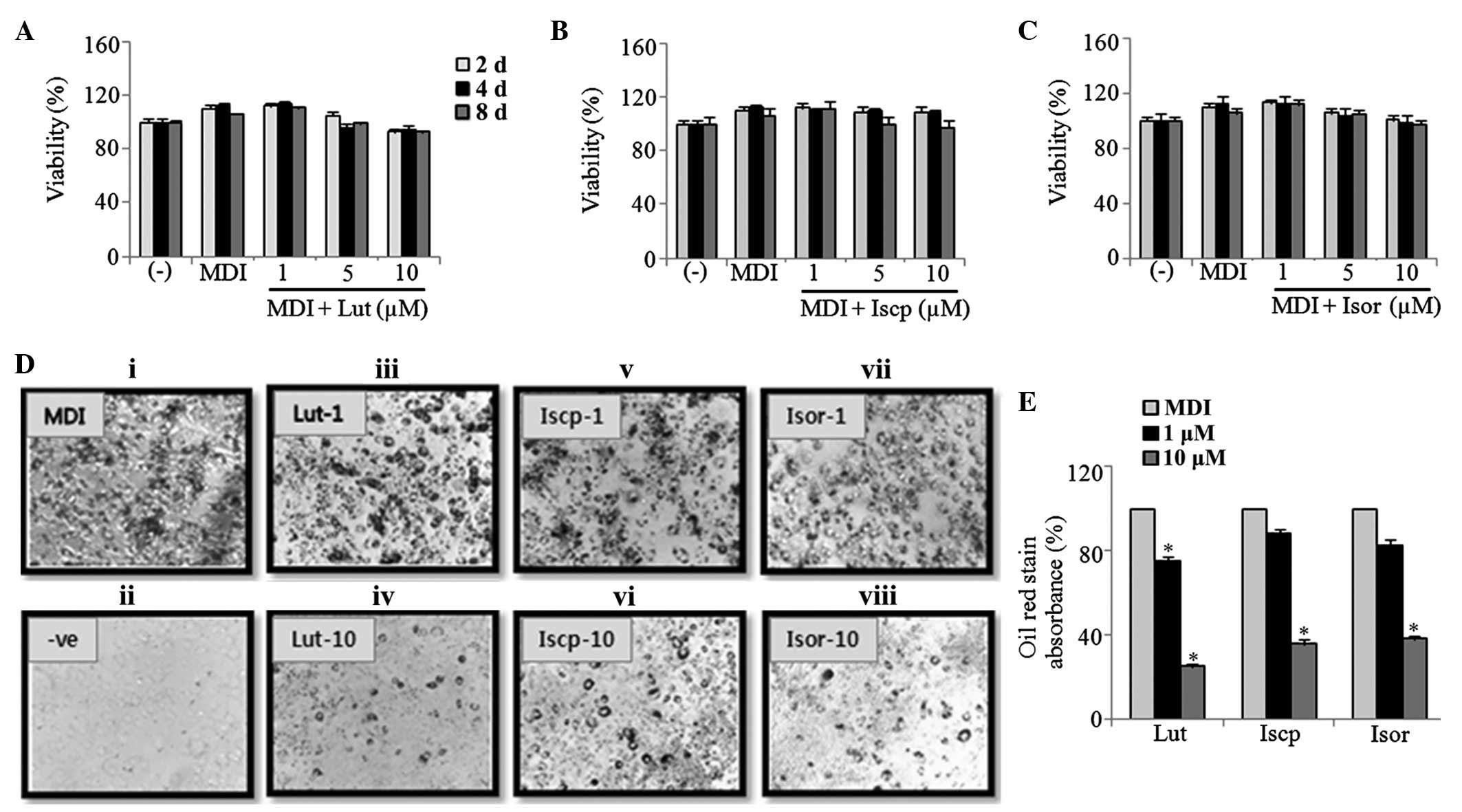
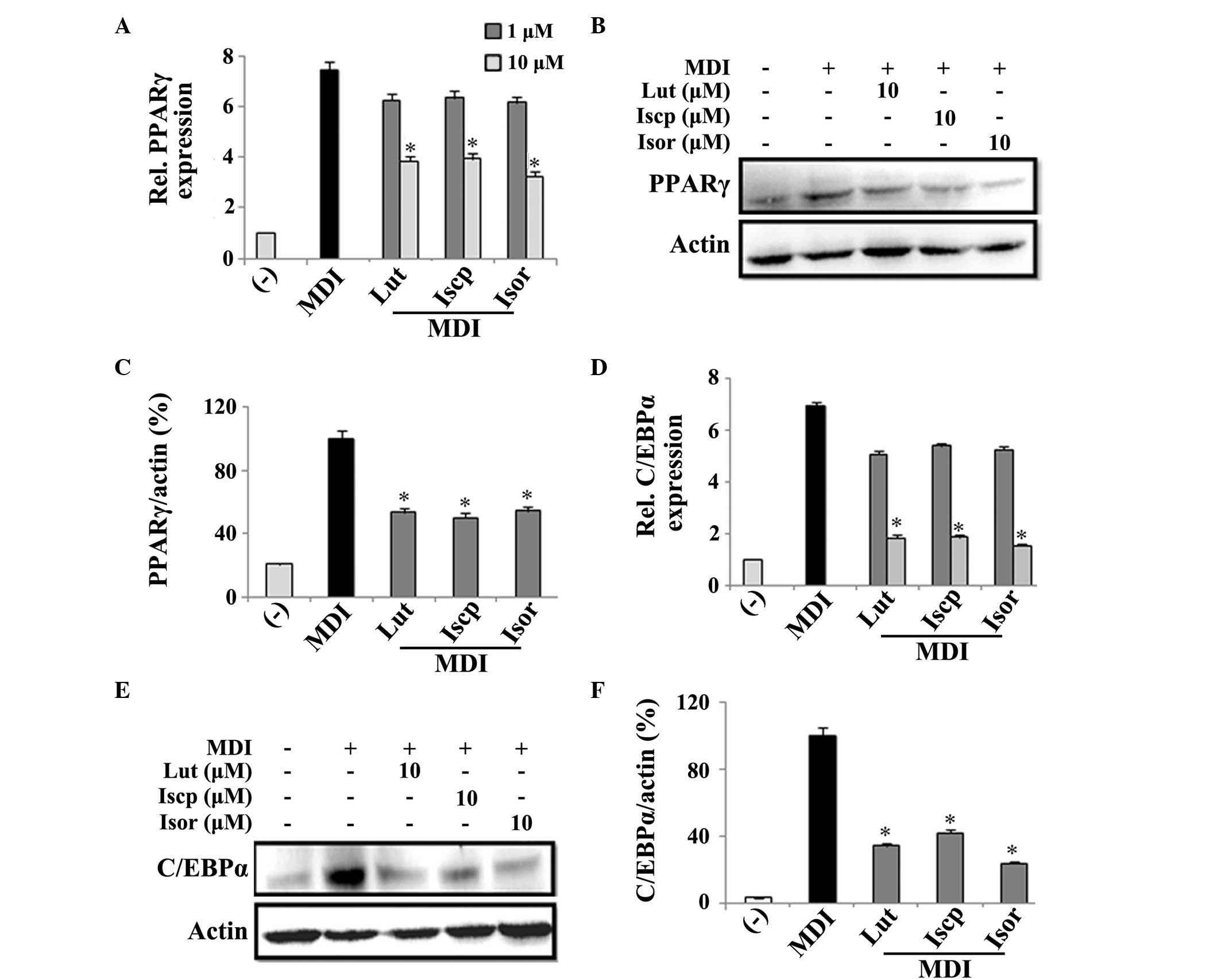
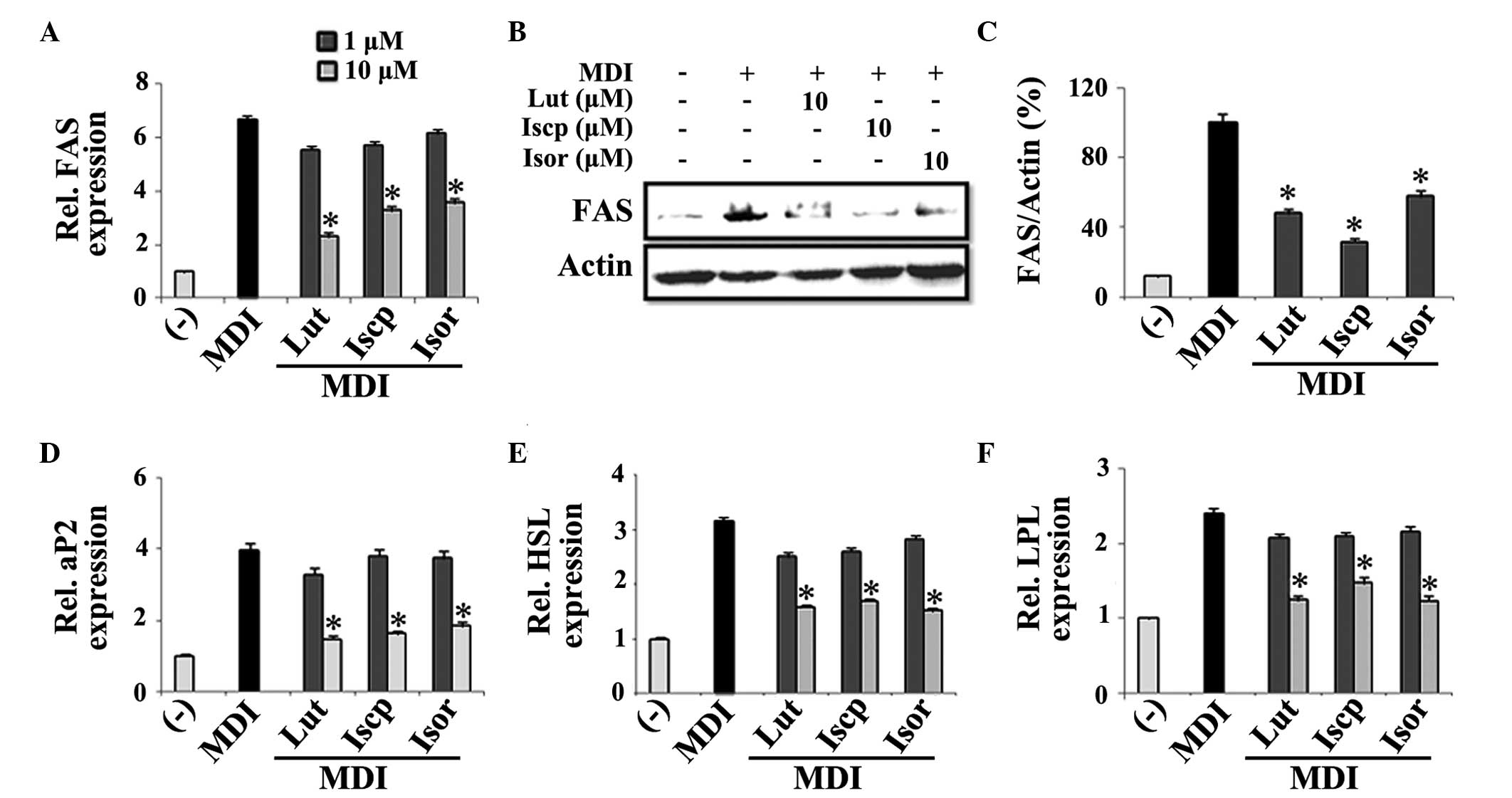
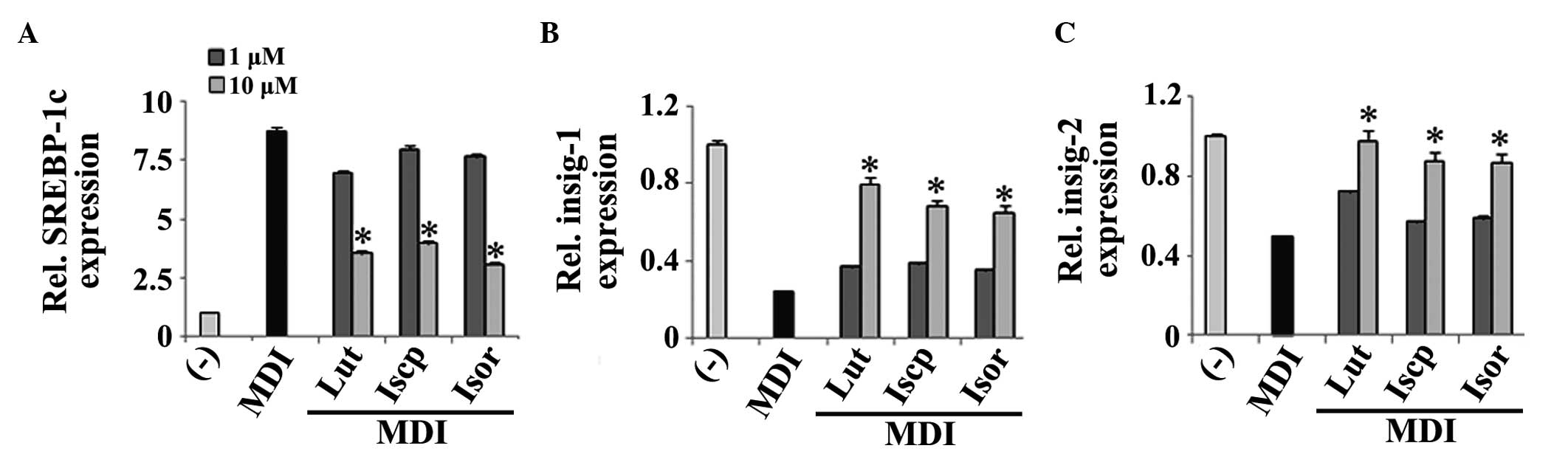
|
1
|
Kanda K, Nishil K, Kadota A, Nishimoto S,
Liu MC and Sagahara T: Nobiletin suppresses adipocyte
differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by an insulin and IBMX mixture
induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:461–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kopelman PG: Obesity as a medical problem.
Nature. 404:635–643. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farmer SR: Regulation of PPARγ activity
during adipogenesis. Int J Obes. 29:13–16. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kwon JY, Seo SG, Heo YS, Yue S, Cheng JX,
Lee KW and Kim KH: Piceatannol, natural polyphenolic stilbene,
inhibits adipogenesis via modulation of mitotic clonal expansion
and insulin receptor-dependent insulin signaling in early phase of
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 287:11566–11578. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
White UA and Stephens JM: Transcriptional
factors that promote formation of white adipose tissue. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 318:10–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Park HS, Kim SH, Kim YS, et al: Luteolin
inhibits adipogenic differentiation by regulating PPARgamma
activation. Biofactors. 35:373–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ka SO, Kim KA, Kwon KB, Park JW and Park
BH: Silibinin attenutates adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes
through potential upregulation of the insig pathway. Int J Mol Med.
23:633–637. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang T, Espenshade PJ, Wright ME, et al:
Crucial step in cholesterol homeostasis: sterols promote binding of
SCAP to INSIG-1, a membrane protein that facilitates retention of
SREBPs in ER. Cell. 110:489–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA and Brown MS:
Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell. 124:35–46. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Montagut G, Blade C, Blay M, et al:
Effects of a grapeseed procy-anidin extract (GSPE) on insulin
resistance. J Nutr Biochem. 21:961–967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee SH, Lim SW, Lee YM, Lee HS and Kim DK:
Polysaccharide isolated from Triticum aestivum stimulates insulin
release from pancreatic cells via the ATP-sensitive K+ channel. Int
J Mol Med. 29:913–919. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee SH, Lee YM, Lee HS and Kim DK:
Anti-oxidative and anti-hyperglycemia effects of Triticum
aestivumwheat sprout water extracts on the streptozotocin-induced
diabetic mice. Korean J Pharmacogn. 40:408–414. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Lee SH, Lim SW, Lee YM, Hur JM, Lee HS and
Kim DK: Anti-diabetic effects of Triticum aestivum L. water
extracts in db/db mice as an animal model of diabetes mellitus type
II. Korean J Pharmacogn. 41:282–288. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Lee SH, Xin M, Luyen BTT, et al:
Inhibitory effect of Triticum aestivum ethanol extract on lipid
accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadi-pocytes. Yakhak Hoeji. 55:478–484.
2011.
|
|
15
|
Lee SH, Lim SW, Lee YM, Lee SH and Kim DK:
Inhibitory effects of Triticum aestivum L. extracts on liver lipid
accumulation in high fat-fed mice. Korean J Pharmacogn. 42:309–316.
2011.
|
|
16
|
Lee SH, Lim SW, Mihn NV, et al:
Administration of Triticum aestivum water extracts reduce the level
of blood glucose and cholesterol in leptin deficient ob/ob mice. J
Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 40:401–408. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Luyen BTT, Tai BH, Thao NP, Cha JY, Lee YM
and Kim YH: A new phenolic component from Triticum aestivum sprouts
and its effects on LPS-stimulated production of nitric oxide and
TNF-alpha in RAW 264.7 cells. Phytother Res. 28:1064–1070. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wojakowska A, Perkowski J, Goral T and
Stobiecki M: Structural characterization of flavanoid glycosides
from leaves of wheat (Triticum aextivum L.) using LC/MS/MS
profiling of the target compounds. J Mass Spectrom. 48:329–339.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Poudel B, Lim SW, Ki HH, Nepali S, Lee YM
and Kim DK: Dioscin inhibits adipogenesis through the AMPK/MAPK
pathway in 3T3-L1 cells and modulates fat accumulation in obese
mice. Int J Mol Med. 34:1401–1408. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poudel B, Yoon DS, Lee JH, Lee YM and Kim
DK: Collagen I enhances functional activities of human
monocyte-derived dendritic cells via discoidin domain receptor 2.
Cell Immunol. 278:95–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morimoto C, Kameda K, Tsujita T and Okuda
H: Relationships between lipolysis I induced by various lipolytic
agents and hormone-sensitive lipase in rat fat cells. J Lipid Res.
42:120–127. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bennett MK, Lopez JM, Sanchez HB and
Osborne TF: Sterol regulation of fatty acid synthase promoter.
Coordinate feedback regulation of two major lipid pathways. J Biol
Chem. 270:25578–25583. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Claycombe KJ, Jones BH, Standridge MK, Guo
Y, Chun JT, Taylor JW and Moustaïd-Moussa N: Insulin increases
fatty acid synthase gene transcription in human adipocytes. Am J
Physiol. 274:1253–1259. 1998.
|
|
24
|
Schmid B, Rippmann JF, Tadayyon M and
Hamilton BS: Inhibition of fatty acid synthase prevents
preadipocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
328:1073–1082. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haunerland NH and Spener F: Fatty
acid-binding proteins-insights from genetic manipulations. Prog
Lipid Res. 43:328–349. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chirala SS, Jayakumar A, Gu ZW and Wakil
SJ: Human fatty acid synthase: role of interdomain in the formation
of cata-lytically active synthase dimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:3104–3108. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gonzales AM and Orlando RA: Role of
adipocyte-derived lipo-protein lipase in adipocyte hypertrophy.
Nutr Metab (Lond). 4:222007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
He Y, Li Y, Zhao T, Wang Y and Sun C:
Ursolic acid inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through
LKB1/AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 8:e701352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang XH, Huang B, Choi SK and See JS:
Anti-obesity effects of resveratrol-amplified grape skin extracts
on 3T3-L1 adipocytes differentiation. Nutr Res Pract. 6:286–293.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li J, Takaishi K, Cook W, McCorkle SK and
Unger RH: Insig-1 ‘brakes’ lipogenesis in adipocytes and inhibits
differentiation of preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:9476–9481. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|