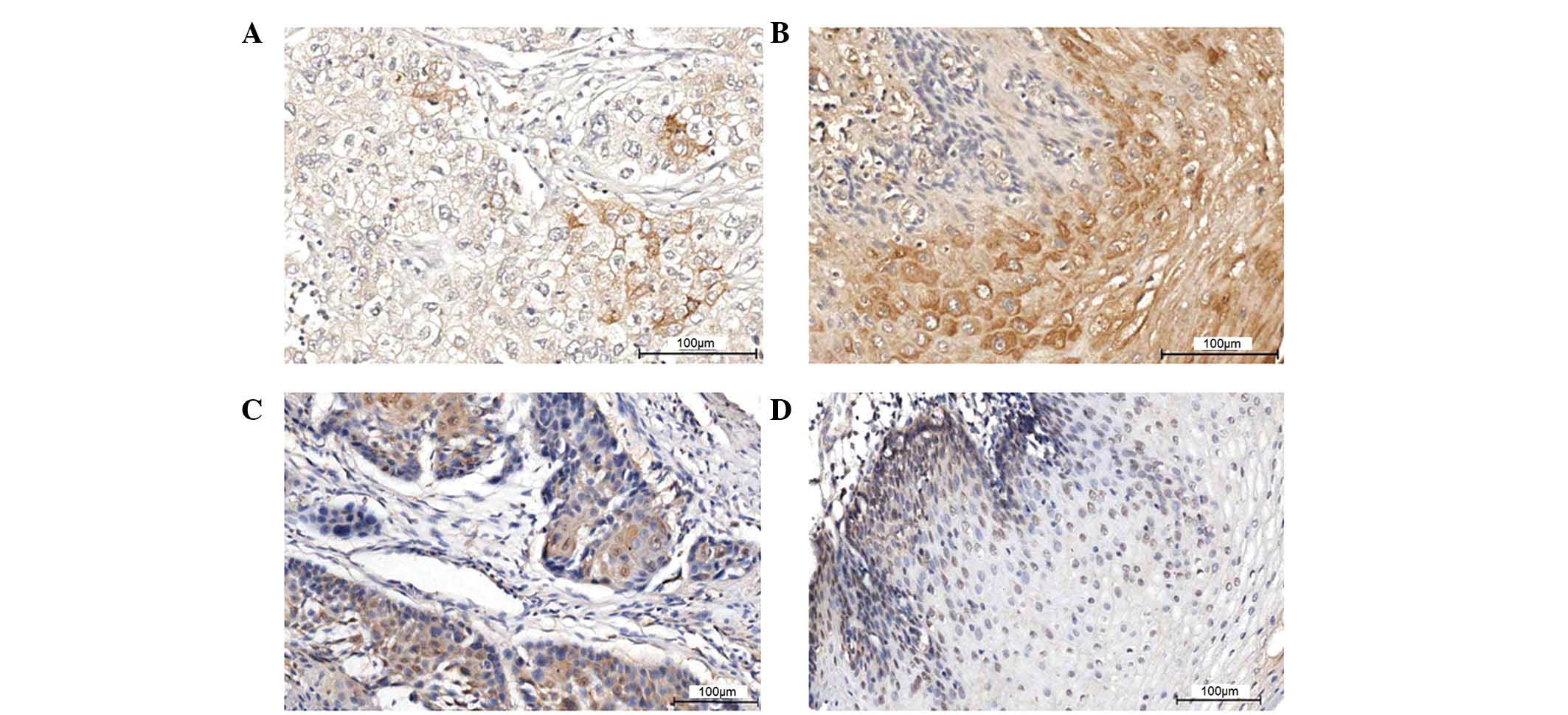
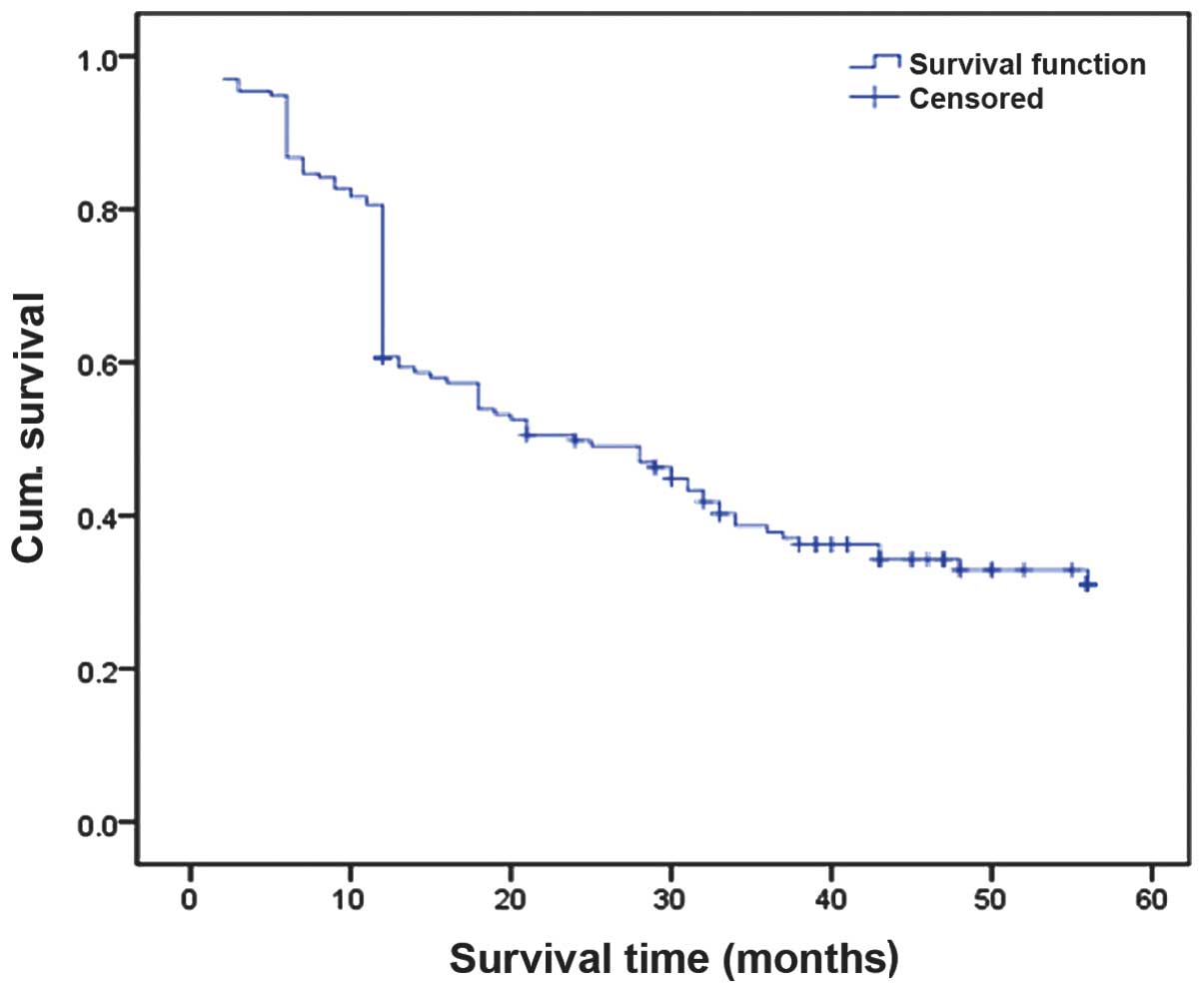
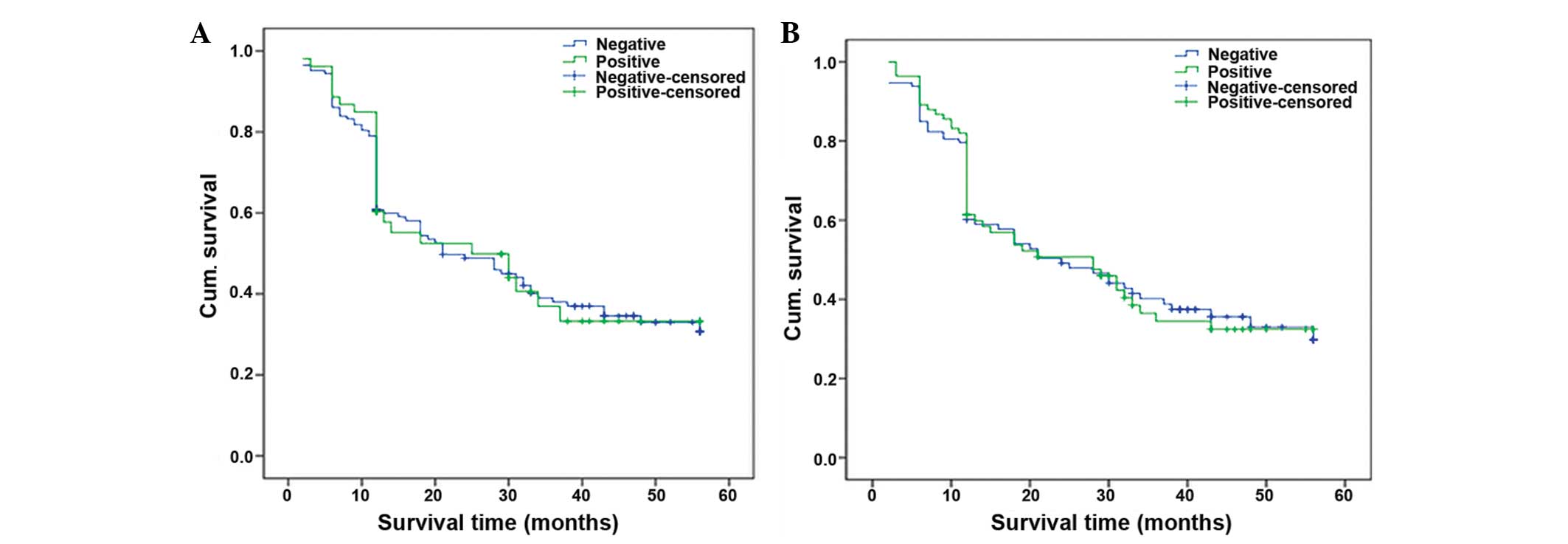
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suntharalingam M: Definitive
chemoradiation in the management of locally advanced esophageal
cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 17:22–28. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rohatgi PR, Swisher SG, Correa AM, Wu TT,
Liao Z, Komaki R, Walsh G, Vaporciyan A, Lynch PM, Rice DC, et al:
Failure patterns correlate with the proportion of residual
carcinoma after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for carcinoma of the
esophagus. Cancer. 104:1349–1355. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Di Fiore F, Lecleire S, Rigal O, Galais
MP, Ben Soussan E, David I, Paillot B, Jacob JH and Michel P:
Predictive factors of survival in patients treated with definitive
chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell esophageal carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:4185–4190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nicolson GL, Nawa A, Toh Y, Taniguchi S,
Nishimori K and Moustafa A: Tumor metastasis-associated human MTA1
gene and its MTA1 protein product: Role in epithelial cancer cell
invasion, proliferation and nuclear regulation. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 20:19–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Toh Y, Ohga T, Endo K, Adachi E, Kusumoto
H, Haraguchi M, Okamura T and Nicolson GL: Expression of the
metastasis-associated MTA1 protein and its relationship to
deacetylation of the histone H4 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 110:362–367. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Holdaway IM, Mason BH, Lethaby AE, Singh
V, Harvey VJ, Thompson PI and Evans BD: Serum insulin-like growth
factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 following
chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer. ANZ J Surg. 73:905–908.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rajah R, Valentinis B and Cohen P:
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 induces
apoptosis and mediates the effects of transforming growth
factor-beta1 on programmed cell death through a p53- and
IGF-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 272:12181–12188. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA,
Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, Rosner B, Speizer FE and Pollak M:
Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor I and risk
of breast cancer. Lancet. 351:1393–1396. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann
PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH and Pollak M: Plasma
insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: A
prospective study. Science. 279:563–566. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu H, Spitz MR, Mistry J, Gu J, Hong WK
and Wu X: Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and lung
cancer risk: A case-control study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:151–156.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, Chan JM,
Tao Y, Hennekens CH and Stampfer MJ: Prospective study of
colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like
growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 91:620–625. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chuang ST, Patton KT, Schafernak KT,
Papavero V, Lin F, Baxter RC, Teh BT and Yang XJ: Over expression
of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. J Urol. 179:445–449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Balasenthil S, Broaddus RR and Kumar R:
Expression of metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) in benign
endometrium and endometrial adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol.
37:656–661. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rice TW, Blackstone EH and Rusch VW: 7th
edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: Esophagus and
esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1721–1724. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang HP, Liu JF, Rao J, Zhang XM, Qian HL,
Niu XQ and Zhao ZL: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3
(IGFBP-3) genetic variant and the risk of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma in a Chinese population. Genet Mol Res. 13:4146–4153.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hwa V, Oh Y and Rosenfeld RG: The
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily.
Endocr Rev. 20:761–787. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gui Y and Murphy LJ: Insulin-like growth
factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) binds to fibronectin (FN):
Demonstration of IGF-I/IGFBP-3/fn ternary complexes in human
plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:2104–2110. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamada PM and Lee KW: Perspectives in
mammalian IGFBP-3 biology: Local vs. systemic action. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 296:C954–C976. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gill ZP, Perks CM, Newcomb PV and Holly
JM: Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP-3)
predisposes breast cancer cells to programmed cell death in a
non-IGF-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 272:25602–25607. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Collard TJ, Guy M, Butt AJ, Perks CM,
Holly JM, Paraskeva C and Williams AC: Transcriptional upregulation
of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein IGFBP-3 by sodium
butyrate increases IGF-independent apoptosis in human colonic
adenoma-derived epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis. 24:393–401. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Torng PL, Lee YC, Huang CY, Ye JH, Lin YS,
Chu YW, Huang SC, Cohen P, Wu CW and Lin CT: Insulin-like growth
factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) acts as an invasion-metastasis
suppressor in ovarian endometrioid carcinoma. Oncogene.
27:2137–2147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Torng PL, Lin CW, Chan MW, Yang HW, Huang
SC and Lin CT: Promoter methylation of IGFBP-3 and p53 expression
in ovarian endometrioid carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 8:1202009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang YS, Wang L, Liu D, Mao L, Hong WK,
Khuri FR and Lee HY: Correlation between insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein-3 promoter methylation and prognosis of
patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
8:3669–3675. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Wang Z, Liang Z, Liu J, Shi W, Bai
P, Lin X, Magaye R and Zhao J: Expression and clinical significance
of IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and IGFBP-7 in serum and lung cancer tissues
from patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
6:1437–1444. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aishima S, Basaki Y, Oda Y, Kuroda Y,
Nishihara Y, Taguchi K, Taketomi A, Maehara Y, Hosoi F, Maruyama Y,
et al: High expression of insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-3 is correlated with lower portal invasion and better
prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
97:1182–1190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Walker G, MacLeod K, Williams AR, Cameron
DA, Smyth JF and Langdon SP: Insulin-like growth factor binding
proteins IGFBP3, IGFBP4, and IGFBP5 predict endocrine
responsiveness in patients with ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:1438–1444. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shariat SF, Lamb DJ, Kattan MW, Nguyen C,
Kim J, Beck J, Wheeler TM and Slawin KM: Association of
preoperative plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor I and
insulin-like growth factor binding proteins-2 and -3 with prostate
cancer invasion, progression, and metastasis. J Clin Oncol.
20:833–841. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tas F, Karabulut S, Bilgin E, Tastekin D
and Duranyildiz D: Clinical significance of serum insulin-like
growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with breast cancer. Tumour Biol.
35:9303–9309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tas F, Karabulut S, Serilmez M, Ciftci R
and Duranyildiz D: Clinical significance of serum insulin-like
growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin like growth factor binding
protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.
Tumour Biol. 35:3125–3132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Seligson DB, Yu H, Tze S, Said J, Pantuck
AJ, Cohen P and Lee KW: IGFBP-3 nuclear localization predicts human
prostate cancer recurrence. Horm Cancer. 4:12–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Kim YH, Sumiyoshi S, Hashimoto S, Masago
K, Togashi Y, Sakamori Y, Okuda C, Mio T and Mishima M: Expressions
of insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and insulin-like growth
factor binding protein 3 in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.
Clin Lung Cancer. 13:385–390. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rohrmann S, Grote VA, Becker S, Rinaldi S,
Tjønneland A, Roswall N, Grønbæk H, Overvad K, Boutron-Ruault MC,
Clavel-Chapelon F, et al: Concentrations of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and
pancreatic cancer risk in the European prospective investigation
into cancer and nutrition. Br J Cancer. 106:1004–1010. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Firth SM and Baxter RC: Cellular actions
of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev.
23:824–854. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grimberg A: Mechanisms by which IGF-I may
promote cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2:630–635. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Buckbinder L, Talbott R, Velasco-Miguel S,
Takenaka I, Faha B, Seizinger BR and Kley N: Induction of the
growth inhibitor IGF-binding protein 3 by p53. Nature. 377:646–649.
1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Binoux M: Insulin-like growth factor
binding proteins (IGFBPs): Physiological and clinical implications.
J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 9(Suppl 3): S285–S288. 1996.
|
|
38
|
Mehta HH, Gao Q, Galet C, Paharkova V, Wan
J, Said J, Sohn JJ, Lawson G, Cohen P, Cobb LJ and Lee KW: IGFBP-3
is a metastasis suppression gene in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
71:5154–5163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao L, He L, Zhang R, Cai MY, Liao YJ,
Qian D, Xi M, Zeng YX, Xie D and Liu MZ: Low expression of IGFBP-3
predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 29:2669–2676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jenkins PJ, Khalaf S, Ogunkolade W,
McCarthy K, David T, Hands RE, Davies D and Bustin SA: Differential
expression of IGF-binding protein-3 in normal and malignant colon
and its influence on apoptosis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:891–901.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Toh Y, Pencil SD and Nicolson GL: A novel
candidate metastasis-associated gene, mta1, differentially
expressed in highly metastatic mammary adenocarcinoma cell lines.
cDNA cloning, expression, and protein analyses. J Biol Chem.
269:22958–22963. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cui Q, Takiguchi S, Matsusue K, Toh Y and
Yoshida MA: Assignment of the human metastasis-associated gene 1
(MTA1) to human chromosome band 14q32.3 by fluorescence in situ
hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 93:139–140. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Roy S, Packman K, Jeffrey R and Tenniswood
M: Histone deacetylase inhibitors differentially stabilize
acetylated p53 and induce cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in
prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 12:482–491. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hofer MD, Menke A, Genze F, Gierschik P
and Giehl K: Expression of MTA1 promotes motility and invasiveness
of PANC-1 pancreatic carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 90:455–462.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|