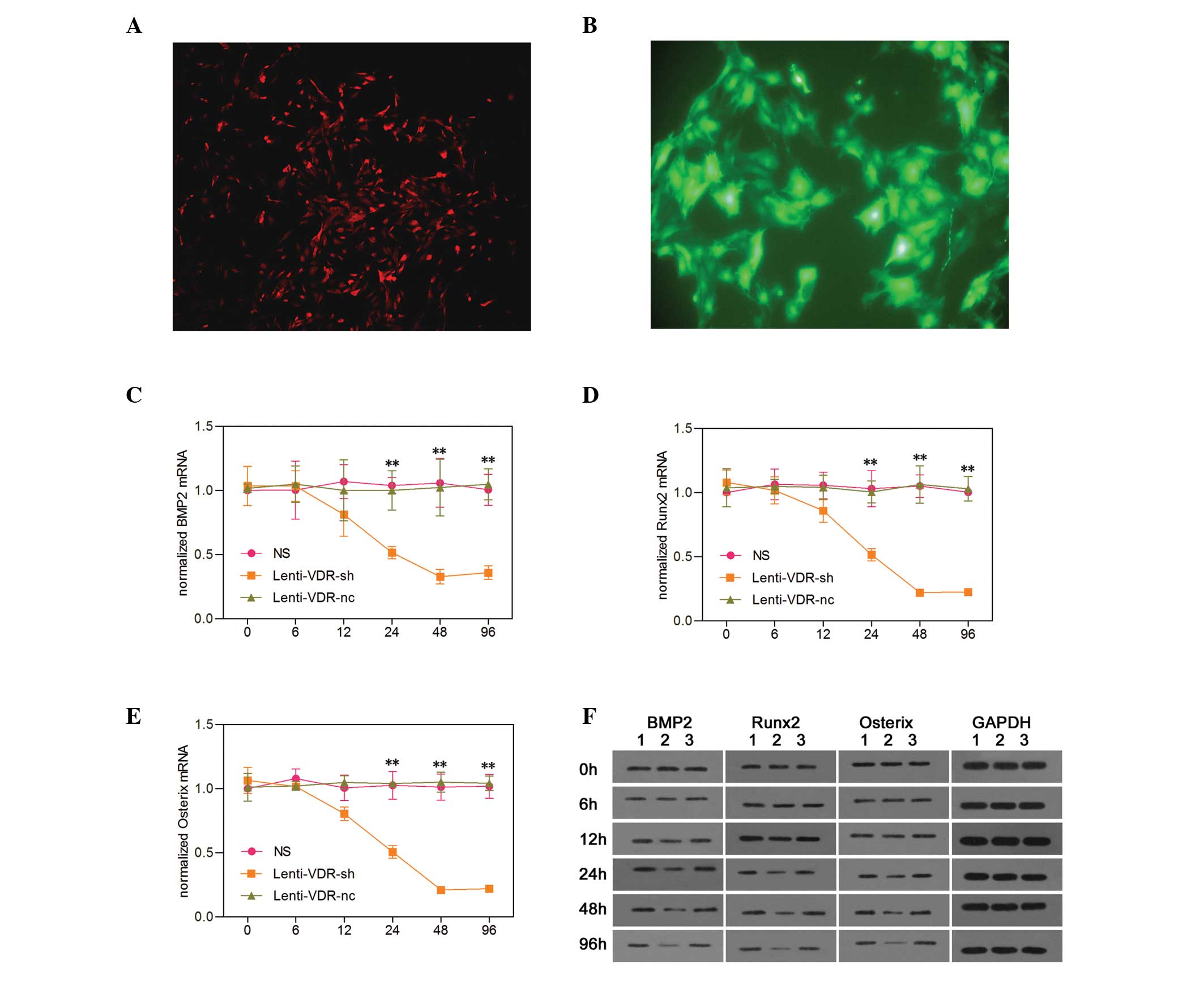
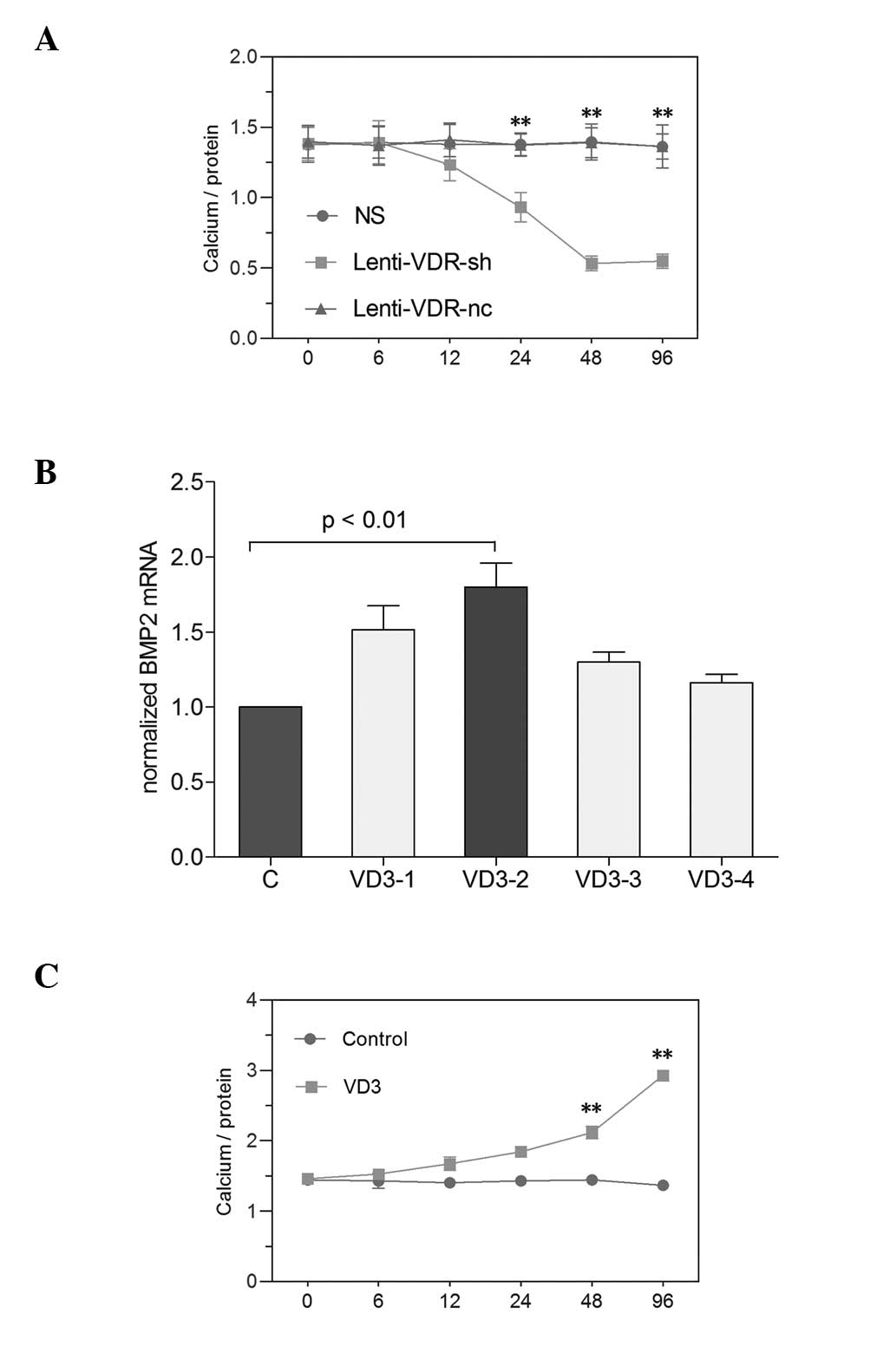
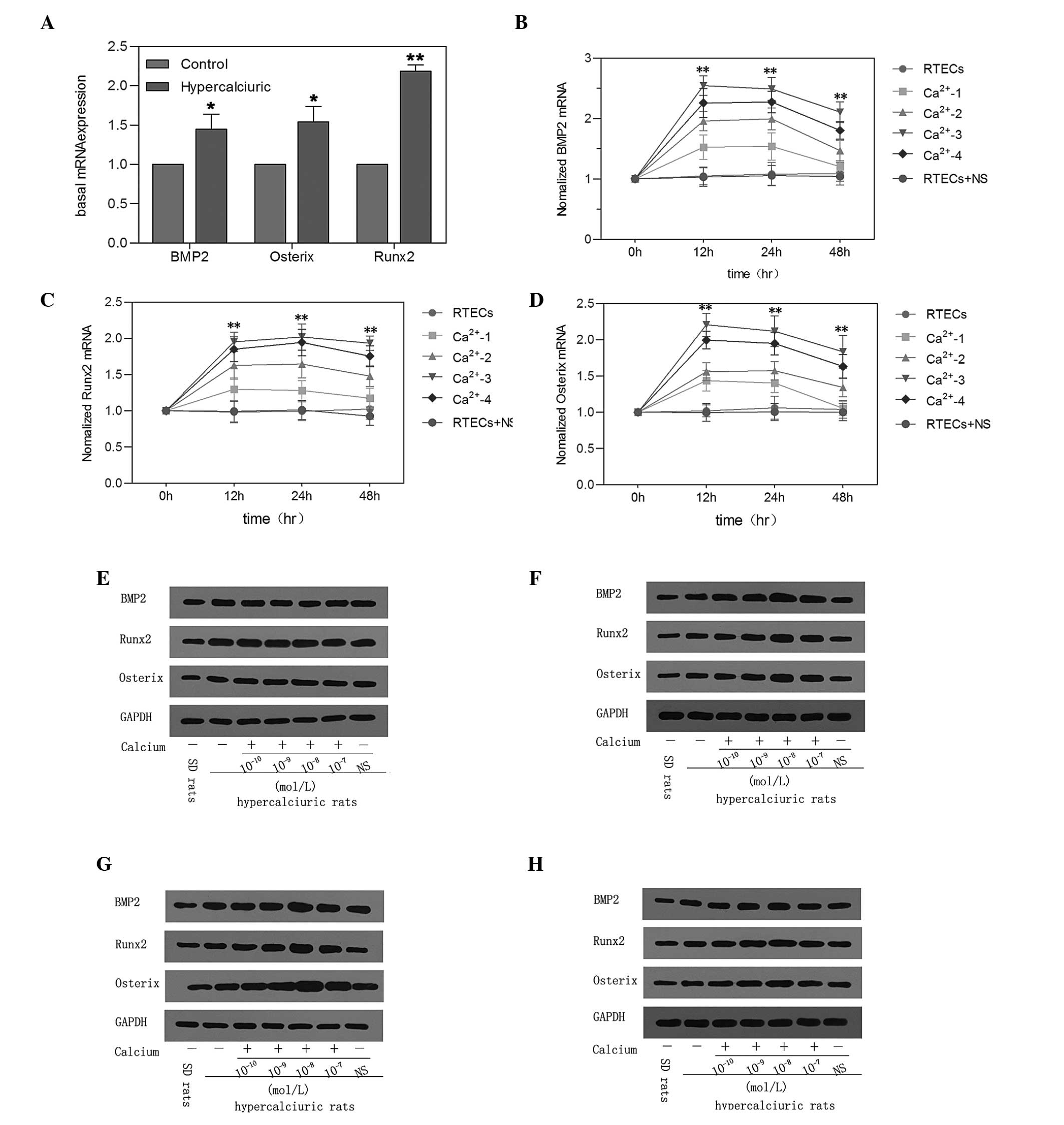
|
1
|
Relan V, Khullar M, Singh SK and Sharma
SK: Association of vitamin D receptor genotypes with calcium
excretion in nephrolithiatic subjects in northern India. Urol Res.
32:236–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Favus MJ, Karnauskas AJ, Parks JH and Coe
FL: Peripheral blood monocyte vitamin D receptor levels are
elevated in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 89:4937–4943. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burton DG, Matsubara H and Ikeda K:
Pathophysiology of vascular calcification: Pivotal role of cellular
senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Gerontol.
45:819–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kanno Y, Into T, Lowenstein CJ and
Matsushita K: Nitric oxide regulates vascular calcification by
interfering with TGF-signalling. Cardiovasc Res. 77:221–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jang WG, Kim EJ, Kim DK, et al: BMP2
protein regulates osteocalcin expression via Runx2-mediated Atf6
gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 287:905–915. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Cai J, Pardali E, Sanchez-Duffhues G and
ten Dijke P: BMP signaling in vascular diseases. FEBS Lett.
586:1993–2002. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang SG, Luo DX and Liu JH: Establishment
of genetic hypercalciuric stone-forming rat’s model. Chin J Urol.
27:63–65. 2006.
|
|
8
|
Xi QL, Wang SG, Ye ZQ, et al: Effect of
silencing VDR gene in kidney on renal epithelial calcium
transporter proteins and urinary calcium excretion in genetic
hypercalciuric stone-forming rats. Urology. 78:1442.e1–e7. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jia Z, Wang S, Tang J, et al: Does crystal
deposition in genetic hypercalciuric rat kidney tissue share
similarities with bone formation? Urology. 83:509.e7–e14. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jono S, McKee MD, Murry CE, et al:
Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification.
Circ Res. 87:E10–E17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan SR: Is oxidative stress, a link
between nephrolithiasis and obesity, hypertension, diabetes,
chronic kidney disease, metabolic syndrome? Urol Res. 40:95–112.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayden MR, Tyagi SC, Kolb L, Sowers JR and
Khanna R: Vascular ossification-calcification in metabolic
syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and
calciphylaxis-calcific uremic arteriolopathy: The emerging role of
sodium thiosulfate. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 4:42005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sage AP, Tintut Y and Demer LL: Regulatory
mechanisms in vascular calcification. Nat Rev Cardiol. 7:528–536.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bunting CH: The formation of true bone
with cellular (red) marrow in a sclerotic aorta. J Exp Med.
8:365–376. 1906. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shao JS, Aly ZA, Lai CF, et al: Vascular
Bmp Msx2 Wnt signaling and oxidative stress in arterial
calcification. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1117:40–50. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moe SM and Chen NX: Mechanisms of vascular
calcification in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:213–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schoppet M, Shroff RC, Hofbauer LC and
Shanahan CM: Exploring the biology of vascular calcification in
chronic kidney disease: what’s circulating? Kidney Int. 73:384–390.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Boström K, Watson KE, Horn S, Wortham C,
Herman IM and Demer LL: Bone morphogenetic protein expression in
human atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Invest. 91:1800–1809. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reddi AH: Bone morphogenetic proteins: an
unconventional approach to isolation of first mammalian morphogens.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 8:11–20. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, et al:
Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and
activities. Science. 242:1528–1534. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li X, Yang HY and Giachelli CM: BMP-2
promotes phosphate uptake, phenotypic modulation and calcification
of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis.
199:271–277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun Y, Byon CH, Yuan K, et al: Smooth
muscle cell-specific runx2 deficiency inhibits vascular
calcification. Circ Res. 111:543–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsubara T, Kida K, Yamaguchi A, et al:
BMP2 regulates Osterix through Msx2 and Runx2 during osteoblast
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 283:29119–29125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, et al: The
novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is
required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell.
108:17–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Komori T: Regulation of osteoblast
differentiation by transcription factors. J Cell Biochem.
99:1233–1239. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zebger-Gong H, Muller D, Diercke M, et al:
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced aortic calcifications in
experimental uremia: up-regulation of osteoblast markers,
calcium-transporting proteins and osterix. J Hypertens. 29:339–348.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bai S, Wang H, Shen J, Zhou R, Bushinsky
DA and Favus MJ: Elevated vitamin D receptor levels in genetic
hypercalciuric stone-forming rats are associated with
downregulation of Snail. J Bone Miner Res. 25:830–840. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Schmidt N, Brandsch C, Kühne H, Thiele A,
Hirche F and Stangl GI: Vitamin D receptor deficiency and low
vitamin D diet stimulate aortic calcification and osteogenic key
factor expression in mice. PLoS One. 7:e353162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|