|
1
|
Yoshizaki T, Ito M, Murono S, Wakisaka N,
Kondo S and Endo K: Current understanding and management of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx. 39:137–144. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Daker M, Bhuvanendran S, Ahmad M, Takada K
and Khoo AS: Deregulation of lipid metabolism pathway genes in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 3:731–741. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Qiu S, Lin S, Tham IW, Pan J, Lu J and Lu
JJ: Intensity-modulated radiation therapy in the salvage of locally
recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
83:676–683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
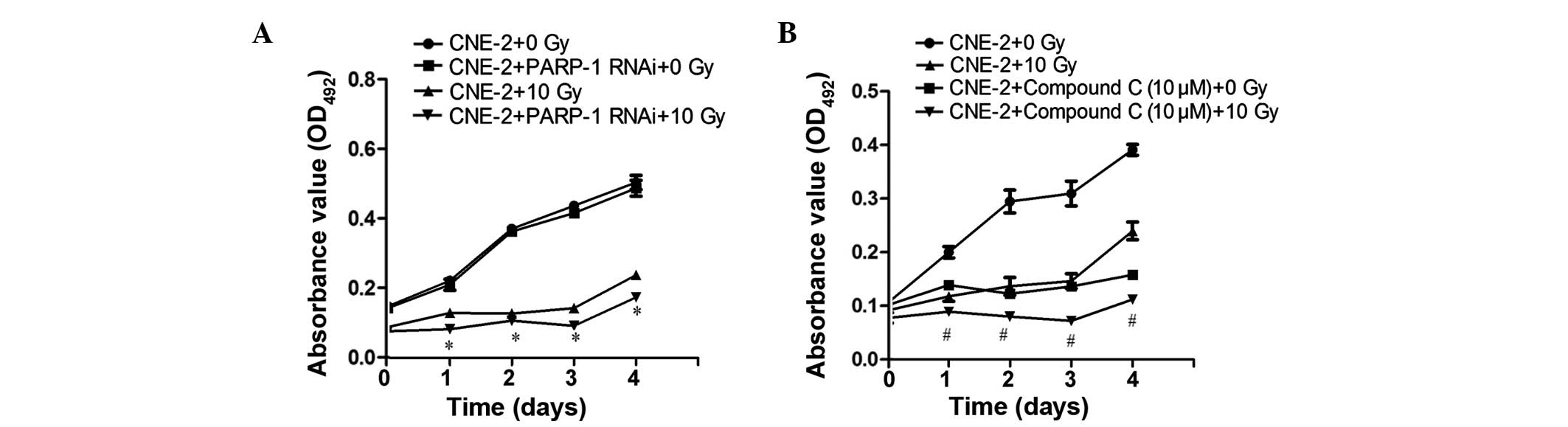
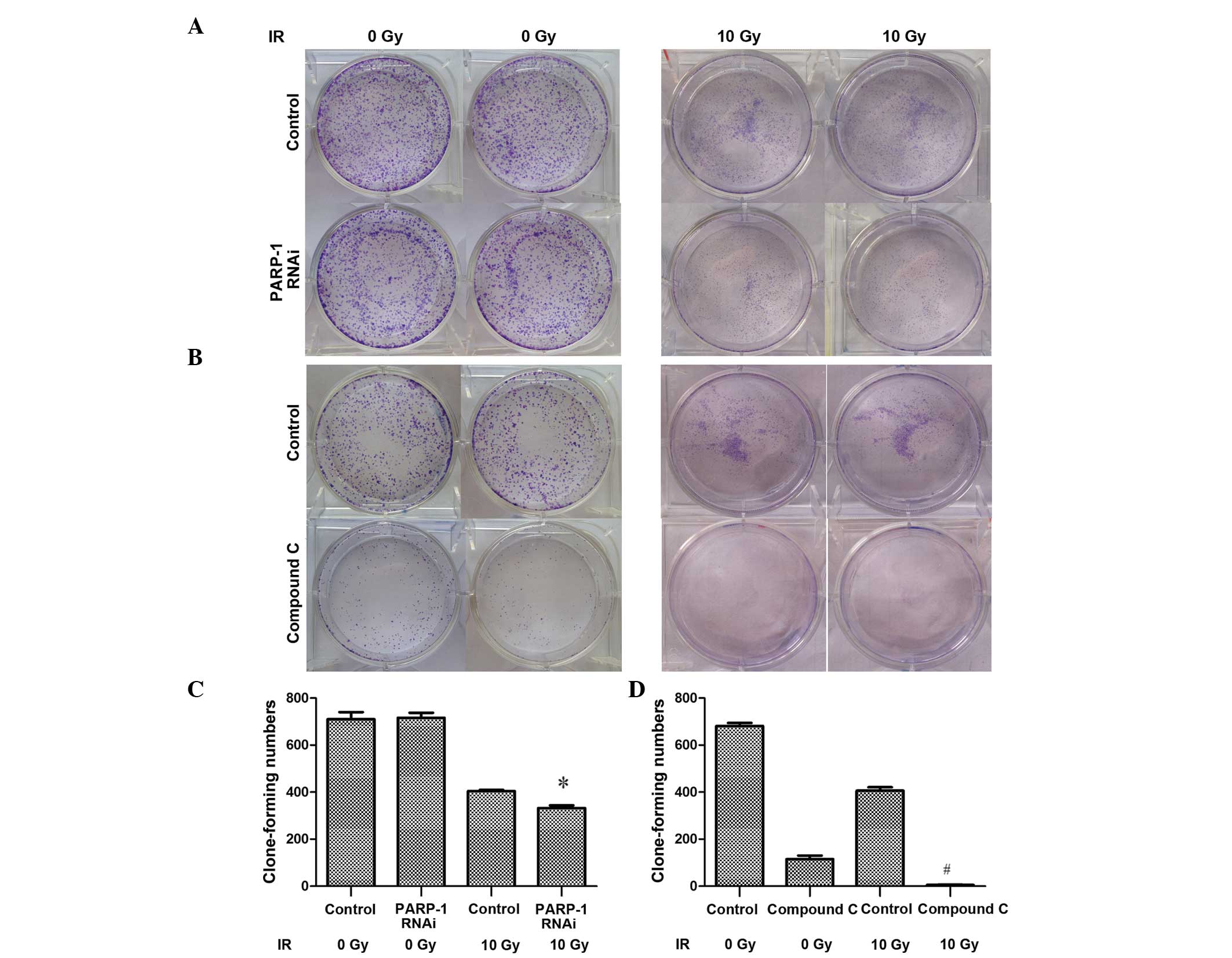
|
|
4
|
Feng XP, Yi H, Li MY, et al:
Identification of biomarkers for predicting nasopharyngeal
carcinoma response to radiotherapy by proteomics. Cancer Res.
70:3450–3462. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo Y, Zhu XD, Qu S, et al: Identification
of genes involved in radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
integrating gene ontology and protein-protein interaction networks.
Int J Oncol. 40:85–92. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Li G, Qiu Y, Su Z, et al: Genome-wide
analyses of radioresistance-associated miRNA expression profile in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma using next generation deep sequencing.
PLoS One. 8:e844862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: an innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Giménez-Xavier P, Francisco R, Santidrián
AF, Gil J and Ambrosio S: Effects of dopamine on LC3-II activation
as a marker of autophagy in a neuroblastoma cell model.
Neurotoxicology. 30:658–665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Holt SV, Wyspianska B, Randall KJ, James
D, Foster JR and Wilkinson RW: The development of an
immunohistochemical method to detect the autophagy-associated
protein LC3-II in human tumor xenografts. Toxicol Pathol.
39:516–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, et al:
A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy
and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao KC, Komata T, Kondo Y, Kanzawa T,
Kondo S and Germano IM: Molecular response of human glioblastoma
multiforme cells to ionizing radiation: cell cycle arrest,
modulation of the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
and autophagy. J Neurosurg. 98:378–384. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ito H, Daido S, Kanzawa T, Kondo S and
Kondo Y: Radiation-induced autophagy is associated with LC3 and its
inhibition sensitizes malignant glioma cells. Int J Oncol.
26:1401–1410. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dalby KN, Tekedereli I, Lopez-Berestein G
and Ozpolat B: Targeting the prodeath and prosurvival functions of
autophagy as novel therapeutic strategies in cancer. Autophagy.
6:322–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Apel A, Herr I, Schwarz H, Rodemann HP and
Mayer A: Blocked autophagy sensitizes resistant carcinoma cells to
radiation therapy. Cancer Res. 68:1485–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marx J: Autophagy: is it cancer’s friend
or foe? Science. 312:1160–1161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu WK, Coffelt SB, Cho CH, et al: The
autophagic paradox in cancer therapy. Oncogene. 31:939–953. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Weaver AN and Yang ES: Beyond DNA repair:
additional functions of PARP-1 in cancer. Front Oncol. 3:2902013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Houtgraaf JH, Versmissen J and van der
Giessen WJ: A concise review of DNA damage checkpoints and repair
in mammalian cells. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 7:165–172. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cho EA, Kim EJ, Kwak SJ and Juhnn YS: cAMP
signaling inhibits radiation-induced ATM phosphorylation leading to
the augmentation of apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Mol
Cancer. 13:362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Veuger SJ, Curtin NJ, Richardson CJ, Smith
GC and Durkacz BW: Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by
the combined use of novel inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein
kinase and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Cancer Res.
63:6008–6015. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou ZR, Zhu XD, Zhao W, et al: Poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 regulates the mechanism of
irradiation-induced CNE-2 human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell
autophagy and inhibition of autophagy contributes to the radiation
sensitization of CNE-2 cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2498–2506.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shackelford DB and Shaw RJ: The LKB1-AMPK
pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:563–575. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Green AS, Chapuis N, Lacombe C, Mayeux P,
Bouscary D and Tamburini J: LKB1/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in
hematological malignancies: from metabolism to cancer cell biology.
Cell Cycle. 10:2115–2120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Q, Wu YT, Tan HL, Ong CN and Shen
HM: A novel function of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in
modulation of autophagy and necrosis under oxidative stress. Cell
Death Differ. 16:264–277. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Miura K, Sakata K, Someya M, et al: The
combination of olaparib and camptothecin for effective
radiosensitization. Radiat Oncol. 7:622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Powell C, Mikropoulos C, Kaye SB, et al:
Pre-clinical and clinical evaluation of PARP inhibitors as
tumour-specific radiosensitisers. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:566–575.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Damia G and D’Incalci M: Targeting DNA
repair as a promising approach in cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer.
43:1791–1801. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Woon EC and Threadgill MD: Poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition-where now? Curr Med Chem.
12:2373–2392. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gu SY, Tang WP, Zeng Y, et al: An
epithelial cell line established from poorly differentiated
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ai Zheng. 2:70–72. 1983.In Chinese.
|
|
31
|
Lu XD: The relation between PARP-1 and
autophagy in CNE-2 cells related to the radiation sensitization.
Guangxi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
32
|
Vallejo D, Crespo I, San-Miguel B, et al:
Autophagic response in the Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease, an animal
model of virally-induced fulminant hepatic failure. Vet Res.
45:152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhuang W, Qin Z and Liang Z: The role of
autophagy in sensitizing malignant glioma cells to radiation
therapy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 41:341–351. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Galluzzi L, Vicencio JM, Kepp O, Tasdemir
E, Maiuri MC and Kroemer G: To die or not to die: that is the
autophagic question. Curr Mol Med. 8:78–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song L, Liu H, Ma L, Zhang X, Jiang Z and
Jiang C: Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA enhances endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1031–1038. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu YL, Jahangiri A, Delay M and Aghi MK:
Tumor cell autophagy as an adaptive response mediating resistance
to treatments such as antiangiogenic therapy. Cancer Res.
72:4294–4299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bae H and Guan JL: Suppression of
autophagy by FIP200 deletion impairs DNA damage repair and
increases cell death upon treatments with anticancer agents. Mol
Cancer Res. 9:1232–1241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shim HJ, Lee EM, Nguyen LD, Shim J and
Song YH: High-dose irradiation induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis
and developmental defects during drosophila oogenesis. PLoS One.
9:e890092014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, et al:
Mediation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by
apoptosis-inducing factor. Science. 297:259–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu SW, Andrabi SA, Wang H, et al:
Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR)
polymer-induced cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:18314–18319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ethier C, Tardif M, Arul L and Poirier GG:
PARP-1 modulation of mTOR signaling in response to a DNA alkylating
agent. PLoS One. 7:e479782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karuman P, Gozani O, Odze RD, et al: The
Peutz-Jegher gene product LKB1 is a mediator of p53-dependent cell
death. Mol Cell. 7:1307–1319. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Memmott RM and Dennis PA: LKB1 and
mammalian target of rapamycin as predictive factors for the
anticancer efficacy of metformin. J Clin Oncol. 27:e2262009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee JH, Koh H, Kim M, et al:
Energy-dependent regulation of cell structure by AMP-activated
protein kinase. Nature. 447:1017–1020. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nilufar E, Yadollah S, Benroz N, et al:
Effect of metformin on the proliferation, migration and MMP-2 and-9
expression of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep.
5:1068–1074. 2012.
|