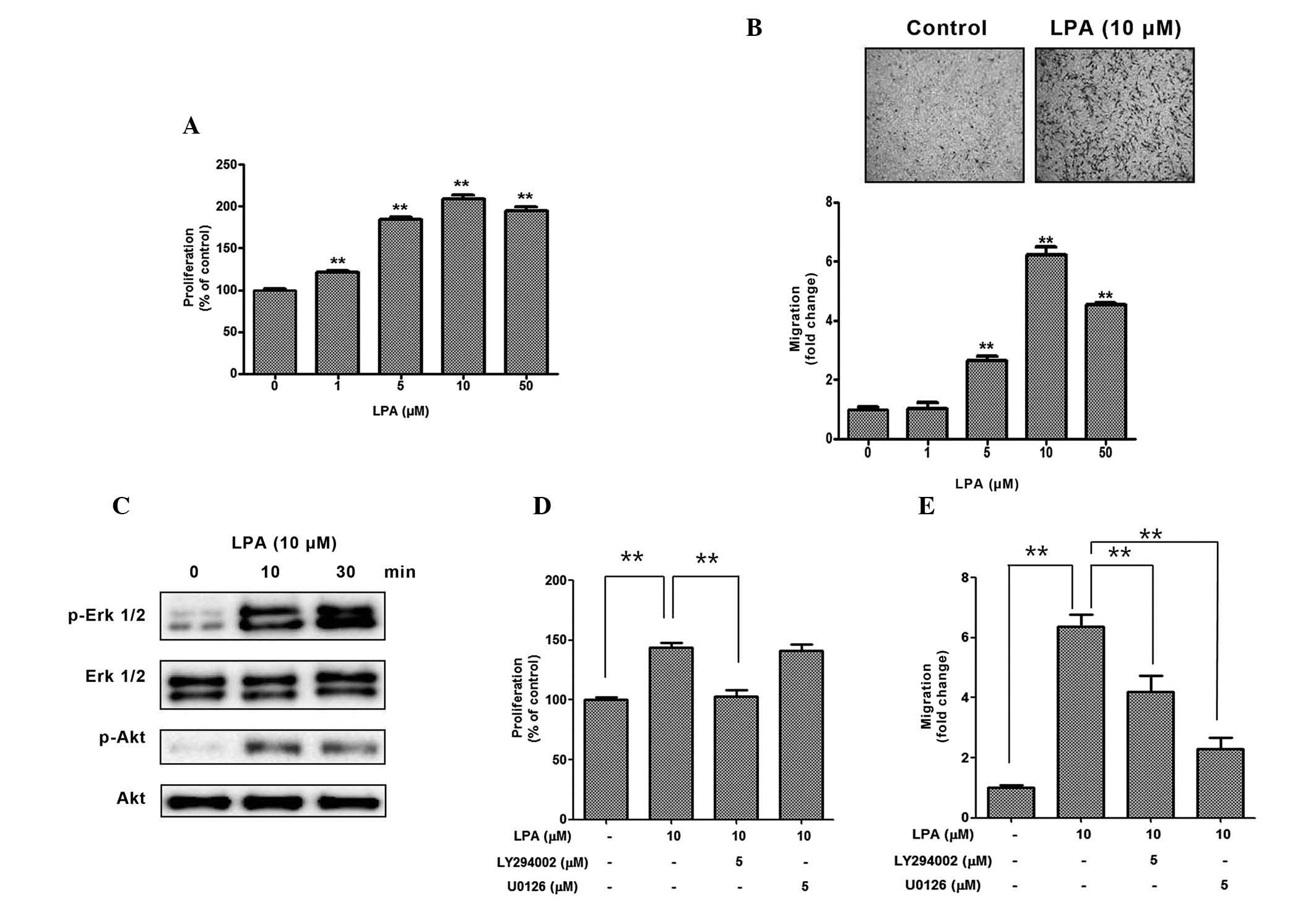
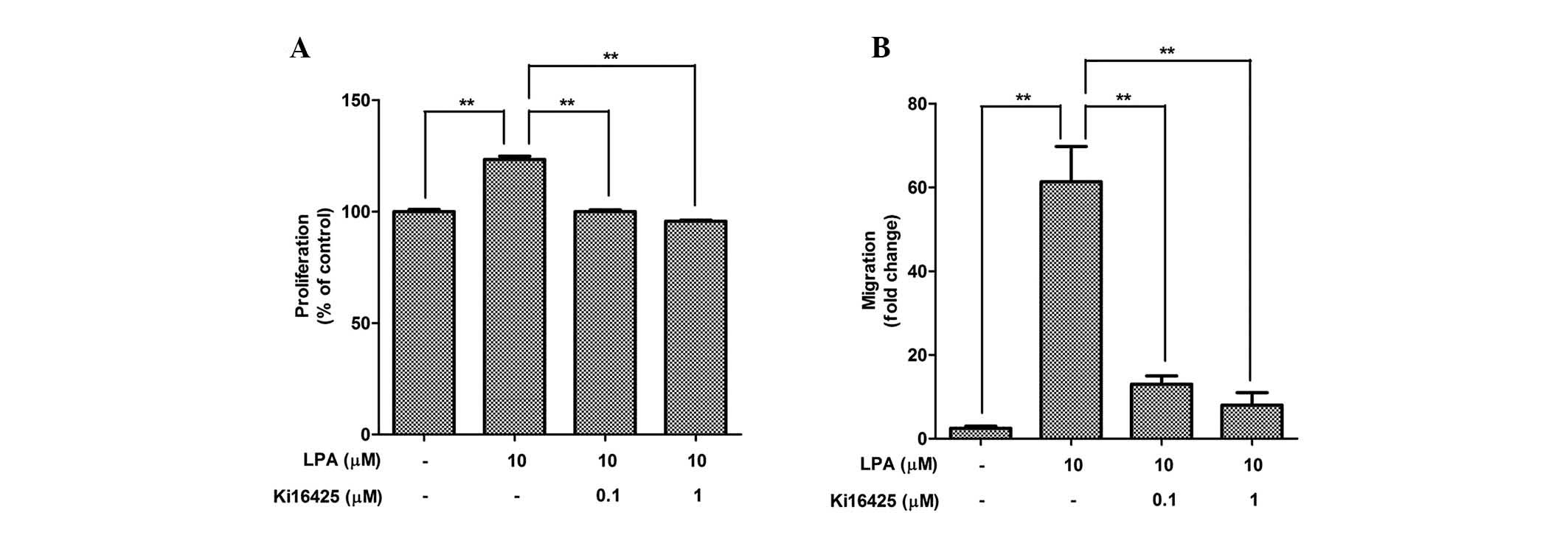
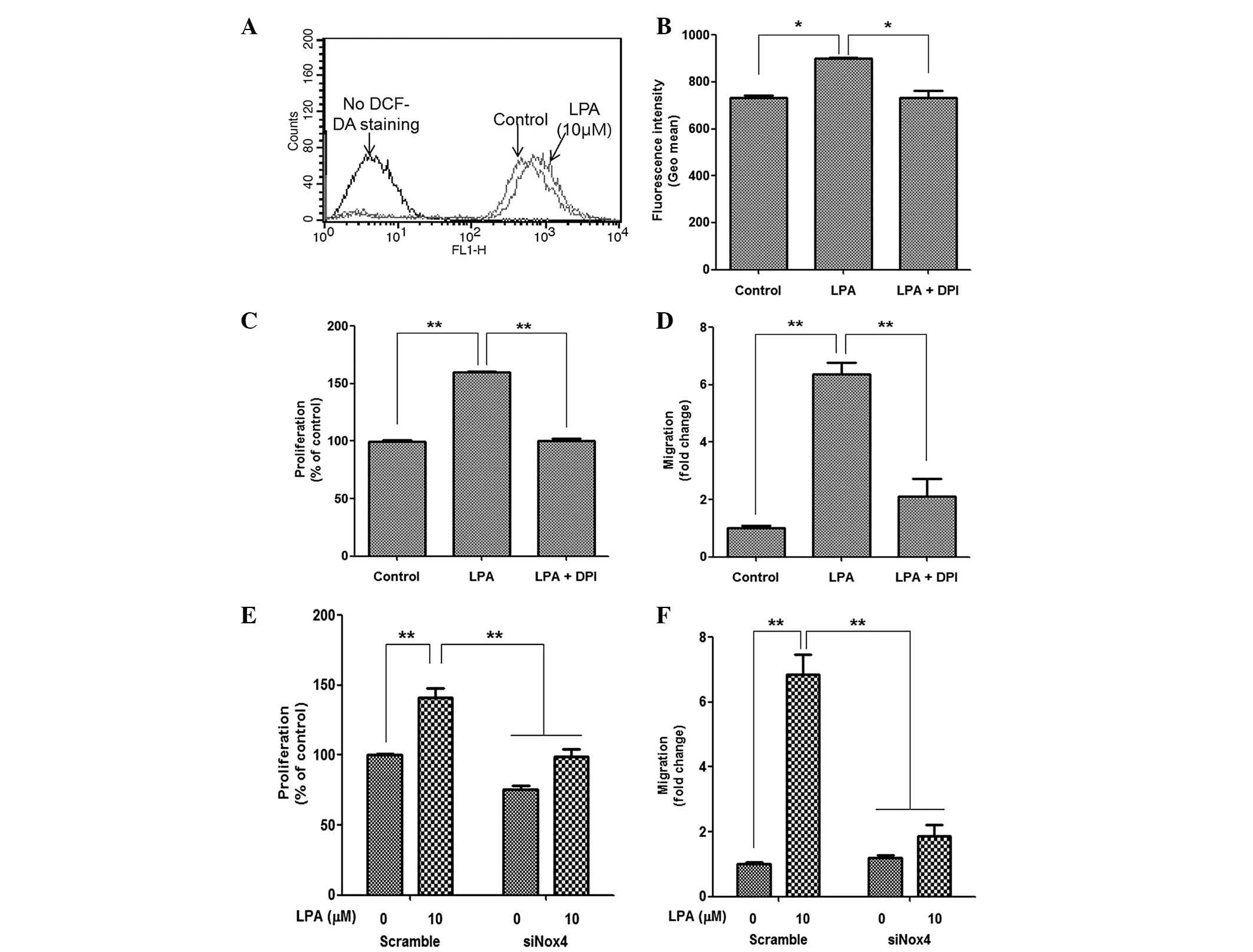
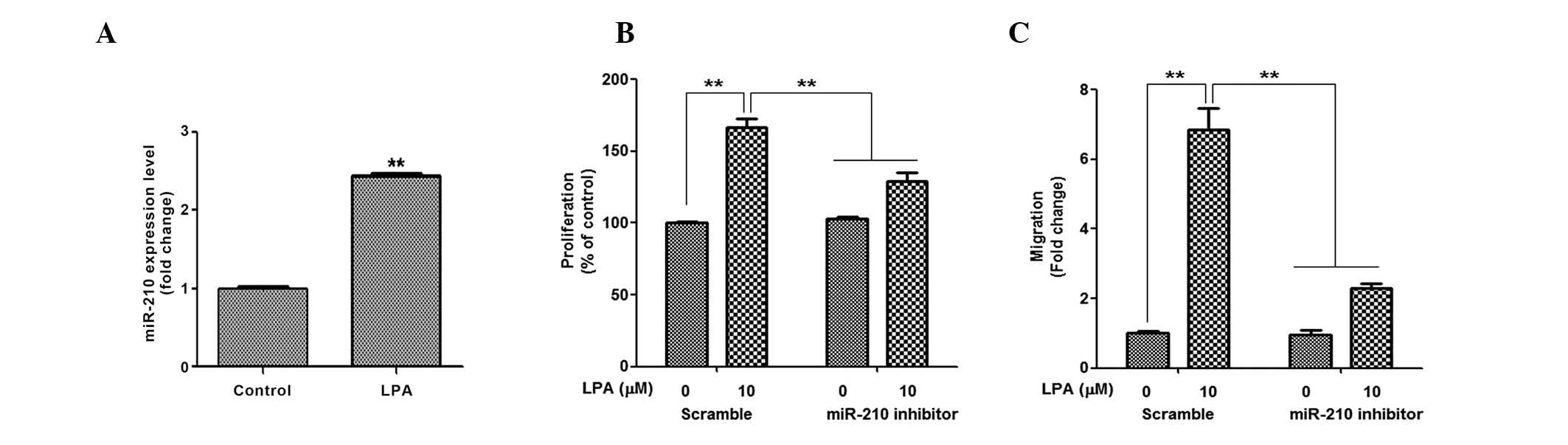
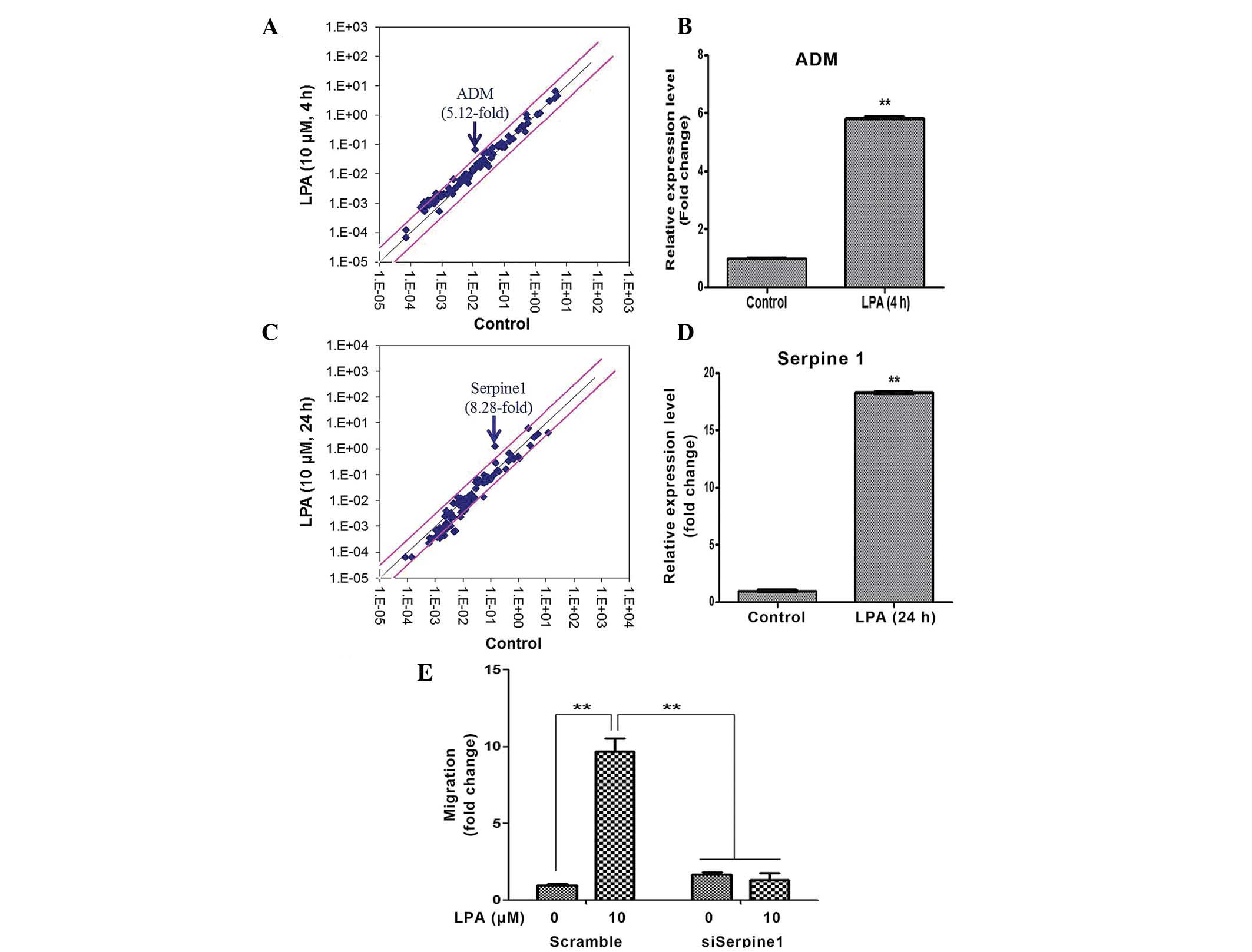
|
1
|
Glazier AT, Blackmore PF, Nolan RD and
Wasilenko WJ: Attenuation of LPA-mediated calcium signaling and
inositol poly-phosphate production in rat-1 fibroblasts transformed
by the v-src oncogene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 245:607–612.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jonkers J and Moolenaar WH: Mammary
tumorigenesis through LPA receptor signaling. Cancer Cell.
15:457–459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sorensen SD, Nicole O, Peavy RD, Montoya
LM, Lee CJ, Murphy TJ, Traynelis SF and Hepler JR: Common signaling
pathways link activation of murine PAR-1, LPA, and S1P receptors to
proliferation of astrocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 64:1199–1209. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tangkijvanich P, Melton AC, Santiskulvong
C and Yee HF Jr: Rho and p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways mediate
LPA-stimulated hepatic myofibroblast migration. J Biomed Sci.
10:352–358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bandoh K, Aoki J, Taira A, Tsujimoto M,
Arai H and Inoue K: Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors of the
EDG family are differentially activated by LPA species.
Structure-activity relationship of cloned LPA receptors. FEBS Lett.
478:159–165. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yanagida K, Kurikawa Y, Shimizu T and
Ishii S: Current progress in non-Edg family LPA receptor research.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:33–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hao F, Tan M, Xu X, Han J, Miller DD,
Tigyi G and Cui MZ: Lysophosphatidic acid induces prostate cancer
PC3 cell migration via activation of LPA(1), p42 and p38alpha.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1771:883–892. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sengupta S, Xiao YJ and Xu Y: A novel
laminin-induced LPA autocrine loop in the migration of ovarian
cancer cells. FASEB J. 17:1570–1572. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shida D, Watanabe T, Aoki J, Hama K,
Kitayama J, Sonoda H, Kishi Y, Yamaguchi H, Sasaki S, Sako A, et
al: Aberrant expression of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors in
human colorectal cancer. Lab Invest. 84:1352–1362. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwon YJ, Sun Y, Kim NH and Huh SO:
Phosphorylation of CREB, a cyclic AMP responsive element binding
protein, contributes partially to lysophosphatidic acid-induced
fibroblast cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
380:655–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee H, Goetzl EJ and An S:
Lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulate
endothelial cell wound healing. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
278:C612–C618. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sauer B, Vogler R, Zimmermann K, Fujii M,
Anzano MB, Schäfer-Korting M, Roberts AB and Kleuser B:
Lysophosphatidic acid interacts with transforming growth
factor-beta signaling to mediate keratinocyte growth arrest and
chemotaxis. J Invest Dermatol. 123:840–849. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tokumura A, Iimori M, Nishioka Y, Kitahara
M, Sakashita M and Tanaka S: Lysophosphatidic acids induce
proliferation of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from rat
aorta. Am J Physiol. 267:C204–C210. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saunders JA, Rogers LC, Klomsiri C, Poole
LB and Daniel LW: Reactive oxygen species mediate lysophosphatidic
acid induced signaling in ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol
Med. 49:2058–2067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Q, Olashaw N and Wu J: Participation
of reactive oxygen species in the lysophosphatidic acid-stimulated
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase activation pathway. J Biol
Chem. 270:28499–28502. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Idzko M, Laut M, Panther E, Sorichter S,
Dürk T, Fluhr JW, Herouy Y, Mockenhaupt M, Myrtek D, Elsner P and
Norgauer J: Lysophosphatidic acid induces chemotaxis, oxygen
radical production, CD11b up-regulation, Ca2+
mobilization, and actin reorganization in human eosinophils via
pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins. J Immunol. 172:4480–4485.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin CC, Lin CE, Lin YC, Ju TK, Huang YL,
Lee MS, Chen JH and Lee H: Lysophosphatidic acid induces reactive
oxygen species generation by activating protein kinase C in PC-3
human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
440:564–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Badri L and Lama VN: Lysophosphatidic acid
induces migration of human lung-resident mesenchymal stem cells
through the β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells. 30:2010–2019. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen J, Baydoun AR, Xu R, Deng L, Liu X,
Zhu W, Shi L, Cong X, Hu S and Chen X: Lysophosphatidic acid
protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and serum
deprivation-induced apoptosis. Stem Cells. 26:135–145. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li Z, Wei H, Liu X, Hu S, Cong X and Chen
X: LPA rescues ER stress-associated apoptosis in hypoxia and serum
deprivation-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
111:811–820. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu YB, Kharode Y, Bodine PV, Yaworsky PJ,
Robinson JA and Billiard J: LPA induces osteoblast differentiation
through interplay of two receptors: LPA1 and LPA4. J Cell Biochem.
109:794–800. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeon ES, Heo SC, Lee IH, Choi YJ, Park JH,
Choi KU, Park do Y, Suh DS, Yoon MS and Kim JH: Ovarian
cancer-derived lysophosphatidic acid stimulates secretion of VEGF
and stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha from human mesenchymal stem
cells. Exp Mol Med. 42:280–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei H, Wang F, Wang X, Yang J, Li Z, Cong
X and Chen X: Lysophosphatidic acid promotes secretion of VEGF by
increasing expression of 150-kD Oxygen-regulated protein (ORP150)
in mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1426–1434.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim JH, Park SG, Song SY, Kim JK and Sung
JH: Reactive oxygen species-responsive miR-210 regulates
proliferation and migration of adipose-derived stem cells via
PTPN2. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JH, Park SH, Park SG, Choi JS, Xia Y
and Sung JH: The pivotal role of reactive oxygen species generation
in the hypoxia-induced stimulation of adipose-derived stem cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 20:1753–1761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim JH, Song SY, Park SG, Song SU, Xia Y
and Sung JH: Primary involvement of NADPH oxidase 4 in
hypoxia-induced generation of reactive oxygen species in
adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 21:2212–2221. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Park SG, Kim JH, Xia Y and Sung JH:
Generation of reactive oxygen species in adipose-derived stem
cells: Friend or foe? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:1297–1306. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Park SH, Kim HK and Sung
JH: Antiwrinkle effect of adipose-derived stem cell: Activation of
dermal fibroblast by secretory factors. J Dermatol Sci. 53:96–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Sung JH, Yang JM, Park
SB, Kwak SJ and Park JS: Wound healing effect of adipose-derived
stem cells: A critical role of secretory factors on human dermal
fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 48:15–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong YM, Sung YK, Kim WK, Kim JH, Kwack
MH, Yoon I, Kim DD and Sung JH: Ultraviolet B preconditioning
enhances the hair growth-promoting effects of adipose-derived stem
cells via generation of reactive oxygen species. Stem Cells Dev.
22:158–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Kue PF, Taub JS, Harrington LB,
Polakiewicz RD, Ullrich A and Daaka Y: Lysophosphatidic
acid-regulated mitogenic ERK signaling in androgen-insensitive
prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Int J Cancer. 102:572–579. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu X, Haney N, Kropp D, Kabore AF,
Johnston JB and Gibson SB: Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) protects
primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells from apoptosis through
LPA receptor activation of the anti-apoptotic protein AKT/PKB. J
Biol Chem. 280:9498–9508. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang JH, Jiang W, Pan CS, Qi YF, Wu QZ,
Pang YZ and Tang CS: Effects of adrenomedullin on cell
proliferation in rat adventitia induced by lysophosphatidic acid.
Regul Pept. 121:49–56. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Wagner AE, Wolffram
S and Rimbach G: Effect of quercetin on inflammatory gene
expression in mice liver in vivo - role of redox factor 1,
miRNA-122 and miRNA-125b. Pharmacol Res. 65:523–530. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ishimoto T, Sugihara H, Watanabe M,
Sawayama H, Iwatsuki M, Baba Y, Okabe H, Hidaka K, Yokoyama N,
Miyake K, et al: Macrophage-derived reactive oxygen species
suppress miR-328 targeting CD44 in cancer cells and promote redox
adaptation. Carcinogenesis. 35:1003–1011. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Marin T, Gongol B, Chen Z, Woo B,
Subramaniam S, Chien S and Shyy JY: Mechanosensitive microRNAs-role
in endothelial responses to shear stress and redox state. Free
Radic Biol Med. 64:61–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|