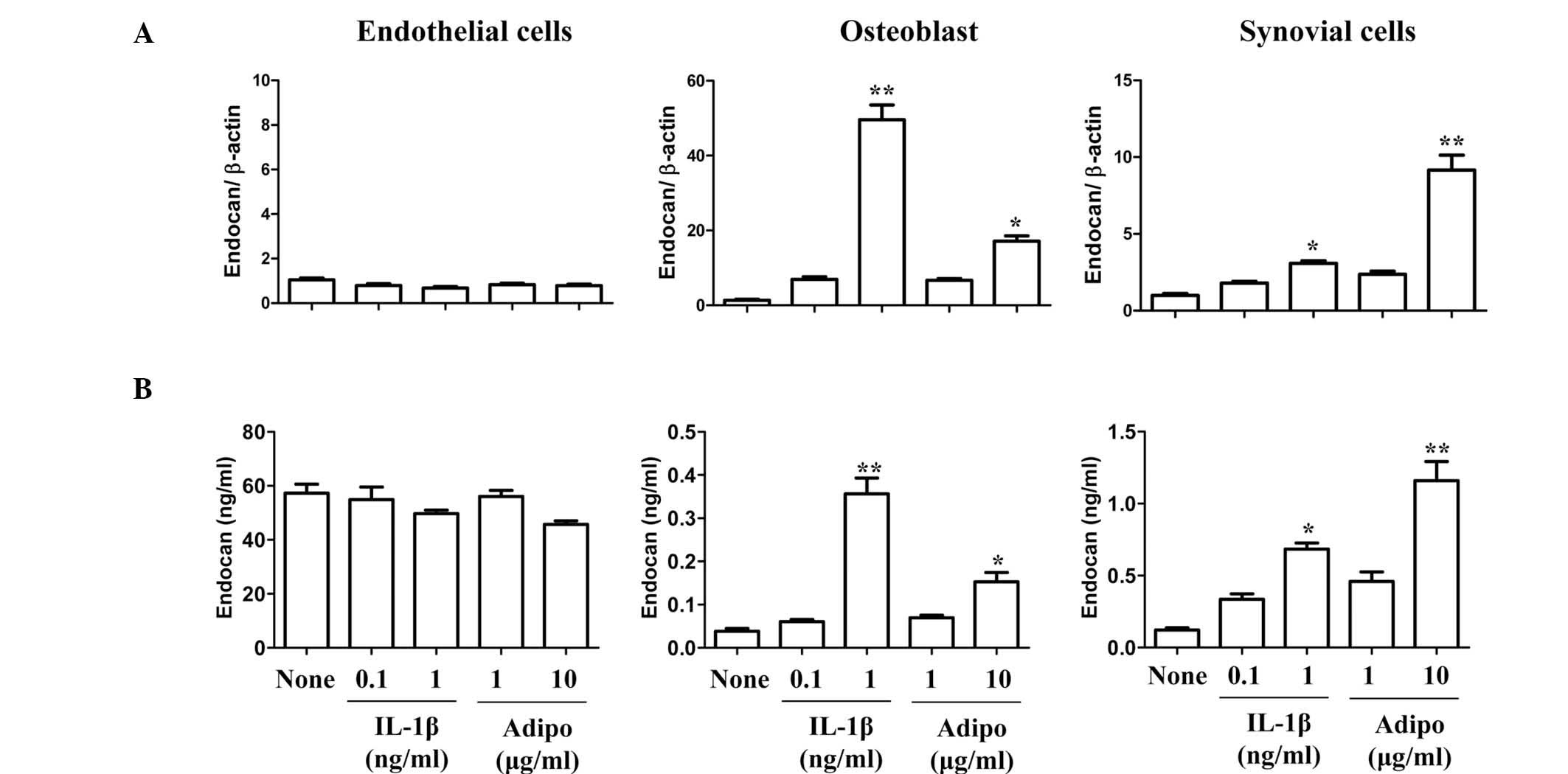
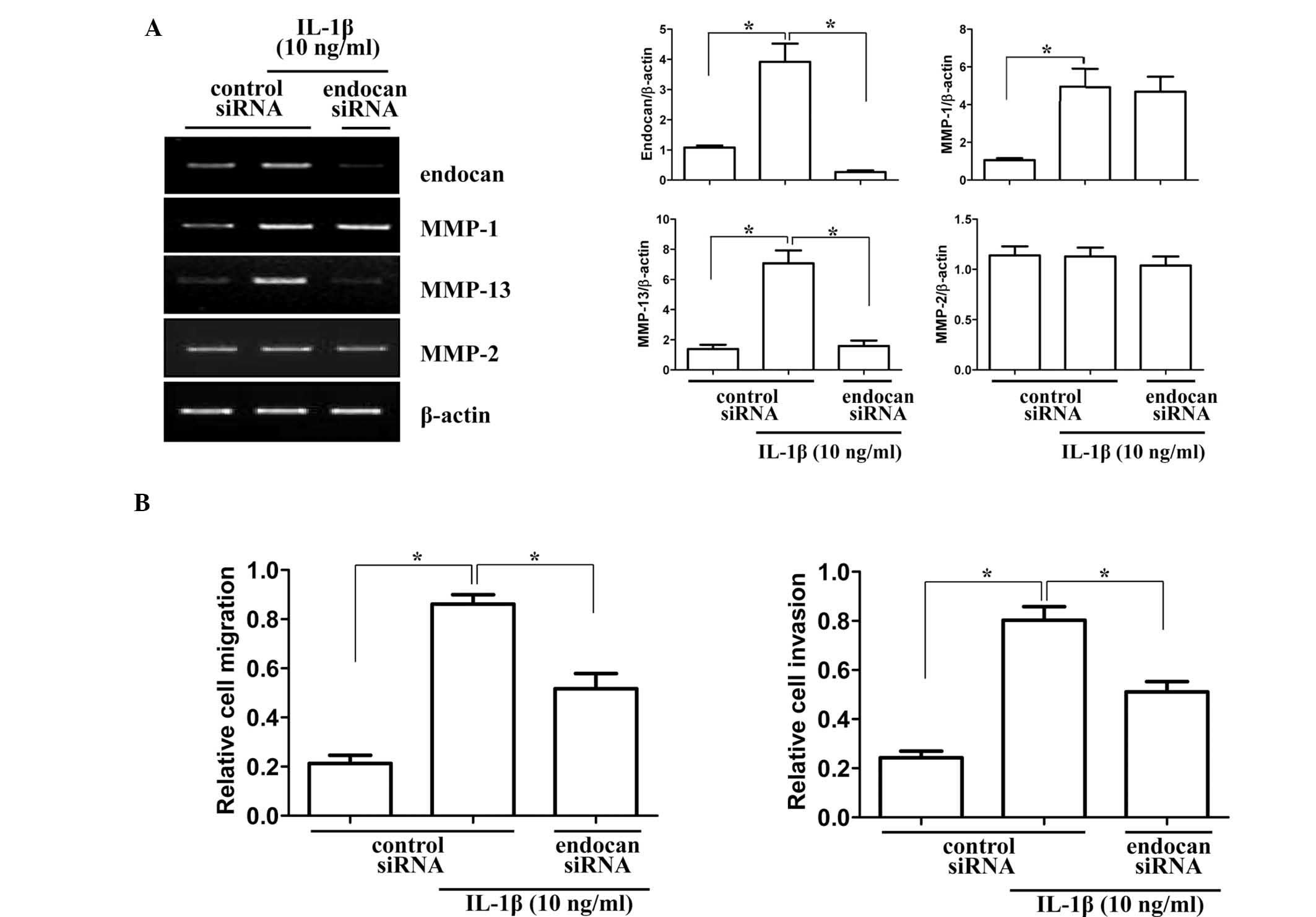
|
1
|
Gravallese EM and Monach PA: Rheumatoid
synovitis and pannus. Rheumatology. Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen
JS, Weinblatt ME and Weisman MH: 4th edition. Elsevier Ltd; London,
UK: pp. 841–865. 2008
|
|
2
|
Bresnihan B: Pathogenesis of joint damage
in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 26:717–719. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Szekanecz Z and Koch AE: Mechanisms of
disease: angiogenesis in inflammatory diseases. Nat Clin Pract
Rheumatol. 3:635–643. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schoettler N and Brahn E: Angiogenesis
inhibitors for the treatment of chronic autoimmune inflammatory
arthritis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 10:425–433. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lainer-Carr D and Brahn E: Angiogenesis
inhibition as a therapeutic approach for inflammatory synovitis.
Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 3:434–442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sarrazin S, Adam E, Lyon M, Depontieu F,
Motte V, Landolfi C, Lortat-Jacob H, Bechard D, Lassalle P and
Delehedde M: Endocan or endothelial cell specific molecule-1
(ESM-1): a potential novel endothelial cell marker and a new target
for cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1765:25–37. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Lassalle P, Molet S, Janin A, Heyden JV,
Tavernier J, Fiers W, Devos R and Tonnel AB: ESM-1 is a novel human
endothelial cell-specific molecule expressed in lung and regulated
by cytokines. J Biol Chem. 271:20458–20464. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Béchard D, Gentina T, Delehedde M,
Scherpereel A, Lyon M, Aumercier M, Vazeux R, Richet C, Degand P,
Jude B, et al: Endocan is a novel chondroitin sulfate/dermatan
sulfate proteoglycan that promotes hepatocyte growth factor/scatter
factor mitogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 276:48341–48349.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Béchard D, Scherpereel A, Hammad H,
Gentina T, Tsicopoulos A, Aumercier M, Pestel J, Dessaint JP,
Tonnel AB and Lassalle P: Human endothelial-cell specific
molecule-1 binds directly to the integrin CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) and
blocks binding to intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol.
167:3099–3106. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang YH, Ji NY, Lee CI, Lee HG, Kim JW,
Yeom YI, Kim DG, Yoon SK, Kim JW, Park PJ and Song EY: ESM-1
silencing decreased cell survival, migration, and invasion and
modulated cell cycle progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Amino
Acids. 40:1003–1013. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Maurage CA, Adam E, Minéo JF, Sarrazin S,
Debunne M, Siminski RM, Baroncini M, Lassalle P, Blond S and
Delehedde M: Endocan expression and localization in human
glioblastomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 68:633–641. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grigoriu BD, Depontieu F, Scherpereel A,
Gourcerol D, Devos P, Ouatas T, Lafitte JJ, Copin MC, Tonnel AB and
Lassalle P: Endocan expression and relationship with survival in
human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4575–4582.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi HM, Lee YA, Lee SH, Hong SJ, Hahm DH,
Choi SY, Yang HI, Yoo MC and Kim KS: Adiponectin may contribute to
synovitis and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by
stimulating vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix
metalloproteinase-1, and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in
fibroblast-like synoviocytes more than proinflammatory mediators.
Arthritis Res Ther. 11:R1612009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim KS, Park EK, Ju SM, Jung HS, Bang JS,
Kim C, Lee YA, Hong SJ, Lee SH, Yang HI and Yoo MC: Taurine
chloramine differentially inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 1 and
13 synthesis in interleukin-1beta stimulated fibroblast-like
synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R802007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roudnicky F, Poyet C, Wild P, Krampitz S,
Negrini F, Huggenberger R, Rogler A, Stöhr R, Hartmann A,
Provenzano M, et al: Endocan is upregulated on tumor vessels in
invasive bladder cancer where it mediates VEGF-A-induced
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 73:1097–1106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Aitkenhead M, Wang SJ, Nakatsu MN, Mestas
J, Heard C and Hughes CC: Identification of endothelial cell genes
expressed in an in vitro model of angiogenesis: induction of ESM-1,
(beta)ig-h3, and NrCAM. Microvasc Res. 63:159–171. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weber AJ and De Bandt M: Angiogenesis:
general mechanisms and implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Joint
Bone Spine. 67:366–383. 2000.
|
|
18
|
Firestein GS: Evolving concepts of
rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423:356–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abid MR, Yi X, Yano K, Shih SC and Aird
WC: Vascular endocan is preferentially expressed in tumor
endothelium. Microvasc Res. 72:136–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bechard D, Meignin V, Scherpereel A, Oudin
S, Kervoaze G, Bertheau P, Janin A, Tonnel A and Lassalle P:
Characterization of the secreted form of endothelial-cell-specific
molecule 1 by specific monoclonal antibodies. J Vasc Res.
37:417–425. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Janke J, Engeli S, Gorzelniak K,
Feldpausch M, Heintze U, Böhnke J, Wellner M, Herse F, Lassalle P,
Luft FC and Sharma AM: Adipose tissue and circulating endothelial
cell specific molecule-1 in human obesity. Horm Metab Res.
38:28–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wellner M, Herse F, Janke J, Gorzelniak K,
Engeli S, Bechart D, Lasalle P, Luft FC and Sharma AM: Endothelial
cell specific molecule-1 - a newly identified protein in
adipocytes. Horm Metab Res. 35:217–221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kang YH, Ji NY, Han SR, Lee CI, Kim JW,
Yeom YI, Kim YH, Chun HK, Kim JW, Chung JW, et al: ESM-1 regulates
cell growth and metastatic process through activation of NF-κB in
colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. 24:1940–1949. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|