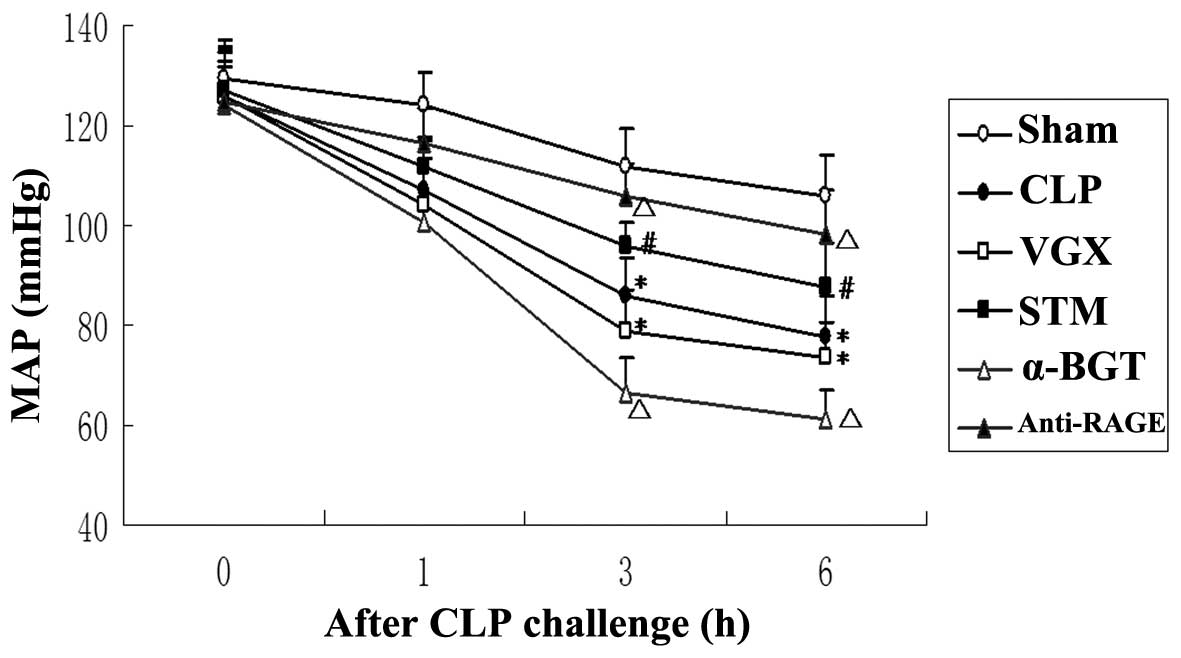
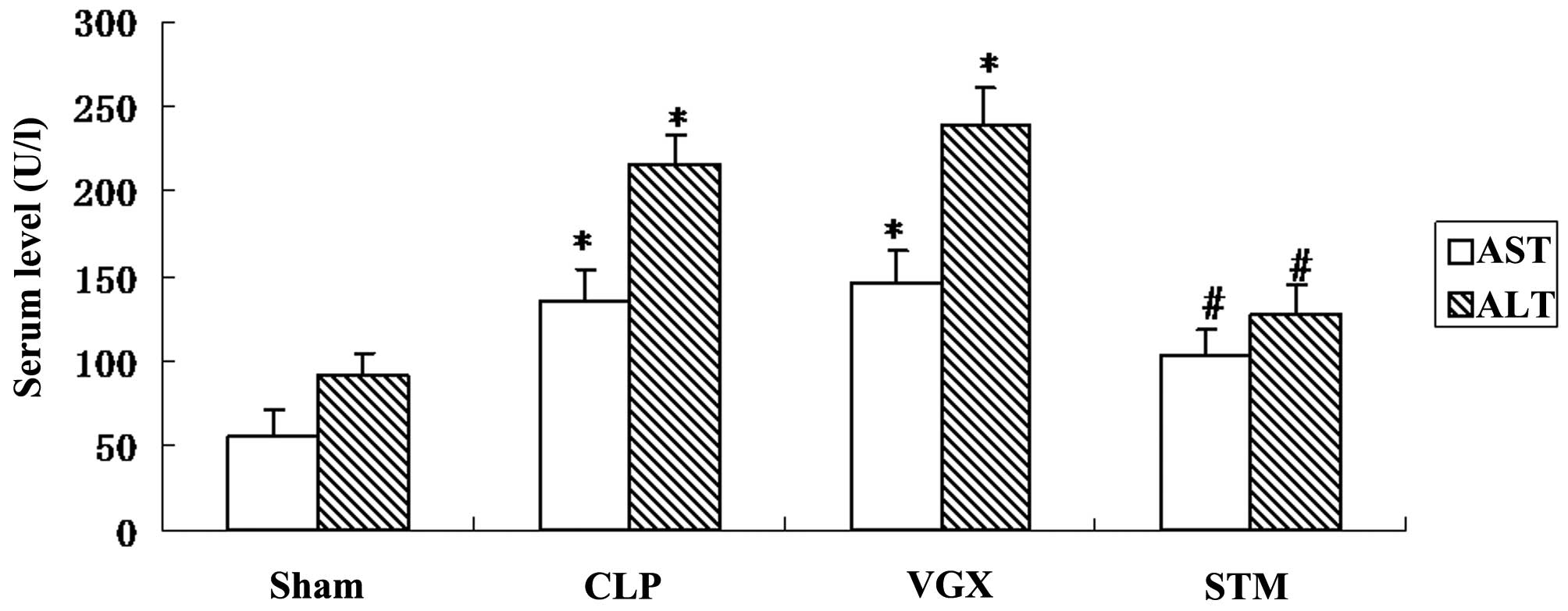
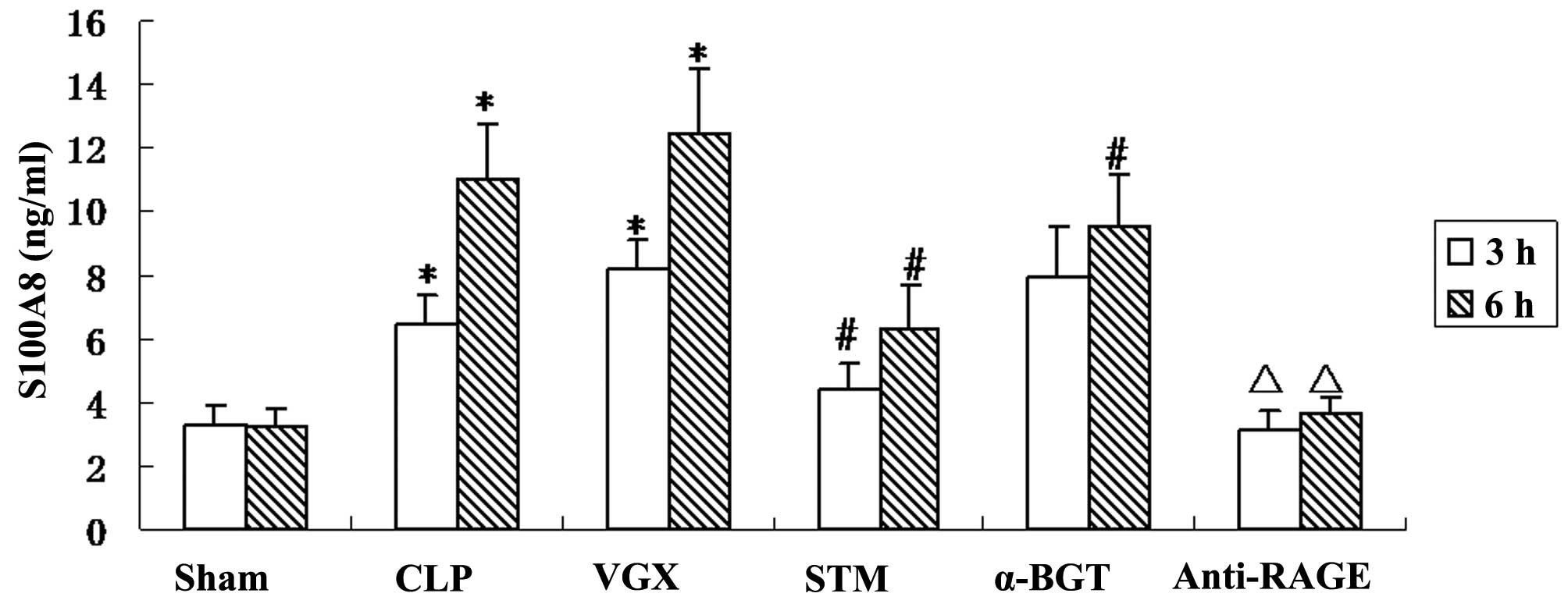
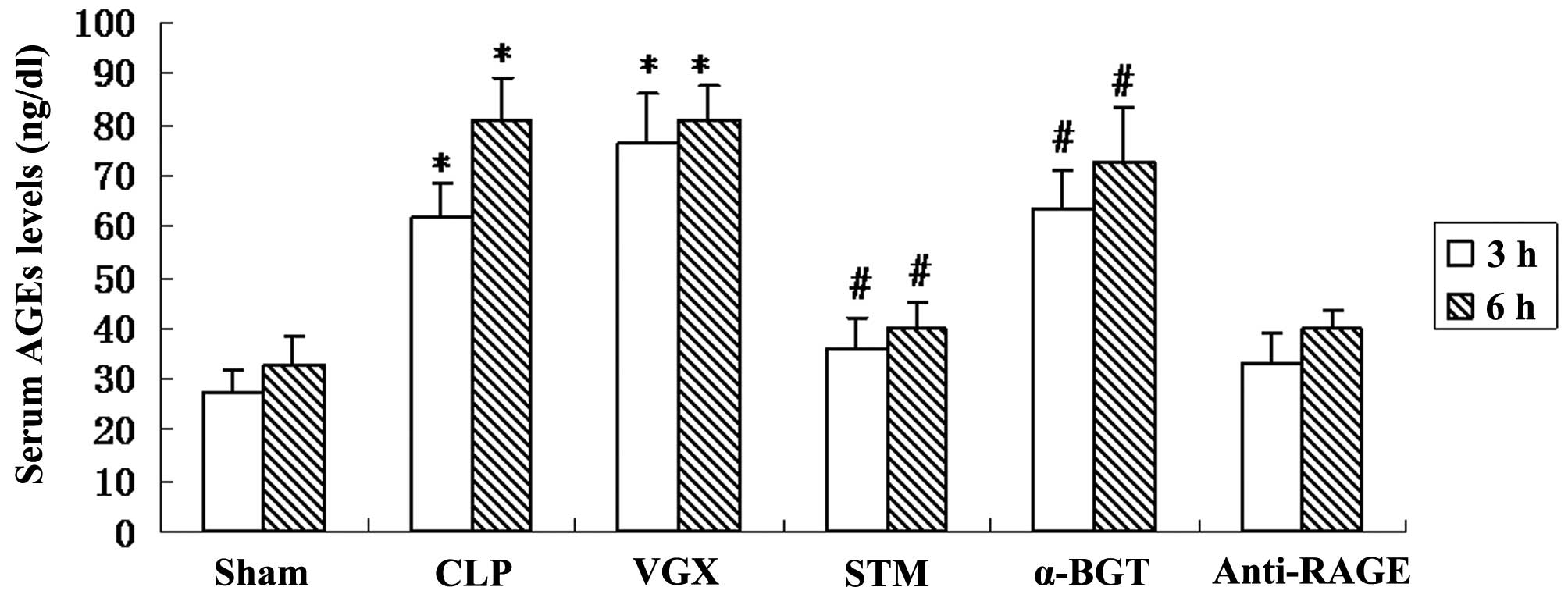
|
1
|
Pravda J: Metabolic theory of septic
shock. World J Crit Care Med. 3:45–54. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schulte W, Bernhagen J and Bucala R:
Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential
therapeutic targets-an updated view. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:1659742013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
King EG, Bauzá GJ, Mella JR and Remick DG:
Pathophysiologic mechanisms in septic shock. Lab Invest. 94:4–12.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Averill MM, Kerkhoff C and Bornfeldt KE:
S100A8 and S100A9 in cardiovascular biology and disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:223–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Goyette J and Geczy CL:
Inflammation-associated S100 proteins: New mechanisms that regulate
function. Amino Acids. 41:821–842. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sohnle PG, Hunter MJ, Hahn B and Chazin
WJ: Zinc-reversible antimicrobial activity of recombinant
calprotectin (migration inhibitory factor-related proteins 8 and
14). J Infect Dis. 182:1272–1275. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Viemann D, Barczyk K, Vogl T, Fischer U,
Sunderkötter C, Schulze-Osthoff K and Roth J: MRP8/MRP14 impairs
endothelial integrity and induces a caspase-dependent and
-independent cell death program. Blood. 109:2453–2460. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ryckman C, Vandal K, Rouleau P, Talbot M
and Tessier PA: Proinflammatory activities of S100: Proteins
S100A8, S100A9, and S100A8/A9 induce neutrophil chemotaxis and
adhesion. J Immunol. 170:3233–3242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Viemann D, Strey A, Janning A, Jurk K,
Klimmek K, Vogl T, Hirono K, Ichida F, Foell D, Kehrel B, et al:
Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 induce a specific inflammatory
response in human microvascular endothelial cells. Blood.
105:2955–2962. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Payen D, Lukaszewicz AC, Belikova I,
Faivre V, Gelin C, Russwurm S, Launay JM and Sevenet N: Gene
profiling in human blood leucocytes during recovery from septic
shock. Intensive Care Med. 34:1371–1376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martelli D, McKinley MJ and McAllen RM:
The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: A critical review. Auton
Neurosci. 182:65–69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mabley JG, Pacher P and Szabo C:
Activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway reduces
ricin-induced mortality and organ failure in mice. Mol Med.
15:166–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnston GR and Webster NR: Cytokines and
the immunomodulatory function of the vagus nerve. Br J Anaesth.
102:453–462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tracey KJ: Physiology and immunology of
the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. J Clin Invest.
117:289–296. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song XM, Li JG, Wang YL, Hu ZF, Zhou Q, Du
ZH and Jia BH: The protective effect of the cholinergic
anti-inflammatory pathway against septic shock in rats. Shock.
30:468–472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilson J, Higgins D, Hutting H, Serkova N,
Baird C, Khailova L, Queensland K, Vu Tran Z, Weitzel L and
Wischmeyer PE: Early propranolol treatment induces lung
heme-oxygenase-1, attenuates metabolic dysfunction and improves
survival following experimental sepsis. Crit Care. 17:R1952013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Singleton KD and Wischmeyer PE: Distance
of cecum ligated influences mortality, tumor necrosis factor-alpha
and interleukin-6 expression following cecal ligation and puncture
in the rat. Eur Surg Res. 35:486–491. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bonaz B, Picq C, Sinniger V and Mayol JF:
From epilepsy to the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:208–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Odink K, Cerletti N, Brüggen J, Clerc RG,
Tarcsay L, Zwadlo G, Gerhards G, Schlegel R and Sorg C: Two
calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid
arthritis. Nature. 330:80–82. 1987. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Farkas G Jr, Tiszlavicz Z, Takács T,
Szabolcs A, Farkas G, Somogyvári F and Mándi Y: Analysis of plasma
levels and polymorphisms of S100A8/9 and S100A12 in patients with
acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 43:485–487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ikemoto M, Matsumoto S, Egawa H, Okitsu T,
Iwanaga Y, Umemoto S, Itoh H, Murayama H and Fujita M: A case with
transient increases in serum S100A8/A9 levels implying acute
inflammatory responses after pancreatic islet transplantation. Ann
Clin Biochem. 44:570–572. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leach ST, Yang Z, Messina I, Song C, Geczy
CL, Cunningham AM and Day AS: Serum and mucosal S100 proteins,
calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) and S100A12, are elevated at diagnosis
in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol.
42:1321–1331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katashima T, Naruko T, Terasaki F, Fujita
M, Otsuka K, Murakami S, Sato A, Hiroe M, Ikura Y, Ueda M, et al:
Enhanced expression of the S100A8/A9 complex in acute myocardial
infarction patients. Circ J. 74:741–748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bealer JF and Colgin M: S100A8/A9: A
potential new diagnostic aid for acute appendicitis. Acad Emerg
Med. 17:333–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Zoelen MA, Vogl T, Foell D, Van Veen
SQ, van Till JW, Florquin S, Tanck MW, Wittebole X, Laterre PF,
Boermeester MA, et al: Expression and role of myeloid-related
protein-14 in clinical and experimental sepsis. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 180:1098–1106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spapen H: Liver perfusion in sepsis,
septic shock and multiorgan failure. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
291:714–720. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ramaiah SK and Jaeschke H: Role of
neutrophils in the pathogenesis of acute inflammatory liver injury.
Toxicol Pathol. 35:757–766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Edgeworth J, Gorman M, Bennett R, Freemont
P and Hogg N: Identification of p8,14 as a highly abundant
heterodimeric calcium binding protein complex of myeloid cells. J
Biol Chem. 266:7706–7713. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moles A, Murphy L, Wilson CL, Chakraborty
JB, Fox C, Park EJ, Mann J, Oakley F, Howarth R, Brain J, et al: A
TLR2/S100A9/CXCL-2 signaling network is necessary for neutrophil
recruitment in acute and chronic liver injury in the mouse. J
Hepatol. 60:782–791. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Nakamura T, Sato E, Fujiwara N, Kawagoe Y,
Suzuki T, Ueda Y, Yamada S, Shoji H, Takeuchi M, Ueda S, et al:
Circulating levels of advanced glycation end products (AGE) and
interleukin-6 (IL-6) are independent determinants of serum
asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) levels in patients with septic
shock. Pharmacol Res. 60:515–518. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakajima Y, Inagaki Y, Kido J and Nagata
T: Advanced glycation end products increase expression of S100A8
and A9 via RAGE-MAPK in rat dental pulp cells. Oral Dis.
21:328–334. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Takahashi HK, Liu K, Wake H, Mori S, Zhang
J, Liu R, Yoshino T and Nishibori M: Effect of nicotine on advanced
glycation end product-induced immune response in human monocytes. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 332:1013–1021. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Jin C, Li Y, Guan S, Han F and
Zhang S: Catalpol improves cholinergic function and reduces
inflammatory cytokines in the senescent mice induced by
D-galactose. Food Chem Toxicol. 58:50–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bopp C, Bierhaus A, Hofer S, Bouchon A,
Nawroth PP, Martin E and Weigand MA: Bench-to-bedside review: The
inflammation-perpetuating pattern-recognition receptor RAGE as a
therapeutic target in sepsis. Crit Care. 12:2012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liliensiek B, Weigand MA, Bierhaus A,
Nicklas W, Kasper M, Hofer S, Plachky J, Gröne HJ, Kurschus FC,
Schmidt AM, et al: Receptor for advanced glycation end products
(RAGE) regulates sepsis but not the adaptive immune response. J
Clin Invest. 113:1641–1650. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bopp C, Hofer S, Weitz J, Bierhaus A,
Nawroth PP, Martin E, Büchler MW and Weigand MA: sRAGE is elevated
in septic patients and associated with patients outcome. J Surg
Res. 147:79–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yamagishi S, Nakamura K and Matsui T:
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and their receptor (RAGE)
system in diabetic retinopathy. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 3:83–88.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yamagishi S, Adachi H, Nakamura K, Matsui
T, Jinnouchi Y, Takenaka K, Takeuchi M, Enomoto M, Furuki K, Hino
A, et al: Positive association between serum levels of advanced
glycation end products and the soluble form of receptor for
advanced glycation end products in nondiabetic subjects.
Metabolism. 55:1227–1231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nakamura K, Yamagishi S, Adachi H, Matsui
T, Kurita-Nakamura Y, Takeuchi M, Inoue H and Imaizumi T: Serum
levels of soluble form of receptor for advanced glycation end
products (sRAGE) are positively associated with circulating AGEs
and soluble form of VCAM-1 in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Microvasc Res. 76:52–56. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eggers K, Sikora K, Lorenz M, Taubert T,
Moobed M, Baumann G, Stangl K and Stangl V: RAGE-dependent
regulation of calcium-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 in human
THP-1. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 119:353–357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Christaki E, Opal SM, Keith JC Jr,
Kessimian N, Palardy JE, Parejo NA, Tan XY, Piche-Nicholas N,
Tchistiakova L, Vlasuk GP, et al: A monoclonal antibody against
RAGE alters gene expression and is protective in experimental
models of sepsis and pneumococcal pneumonia. Shock. 35:492–498.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|