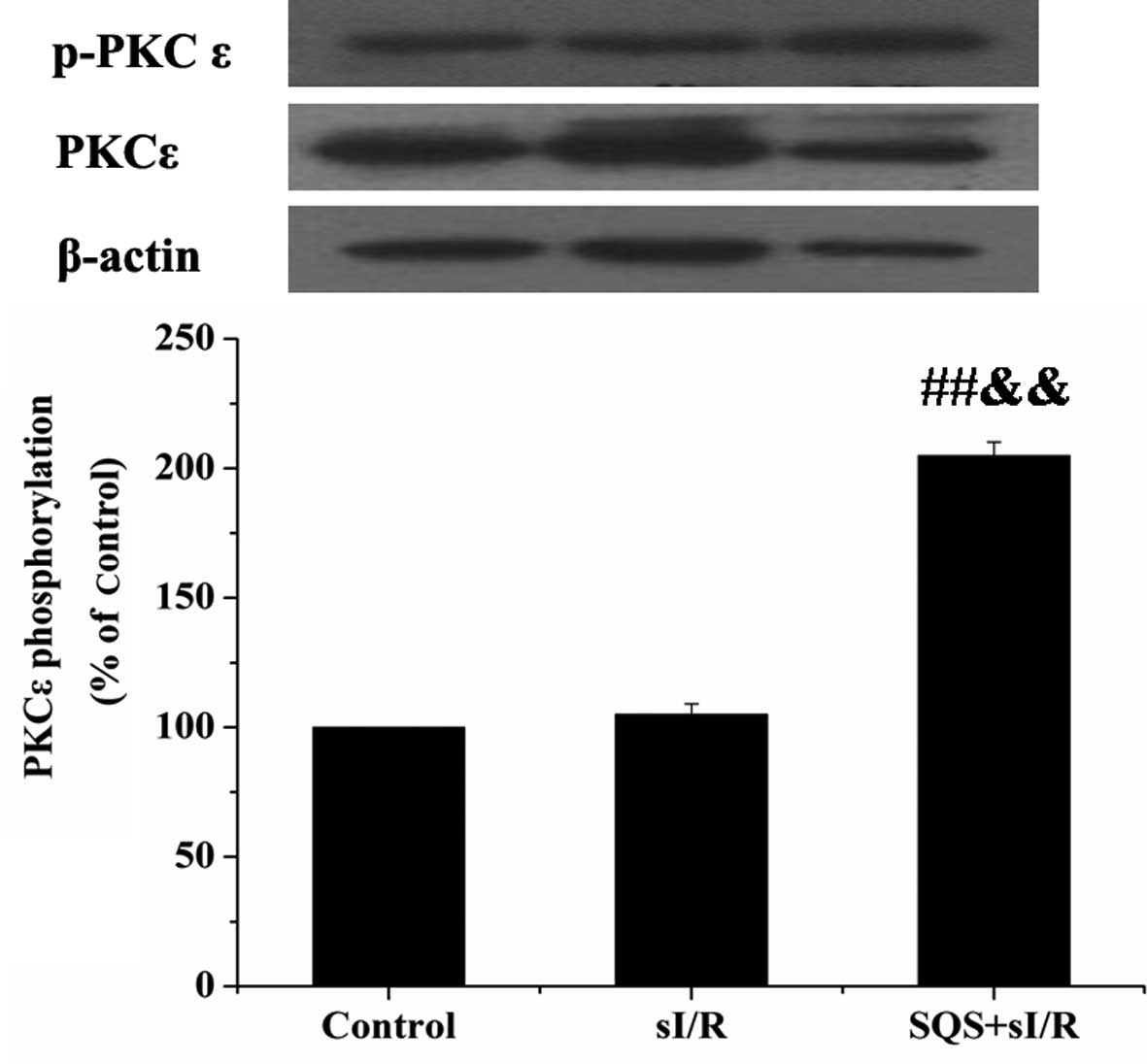
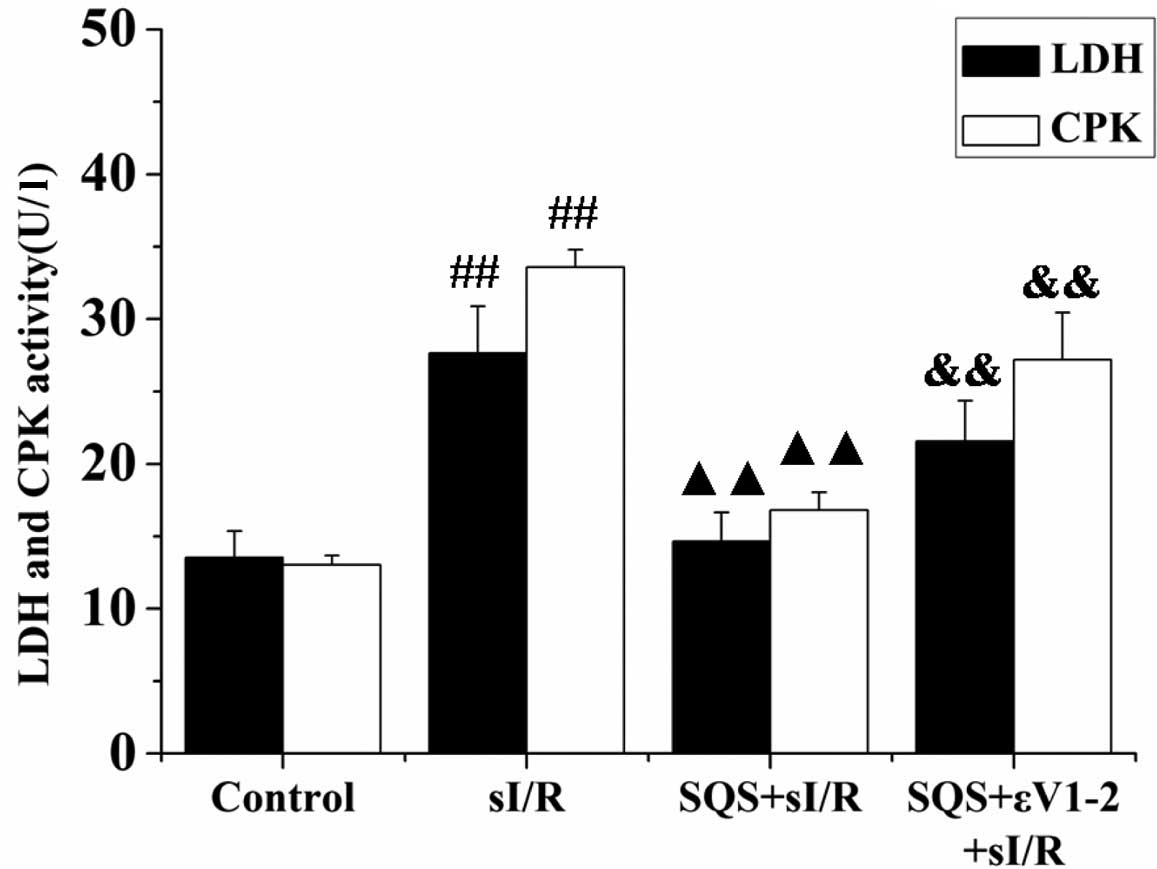
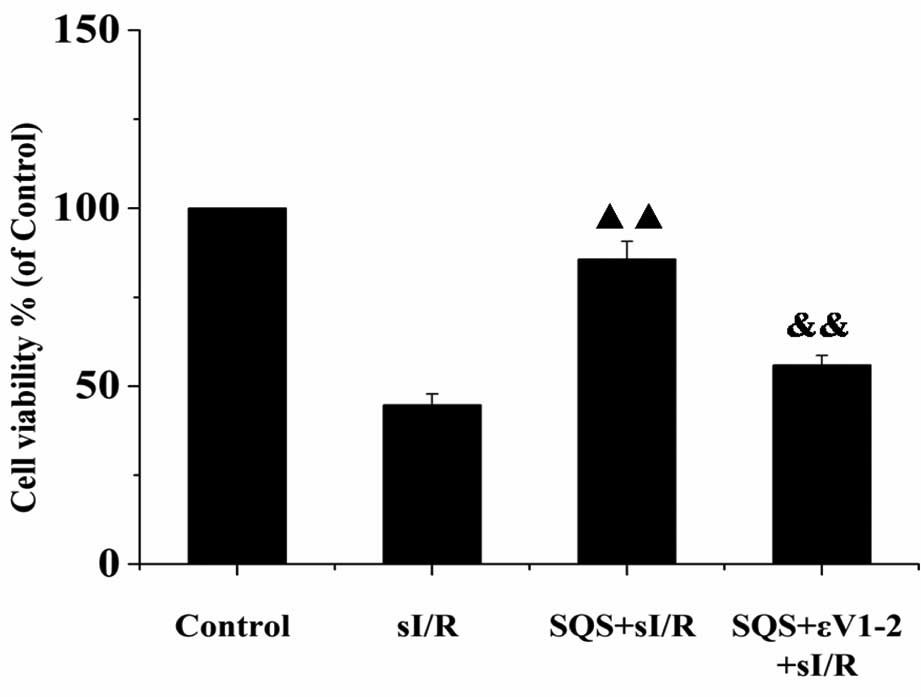
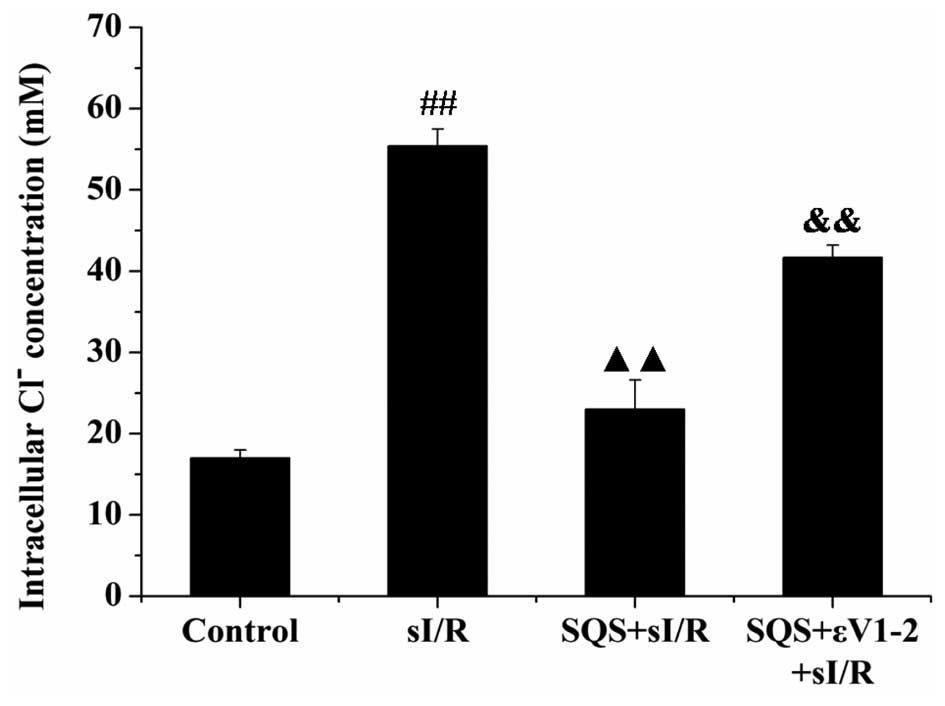
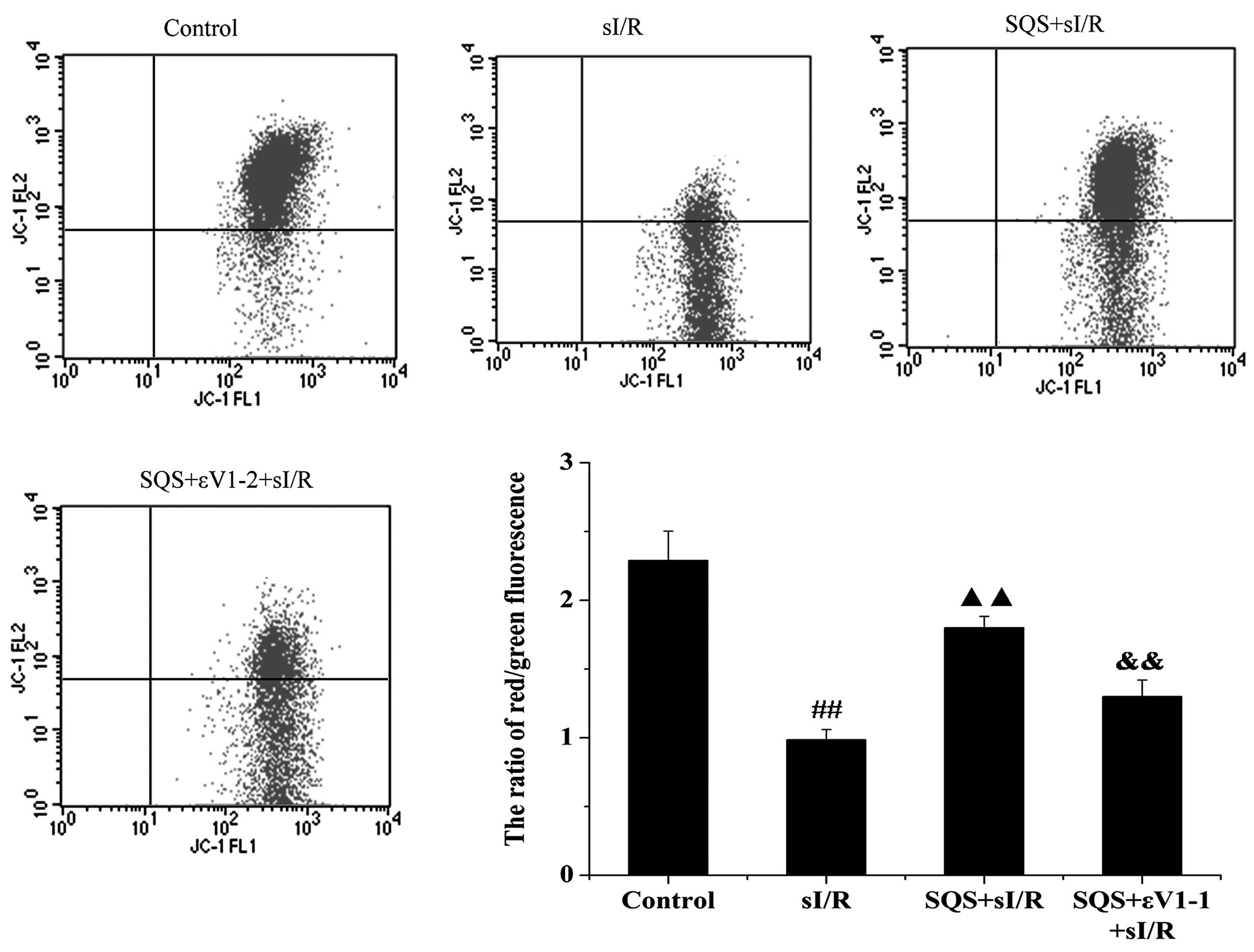
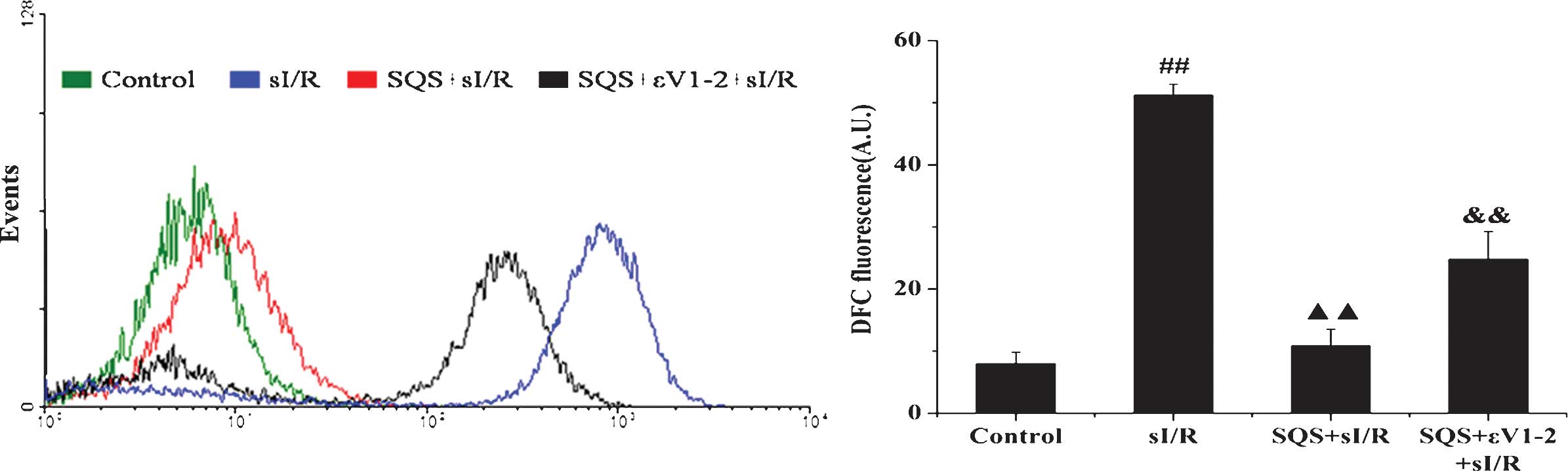
|
1
|
Lee YM, Cheng PY, Chen SY, Chung MT and
Sheu JR: Wogonin suppresses arrhythmias, inflammatory responses and
apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 58:133–142. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hume JR, Duan D, Collier ML, Yamazaki J
and Horowitz B: Anion transport in heart. Physiol Rev. 80:31–81.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alvarez BV, Kieller DM, Quon AL, Markovich
D and Casey JR: Slc26a6: A cardiac chloride-hydroxyl exchanger and
predominant chloride-bicarbonate exchanger of the mouse heart. J
Physiol. 561:721–734. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang QR, Li Q, Chen YH, Li L, Liu LL, Lei
SH, Chen HP, Peng WJ and He M: Involvement of anion exchanger-2 in
apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by high glucose through an
mPTP-ROS-Caspase-3 dependent pathway. Apoptosis. 15:693–704. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S and
Zhivotovsky B: Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death.
Apoptosis. 12:913–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu CX and Xiao PG: Recent advances on
ginseng research in China. J Ethnopharmacol. 36:27–38. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Attele AS, Wu JA and Yuan CS: Ginseng
pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem
Pharmacol. 58:1685–1693. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lai ZF, Shao Z, Chen YZ, He M, Huang Q and
Nishi K: Effects of sasanquasaponin on ischemia and reperfusion
injury in mouse hearts. J Pharmacol Sci. 94:313–324. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen HP, He M, Mei ZJ, Huang QR, Peng W
and Huang M: Anion exchanger 3 is required for sasanquasaponin to
inhibit ischemia/reperfusion-induced elevation of intracellular
Cl-concentration and to elicit cardioprotection. J Cell Biochem.
112:2803–2812. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ono Y, Fujii T, Ogita K, Kikkawa U,
Igarashi K and Nishizuka Y: The structure, expression and
properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J
Biol Chem. 263:6927–6932. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ohno S, Akita Y, Konno Y, Imajoh S and
Suzuki K: A novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC,
distantly related to the protein kinase C family. Cell. 53:731–741.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Akita Y: Protein kinase C-epsilon
(PKC-epsilon): Its unique structure and function. J Biochem.
132:847–852. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu GS, Cohen MV, Mochly-Rosen D and
Downey JM: Protein kinase C-epsilon is responsible for the
protection of preconditioning in rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 31:1937–1948. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ogbi M and Johnson JA: Protein kinase
Cepsilon interacts with cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV and
enhances cytochrome c oxidase activity in neonatal cardiac myocyte
preconditioning. Biochem J. 393:191–199. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Ping PP, Takano H, Zhang J, Tang XL, Qiu
Y, Li RC, Banerjee S, Dawn B, Balafonova Z and Bolli R:
Isoform-selective activation of protein kinase c by nitric oxide in
the heart of conscious rabbits: A signaling mechanism for both
nitric oxide-induced and ischemia-induced preconditioning. Circ
Res. 84:587–604. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Budas GR, Churchill EN, Disatnik MH, Sun L
and Mochly-Rosen D: Mitochondrial import of PKCepsilon is mediated
by HSP90: A role in cardioprotection from ischaemia and reperfusion
injury. Cardiovasc Res. 88:83–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watkins SJ, Borthwick GM and Arthur HM:
The H9C2 cell line and primary neonatal cardiomyocyte cells show
similar hypertrophic responses in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 47:125–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tang L, Peng Y, Xu T, Yi X, Liu Y, Luo Y,
Yin D and He M: The effects of quercetin protect cardiomyocytes
from A/R injury is related to its capability to increasing
expression and activity of PKCε protein. Mol Cell Biochem.
382:145–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen HP, He M, Huang QR, Liu D and Huang
M: Sasanquasaponin protects rat cardiomyocytes against oxidative
stress induced by anoxia-reoxygenation injury. Eur J Pharmacol.
575:21–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akagi M, Fukuishi N, Kan T, Sagesaka YM
and Akagi R: Anti-allergic effect of tea-leaf saponin (TLS) from
tea leaves (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis). Biol Pharm Bull.
20:565–567. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sur P, Chaudhuri T, Vedasiromoni JR, Gomes
A and Ganguly DK: Antiinflammatory and antioxidant property of
saponins of tea [Camellia sinensis (L) O. Kuntze] root extract.
Phytother Res. 15:174–176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu D, He H, Li GL, Chen J, Yin D, Liao
ZP, Tang L, Huang QR, Lai ZF and He M: Mechanisms of chloride in
cardiomyocyte anoxia-reoxygenation injury: The involvement of
oxidative stress and NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biochem.
355:201–209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao Z, Yin D, Wang W, Zeng G, Liu D, Chen
H, Huang Q and He M: Cardioprotective effect of sasanquasaponin
preconditioning via bradykinin-NO pathway in isolated rat heart.
Phytother Res. 23:1146–1153. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hiraoka M, Kawano S, Hirano Y and Furukawa
T: Role of cardiac chloride currents in changes in action potential
characteristics and arrhythmias. Cardiovasc Res. 40:23–33. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ping P, Song C, Zhang J, Guo Y, Cao X, Li
RC, Wu W, Vondriska TM, Pass JM, Tang XL, et al: Formation of
protein kinase C (epsilon)-Lck signaling modules confers
cardioprotection. J Clin Invest. 109:499–507. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schwanke U, Konietzka I, Duschin A, Li X,
Schulz R and Heusch G: No ischemic preconditioning in heterozygous
connexin43-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
283:H1740–H1742. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schulz R, Cohen MV, Behrends M, Downey JM
and Heusch G: Signal transduction of ischemic preconditioning.
Cardiovasc Res. 52:181–198. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alper SL, Darman RB, Chernova MN and Dahl
NK: The AE gene family of Cl/HCO3 exchangers. J Nephrol.
15(Suppl 5): S41–S53. 2002.
|
|
29
|
Alvarez BV, Fujinaga J and Casey JR:
Molecular basis for angiotensin II-induced increase of
chloride/bicarbonate exchange in the myocardium. Circ Res.
89:1246–1253. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|