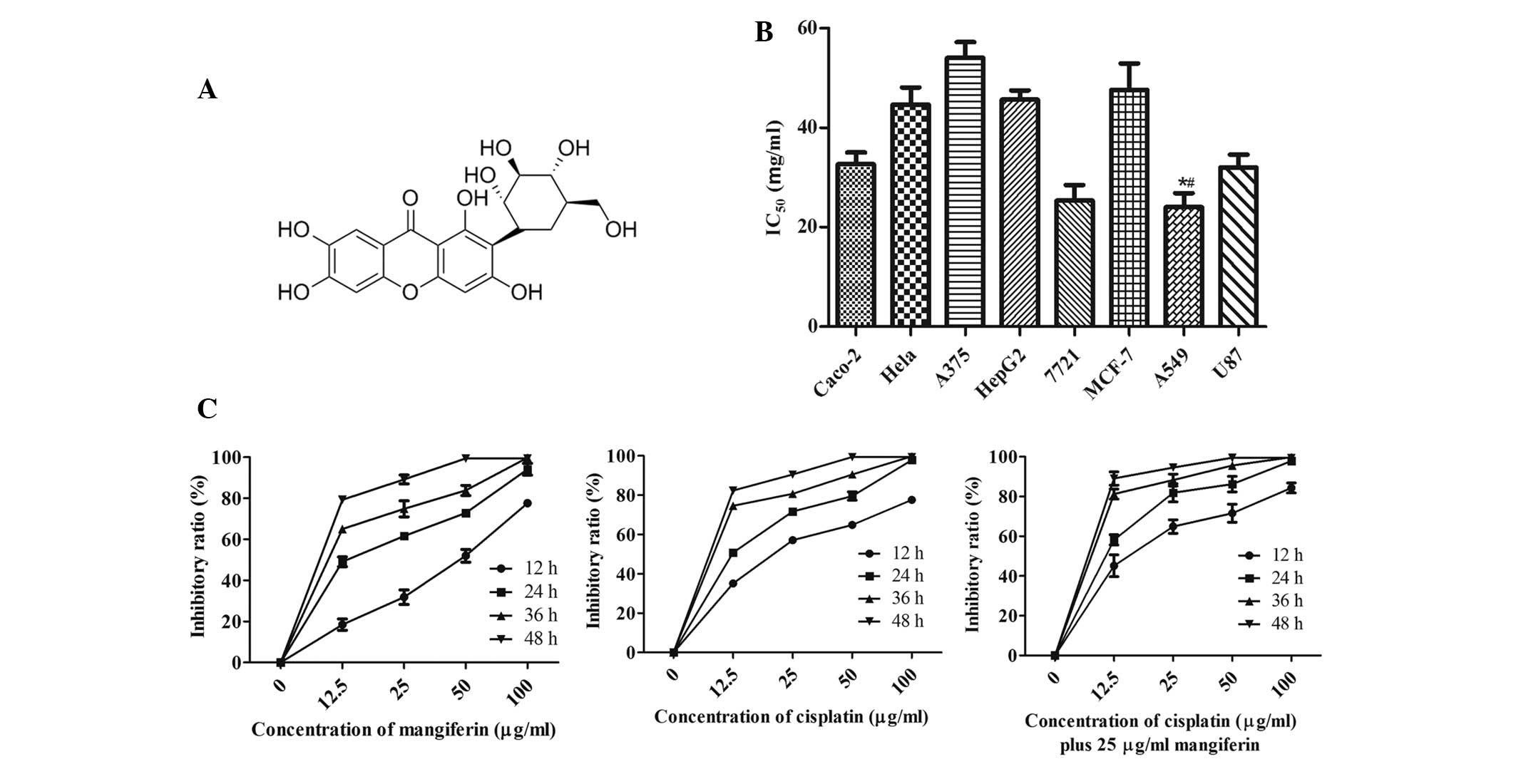
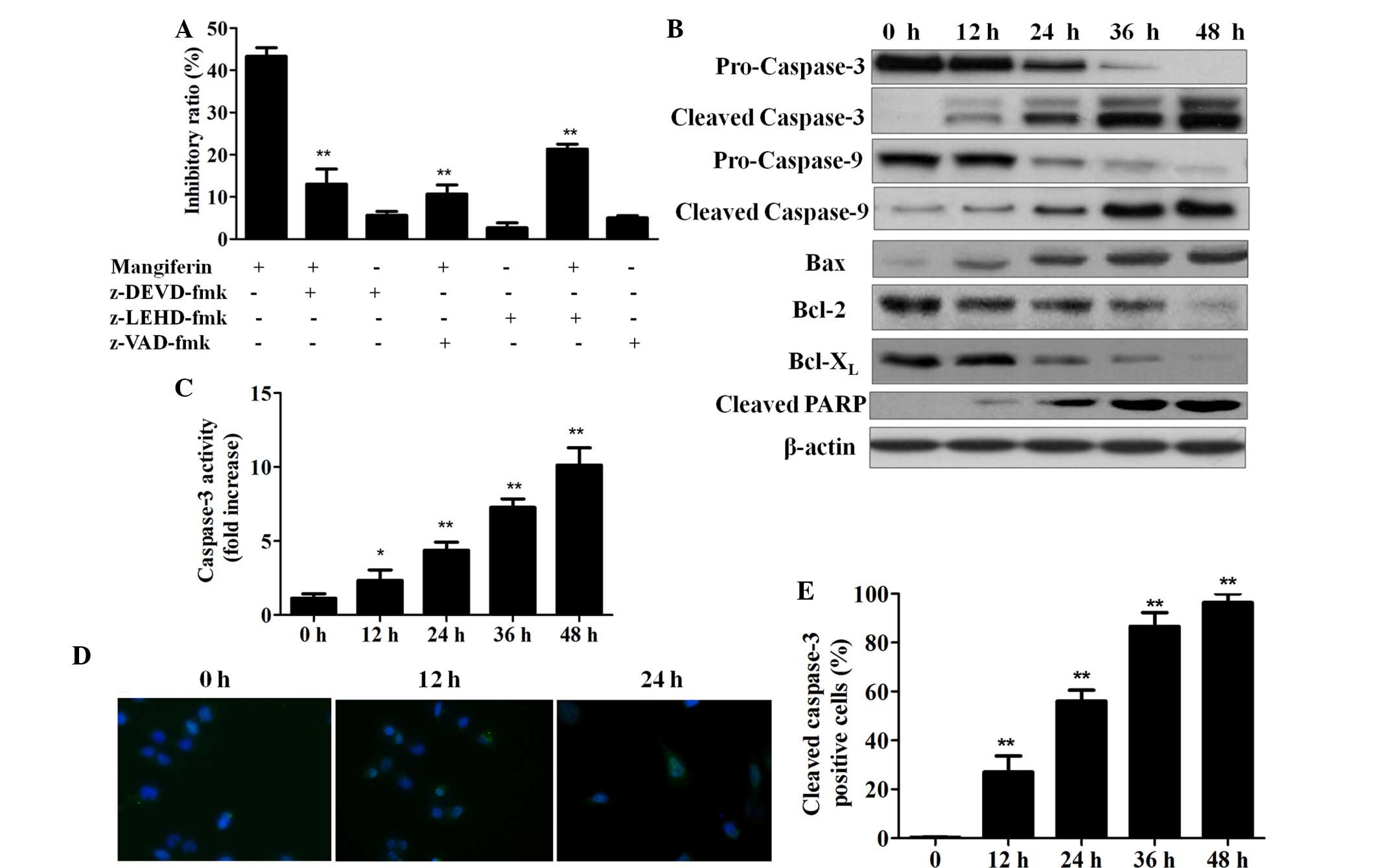
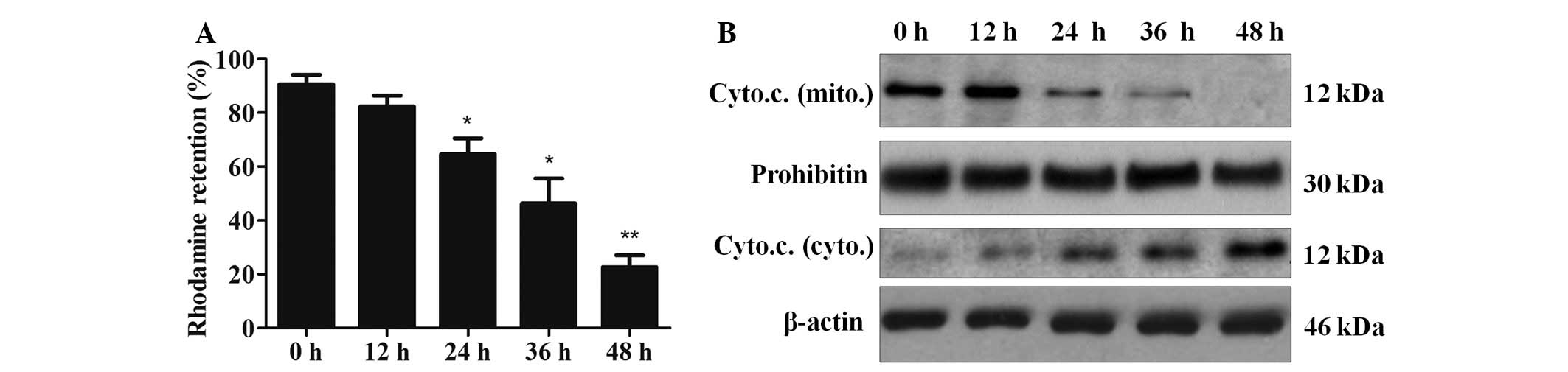
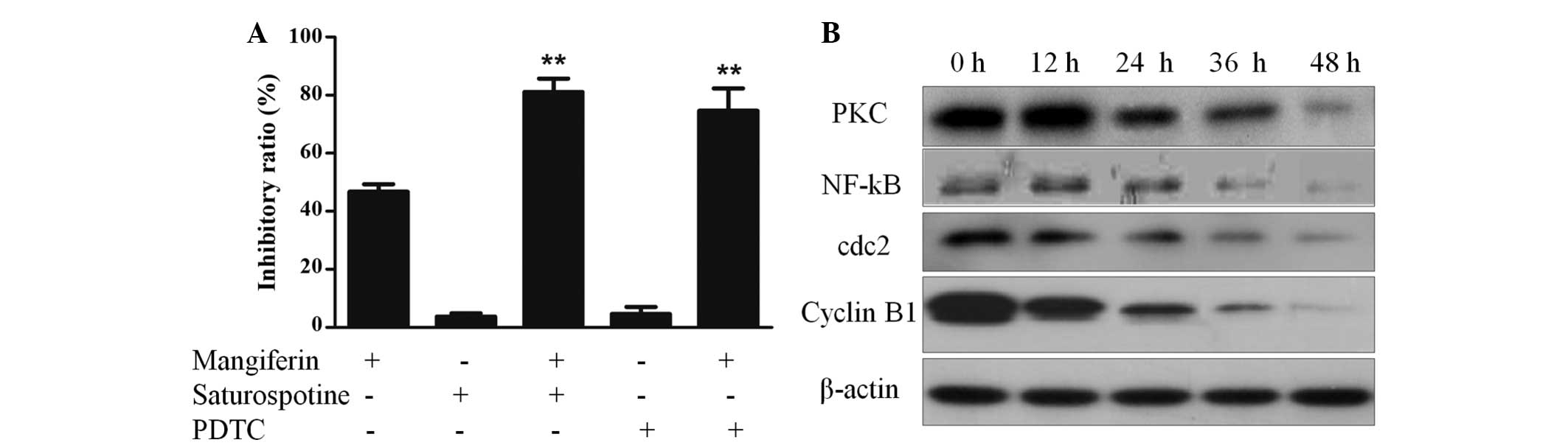
|
1
|
Sánchez GM, Re L, Giuliani A, Núñez-Sellés
AJ, Davison GP and León-Fernández OS: Protective effects of
Mangifera indica L. extract, mangiferin and selected antioxidants
against TPA-induced biomolecules oxidation and peritoneal
macrophage activation in mice. Pharmacol Res. 42:565–573. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dar A, Faizi S, Naqvi S, Roome T,
Zikr-ur-Rehman S, Ali M, Firdous S and Moin ST: Analgesic and
antioxidant activity of mangiferin and its derivatives: The
structure activity relationship. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:596–600. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guha S, Ghosal S and Chattopadhyay U:
Antitumor, immunomodulatory and anti-HIV effect of mangiferin, a
naturally occurring glucosylxanthone. Chemotherapy. 42:443–451.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Duang XY, Wang Q, Zhou XD and Huang DM:
Mangiferin: A possible strategy for periodontal disease to therapy.
Med Hypotheses. 76:486–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
García-Rivera D, Delgado R, Bougarne N,
Haegeman G and Berghe WV: Gallic acid indanone and mangiferin
xanthone are strong determinants of immunosuppressive anti-tumour
effects of Mangifera indica L. bark in MDA-MB231 breast cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 305:21–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Noratto GD, Bertoldi MC, Krenek K, Talcott
ST, Stringheta PC and Mertens-Talcott SU: Anticarcinogenic effects
of polyphenolics from mango (Mangifera indica) varieties. J Agric
Food Chem. 58:4104–4112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chieli E, Romiti N, Rodeiro I and Garrido
G: In vitro effects of Mangifera indica and polyphenols derived on
ABCB1/P-glycoprotein activity. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2703–2710.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng P, Peng ZG, Yang J and Song SJ: The
effect of mangiferin on telomerase activity and apoptosis in
leukemic K562 cells. Zhong Yao Cai. 30:306–309. 2007.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peng ZG, Luo J, Xia LH, Chen Y and Song
SJ: CML cell line K562 cell apoptosis induced by mangiferin.
Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 12:590–594. 2004.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Percival SS, Talcott ST, Chin ST, Mallak
AC, Lounds-Singleton A and Pettit-Moore J: Neoplastic
transformation of BALB/3T3 cells and cell cycle of HL-60 cells are
inhibited by mango (Mangifera indica L.) juice and mango juice
extracts. J Nutr. 136:1300–1304. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chari NS, Pinaire NL, Thorpe L, Medeiros
LJ, Routbort MJ and McDonnell TJ: The p53 tumor suppressor network
in cancer and the therapeutic modulation of cell death. Apoptosis.
14:336–347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hartwell LH and Kastan MB: Cell cycle
control and cancer. Science. 266:1821–1828. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan
GI and Green DR: The coordinate release of cytochrome c during
apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat Cell
Biol. 2:156–162. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li CY, Wang Y, Wang HL, Shi Z, An N, Liu
YX, Liu Y, Zhang J, Bao JK and Deng SP: Molecular mechanisms of
Lycoris aurea agglutinin-induced apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle
arrest in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells, both in vitro and
in vivo. Cell Prolif. 46:272–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sarkar A, Sreenivasan Y, Ramesh GT and
Manna SK: beta-D-Glucoside suppresses tumor necrosis factor-induced
activation of nuclear transcription factor kappaB but potentiates
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:33768–33781. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rajendran P, Ekambaram G and Sakthisekaran
D: Protective role of mangiferin against Benzo(a)pyrene induced
lung carcinogenesis in experimental animals. Biol Pharm Bull.
31:1053–1058. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Touny LH and Banerjee PP: Identification
of both Myt-1 and Wee-1 as necessary mediators of the
p21-independent inactivation of the cdc-2/cyclin B1 complex and
growth inhibition of TRAMP cancer cells by genistein. Prostate.
66:1542–1555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hoffmann TK, Trellakis S, Okulicz K,
Schuler P, Greve J, Arnolds J, Bergmann C, Bas M, Lang S, Lehnerdt
G, et al: Cyclin B1 expression and p53 status in squamous cell
carcinomas of the head and neck. Anticancer Res. 31:3151–3157.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen H, Huang Q, Dong J, Zhai DZ, Wang AD
and Lan Q: Overexpression of CDC2/CyclinB1 in gliomas, and CDC2
depletion inhibits proliferation of human glioma cells in vitro and
in vivo. BMC Cancer. 8:292008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vairapandi M, Balliet AG, Hoffman B and
Liebermann DA: GADD45b and GADD45g are cdc2/cyclinB1 kinase
inhibitors with a role in S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoints induced
by genotoxic stress. J Cell Physiol. 192:327–338. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen H, Huang Q, Dong J, Zhai DZ, Wang AD
and Lan Q: Overexpression of CDC2/CyclinB1 in gliomas, and CDC2
depletion inhibits proliferation of human glioma cells in vitro and
in vivo. BMC Cancer. 8:292008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reyland ME: Protein kinase Cdelta and
apoptosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 35:1001–1004. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mezzano S, Aros C, Droguett A, Burgos ME,
Ardiles L, Flores C, Schneider H, Ruiz-Ortega M and Egido J:
NF-kappaB activation and overexpression of regulated genes in human
diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 19:2505–2512. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|