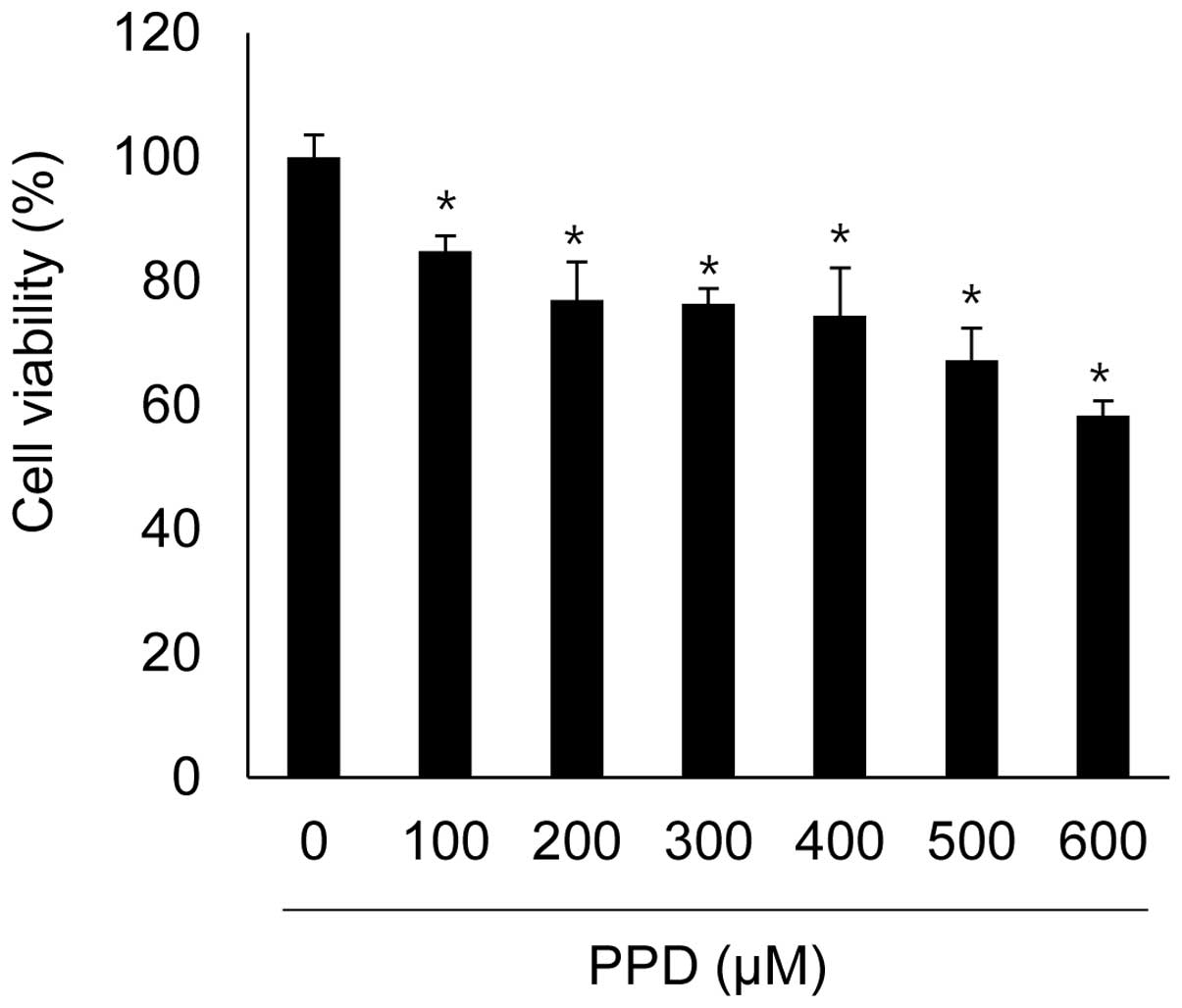
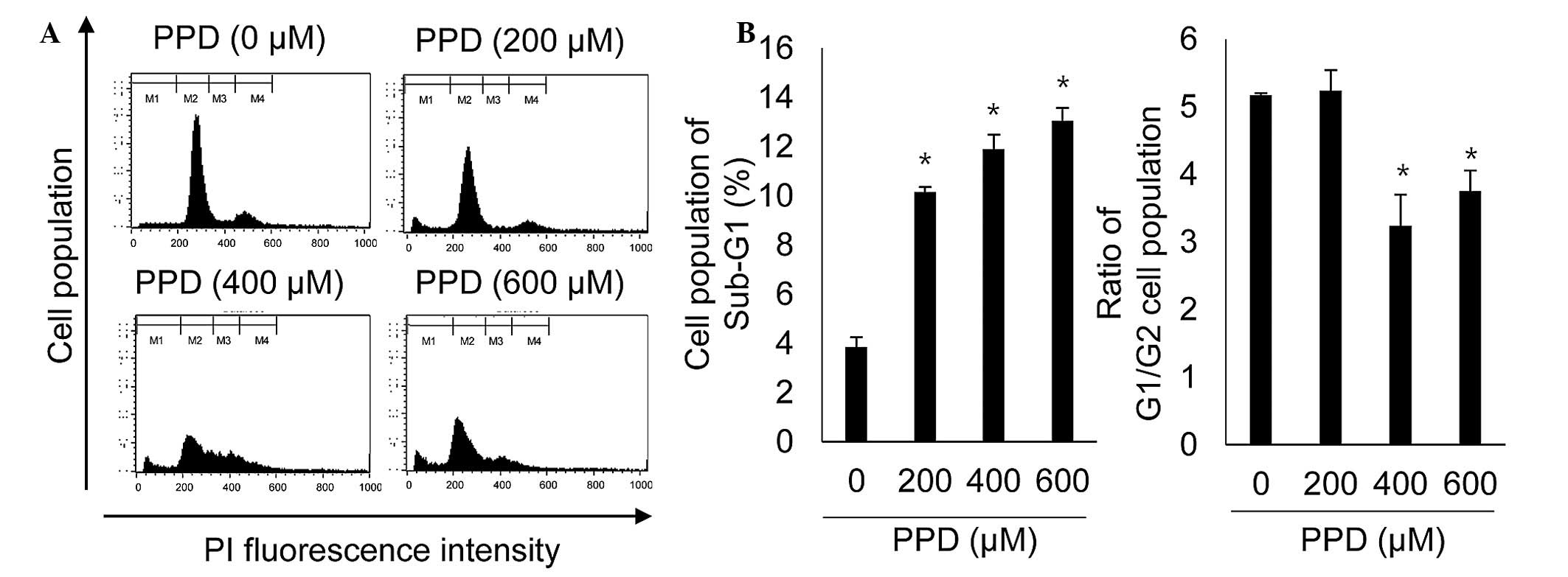
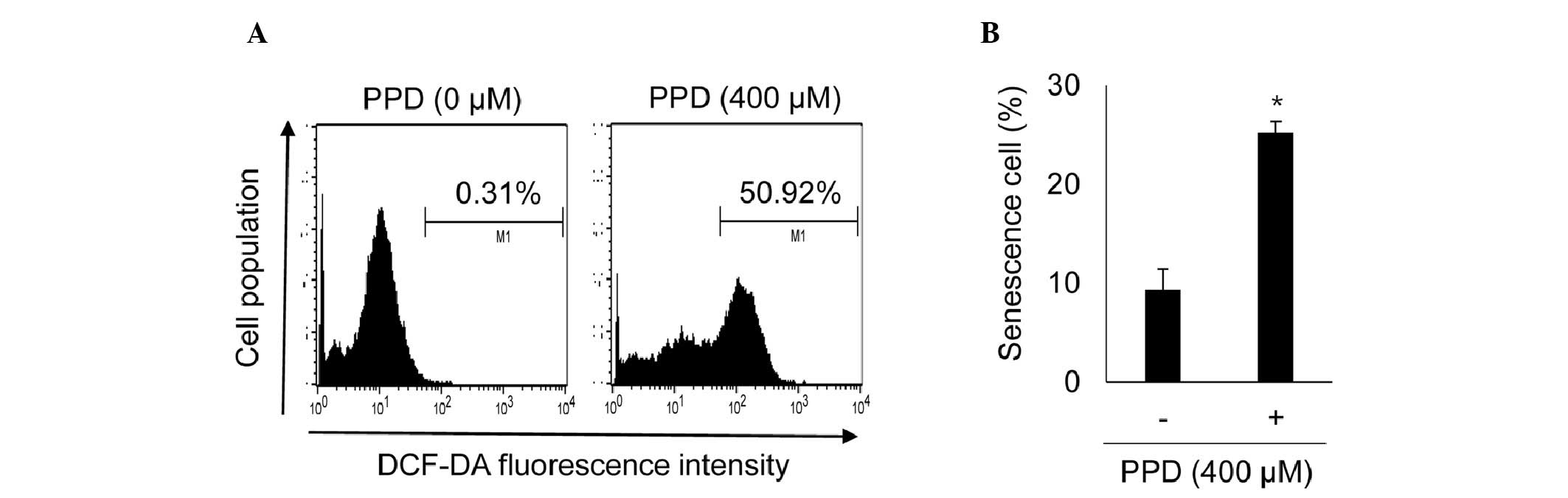
|
1
|
Anderson JS: The chemistry of hair
colorants. Colorant Tech. 116:193–196. 2000.
|
|
2
|
Corbett JF: An historical review of the
use of dye precursors in the formulation of commercial oxidation
hair dyes. Dyes Pigments. 41:127–136. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tukenmez Demirci G, Kivanc Altunay I, Atis
G and Kucukunal A: Allergic contact dermatitis mimicking angioedema
due to para-phenylendiamine hypersensitivity: a case report. Cutan
Ocul Toxicol. 31:250–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Marcoux D, Couture-Trudel PM,
Riboulet-Delmas G and Sasseville D: Sensitization to
para-phenylenediamine from a streetside temporary tattoo. Pediatr
Dermatol. 19:498–502. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coulter EM, Farrell J, Mathews KL, Maggs
JL, Pease CK, Lockley DJ, Basketter DA, Park BK and Naisbitt DJ:
Activation of human dendritic cells by p-phenylenediamine. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:885–892. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rojanapo W, Kupradinun P, Tepsuwan A,
Chutimataewin S and Tanyakaset M: Carcinogenicity of an oxidation
product of p-phenylenediamine. Carcinogenesis. 7:1997–2002. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sontag JM: Carcinogenicity of
substituted-benzenediamines (phenylenediamines) in rats and mice. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 66:591–602. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chye SM, Tiong YL, Yip WK, Koh RY, Len YW,
Seow HF, Ng KY, Ranjit DA and Chen SC: Apoptosis induced by
para-phenylenediamine involves formation of ROS and activation of
p38 and JNK in chang liver cells. Environ Toxicol. 29:981–990. Nov
22–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang YC, Hung WC, Chye SM, Chen WT and
Chai CY: para-Phenylenediamine-induced autophagy in human
uroepithelial cell line mediated mutant p53 and activation of ERK
signaling pathway. Toxicol In Vitro. 25:1630–1637. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishida W, Makino T and Shimizu T: Severe
hair loss of the scalp due to a hair dye containing para
phenylenediamine. ISRN Dermatol. 2011:9472842011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carrington JC and Ambros V: Role of
microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science. 301:336–338.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wan G, Mathur R, Hu X, Zhang X and Lu X:
miRNA response to DNA damage. Trends Biochem Sci. 36:478–484. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mardaryev AN, Ahmed MI, Vlahov NV, Fessing
MY, Gill JH, Sharov AA and Botchkareva NV: Micro-RNA-31 controls
hair cycle-associated changes in gene expression programs of the
skin and hair follicle. FASEB J. 24:3869–3881. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amelio I, Lena AM, Bonanno E, Melino G and
Candi E: miR-24 affects hair follicle morphogenesis targeting
Tcf-3. Cell Death Dis. 4:e9222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andl T, Murchison EP, Liu F, Zhang Y,
Yunta-Gonzalez M, Tobias JW, Andl CD, Seykora JT, Hannon GJ and
Millar SE: The miRNA-processing enzyme dicer is essential for the
morphogenesis and maintenance of hair follicles. Curr Biol.
16:1041–1049. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Coulter EM, Farrell J, Mathews KL, Maggs
JL, Pease CK, Lockley DJ, Basketter DA, Park BK and Naisbitt DJ:
Activation of human dendritic cells by p-phenylenediamine. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:885–892. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
So Y, Shin C, Song M, Rha Y and Ryu J:
Gene expression profiling of hair-dying agent,
para-phenylenediamine, in human keratinocytes (HaCaT) cells. Mol
Cell Toxicol. 7:339–346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Colavitti R and Finkel T: Reactive oxygen
species as mediators of cellular senescence. IUBMB Life.
57:277–281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akelma AZ, Cizmeci MN, Sarifakioglu E and
Mete E: A child with allergic contact dermatitis due to
para-phenylenediamine. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 1:399–400.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Goebel C, Troutman J, Hennen J, Rothe H,
Schlatter H, Gerberick GF and Blömeke B: Introduction of a
methoxymethyl side chain into p-phenylenediamine attenuates its
sensitizing potency and reduces the risk of allergy induction.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 274:480–487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen SC, Chen CH, Chern CL, Hsu LS, Huang
YC, Chung KT and Chye SM: p-Phenylenediamine induces p53-mediated
apoptosis in Mardin-Darby canine kidney cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
20:801–807. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen SC, Chen CH, Tioh YL, Zhong PY, Lin
YS and Chye SM: Para-phenylenediamine induced DNA damage and
apoptosis through oxidative stress and enhanced caspase-8 and -9
activities in Mardin-Darby canine kidney cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1197–1202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Orjalo AV, Rodier F, Lithgow GJ and Campisi J: MicroRNAs
miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated
inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8. Aging (Albany NY). 1:402–411.
2009.
|
|
25
|
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH and Yang BB:
MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth and angiogenesis
by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:20350–20355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Teo JL and Kahn M: The Wnt signaling
pathway in cellular proliferation and differentiation: A tale of
two coactivators. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 62:1149–1155. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B, Cotsarelis
G and Birchmeier W: beta-Catenin controls hair follicle
morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell.
105:533–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Beaudoin GM III, Sisk JM, Coulombe PA and
Thompson CC: Hairless triggers reactivation of hair growth by
promoting Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:14653–14658.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|