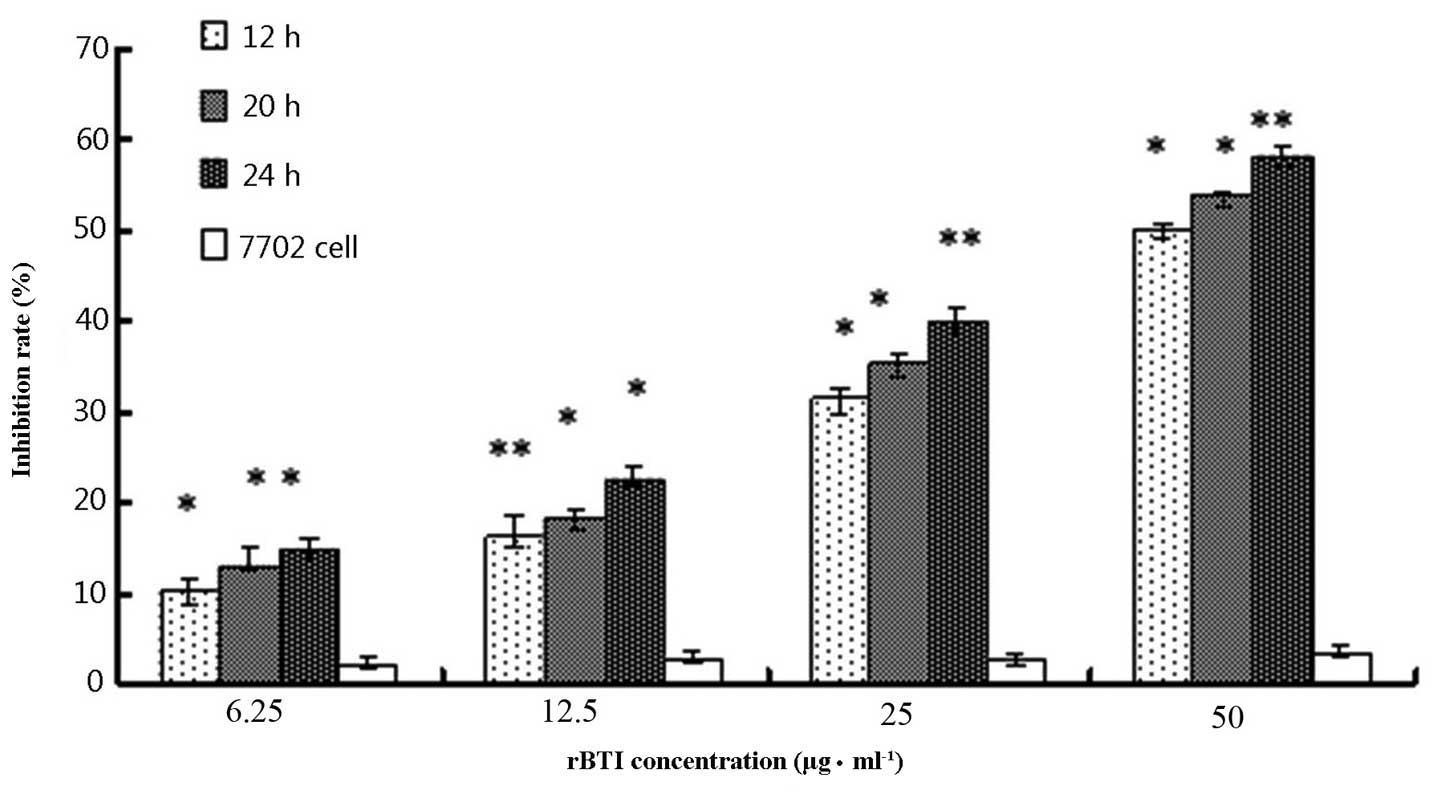
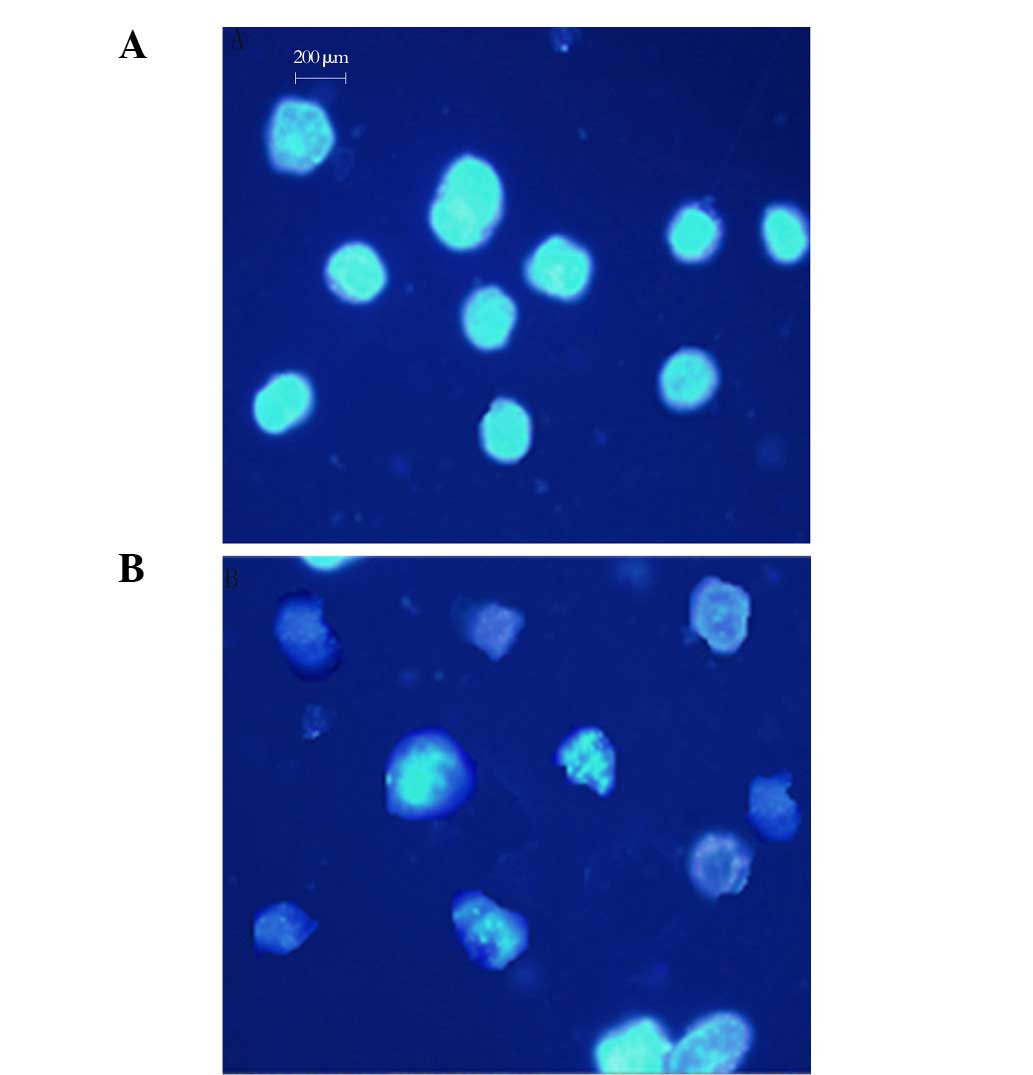
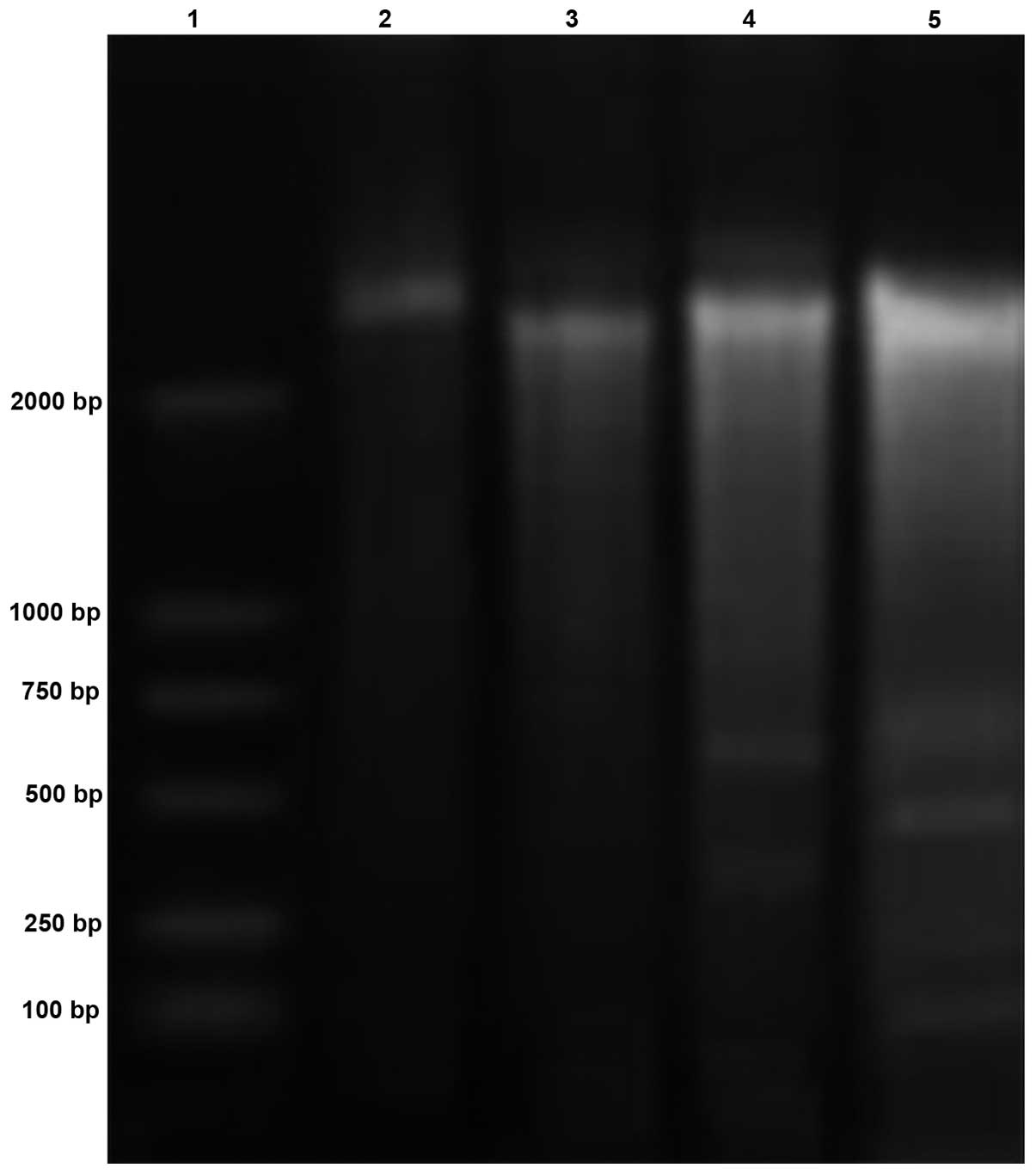
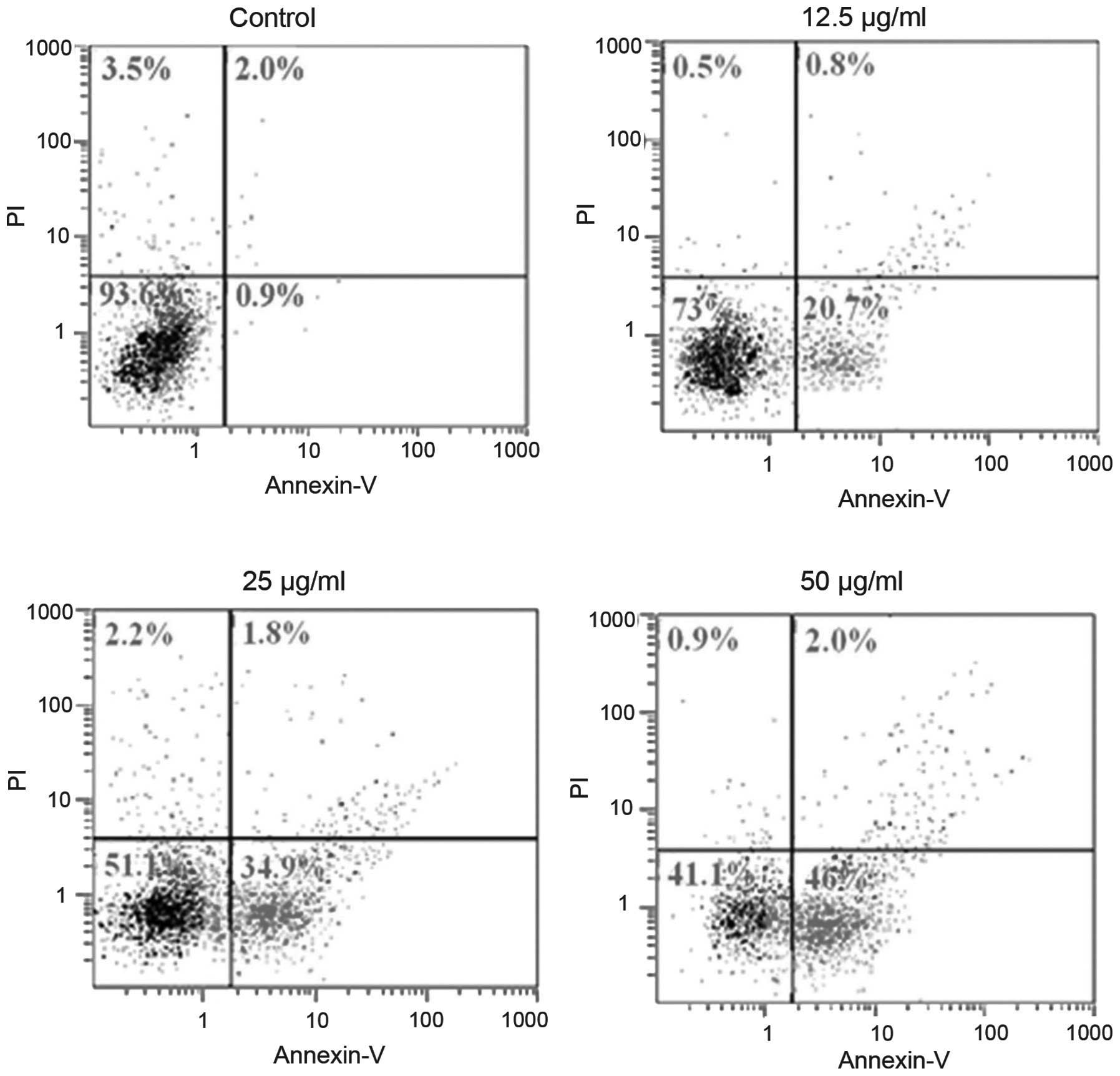
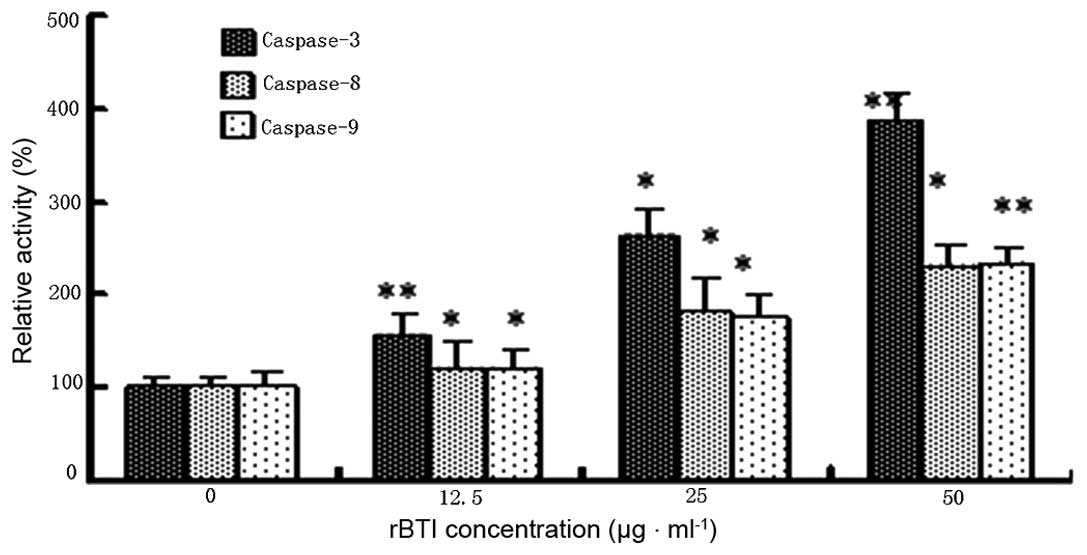
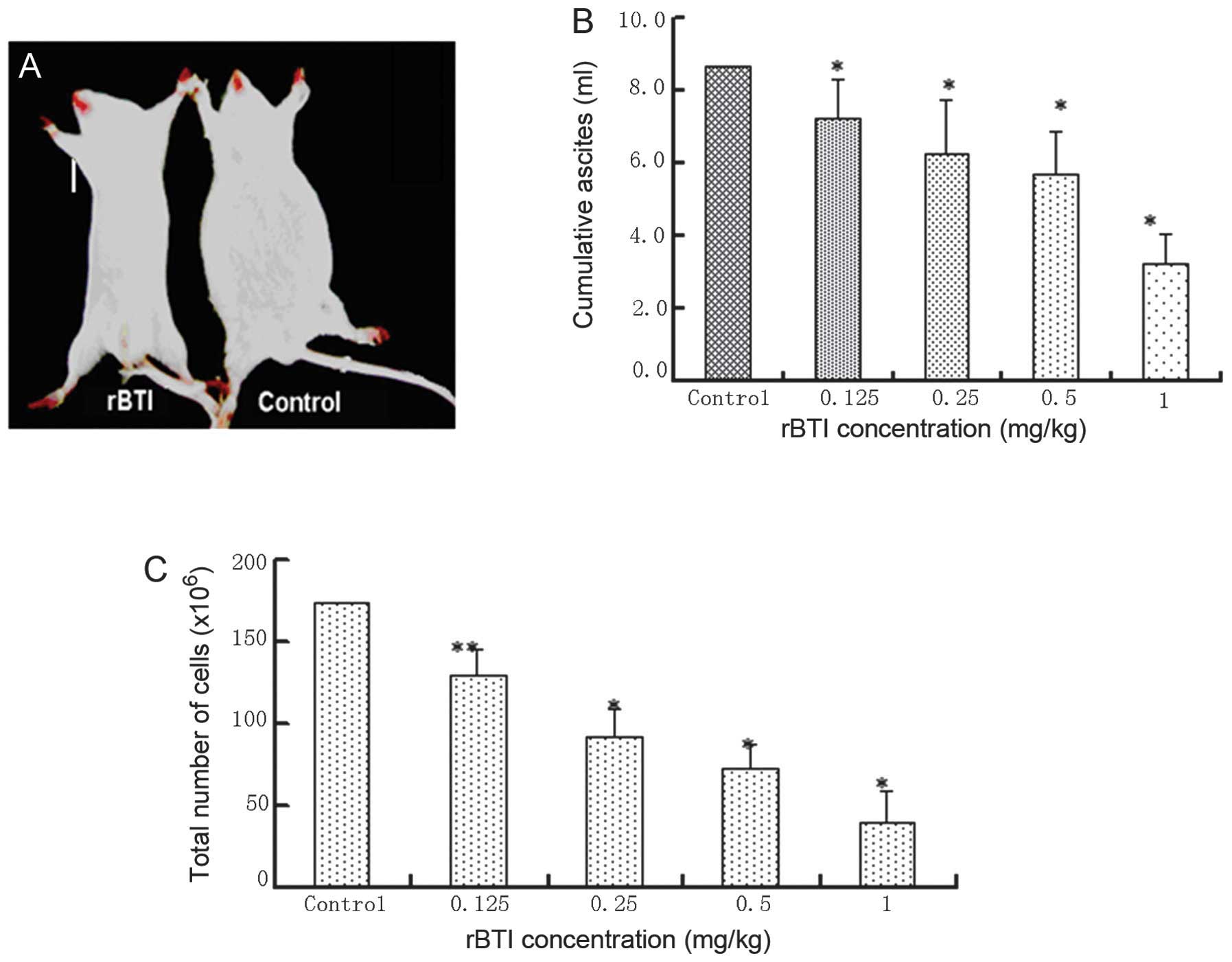
|
1
|
Li CH, Kobayasshi K, Yoshida Y and Ohsawa
R: Genetic analyses of agronomic traits in Tartary buckwheat
(Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn.). Breed Sci. 62:303–309. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pomeranz Y and Robbins GS: Amino acid
composition of buckwheat protein. J Agric Food Chem. 20:270–274.
1972. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ikeda K and Kishida M: Digestibility of
proteins in buckwheat seed. Fagopyrum. 13:21–24. 1993.
|
|
4
|
Zhang Z, Li YY, Shi XR, et al: Gene
cloning and sequencing of common buckwheat trypsin inhibitor. Acta
Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica. 25:46–51. 2005.
|
|
5
|
Htay HH, Tsubouchi R, Haneda M, Murakami K
and Yoshino M: Induction of apoptosis of HL60 cells by gallic acid
derivatives. Biomed Res. 23:127–134. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gardner PR: Aconitase: Sensitive target
and measure of superoxide. Methods Enzymol. 349:9–23.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gladysheva IP, Moroz NA, Karmakova TA,
Nemtsova ER, Yakubovskaya RI and Larionova NI: Immunoconjugates of
soybean Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor as targeted antitumor
polymeric agents. J Drug Target. 9:303–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Marschütz MK and Bernkop-Schnürch A: Oral
peptide drug delivery: Polymer-inhibitor conjugates protecting
insulin from enzymatic degradation in vitro. Biomaterials.
21:1499–1507. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malkowicz SB, Liu SP, Broderick GA, Wein
AJ, Kennedy AR and Levin RM: Effect of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor (a
soy protein) on in vitro bladder neck/urethral and penile corporal
smooth muscle activity. Neurourol Urodyn. 22:54–57. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Supuran CT, Casini A and Scozzafava A:
Protease inhibitors of the sulfonamide type: Anticancer,
antiinflammatory, and antiviral agents. Med Res Rev. 23:535–558.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Birk Y: The Bowman-Birk inhibitor.
Trypsin- and chymotrypsin-inhibitor from soybeans. Int J Pept
Protein Res. 25:113–131. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yavelow J, Finlay TH, Kennedy AR and Troll
W: Bowman-Birk soybean protease inhibitor as an anticarcinogen.
Cancer Res. 43(Suppl): 2454s–2459s. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cryns V and Yuan J: Proteases to die for.
Genes Dev. 12:1551–1570. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu W and Kavanagh JJ: Anticancer therapy
targeting the apoptotic pathway. Lancet Oncol. 4:721–729. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dias N and Bailly C: Drugs targeting
mitochondrial functions to control tumor cell growth. Biochem
Pharmacol. 70:1–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schulze-Osthoff K, Ferrari D, Los M,
Wesselborg S and Peter ME: Apoptosis signaling by death receptors.
Eur J Biochem. 254:439–459. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rao RV, Ellerby HM and Bredesen DE:
Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program.
Cell Death Differ. 11:372–380. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R and
Wang X: Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts:
Requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 86:147–157. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thorburn A: Death receptor-induced cell
killing. Cell Signal. 16:139–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lacour S, Micheau O, Hammann A, Drouineaud
V, Tschopp J, Solary E and Dimanche-Boitrel MT: Chemotherapy
enhances TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand DISC assembly in
HT29 human colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 22:1807–1816. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Li Y, Li C, Yuan J and Wang Z:
Expression of a buckwheat trypsin inhibitor gene in Escherichia
coli and its effect on multiple myeloma IM-9 cell proliferation.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 39:701–707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang ZH, Gao L, Li YY, Zhang Z, Yuan JM,
Wang HW, Zhang L and Zhu L: Induction of apoptosis by buckwheat
trypsin inhibitor in chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells. Biol
Pharm Bull. 30:783–786. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park SS and Ohba H: Suppressive activity
of protease inhibitors from buckwheat seeds against human T-acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Appl Biochem Biotechnol.
117:65–74. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stennicke HR and Salvesen GS: Properties
of the caspases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1387:17–31. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park JW, Choi YJ, Suh SI, Baek WK, Suh MH,
Jin IN, Min DS, Woo JH, Chang JS, Passaniti A, et al: Bcl-2
overexpression attenuates resveratrol-induced apoptosis in U937
cells by inhibition of caspase-3 activity. Carcinogenesis.
22:1633–1639. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kaufmann SH and Hengartner MO: Programmed
cell death: Alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol.
11:526–534. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Narayanan S, Surolia A and Karande AA:
Ribosome-inactivating protein and apoptosis: Abrin causes cell
death via mitochondrial pathway in Jurkat cells. Biochem J.
377:233–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Smith EM and Jayson GC: The current and
future management of malignant ascites. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol).
15:59–72. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|