Introduction
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with
thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTSs) are secretory proteins that are
involved in a variety of biological processes, such as
angiogenesis, cell adhesion, proteolytic shedding and cell
signaling. ADAMTS type 1 motif 9 (ADAMTS9) is involved in
proteoglycan degradation (1,2).
IL-1β was found to induce ADAMTS9 gene expression in OUMS-27
chondrosarcoma cells in a previous investigation (3). ADAMTS9 gene expression was
synergistically induced by a combination of IL-1β and tumor
necrosis factor α (TNF α), suggesting that the induction of ADAMTS9
may be associated with cartilage inflammation (4). The human ADAMTS9 promoter region
contains nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1) consensus
sites. Following treatment with IL-1β, NFATc1 was activated in
human chondrocytic cells (5). A
previous investigation demonstrated that, following treatment with
a combination of TNF and IL-1β, the expression of activated
activator protein 1 and NF-κB transcription factors was enhanced in
human chondrocytic cells (6).
NF-κB is a pro-inflammatory transcription factor,
the expression of which is activated by inflammatory cytokines such
as TNF α and IL-1, and a number of chemokines (7–9).
NF-κB activation may occur via classical or canonical pathways
(10). NF-κB is composed of
homodimers and heterodimers of five members of the Rel family,
which exhibit different binding specificities, including p65/RelA,
RelB, c-Rel, p50/p105 and p52/p100. One of the predominant types of
heterodimers consists of p65 and p50 subunits. NF-κB is typically
found in the cytoplasm. The nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide
gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor (IκB) kinase complex (IKK
complex) is composed of two catalytic subunits (IKKα and IKKβ). The
IKK complex binds with the regulatory subunit IKKγ/NF-κB essential
modulator, which subsequently forms the TNF-α receptor complex, and
promotes IκB phosphorylation. Phosphorylated IκB-α is rapidly
ubiquitinated and degraded via a proteasome pathway. Degradation of
IκB-α leads to the expression of NF-κB, which translocates into the
nucleus where it binds to specific binding sites within the
promoter regions of target genes (9).
In the present study, the association between NF-κB
and IL-1β stimulation was examined, and the involvement of NF-κB
and IL-1β in ADAMTS9 promoter activation was analyzed in OUMS-27
cells.
Materials and methods
Antibodies and reagents
Mouse monoclonal antibodies against the
phosphorylated NF-κB-p65 subunit (sc-33020; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA), total NF-κB-p65 (sc-372;
Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) and IκB-α (9242; Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA) were used for western blot
analysis at a dilution of 1:1,000. Recombinant human IL-1β and BAY
11-7085 were purchased from R&D Systems, Inc. (Minneapolis, MN,
USA) and EMD Millipore (Billerica, MA, USA), respectively. For the
chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay of the ADAMTS9 promoter
region, a ChIP assay kit was used (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt,
Germany). The primers used for ChIP and the conjugated
oligonucleotides used for electromobility shift assays (EMSA) were
purchased from Alpha DNA technologies (Montreal, Canada). A Light
Shift chemiluminescence EMSA kit was purchased from Thermo Fisher
Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA).
Cell cultures and cytokine treatment
The OUMS-27 human chondrosarcoma cell line was
obtained from Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine
Dentistry and Pharmacological Sciences (Okayama, Japan). Cells were
maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium-low glucose
(Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum
(Thermo Fisher Scientific), 100 U/ml penicillin (Thermo Fisher
Scientific) and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (Thermo Fisher
Scientific) at 37°C in 5% CO2. Cells were treated with
or without 10 ng/ml IL-1β, and 5, 10 or 20 μg/ml BAY-117085
was added to the cultures.
Western blotting
Cell lysates were separated using 10% SDS-PAGE
(Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and transferred to
polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (EMD Millipore). The membrane
was treated with 5% non-fat milk (Cell Signalling Technologies,
Inc., Danvers, MA, USA) for 1 h at room temperature and probed with
the p-NF-κB-p65 subunit, total NF-κB-p65 and IkB-α primary
antibodies overnight at 4°C. The primary antibodies were detected
using horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit and
anti-mouse secondary antibodies (IgG; Santa Cruz Biotechnology,
Inc.), and visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence (Thermo
Fisher Scientific).
ChIP assay
ChIP analysis was performed according to the
manufacturer’s instructions (EMD Millipore). Following treatment
with IL-1β, OUMS-27 cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde
(Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 min. The cells were lysed in SDS lysis buffer
(Thermo Fisher Scientific). Subsequently the chromatin was
sonicated to an average size of 0.5–1 kb. Chromatin solutions were
precipitated overnight at 4°C using an anti-p65 antibody. Immune
complexes were recovered using a salmon sperm DNA-saturated protein
A agarose gel (EMD Millipore). In order to reverse the cross-linked
and immunoprecipitated chromatin, solutions were incubated at 65°C
overnight. DNA was extracted using phenol/chloroform
(Sigma-Aldrich) and precipitated with ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich)
following proteinase K (Sigma-Aldrich) treatment. PCR was conducted
in order to amplify 205 and 260 bp fragments of the ADAMTS9
promoter region (−1335/−1177), using the following PCR protocol:
96°C for 5 min and 96°C for 30 sec, followed by 30 cycles of 56°C
for 30 sec and 72°C for 40 sec. The primers for ADAMTS9 promoter
regions (−1335 and −1177) were obtained from Alpha DNA
Technologies, and are shown in Table
I. SoniGenomic DNA (EMD Millipore), following sonification, was
used as a positive control and immunoprecipitated DNA-conjugated
mouse IgG (EMD Millipore) was used as a negative control for the
experiments.
 | Table IPrimers used in the chromatin
immunoprecipitation analysis. |
Table I
Primers used in the chromatin
immunoprecipitation analysis.
| NF-κB consensus site
in ADAMTS9 promoter | Sense (5′–3′) | Antisense
(3′–5′) | PCR product (bp) |
|---|
| −1335 |
CCACTGAACCACCCAAGATT |
GGAGTGTAAAGTTGTAGATCC | 205 |
| −1177 |
GGATCTACAACTTTACACTCC |
TGGGGTTCTTAATCCTGCAGGTC | 260 |
| −618 |
GGAAAGGGAGAGAACTTTCC |
TTCCAGACCATGTCCCCTCC | 196 |
| −460 |
GGAGGGGACATGGTCTGGAA |
GGATAGCTGAGCGGCTTCTT | 402 |
| −130 |
AAGAAGCCGCTCAGCTATCC |
CGCCAACTTTTGACTTTAGG | 258 |
EMSA
EMSA was performed using the LightShift
Chemiluminescent EMSA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific), according to
the manufacturer’s instructions. Nuclear extracts were prepared
from OUMS-27 cells and probed with HRP-conjugated DNA oligos, which
were homologous to the consensus NF-κB site at −1335 upstream of
the ADAMTS9 promoter region. A biotin-labeled
5′GGCTGAAAGCAAGCGGAAGTGATTGAGAAATCCCTCCAG3′ oligo was used.
Protein-DNA complexes were separated on a 6% polyacrylamide gel
using electrophoresis. A super shift assay was performed using
nuclear extracts pretreated with antibodies against the NF-κB-p65
protein (as used in western blot analysis). The NF-κB competitor
probe, a nonlabeled (“cold”) oligonucleotide, was added in excess
to be used as a negative control, and the H4 histone protein was
used as a positive control (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Results
IL-1β-stimulated NF-κB-p65
phosphorylation is reversed by BAY 11-7085
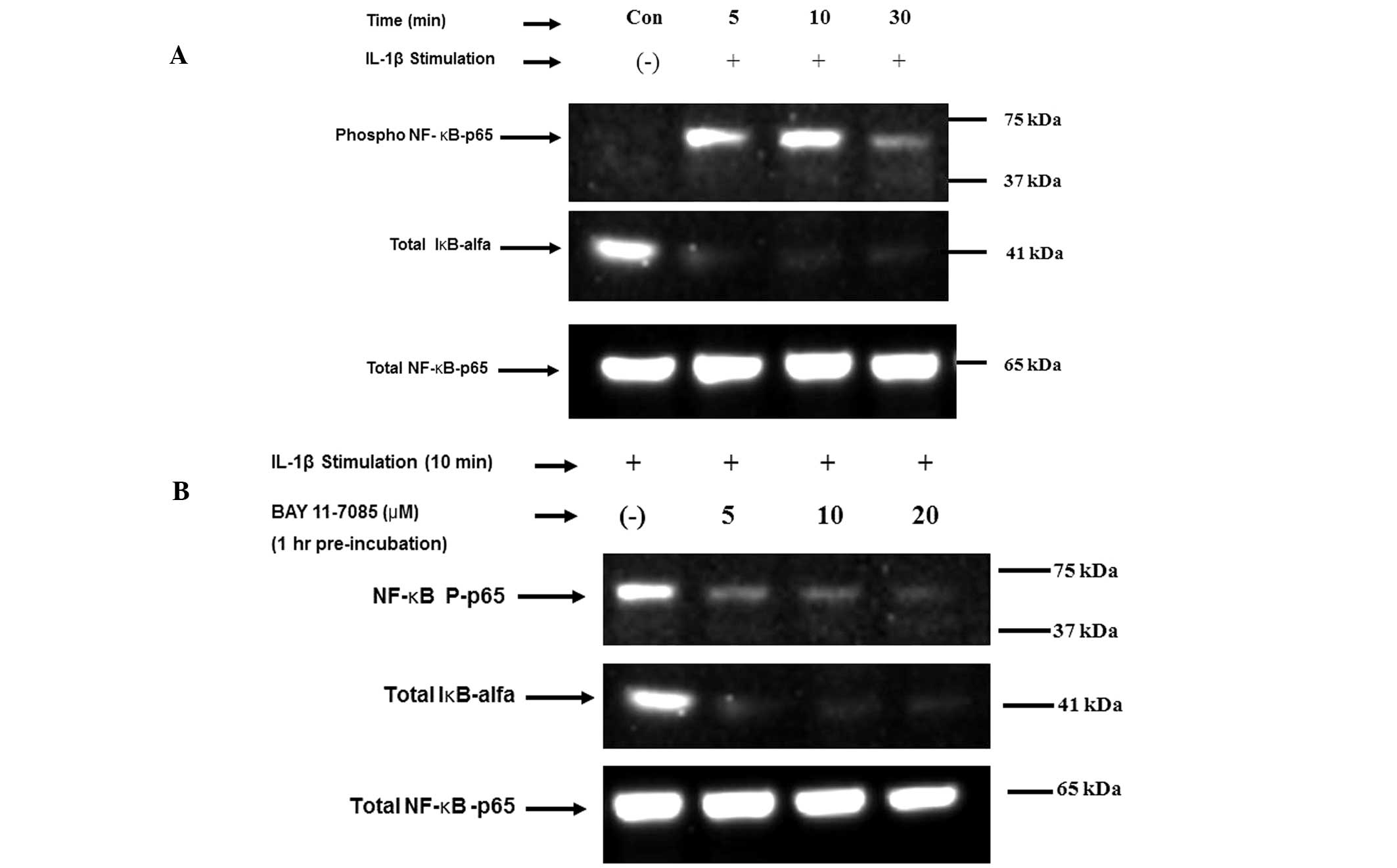
A western blot analysis was performed in order to
analyze NF-κB-p65 phosphorylation following IL-1β treatment.
According to results from gel electrophoresis, the level of
expression of phosphorylated NF-κB-p65 in OUMS-cells was greater
following 10 min of IL-1β treatment compared with that following 5
min of treatment (Fig. 1A).
Following 30 min of IL-1β treatment, phosphorylated NF-κB-p65
expression levels had decreased. In the negative control cells (no
IL-1β treatment), phosphorylated NF-κB-p65 was not expressed. IκB-α
was expressed in the negative control OUMS-27 cells but not in the
IL-1β treated OUMS-27 cells. Following treatment with BAY-117085
(an NF-κB pathway inhibitor), the expression of phosphorylated
NF-κB-p65 in the cells decreased, in a time-dependent manner. By
contrast, the level of phosphory-lated NF-κB-p65 expression in the
negative control cells was comparable to that of total NF-κB
expression (Fig. 1B).
NF-κB-p65-binding sites in the ADAMTS9
promoter
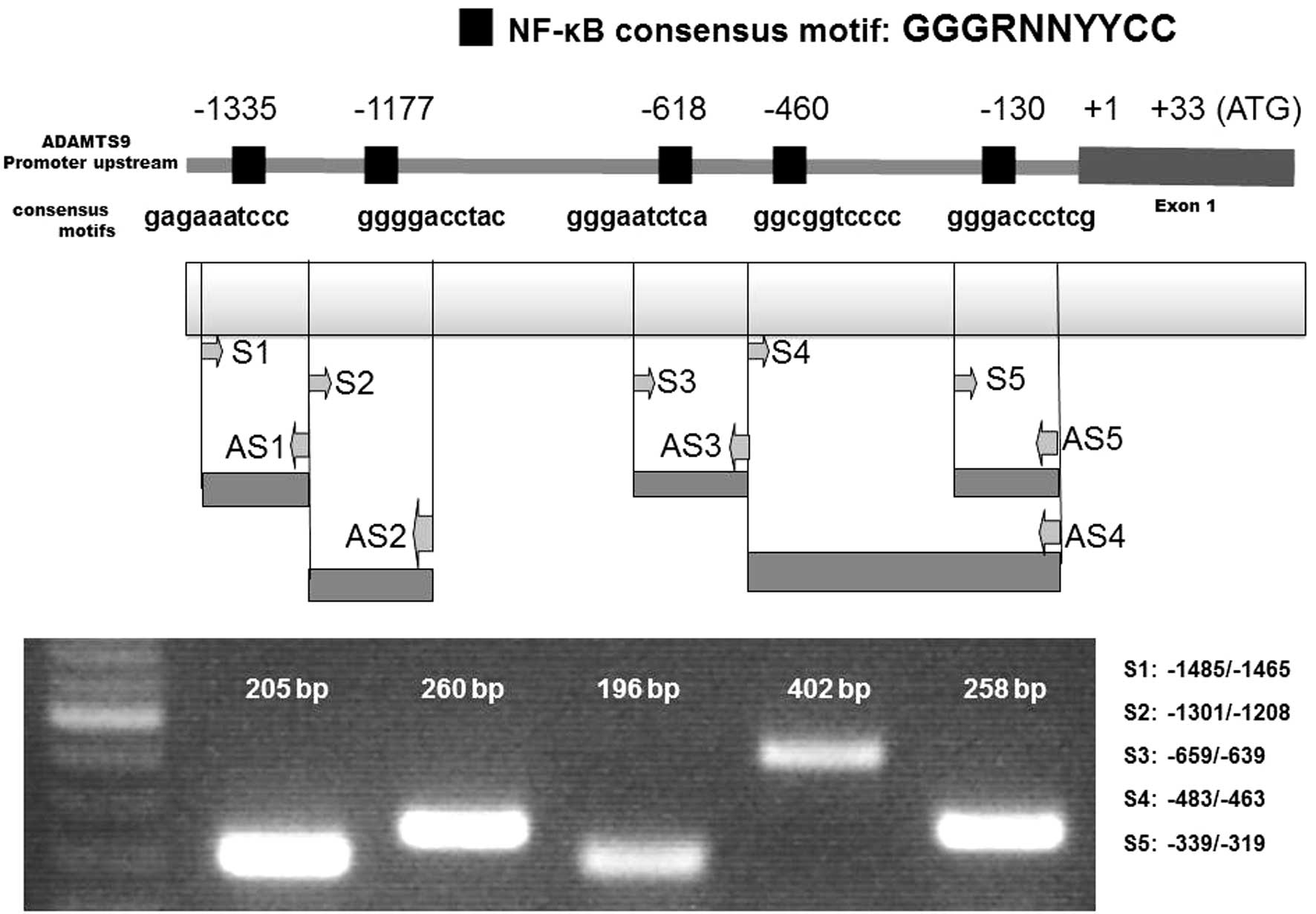
A previous investigation demonstrated that NFATc1
binding consensus sites may activate ADAMTS9 gene expression
(2). In the present study, cloned
human ADAMTS9 gene sequences were analyzed in order to investigate
the involvement of other putative transcription factor binding
sites in ADAMTS9 gene expression. The consensus DNA-binding
sequence of NF-κB is GGGRNNYYCC (N = any base, R = purine, and Y =
pyrimidine) (11). DNA sequences
that were highly homologous to the consensus DNA-binding sequence
of NF-κB were identified in the ADAMTS9 genome data base (Fig. 2). In the present study, two
sequences located −1335 and −1177 bp upstream of the transcription
start site of ADAMTS9 were used for further analysis due to the
ChIP experiments. Other sites defined as −130, −460 and −618 did
not exhibit effective NF-κB binding of ADAMTS9, according to the
ChIP experiments (data not shown). Immunoprecipitation analysis was
performed and the amplification of potential consensus sites was
assessed via PCR amplification using the primers in Table I.
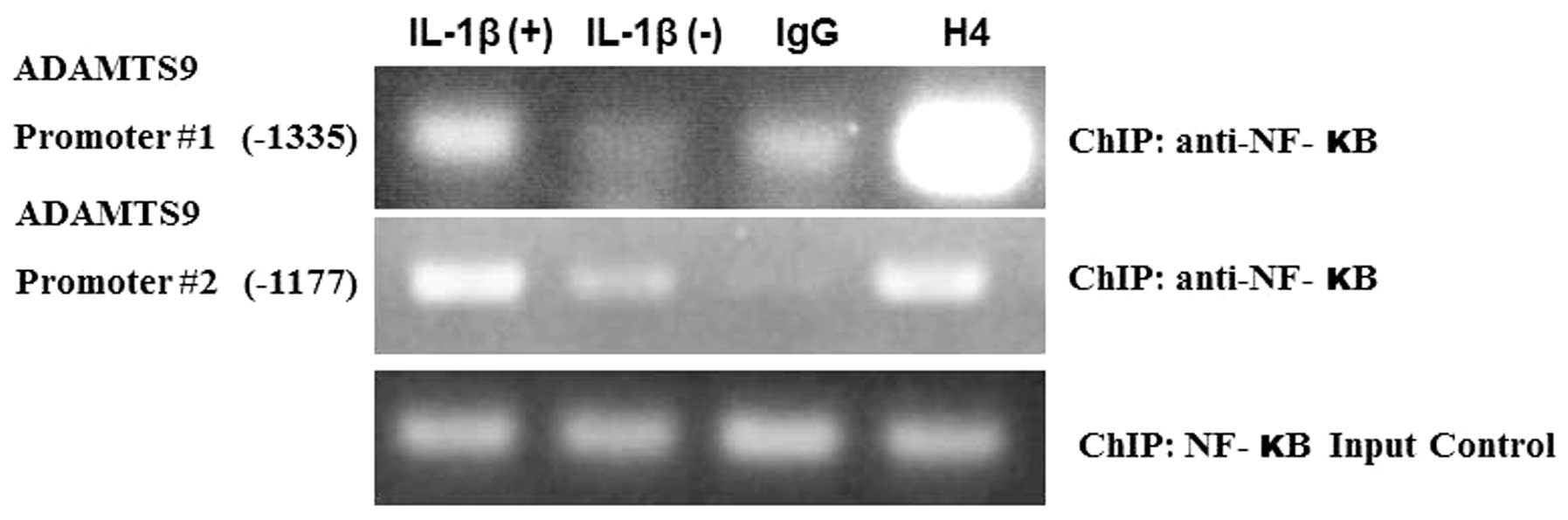
Following 20 min of OUMS-27 cell treatment with
IL-1β, ChIP analysis suggested that NF-κB successfully bound with
the ADAMTS9 promoter consensus sites, −1335 and −1177 (Fig. 3). However, NF-κB did not bind with
the ADAMTS9 promoter #1 consensus site (−1335) in the negative
control OUMS-27 cells (no IL-1β treatment). IgG was used as a
negative control and H4 histone protein was used as a positive
control for the experiment. For promoter #2, there was decreased
binding of NF-κB in the IL-1β untreated cells, as compared with the
treated cells at −1177 bp upstream of the ADAMTS9 promoter
(Fig. 3).
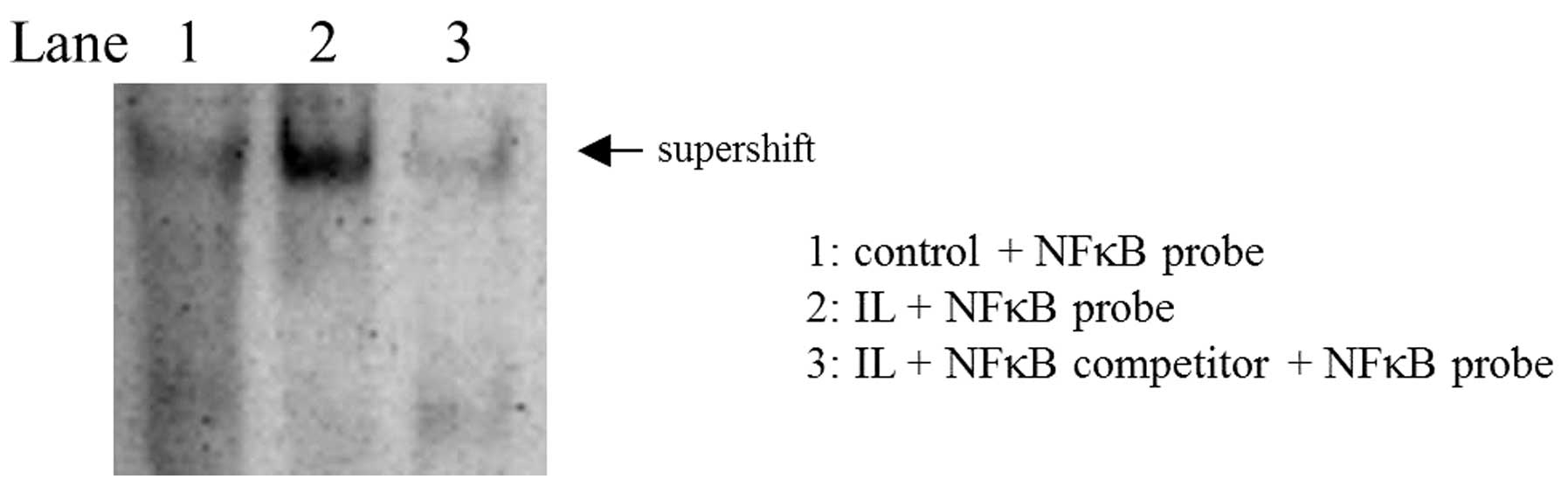
In order to confirm the presence of NF-κB binding
sites in the ADAMTS9 promoter region an EMSA assay was performed. A
supershift assay suggested that, following IL-1β treatment, NF-κB
bound to ADAMTS9 promotors in OUMS-27 cells. However, in cells not
treated with IL-1β, NF-κB did not bind to ADAMTS9 promotors. By
contrast, in negative control cells, using a cold NF-κB competitor,
there was no evidence of NF-κB binding to the ADAMTS9 promoters. In
the positive control cells, only a ‘free probe’ was expressed
(Fig. 4).
Discussion
The results of the present study suggested that the
human ADAMTS9 promoter region exhibits NF-κB binding elements and
may be a target gene for NF-κB gene expression. IL-1β-induced NF-κB
is capable of binding with ADAMTS9 promoters in OUMS-27
chondrosarcoma cells. ADAMTSs are secreted proteinases, which are
involved in cell adhesion, proteolytic shedding and cell signaling
(12).
The ADAMTS9 gene is localized to chromosome 3p14.2
and is the most highly conserved member of the ADAMTS family.
ADAMTS9 cleaves versican and aggrecan proteins, and may therefore
be termed aggrecan. Previous studies have indicated that
aggrecanases are associated with the development of a number of
diseases, due their involvement in cell development, angiogenesis,
cancer and inflammatory processes (13–15).
In osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, ADAMTS9 is involved in
inflammatory responses associated with cartilage damage (13,15).
Therefore, elucidation of the regulatory mechanisms underlying
ADAMTS9 expression and activation is required. A number of studies
have revealed that various signaling pathways, such as the
mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway, are associated
with the regulation of ADAMTS9 gene expression (3–5).
ADAMTS9 gene expression was found to be downregulated following
treatment with SB600125 and BAY 11-7085, which are inhibitors of
MAPK and NF-κB, respectively (4,6). The
phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway does not appear to be
associated with ADAMTS9 gene expression (3). There is evidence to suggest that
ADAMTS9 expression may be regulated by IL-1β and TNF-α treatment
(4). A previous study demonstrated
that, following IL-1β treatment of isolated chon-drosarcoma and
chondrosarcoma cells, ADAMTS9 expression was induced to a greater
degree than that of all other aggrecanase genes (4). IL-1β may activate the expression of a
number of inflammation-associated transcription factors. A previous
study demonstrated that the transcription factor, NFATc1, is
capable of activating the expression of ADAMTS9 following IL-1β
treatment in human chondrocytes (5). The results of the present study
suggested that NF-κB activation, following IL-1β treatment, is
associated with ADAMTS9 expression in OUMS 27 cells.
NF-κB is involved in the activation of a number of
genes that encode adhesion molecules, such as E-selectin. These
molecules mediate leukocyte tethering and rolling, which is
involved in acute and chronic inflammatory processes that are
associated with inflammatory injury and rheumatoid artritis
(16,17). The present study demonstrated that
the ADAMTS9 promoter region contains five NF-κB consensus binding
sites at −130, −460, −618, −1177 and −1335 bp. A previous study
suggested that NF-κB phosphorylation may be induced following IL-1β
treatment in Jurkat cell lines derived from an immortalized line of
T lymphocytes and HEK293 (human embryonic kidney cells) (7). In the present study, NF-κB-p65 was
phosphorylated following IL-1β treatment of OUMS-27 cells. The
results suggest that NF-κB-p65 phosphorylation may induce the
binding of NF-κB-p65 to specific consensus sites of the ADAMTS9
promoter region at locations −1177 and −1335 bp, following
treatment with IL-1β. According to the electrophoresis gel image
(Fig. 3), this bond was most
prominent at location −1335 bp, compared with location −1177 bp of
the ADAMTS9 promoter region. By contrast, in negative control
OUMS-27 cells, NF-κB did not bind to the ADAMTS9 promoter
region.
In conclusion, the results of the present study
suggested that the human ADAMTS9 promoter region exhibits NF-κB
consensus sites, which are potential targets for NF-κB
transcription factor binding. IL-1β-induced NF-κB-p65 subunit
binding to the ADAMTS9 promoter region in OUMS-27 cells. The
present study provides a novel approach for ADAMTS9 gene-targeted
therapy and ADAMTS9 inhibition. These results may be suitable for
the development of treatment for a number of pathological
conditions, including cartilage injury.
Acknowledgments
Dr T. Kunisida (Okayama University Graduate School
of Medicine and Dentistry, Okayama, Japan) provided the OUMS-27
chondrosarcoma cell line.
References
|
1
|
Tortorella MD, Burn TC, Pratta MA, et al:
Purification and cloning of aggrecanase-1: a member of the ADAMTS
family of proteins. Science. 284:1664–1666. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Apte SS: A disintegrin-like and
metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1
motifs: the ADAMTS family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:981–985.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Uysal S, Ünal ZN, Erdoǧan S, et al:
Augmentation of ADAMTS9 gene expression by IL-1β is reversed by
NF-κB and MAPK inhibitors, but not PI3 kinase inhibitors. Cell
Biochem Funct. 31:539–544. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Demircan K, Hirohata S, Nishida K, et al:
ADAMTS-9 is synergistically induced by interleukin-1beta and tumor
necrosis factor alpha in OUMS-27 chondrosarcoma cells and in human
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1451–1460. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yaykasli KO, Oohashi T, Hirohata S,
Hatipoglu OF, Inagawa K, Demircan K and Ninomiya Y: ADAMTS9
activation by interleukin 1 beta via NFATc1 in OUMS-27
chondrosarcoma cells and in human chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biochem.
323:69–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Xu YX, Pindolia KR, Janakiraman N, Chapman
RA and Gautam SC: Curcumin inhibits IL1 alpha and TNF-alpha
induction of AP-1 and NF-κB DNA-binding activity in bone marrow
stromal cells. Hematopathol Mol Hematol. 11:49–62. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen D, Li X, Zhai Z and Shu HB: A novel
zinc finger protein interacts with receptor-interacting protein
(RIP) and inhibits tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- and IL1-induced
NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem. 277:15985–15991. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cogswell JP, Godlevski MM, Wisely GB, et
al: NF-kappa B regulates IL-1 beta transcription through a
consensus NF-kappa B binding site and a nonconsensus CRE-like site.
J Immunol. 153:712–723. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Barnes PJ and Karin M: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic
inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 336:1066–1071. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bret C, Hose D, Reme T, et al: Gene
expression profile of ADAMs and ADAMTSs metalloproteinases in
normal and malignant plasma cells and in the bone marrow
environment. Exp Hematol. 39:546–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Demircan K, Yonezawa T, Takigawa T, et al:
ADAMTS1, ADAMTS5, ADAMTS9 and aggrecanase-generated proteoglycan
fragments are induced following spinal cord injury in mouse.
Neurosci Lett. 544:25–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin EA and Liu CJ: The role of ADAMTSs in
arthritis. Protein Cell. 1:33–47. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kevorkian L, Young DA, Darrah C, et al:
Expression profiling of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in
cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 50:131–141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng X, Zhu S, Chang S, et al: Protective
effects of chronic resveratrol treatment on vascular inflammatory
injury in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats: Role of
NF-kappa B signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 25:S0014–2999. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Choi YJ, Lee WS, Lee EG, Sung MS and Yoo
WT: Sulforaphane inhibits IL-1β-induced proliferation of rheumatoid
arthritis synovial fibroblasts and the production of MMPs, COX-2,
and PGE2. Inflammation. 37:1496–1503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|