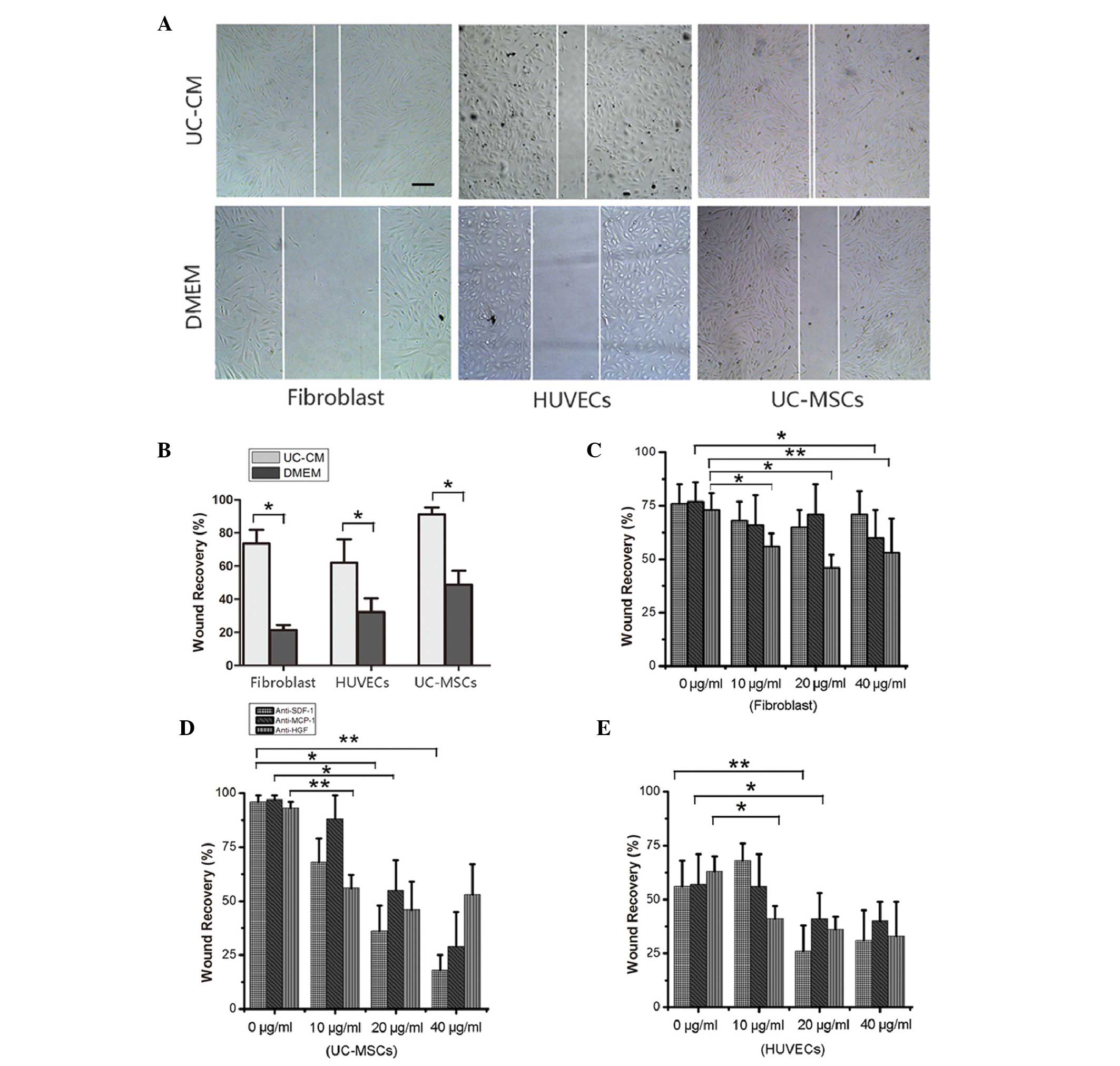
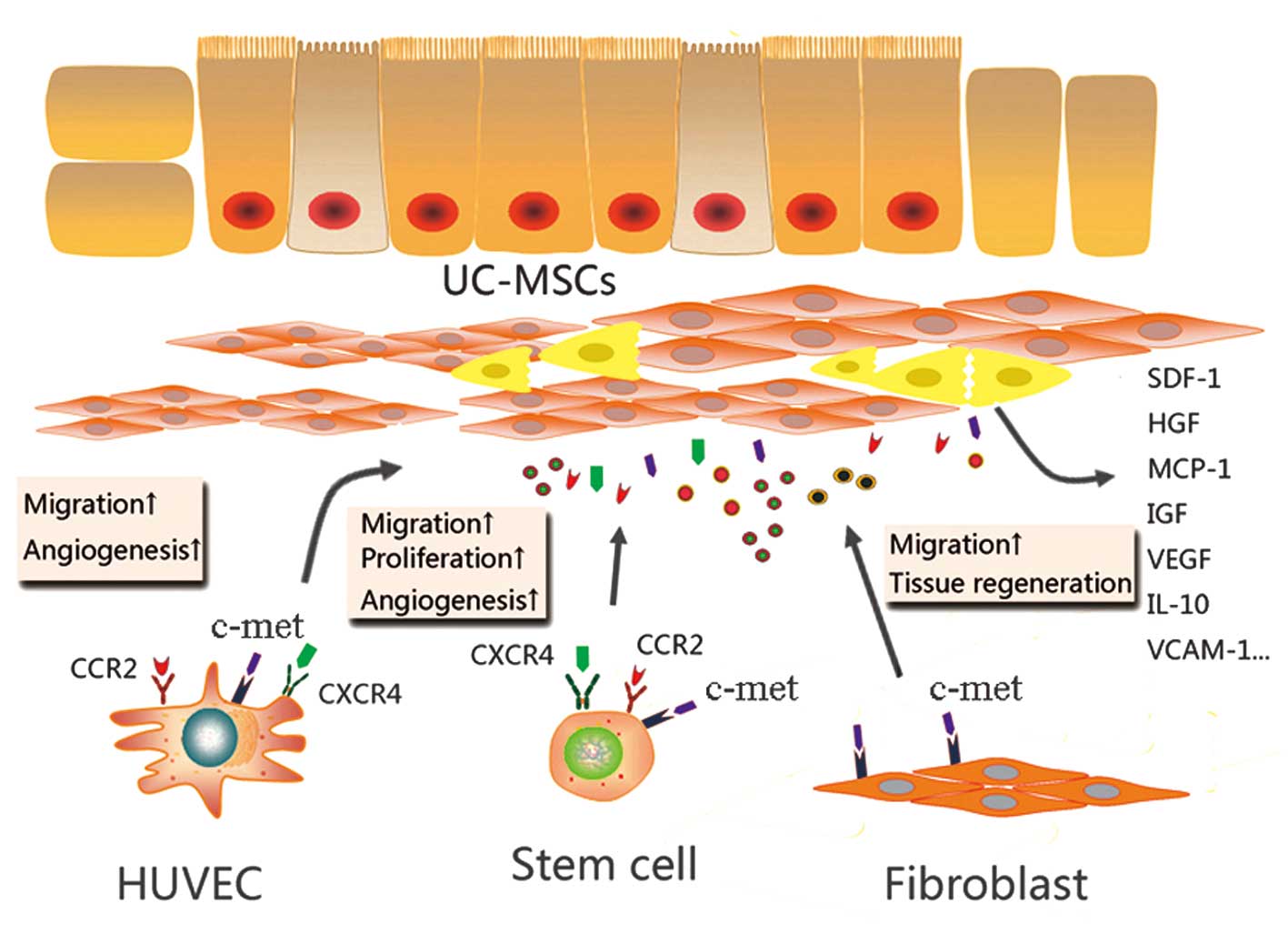
|
1
|
Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton’s jelly of the human
umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 22:1330–1337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Madlambayan G and Rogers I: Umbilical
cord-derived stem cells for tissue therapy: current and future
uses. Regen Med. 1:777–787. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ruan ZB, Zhu L, Yin YG and Chen GC: The
mechanism underlying the differentiation of human umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myocardial cells induced
by 5-azacytidine. Indian J Med Sci. 64:402–407. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schneider RK, Püllen A, Kramann R, et al:
Long-term survival and characterisation of human umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on dermal equivalents.
Differentiation. 79:182–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rabb H: Paracrine and differentiation
mechanisms underlying stem cell therapy for the damaged kidney. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 289:F29–30. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deschepper M, Oudina K, David B, et al:
Survival and function of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) depend on
glucose to overcome exposure to long-term, severe and continuous
hypoxia. J Cell Mol Med. 15:1505–1514. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nagaya N, Kangawa K, Itoh T, et al:
Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function
in a rat model of dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation.
112:1128–1135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Müller-Ehmsen J, Krausgrill B, Burst V, et
al: Effective engraftment but poor mid-term persistence of
mononuclear and mesenchymal bone marrow cells in acute and chronic
rat myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 41:876–884. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao JJ, Liu JL, Liu L and Jia HY:
Protection of mesenchymal stem cells on acute kidney injury. Mol
Med Rep. 9:91–96. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Chen Y, Xiang LX, Shao JZ, et al:
Recruitment of endogenous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
towards injured liver. J Cell Mol Med. 14:1494–1508. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tasso R, Augello A, Boccardo S, et al:
Recruitment of a host’s osteoprogenitor cells using exogenous
mesenchymal stem cells seeded on porous ceramic. Tissue Eng Part A.
15:2203–2212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tögel F, Isaac J, Hu Z, Weiss K and
Westenfelder C: Renal SDF-1 signals mobilization and homing of
CXCR4-positive cells to the kidney after ischemic injury. Kidney
Int. 67:1772–1784. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma J, Ge J, Zhang S, et al: Time course of
myocardial stromal cell-derived factor 1 expression and beneficial
effects of intravenously administered bone marrow stem cells in
rats with experimental myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol.
100:217–223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Son BR, Marquez-Curtis LA, Kucia M, et al:
Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in
vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-1-CXCR4 and hepatocyte
growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloproteinases.
Stem Cells. 24:1254–1264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Somerset DA, Li XF, Afford S, et al:
Ontogeny of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor (c-met)
in human placenta: reduced HGF expression in intrauterine growth
restriction. Am J Pathol. 153:1139–1147. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liao WT, Yu HS, Arbiser JL, et al:
Enhanced MCP-1 release by keloid CD14+ cells augments fibroblast
proliferation: role of MCP-1 and Akt pathway in keloids. Exp
Dermatol. 19:e142–e150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Furuichi K, Wada T, Iwata Y, et al: CCR2
signaling contributes to ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 14:2503–2515. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shyu WC, Lee YJ, Liu DD, Lin SZ and Li H:
Homing genes, cell therapy and stroke. Front Biosci. 11:899–907.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ashrafpour H, Huang N, Neligan PC, et al:
Vasodilator effect and mechanism of action of vascular endothelial
growth factor in skin vasculature. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
286:H946–H954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Morimoto N, Saso Y, Tomihata K, et al:
Viability and function of autologous and allogeneic fibroblasts
seeded in dermal substitutes after implantation. J Surg Res.
125:56–67. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lamme EN, van Leeuwen RT, Mekkes JR and
Middelkoop E: Allogeneic fibroblasts in dermal substitutes induce
inflammation and scar formation. Wound Repair Regen. 10:152–160.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cavallari G, Olivi E, Bianchi F, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells and islet cotransplantation in diabetic
rats: improved islet graft revas-cularization and function by human
adipose tissue-derived stem cells preconditioned with natural
molecules. Cell Transplant. 21:2771–2781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wynn RF, Hart CA, Corradi-Perini C, et al:
A small proportion of mesenchymal stem cells strongly expresses
functionally active CXCR4 receptor capable of promoting migration
to bone marrow. Blood. 104:2643–2645. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dai W, Hale SL and Kloner RA: Role of a
paracrine action of mesen-chymal stem cells in the improvement of
left ventricular function after coronary artery occlusion in rats.
Regen Med. 2:63–68. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Z, Guo J, Chang Q and Zhang A:
Paracrine role for mesen-chymal stem cells in acute myocardial
infarction. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1343–1346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ohnishi S, Sumiyoshi H, Kitamura S and
Nagaya N: Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate cardiac fibroblast
proliferation and collagen synthesis through paracrine actions.
FEBS Lett. 581:3961–3966. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakanishi C, Yamagishi M, Yamahara K, et
al: Activation of cardiac progenitor cells through paracrine
effects of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
374:11–16. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dwyer RM, Potter-Beirne SM, Harrington KA,
et al: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 secreted by primary breast
tumors stimulates migration of mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:5020–5027. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Z, Htay A, Dos Santos W, et al: In
vitro angiogenesis by human umbilical vein endothelial cells
(HUVEC) induced by three-dimensional co-culture with glioblastoma
cells. J Neurooncol. 92:121–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jacob M, Chang L and Puré E: Fibroblast
activation protein in remodeling tissues. Curr Mol Med.
12:1220–1243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mbalaviele G, Orcel P, Bouizar Z,
Jullienne A and De Vernejoul MC: Transforming growth factor-beta
enhances calcitonin-induced cyclic AMP production and the number of
calcitonin receptors in long-term cultures of human umbilical cord
blood monocytes in the presence of 1,25-dihydroxychole-calciferol.
J Cell Physiol. 152:486–493. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peled A, Kollet O, Ponomaryov T, et al:
The chemokine SDF-1 activates the integrins LFA-1, VLA-4, and VLA-5
on immature human CD34(+) cells: role in transendothelial/stromal
migration and engraftment of NOD/SCID mice. Blood. 95:3289–3296.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Li Y, Chen J, et al: Ischemic
cerebral tissue and MCP-1 enhance rat bone marrow stromal cell
migration in interface culture. Exp Hematol. 30:831–836. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patel AV and Krimm RF: BDNF is required
for the survival of differentiated geniculate ganglion neurons. Dev
Biol. 340:419–429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sohni A and Verfaillie CM: Mesenchymal
stem cells migration homing and tracking. Stem Cells Int.
130763:20132013.
|
|
36
|
Lapidot T and Kollet O: The essential
roles of the chemokine SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in human stem
cell homing and repopulation of transplanted immune-deficient
NOD/SCID and NOD/SCID/B2m(null) mice. Leukemia. 16:1992–2003. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ringe J, Strassburg S, Neumann K, et al:
Towards in situ tissue repair: human mesenchymal stem cells express
chemokine receptors CXCR1, CXCR2 and CCR2, and migrate upon
stimulation with CXCL8 but not CCL2. J Cell Biochem. 101:135–146.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM:
Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for
invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:289–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E and
Vande Woude GF: Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:915–925. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Duan HF, Wu CT, Wu DL, et al: Treatment of
myocardial ischemia with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor. Mol Ther. 8:467–474. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oyagi S, Hirose M, Kojima M, et al:
Therapeutic effect of transplanting HGF-treated bone marrow
mesenchymal cells into CCl4-injured rats. J Hepatol. 44:742–748.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Burgazli KM, Bui KL, Mericliler M,
Albayrak AT, Parahuleva M and Erdogan A: The effects of different
types of statins on proliferation and migration of HGF-induced
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 17:2874–2883. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|