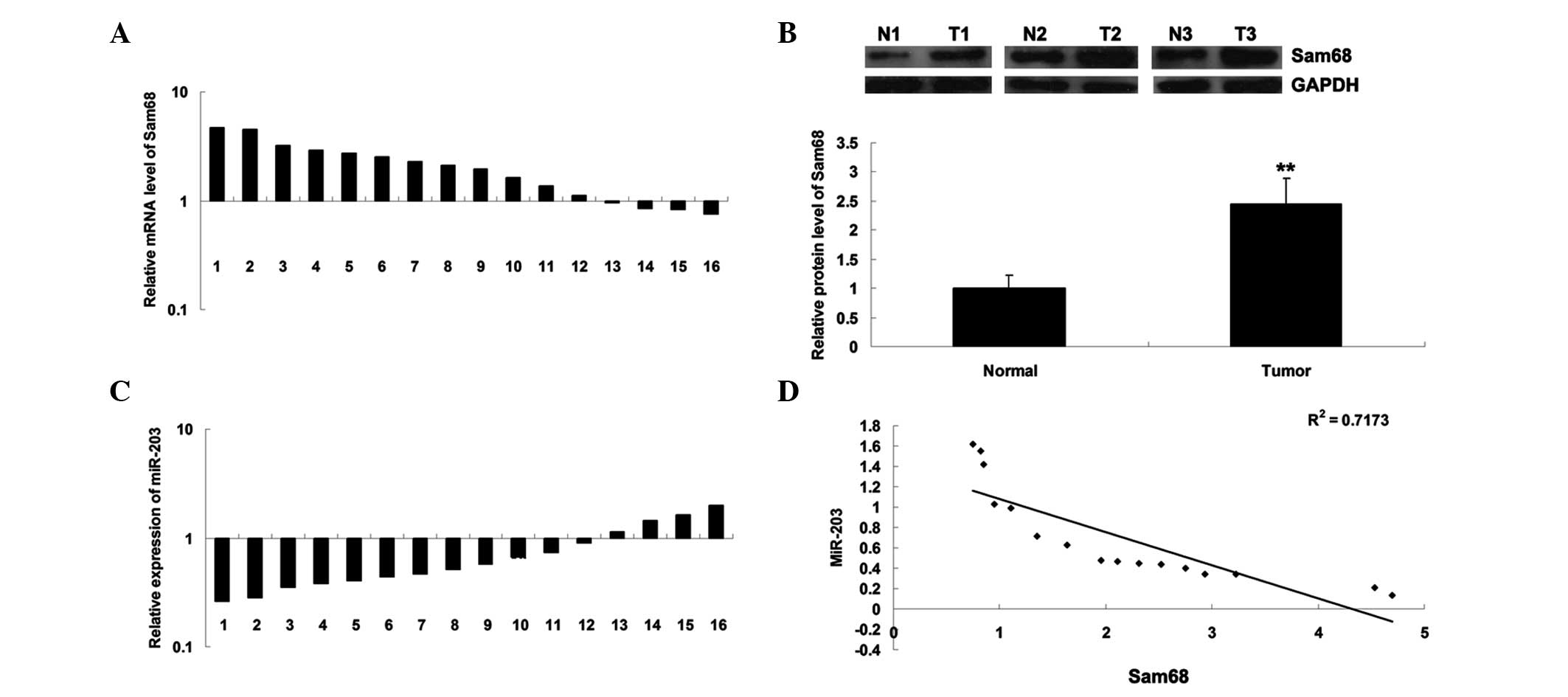
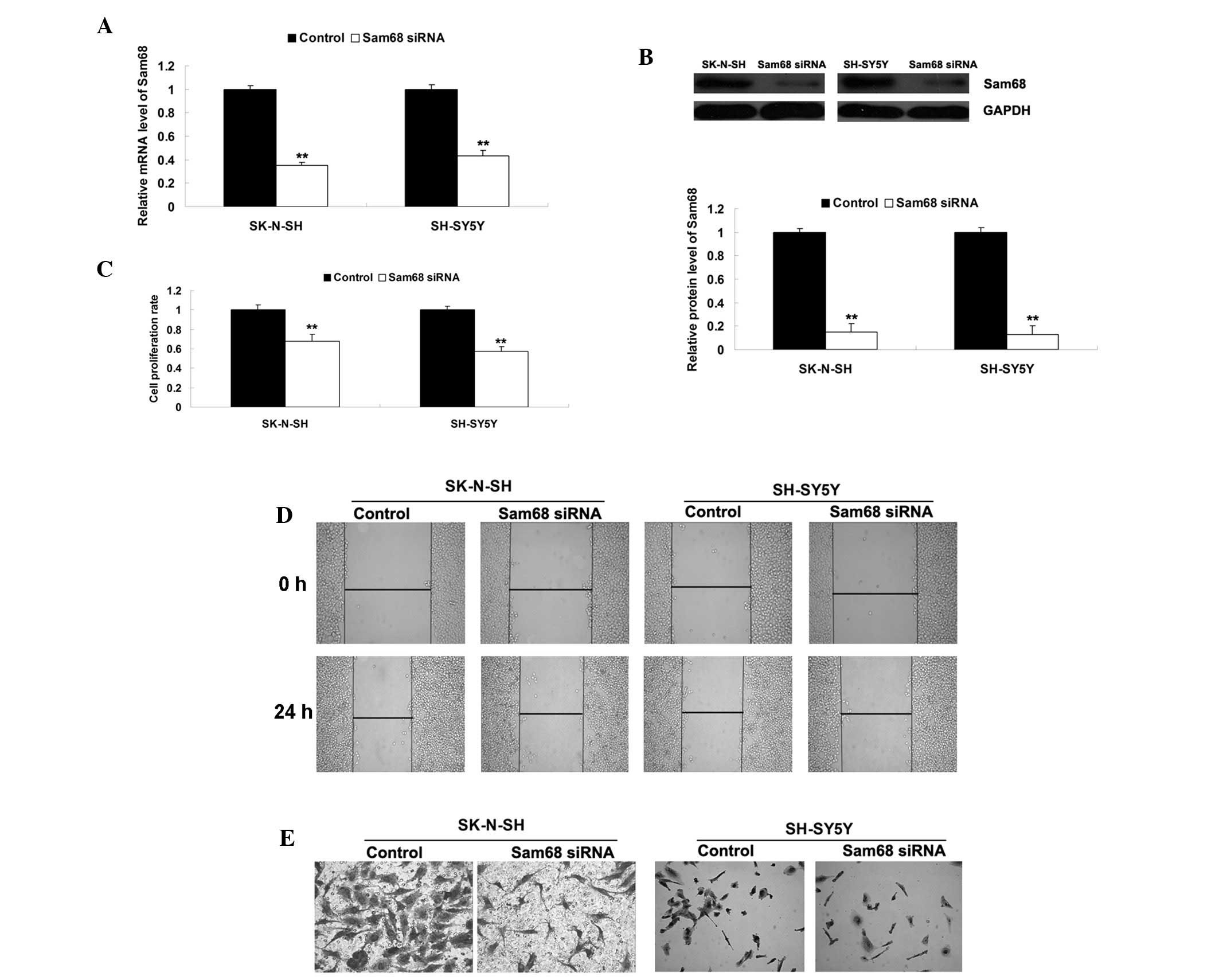
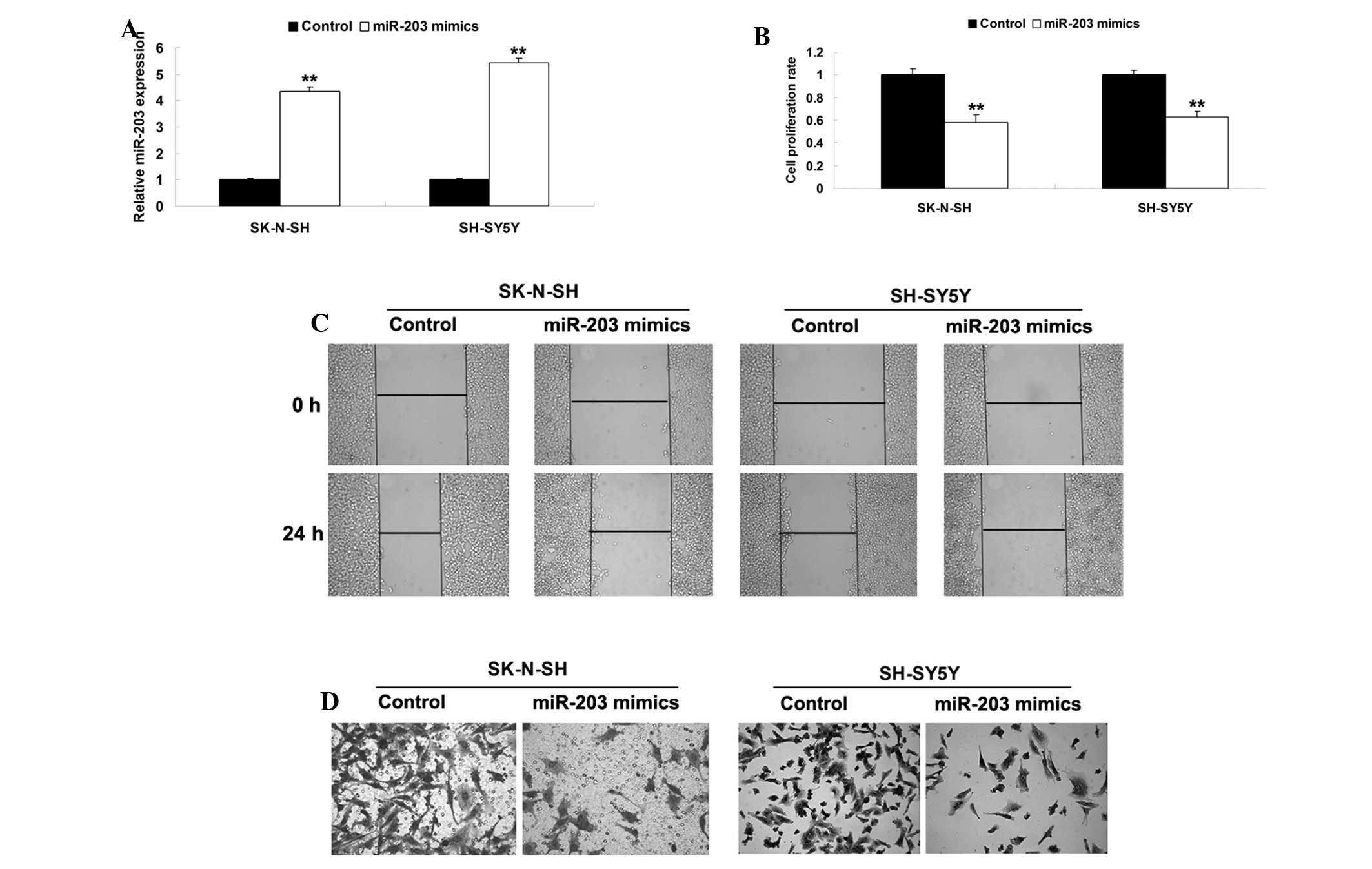
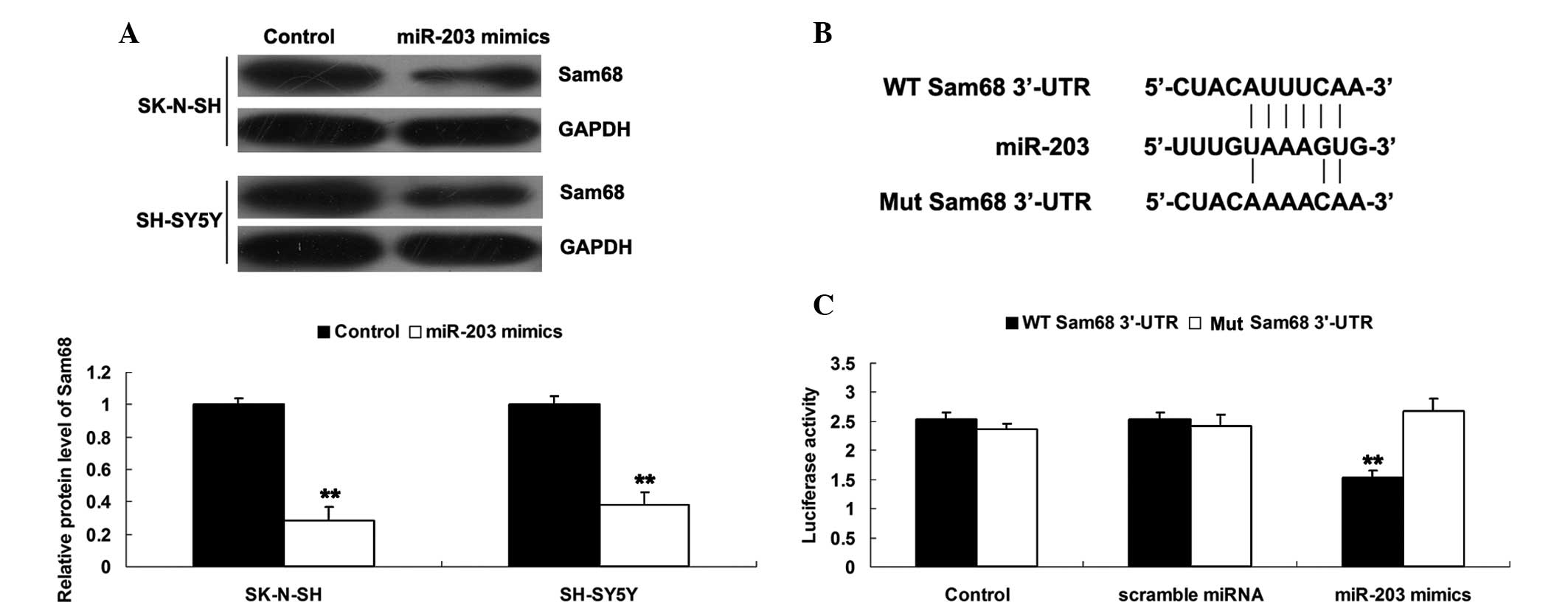
|
1
|
Fulda S: The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as
therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
9:729–737. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jrebi NY, Iqbal CW, Joliat GR, Sebo TJ and
Farley DR: Review of our experience with neuroblastoma and
ganglioneuroblastoma in adults. World J Surg. 2871–2874. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vogel G and Richard S: Emerging roles for
Sam68 in adipogenesis and neuronal development. RNA Biol.
9:1129–1133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Najib S, Martin-Romero C, Gonzalez-Yanes C
and Sanchez-Margalet V: Role of Sam68 as an adaptor protein in
signal transduction. Cell Mol Life Sci. 62:36–43. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lukong KE and Richard S: Sam68, the KH
domain-containing superSTAR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1653:73–86.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen SW, Zhang Q, Yang AK, Li Z, Zhong Y,
Li H, Zeng Y, Zhuang SM, Wang LP, Song LB, et al: Overexpression
and cytoplasmic localization of Sam68 correlate with tumour
progression and poor prognosis in patients with clinically N0 oral
tongue cancer. Head Neck Oncol. 4:612012.
|
|
9
|
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Sun N, Zhang M, Xie J and
Jiang Z: High Sam68 expression predicts poor prognosis in non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 16:886–891. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arocho A, Chen B, Ladanyi M and Pan Q:
Validation of the 2-DeltaDeltaCt calculation as an alternate method
of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts.
Diagn mol pathol. 15:56–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sánchez-Jiménez F and Sánchez-Margalet V:
Role of Sam68 in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:23402–23419. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu K, Sun X, Zheng W, Wier EM, Hodgson A,
Tran DQ, Richard S and Wan F: Sam68 modulates the promoter
specificity of NF-kB and mediates expression of CD25 in activated T
cells. Nat Commun. 4:19092013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liao WT, Liu JL, Wang ZG, Cui YM, Shi L,
Li TT, Zhao XH, Chen XT, Ding YQ and Song LB: High expression level
and nuclear localization of Sam68 are associated with progression
and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. BMC Gastroenterol.
14:1262014.
|
|
14
|
Li Z, Yu CP, Zhong Y, Liu TJ, Huang QD,
Zhao XH, Huang H, Tu H, Jiang S, Zhang Y, et al: Sam68 expression
and cytoplasmic localization is correlated with lymph node
metastasis as well as prognosis in patients with early-stage
cervical cancer. Ann Oncol. 23:638–646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhao X, Li Z, He B, Liu J, Li S, Zhou L,
Pan C, Yu Z and Xu Z: Sam68 is a novel marker for aggressive
neuroblastoma. Onco Targets Ther. 6:1751–1760. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S,
Imoto I and Inazawa J: miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically
silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 31:766–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Greither T, Grochola LF, Udelnow A,
Lautenschlager C, Wurl P and Taubert H: Elevated expression of
microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated
with poorer survival. Int J Cancer. 126:73–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
He J, Deng Y, Yang G and Xie W:
MicroRNA-203 down-regulation is associated with unfavorable
prognosis in human glioma. J Surg Oncol. 108:121–125. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheung TH, Man KN, Yu MY, Yim SF, Siu NS,
Lo KW, Doran G, Wong RR, Wang VW, Smith DI, et al: Dysregulated
microRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of cervical neoplasm.
Cell Cycle. 11:2876–2884. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boll K, Reiche K, Kasack K, Mörbt N,
Kretzschmar AK, Tomm JM, Verhaegh G, Schalken J, von Bergen M, Horn
F, et al: MiR-130a, miR-203 and miR-205 jointly repress key
oncogenic pathways and are downregulated in prostate carcinoma.
Oncogene. 32:277–285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kozubek J, Ma Z, Fleming E, Duggan T, Wu
R, Shin DG and Dadras SS: In-depth characterization of microRNA
transcriptome in melanoma. PLoS One. 8:e726992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti
KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang C, Wang X, Liang H, Wang T, Yan X,
Cao M, Wang N, Zhang S, Zen K, Zhang C, et al: miR-203 Inhibits
cell proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells by targeting
PKCα. PLoS One. 8:e739852013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C and Shi Y:
MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by
targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuan Y, Zeng ZY, Liu XH, Gong DJ, Tao J,
Cheng HZ and Huang SD: MicroRNA-203 inhibits cell proliferation by
repressing ΔNp63 expression in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:572011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tian L, Li M, Ge J, Guo Y, Sun Y, Liu M
and Xiao H: MiR-203 is downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma and can suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis of
tumours. Tumour Biol. 35:5953–5963. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bian K, Fan J, Zhang X, Yang XW, Zhu HY,
Wang L, Sun JY, Meng YL, Cui PC, Cheng SY, et al: MicroRNA-203
leads to G1 phase cell cycle arrest in laryngeal carcinoma cells by
directly targeting survivin. FEBS Lett. 586:804–809. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abella V, Valladares M, Rodriguez T, Haz
M, Blanco M, Tarrío N, Iglesias P, Aparicio LA and Figueroa A:
miR-203 regulates cell proliferation through its influence on Hakai
expression. PLoS One. 7:e525682012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dontula R, Dinasarapu A, Chetty C, Pannuru
P, Herbert E, Ozer H and Lakka SS: MicroRNA 203 modulates glioma
cell migration via Robo1/ERK/MMP-9 Signaling. Genes Cancer.
4:285–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Noguchi S, Kumazaki M, Yasui Y, Mori T,
Yamada N and Akao Y: MicroRNA-203 regulates melanosome transport
and tyrosinase expression in melanoma cells by targeting kinesin
superfamily protein 5b. J Invest Dermatol. 134:461–469. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Noguchi S, Mori T, Otsuka Y, Yamada N,
Yasui Y, Iwasaki J, Kumazaki M, Maruo K and Akao Y: Anti-oncogenic
microRNA-203 induces senescence by targeting E2F3 protein in human
melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 287:11769–11777. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takeshita N, Mori M, Kano M, Hoshino I,
Akutsu Y, Hanari N, Yoneyama Y, Ikeda N, Isozaki Y, Maruyama T, et
al: miR-203 inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma by regulating LASP1. Int J Oncol.
41:1653–1661. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu X, Jiang X, Li H, Guo L, Jiang W and Lu
SH: MiR-203 inhibits the proliferation and self-renewal of
esophageal cancer stem-like cells by suppressing stem renewal
factor Bmi-1. Stem Cells Dev. 23:576–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|