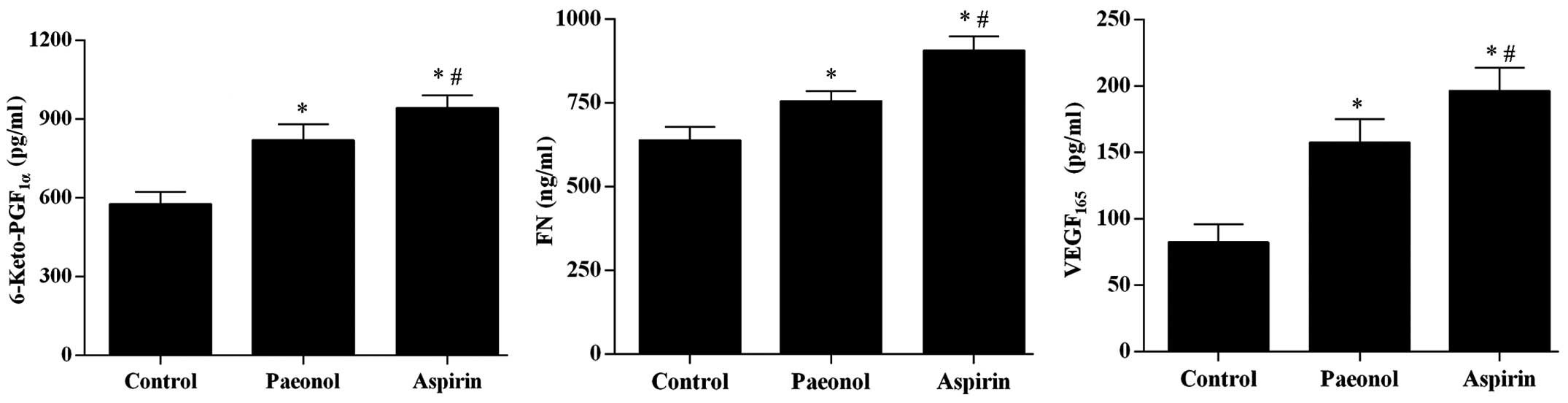
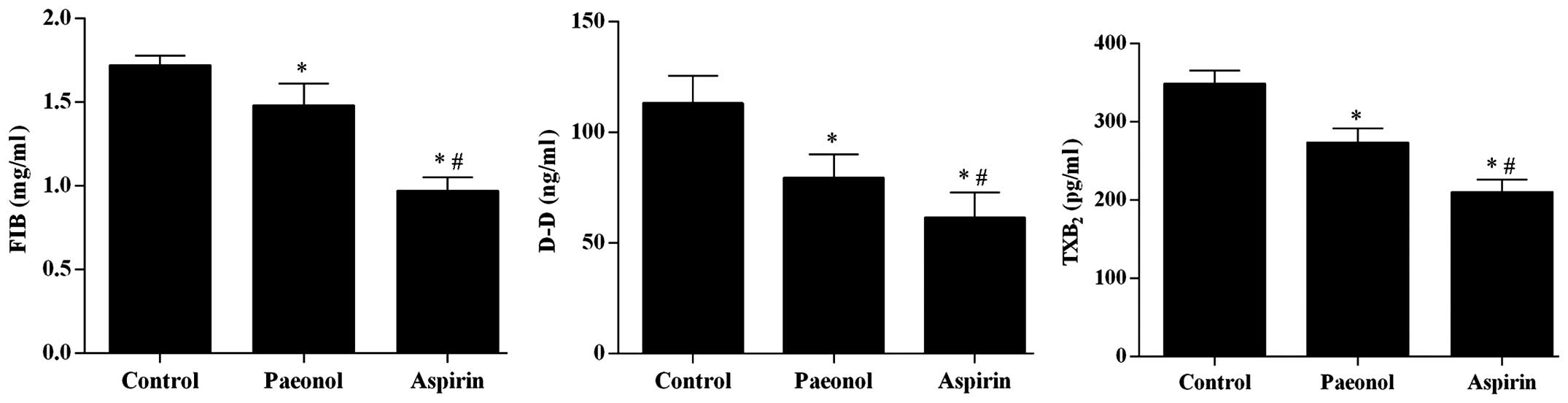
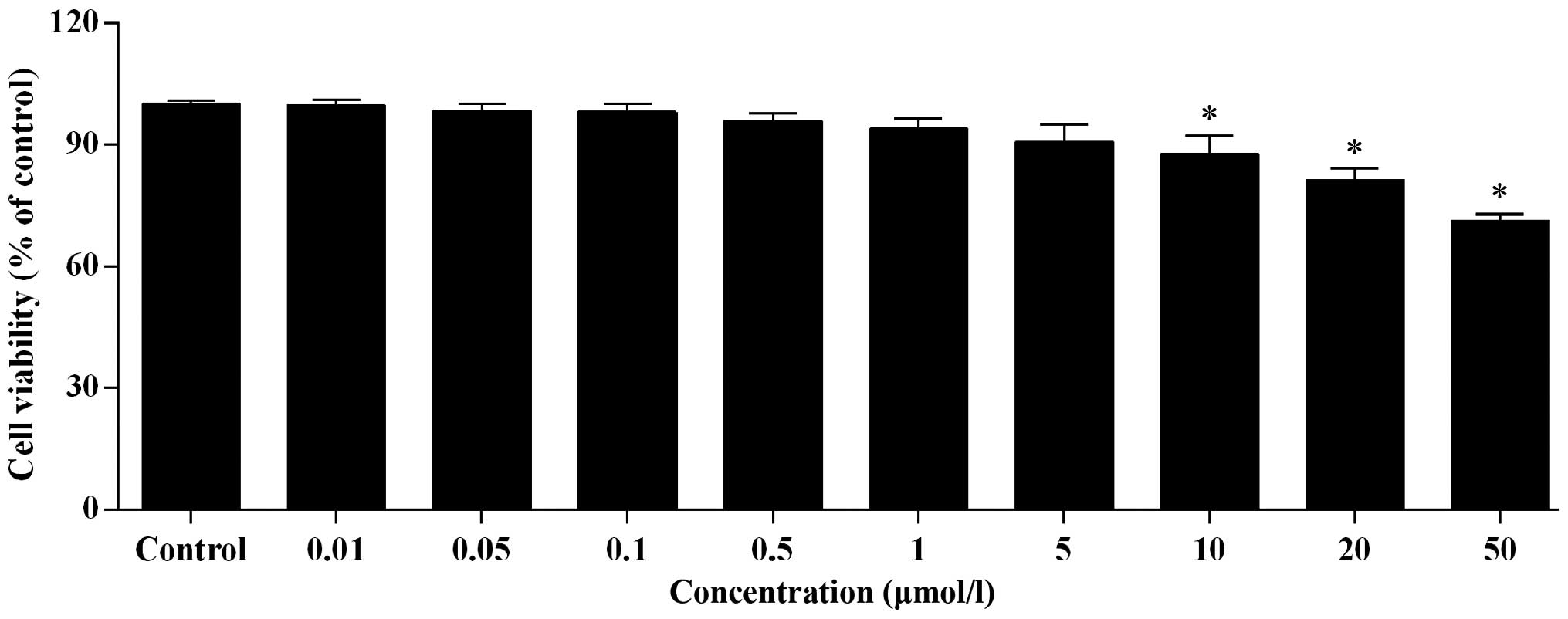
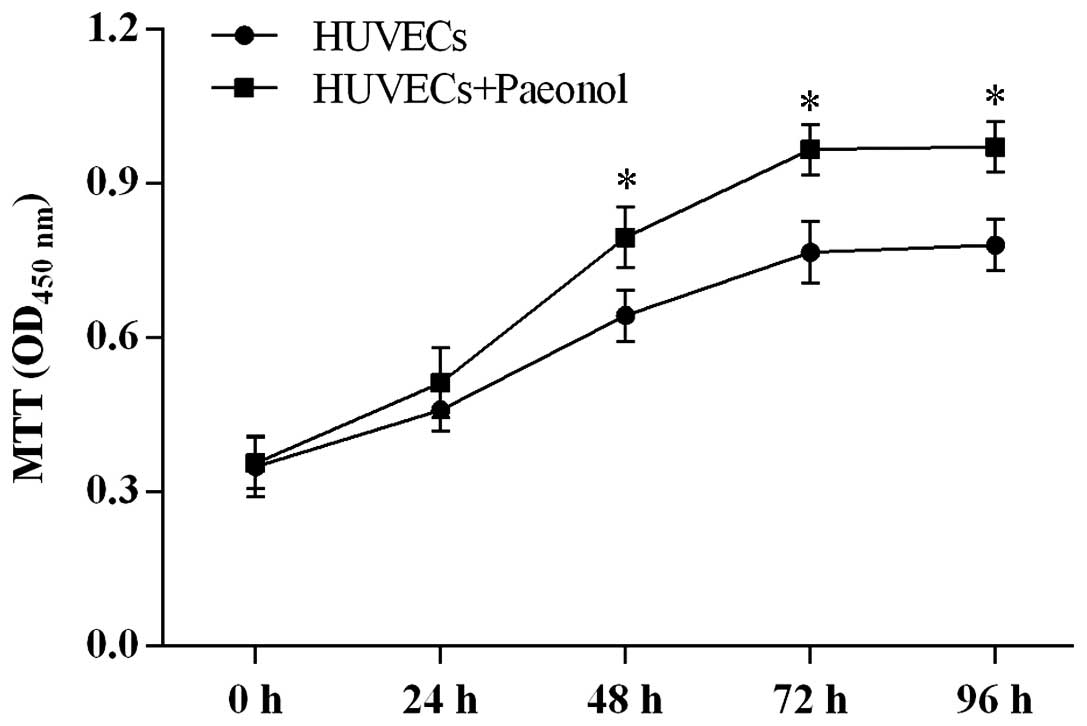
|
1
|
Packham MA: Role of platelets in
thrombosis and hemostasis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 72:278–284.
1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dupont AG, Gabriel DA and Cohen MG:
Antiplatelet therapies and the role of antiplatelet resistance in
acute coronary syndrome. Thromb Res. 124:6–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Konkle BA, Simon D and Schafer AI:
Hemostasis, thrombosis, fibrinolysis and cardiovascular disease.
Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine.
Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL and Zipes DP: 8th edition. Saunders
Elsevier; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 2049–2078. 2008
|
|
4
|
Schrör K: Antiplatelet drugs. A
comparative review. Drugs. 50:7–28. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ni H and Freedman J: Platelets in
hemostasis and thrombosis: Role of integrins and their ligands.
Transfus Aphe Sci. 28:257–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Barrett NE, Holbrook L, Jones S, Kaiser
WJ, Moraes LA, Rana R, Sage T, Stanley RG, Tucker KL, Wright B and
Gibbins JM: Future innovations in anti-platelet therapies. Br J
Pharmacol. 154:918–939. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bird JE, Giancarli MR, Allegretto N,
Barbera F, Wong P, Schumacher WA, Ogletree ML and Seiffert D:
Prediction of the therapeutic index of marketed anti-coagulants and
anti-platelet agents by guinea pig models of thrombosis and
hemostasis. Thromb Res. 123:146–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin HC, Ding HY, Ko FN, Teng CM and Wu YC:
Aggregation inhibitory activity of minor acetophenones from Paeonia
species. Planta Med. 65:595–599. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yasuda T, Kon R, Nakazawa T and Ohsawa K:
Metabolism of paeonol in rats. J Nat Prod. 62:1142–1144. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chou TC: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic
effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Br J
Pharmacol. 139:1146–1152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koo YK, Kim JM, Koo JY, Kang SS, Bae K,
Kim YS, Chung JH and Yun-Choi HS: Platelet anti-aggregatory and
blood anti-coagulant effects of compounds isolated from Paeonia
lactiflora and Paeonia suffruticosa. Pharmazie. 65:624–628.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin C, Lin HY, Chen JH, Tseng WP, Ko PY,
Liu YS, Yeh WL and Lu DY: Effects of paeonol on
anti-neuroinflammatory responses in microglial cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:8844–8860. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wen FS, Zhao HW, Jin XG and Yu HZ: Effect
of paeonol on intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression after
cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Chin J Clin Rehabil.
8:3792–3793. 2004.
|
|
14
|
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S and
Poltorak Z: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its
receptors. FASEB J. 13:9–22. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waltham M, Burnand KG, Collins M,
McGuinness CL, Singh I and Smith A: Vascular endothelial growth
factor enhances venous thrombus recanalisation and organisation.
Thromb Haemost. 89:169–176. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee HJ, Kim SA, Lee HJ, Jeong SJ, Han I,
Jung JH, Lee EO, Zhu S, Chen CY and Kim SH: Paeonol oxime inhibits
bFGF-induced angiogenesis and reduces VEGF levels in fibrosarcoma
cells. PLoS One. 5:e123582010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 7th edition. National Academy
Press; Washington, DC: 1996
|
|
18
|
Lee KS, Oh KW, Bae KH, Kim YH, Lee MY, Cho
MR, Jin YR and Yun YP: Inhibitory effects of moutan cortex radicis
extracts and paeonol on rabbit platelet aggregation. Journal of
Food Hygiene and Safety. 19:167–170. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Kovacic JC, Lee P, Karajgikar R, Baber U,
Narechania B, Suleman J, Moreno PR, Sharma SK and Kini AS: Safety
of temporary and permanent suspension of anti-platelet therapy
after drug eluting stent implantation in contemporary “real-world”
practice. J Interv Cardiol. 25:482–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Folkman J: Angiogenic therapy of the human
heart. Circulation. 97:628–629. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Folkman J: Therapeutic angiogenesis in
ischemic limbs. Circulation. 97:1108–1110. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baumgartner I, Pieczek A, Manor O, Blair
R, Kearney M, Walsh K and Isner JM: Constitutive expression of
phVEGF165 after intramuscular gene transfer promotes collateral
vessel development in patients with critical limb ischemia.
Circulation. 97:1114–1123. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Waltham M, Burnand K, Fenske C, Modarai B,
Humphries J and Smith A: Vascular endothelial growth factor naked
DNA gene transfer enhances thrombus recanalization and resolution.
J Vasc Surg. 42:1183–1189. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milanini J, Richard DE, Berra E, Gothié E,
Viñals F and Pouysségur J: Signaling angiogenesis via p42/p44 MAP
kinase cascade. Ann NY Acad Sci. 902:187–200. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Minet E, Arnould T, Michel G, Roland I,
Mottet D, Raes M, Remacle J and Michiels C: ERK activation upon
hypoxia: Involvement in HIF-1 activation. FEBS Lett. 468:53–58.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nizamutdinova IT, Oh HM, Min YN, Park SH,
Lee MJ, Kim JS, Yean MH, Kang SS, Kim YS, Chang KC and Kim HJ:
Paeonol suppresses intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in
tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human umbilical vein
endothelial cells by blocking p38, ERK and nuclear factor-kappaB
signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:343–350. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|