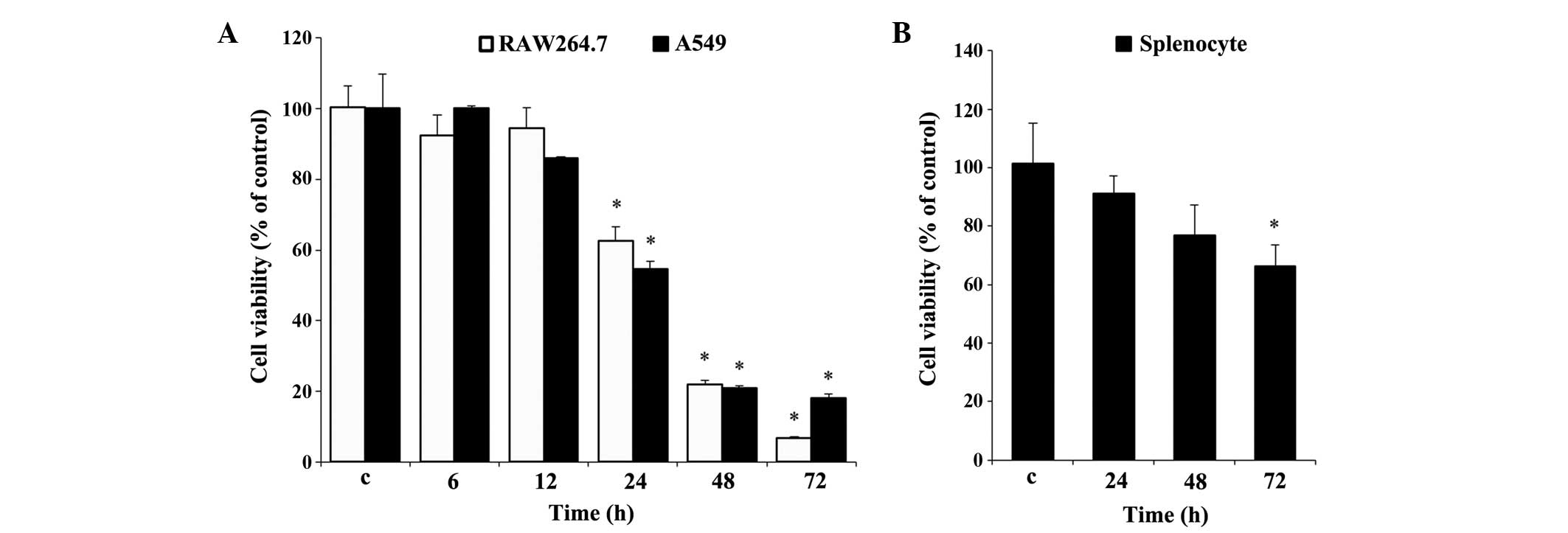
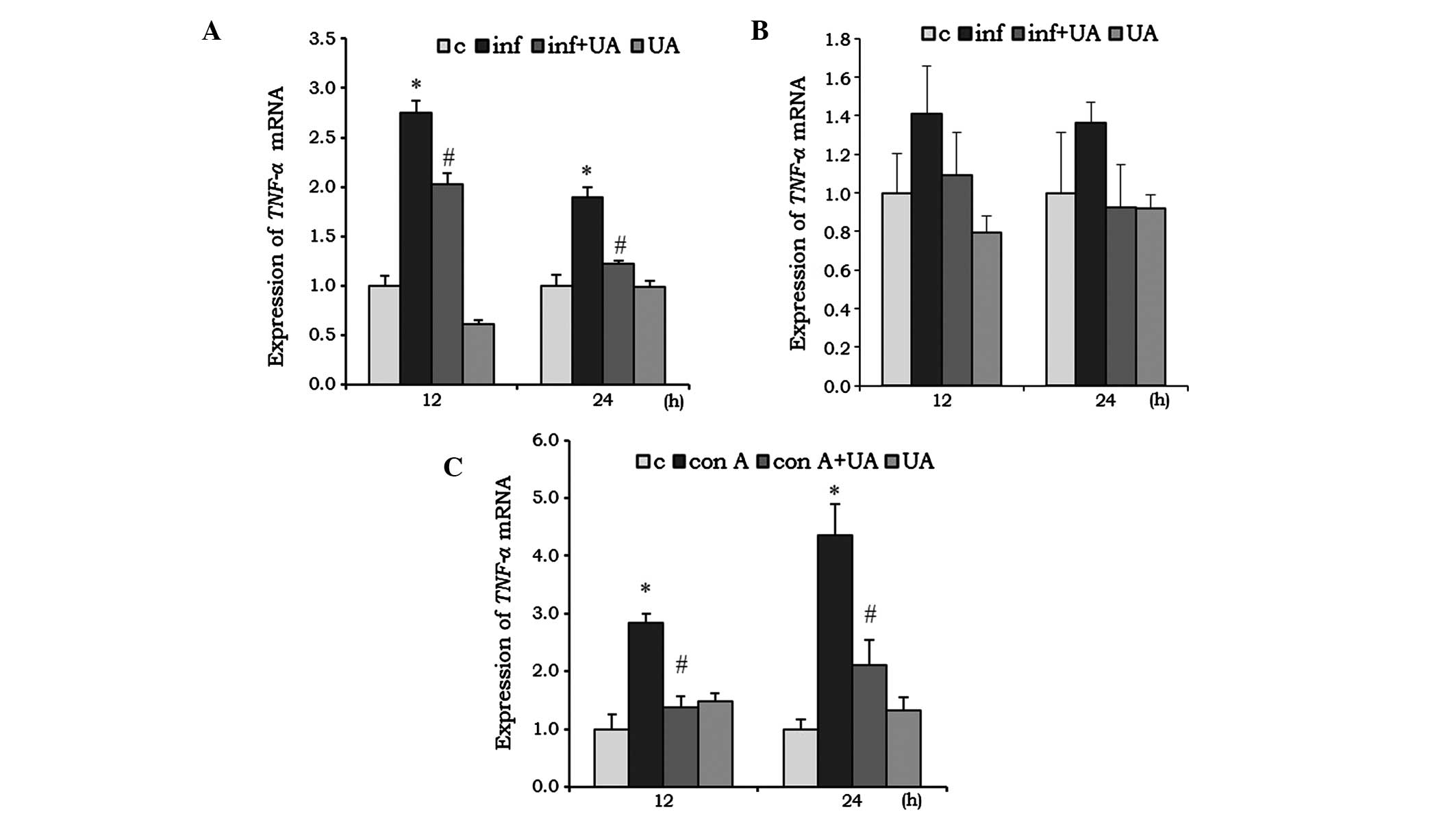
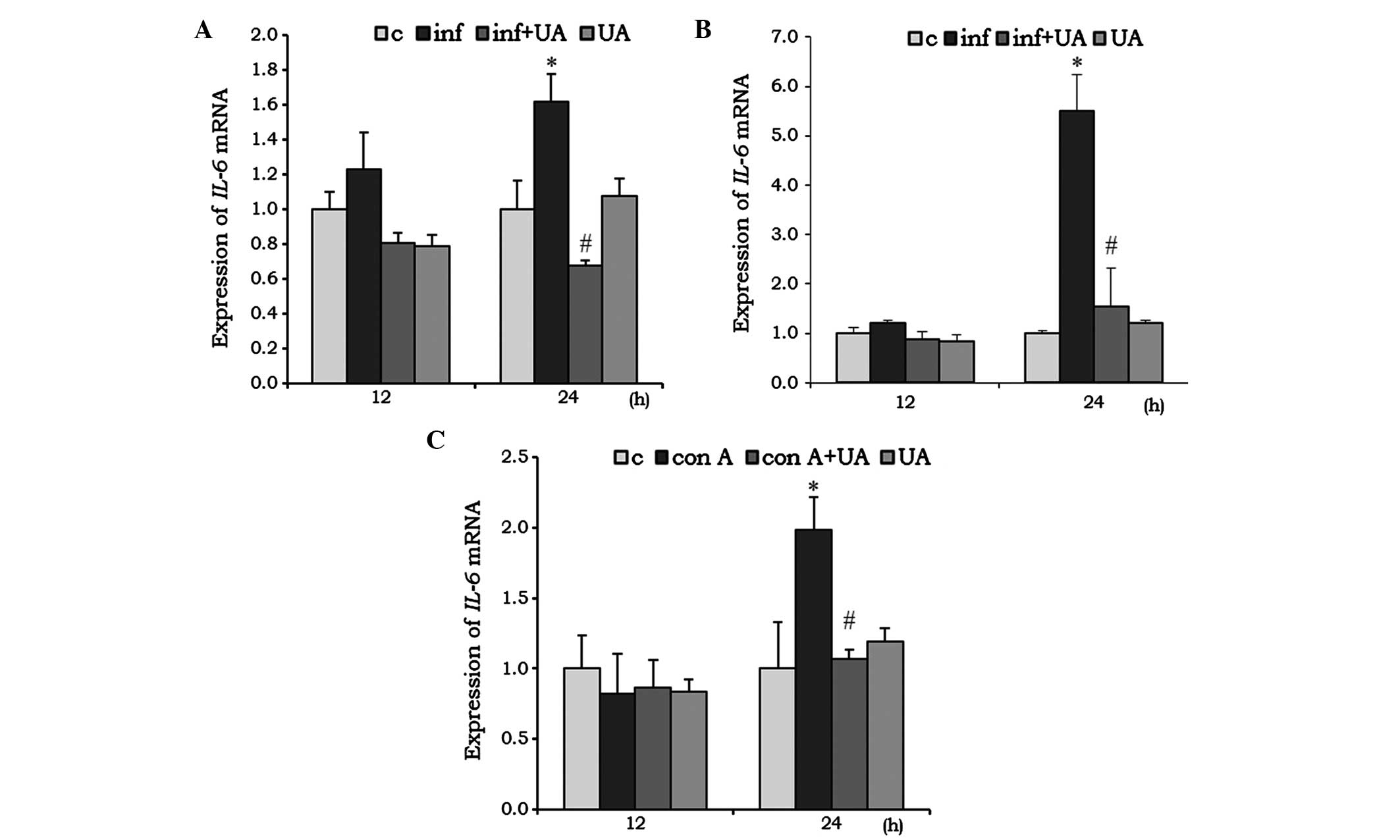
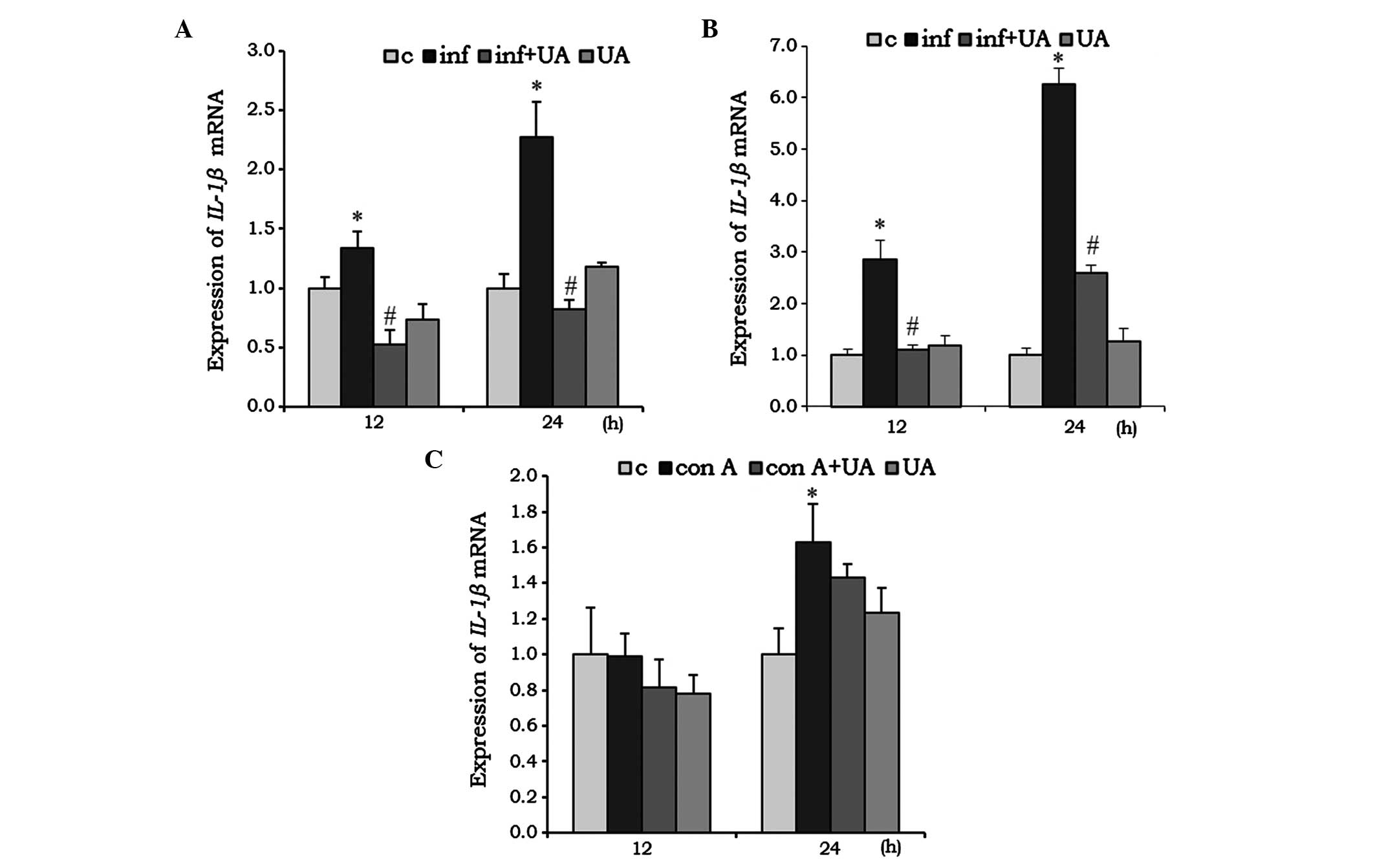
|
1
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Checker R, Sandur SK, Sharma D, Patwardhan
RS, Jayakumar S, Kohli V, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB and Sainis KB:
Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid
antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-kB, AP-1 and
NF-AT. PLoS One. 7:e313182012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dalgleish AG and O'Byrne KJ: Chronic
immune activation and inflammation in the pathogenesis of AIDS and
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 84:231–276. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kaser A, Zeissig S and Blumberg RS:
Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 28:573–621. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ishiguro Y: Mucosal proinflammatory
cytokine production correlates with endoscopic activity of
ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol. 34:66–74. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scott DL, Wolfe F and Huizinga TW:
Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 376:1094–1108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YJ, Han SB, Nam SY, Oh KW and Hong JT:
Inflammation and alzheimer's disease. Arch Pharm Res. 33:1539–1556.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Achoui M, Appleton D, Abdulla MA, Awang K,
Mohd MA and Mustafa MR: In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory
activity of 17-O acetylacuminolide through the inhibition of
cytokines, NF-kB translocation and IKKβ activity. PLoS One.
5:e151052010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zumla A, Rao M, Parida SK, Keshavjee S,
Cassell G, Wallis R, Axelsson-Robertsson R, Doherty M, ersson J and
Maeurer M: Inflammation and tuberculosis: Host-directed therapies.
J Intern Med. 277:373–387. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ellner JJ: Review: The immune response in
tuberculosis implication for tuberculosis control. J Infect Dis.
176:1351–1359. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fenton MJ and Vermeulen MW:
Immunopathology of tuberculosis: Roles of macrophages and
monocytes. Infect Immun. 64:683–690. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rich EA, Torres M, Sada E, Finegan CK,
Hamilton BD and Toossi Z: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
(MTB)-stimulated production of nitric oxide by human alveolar
macrophages and relationship of nitric oxide production to growth
inhibition of MTB. Tubercle Lung Dis. 78:247–255. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Roy S, Sharma S, Sharma M, Aggarwal R and
Bose M: Induction of nitric oxide release from the human alveolar
epithelial cell line A549: An in vitro correlate of innate immune
response to mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunology. 112:471–480.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Celada A and Nathan C: Macrophage
activation revisited. Immunol Today. 15:100–102. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nathan CF and Hibbs JB Jr: Role of nitric
oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin
Immunol. 3:65–70. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu J: Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and
ursolic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 49:57–68. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ikeda Y, Murakami A and Ohigashi H:
Ursolic acid: An anti- and proinflammatory triterpenoid. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 52:26–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsai SJ and Yin MC: Antioxidative and
anti-inflammatory protection of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in
PC12 cells. J Food Sci. 73:H174–H178. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shishodia S, Majumdar S, Banerjee S and
Aggarwal BB: Ursolic acid inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation
induced by carcinogenic agents through suppression of IkappaBalpha
kinase and p65 phosphorylation: Correlation with down-regulation of
cyclooxygenase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 9 and cyclin D1. Cancer
Res. 63:4375–4383. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Martin A, Camacho M, Portaels F and
Palomino JC: Resazurin microtiter assay plate testing of
mycobacterium tuberculosis susceptibilities to second-line drugs:
Rapid, simple and inexpensive method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
47:3616–3619. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Diacon AH, Maritz JS, Venter A, van Helden
PD, Andries K, McNeeley DF and Donald PR: Time to detection of the
growth of mycobacterium tuberculosis in MGIT 960 for determining
the early bactericidal activity of antituberculosis agents. Eur J
Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 29:1561–1565. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zerin T, Lee M, Jang WS, Nam KW and Song
HY: Ursolic acid reduces Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced nitric
oxide release in human alveolar A549 cells. Mol Cells. 38:610–615.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zerin T, Kim YS, Hong SY and Song HY:
Protective effect of methylprednisolone on paraquat-induced A549
cell cytotoxicity via induction of efflux transporter,
P-glycoprotein expression. Toxicol Lett. 208:101–107. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee HJ, Zerin T, Kim YH, Lee BE and Song
HY: Immunomodulation potential of Artemisia capillaris extract in
rat splenocytes. Intern J Phytomed. 5:356–361. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Wallace JL: Nitric oxide as a regulator of
inflammatory processes. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 100(Suppl 1): S5–S9.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Medzhitov R: Origin and physiological
roles of inflammation. Nature. 454:428–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Subbian S, Tsenova L, O'Brien P, Yang G,
Koo MS, Peixoto B, Fallows D, Dartois V, Muller G and Kaplan G:
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition alters gene expression and improves
isoniazid-mediated clearance of mycobacterium tuberculosis in
rabbit lungs. PLoS Pathog. 7:e10022622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tobin DM, Roca FJ, Oh SF, McFarland R,
Vickery TW, Ray JP, Ko DC, Zou Y, Bang ND, Chau TT, et al: Host
genotype-specific therapies can optimize the inflammatory response
to mycobacterial infections. Cell. 148:434–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Skerry C, Harper J, Klunk M, Bishai WR and
Jain SK: Adjunctive TNF inhibition with standard treatment enhances
bacterial clearance in a murine model of necrotic TB granulomas.
PLoS One. 7:e396802012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bermudez LE and Goodman J: Mycobacterium
tuberculosis invades and replicates within type II alveolar cells.
Infect Immun. 64:1400–1406. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garcia-Perez BE, Mondragon-Flores R and
Luna-Herrera J: Internalization of mycobacterium tuberculosis by
macropinocytosis in non-phagocytic cells. Microb Pathog. 35:49–55.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suh N, Honda T, Finlay HJ, Barchowsky A,
Williams C, Benoit NE, Xie QW, Nathan C, Gribble GW and Sporn MB:
Novel triterpenoids suppress inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)
and inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2) in mouse macrophages. Cancer
Res. 58:717–723. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ryu SY, Oak MH, Yoon SK, Cho DI, Yoo GS,
Kim TS and Kim KM: Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory triterpenes
from the herb of Prunella vulgaris. Planta Med. 66:358–360. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Checker R, Sandur SK, Sharma D, Patwardhan
RS, Jayakumar S, Kohli V, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB and Sainis KB:
Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid
antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-κB, AP-1 and
NF-AT. PLoS One. 7:e313182012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Moita E, Gil-Izquierdo A, Sousa C,
Ferreres F, Silva LR, Valentão P, Domínguez-Perles R, Baenas N and
Andrade PB: Integrated analysis of COX-2 and iNOS derived
inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW macrophages
pre-exposed to Echium plantagineum L. bee pollen extract. PLoS One.
8:e591312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim JB, Han AR, Park EY, Kim JY, Cho W,
Lee J, Seo EK and Lee KT: Inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2 and
cytokines expression by poncirin through the NF-kappaB inactivation
in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:2345–2351. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weinberg JB: Nitric oxide synthase 2 and
cyclooxygenase 2 interactions in inflammation. Immunol Res.
22:319–341. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Camuesco D, Comalada M, Rodríguez-Cabezas
ME, Nieto A, Lorente MD, Concha A, Zarzuelo A and Gálvez J: The
intestinal anti-inflammatory effect of quercitrin is associated
with an inhibition in iNOS expression. Br J Pharmacol. 143:908–918.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Roy S, Sharma S, Sharma M, Aggarwal R and
Bose M: Induction of nitric oxide release from the human alveolar
epithelial cell line A549: An in vitro correlate of innate immune
response to mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunology. 112:471–480.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|