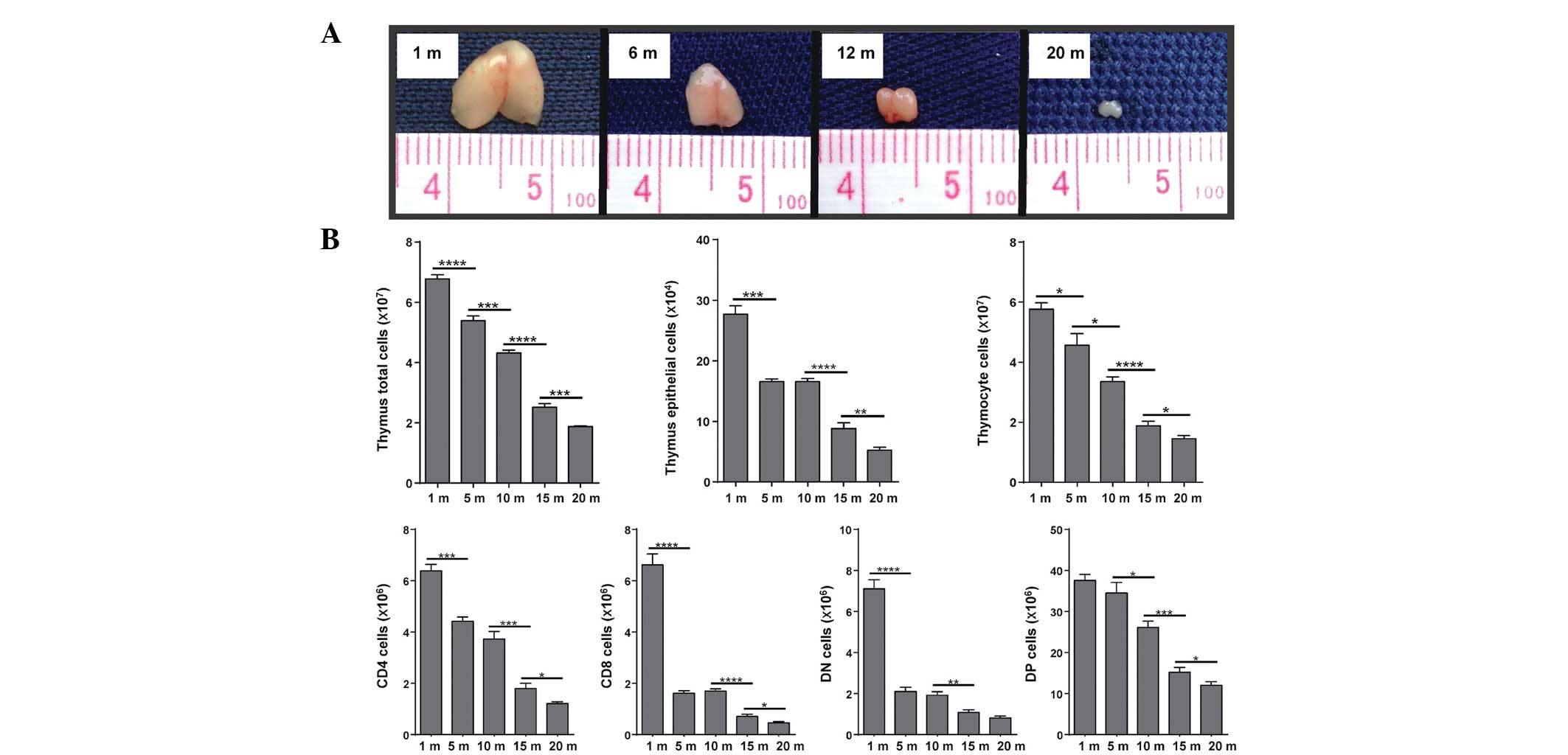
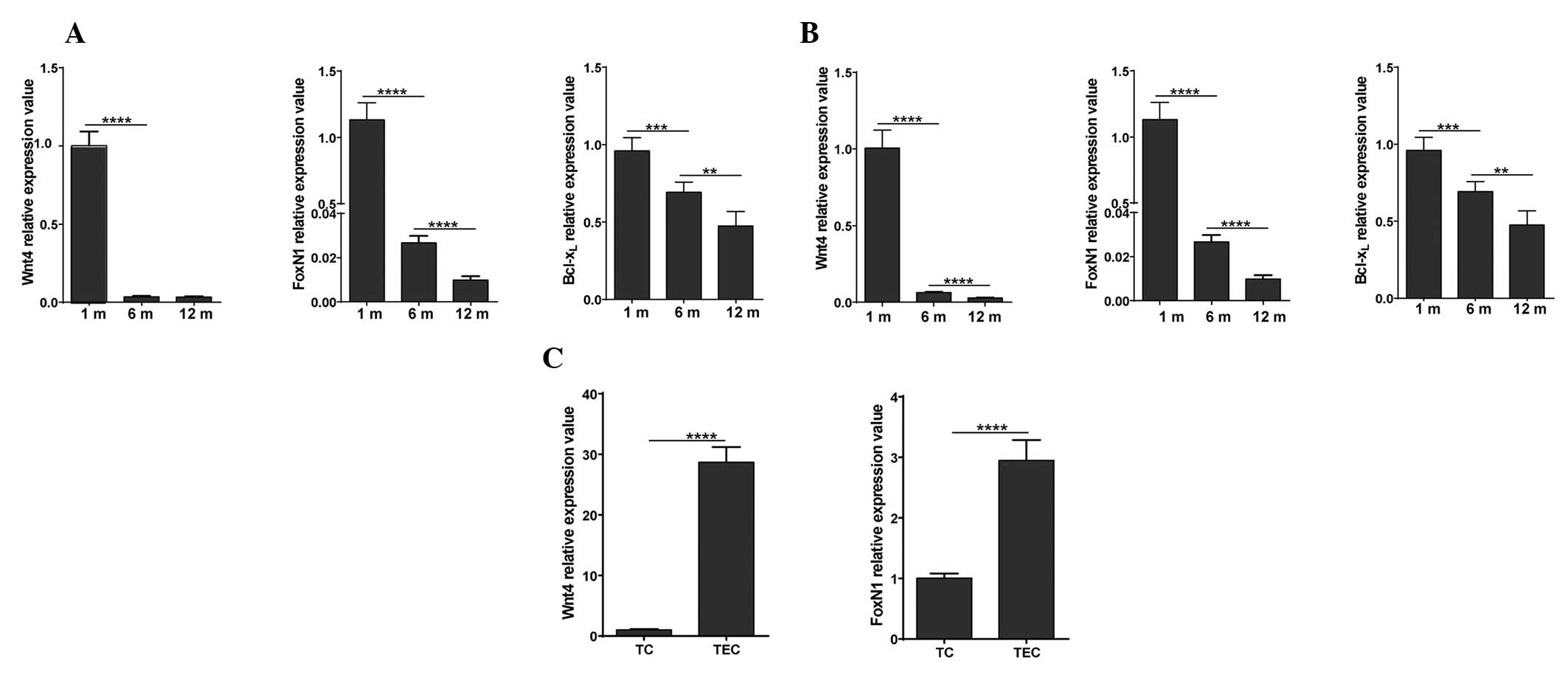
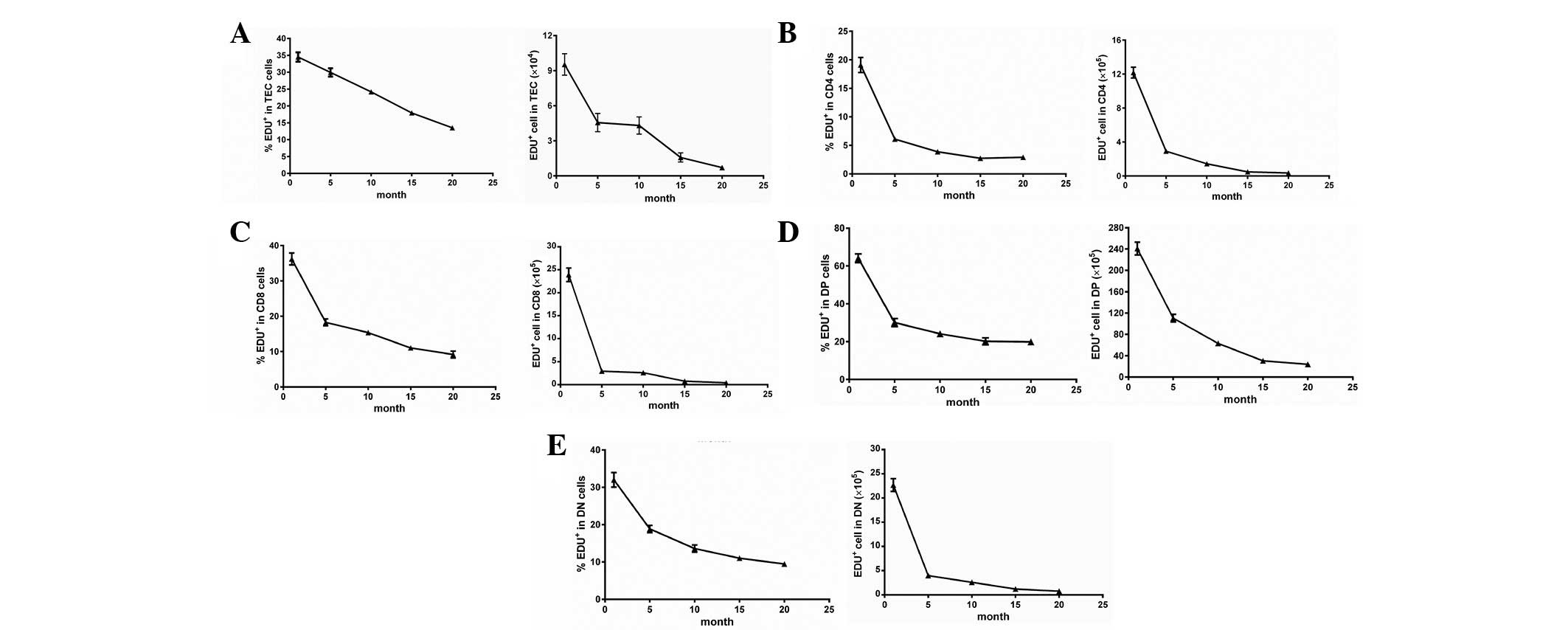
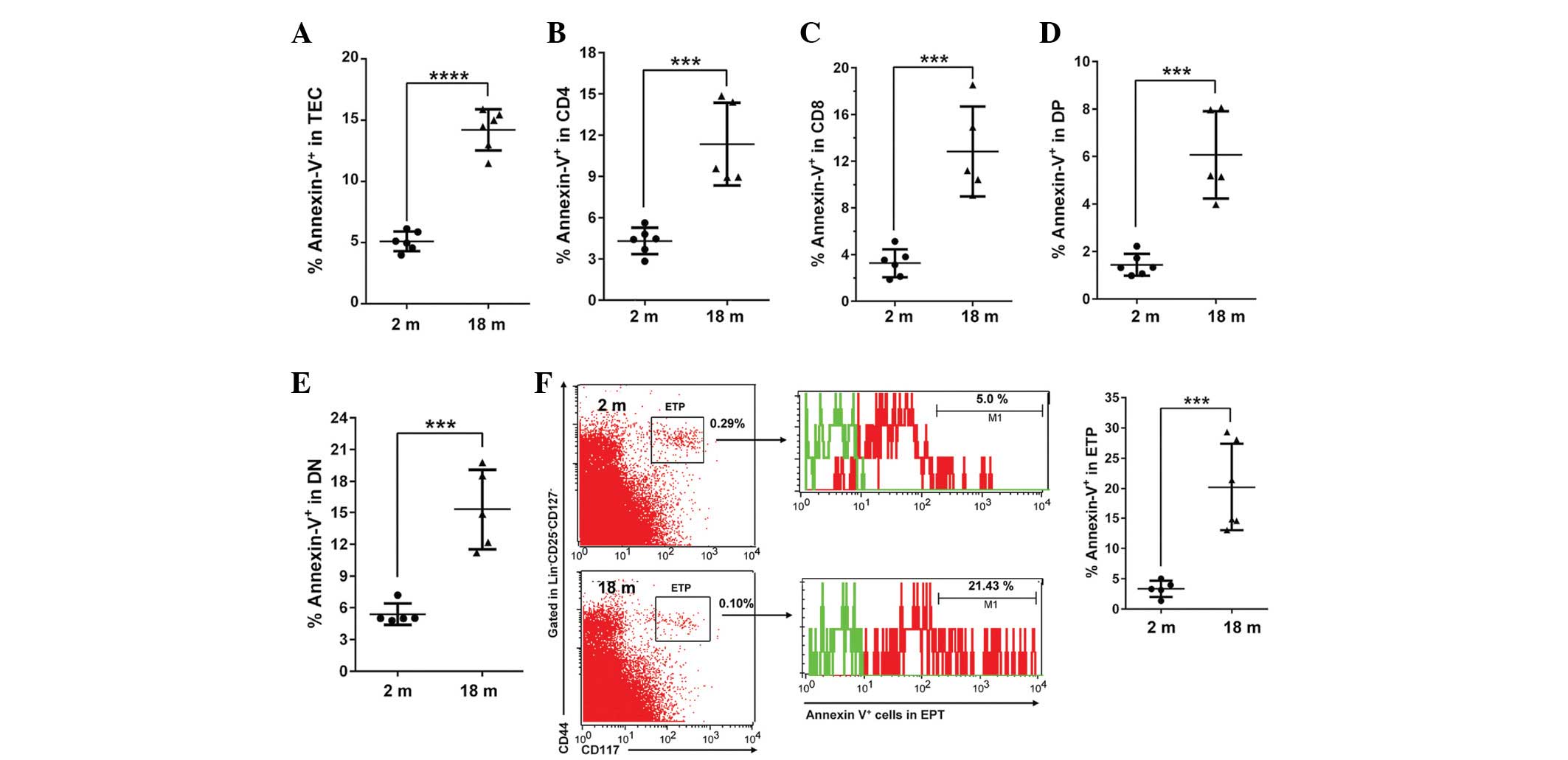
|
1
|
Petrie HT and Zúñiga-Pflücker JC: Zoned
out: Functional mapping of stromal signaling microenvironments in
the thymus. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:649–679. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Savage PA and Davis MM: A kinetic window
constricts the T cell receptor repertoire in the thymus. Immunity.
14:243–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Osada M, Jardine L, Misir R, Andl T,
Millar SE and Pezzano M: DKK1 mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling
in postnatal mice leads to loss of TEC progenitors and thymic
degeneration. PLoS One. 5:e90622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dixit VD: Adipose-immune interactions
during obesity and caloric restriction: Reciprocal mechanisms
regulating immunity and health span. J Leukoc Biol. 84:882–892.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McElhaney JE and Effros RB:
Immunosenescence: what does it mean to health outcomes in older
adults? Curr Opin Immunol. 21:418–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lynch HE, Goldberg GL, Chidgey A, Van den
Brink MR, Boyd R and Sempowski GD: Thymic involution and immune
reconstitution. Trends Immunol. 30:366–373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Holland AM and van den Brink MR:
Rejuvenation of the aging T cell compartment. Curr Opin Immunol.
21:454–459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Min H, Montecino-Rodriguez E and Dorshkind
K: Reduction in the developmental potential of intrathymic T cell
progenitors with age. J Immunol. 173:245–250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zediak VP, Maillard I and Bhandoola A:
Multiple prethymic defects underlie age-related loss of T
progenitor competence. Blood. 110:1161–1167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gray DH, Seach N, Ueno T, Milton MK,
Liston A, Lew AM, Goodnow CC and Boyd RL: Developmental kinetics,
turnover, and stimulatory capacity of thymic epithelial cells.
Blood. 108:3777–3785. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Xiao S and Manley NR: Foxn1 is
required to maintain the postnatal thymic microenvironment in a
dosage-sensitive manner. Blood. 113:567–574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Nobori S, Shimizu A, Okumi M,
Samelson-Jones E, Griesemer A, Hirakata A, Sachs DH and Yamada K:
Thymic rejuvenation and the induction of tolerance by adult thymic
grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:19081–19086. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gui J, Zhu X, Dohkan J, Cheng L, Barnes PF
and Su DM: The aged thymus shows normal recruitment of
lymphohemato-poietic progenitors but has defects in thymic
epithelial cells. Int Immunol. 19:1201–1211. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu X, Gui J, Dohkan J, Cheng L, Barnes PF
and Su DM: Lymphohematopoietic progenitors do not have a
synchronized defect with age-related thymic involution. Aging Cell.
6:663–672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flores KG, Li J, Sempowski GD, Haynes BF
and Hale LP: Analysis of the human thymic perivascular space during
aging. J Clin Invest. 104:1031–1039. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang H, Youm YH, Sun Y, Rim JS, Galbán CJ,
Vandanmagsar B and Dixit VD: Axin expression in thymic stromal
cells contributes to age-related increase in thymic adiposity and
associated with reduced thymopoiesis independently of ghrelin
signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 85:928–938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van Ewijk W, Holländer G, Terhorst C and
Wang B: Stepwise development of thymic microenvironments in vivo is
regulated by thymocyte subsets. Development. 127:1583–1591.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van Ewijk W, Wang B, Hollander G, Kawamoto
H, Spanopoulou E, Itoi M, Amagai T, Jiang YF, Germeraad WT, Chen WF
and Katsura Y: Thymic microenvironments, 3-D versus 2-D? Semin
Immunol. 11:57–64. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bleul C and Boehm T: BMP signaling is
required for normal thymus development. J Immunol. 175:5213–5221.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anderson G, Pongracz J, Parnell S and
Jenkinson EJ: Notch ligand-bearing thymic epithelial cells initiate
and sustain Notch signaling in thymocytes independently of T cell
receptor signaling. Eur J Immunol. 31:3349–3354. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Osada M, Ito E, Fermin HA, Vasquez-Cintron
E, Venkatesh T, Friedel RH and Pezzano M: The Wnt signaling
antagonist Kremen1 is required for development of thymic
architecture. Clin Dev Immunol. 13:299–319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luis TC, Weerkamp F, Naber BA, Baert MR,
de Haas EF, Nikolic T, Heuvelmans S, De Krjiger RR, van Dongen JJ
and Staal FJ: Wnt3a deficiency irreversibly impairs hematopoietic
stem cell self-renewal and leads to defects in progenitor cell
differentiation. Blood. 113:546–554. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Manolagas SC and Almeida M: Gone with the
Wnts: Beta-catenin, T-cell factor, forkhead box O, and oxidative
stress in age-dependent diseases of bone, lipid, and glucose
metabolism. Mol Endocrinol. 21:2605–2614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kléber M and Sommer L: Wnt signaling and
the regulation of stem cell function. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:681–687. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Balciunaite G, Keller MP, Balciunaite E,
Piali L, Zuklys S, Mathieu YD, Gill J, Boyd R, Sussman DJ and
Holländer GA: Wnt glycoproteins regulate the expression of FoxN1,
the gene defective in nude mice. Nat Immunol. 3:1102–1108. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pongracz J, Hare K, Harman B, Anderson G
and Jenkinson EJ: Thymic epithelial cells provide WNT signals to
developing thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 33:1949–1956. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weerkamp F, Baert MR, Naber BA, Koster EE,
de Haas EF, Atkuri KR, van Dongen JJ, Herzenberg LA and Staal FJ:
Wnt signaling in the thymus is regulated by differential expression
of intracellular signaling molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:3322–3326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cadigan KM and Liu YI: Wnt signaling:
Complexity at the surface. J Cell Sci. 119:395–402. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miller JR: The Wnts. Genome Biol.
3:REVIEWS30012002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kvell K, Varecza Z, Bartis D, Hesse S,
Parnell S, Anderson G, Jenkinson EJ and Pongracz JE: Wnt4 and
LAP2alpha as pacemakers of thymic epithelial senescence. PLoS One.
5:e107012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirokawa K, Utsuyama M, Kasai M, Kurashima
C, Ishijima S and Zeng YX: Understanding the mechanism of the
age-change of thymic function to promote T cell differentiation.
Immunol Lett. 40:269–277. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ioannidis V, Beermann F, Clevers H and
Held W: The beta-catenin - TCF-1 pathway ensures CD4(+)CD8(+)
thymocyte survival. Nat Immunol. 2:691–697. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Youm YH, Yang H, Sun Y, Smith RG, Manley
NR, Vandanmagsar B and Dixit VD: Deficient ghrelin
receptor-mediated signaling compromises thymic stromal cell
microenvironment by accelerating thymic adiposity. J Biol Chem.
284:7068–7077. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Beardsley TR, Pierschbacher M, Wetzel GD
and Hays EF: Induction of T-cell maturation by a cloned line of
thymic epithelium (TEPI). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:6005–6009.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. 8th edition. National Academies Press; Washington, DC:
2011
|
|
37
|
Talaber G, Kvell K, Varecza Z, Boldizsar
F, Parnell SM, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G, Berki T and Pongracz JE:
Wnt-4 protects thymic epithelial cells against
dexamethasone-induced senescence. Rejuvenation Res. 14:241–248.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prockop SE and Petrie HT: Regulation of
thymus size by competition for stromal niches among early T cell
progenitors. J Immunol. 173:1604–1611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jenkinson WE, Bacon A, White AJ, Anderson
G and Jenkinson EJ: An epithelial progenitor pool regulates thymus
growth. J Immunol. 181:6101–6108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dixit VD: Thymic fatness and approaches to
enhance thymopoietic fitness in aging. Curr Opin Immunol.
22:521–528. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hocevar BA, Mou F, Rennolds JL, Morris SM,
Cooper JA and Howe PH: Regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway by
disabled-2 (Dab2). EMBO J. 22:3084–3094. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heinonen KM, Vanegas JR, Brochu S, Shan J,
Vainio SJ and Perrault C: Wnt4 regulates thymic cellularity through
the expansion of thymic epithelial cells and early thymic
progenitors. Blood. 118:5163–5173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xie H, Huang Z, Sadim MS and Sun Z:
Stabilized beta-catenin extends thymocyte survival by up-regulating
Bcl-xL. J Immunol. 175:7981–7988. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|