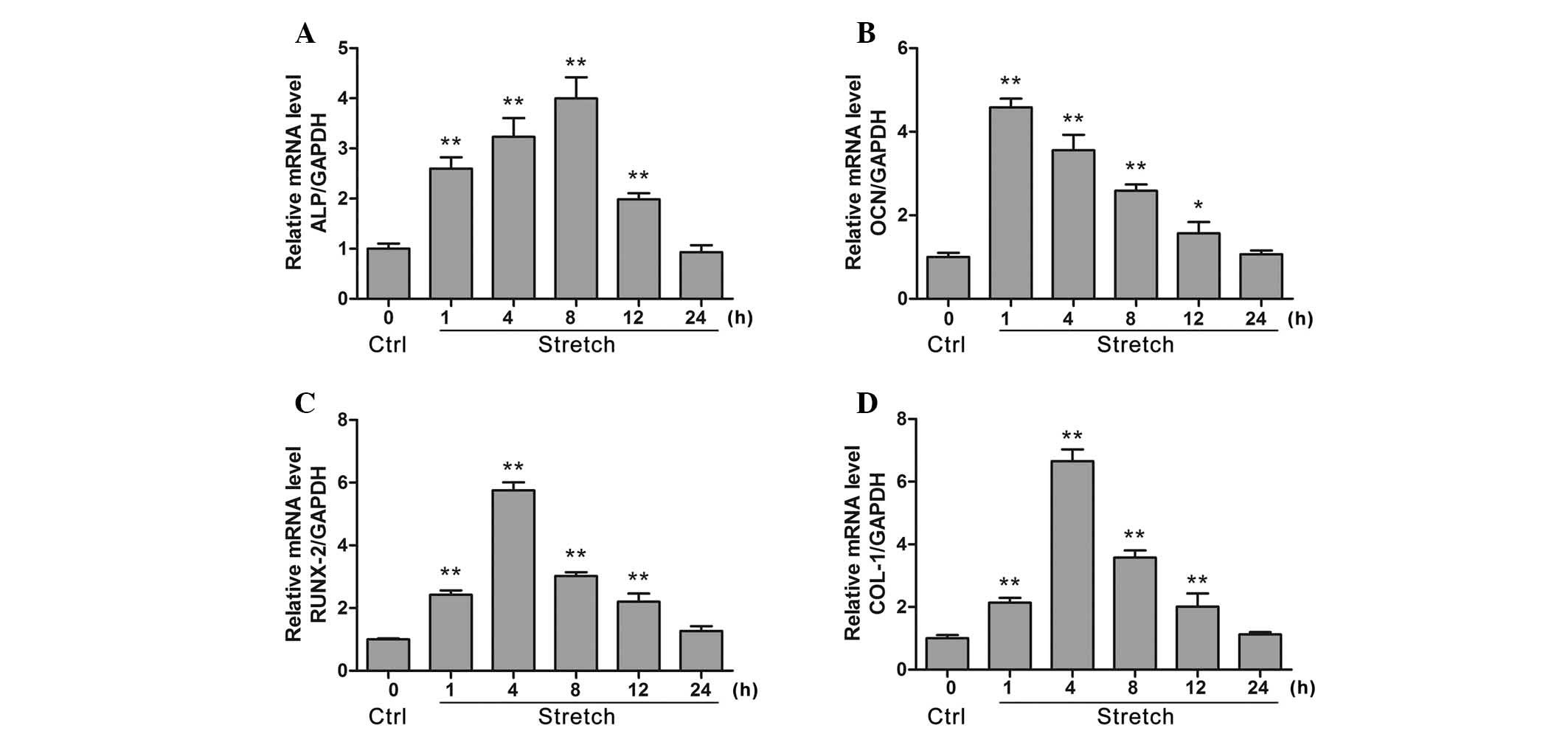
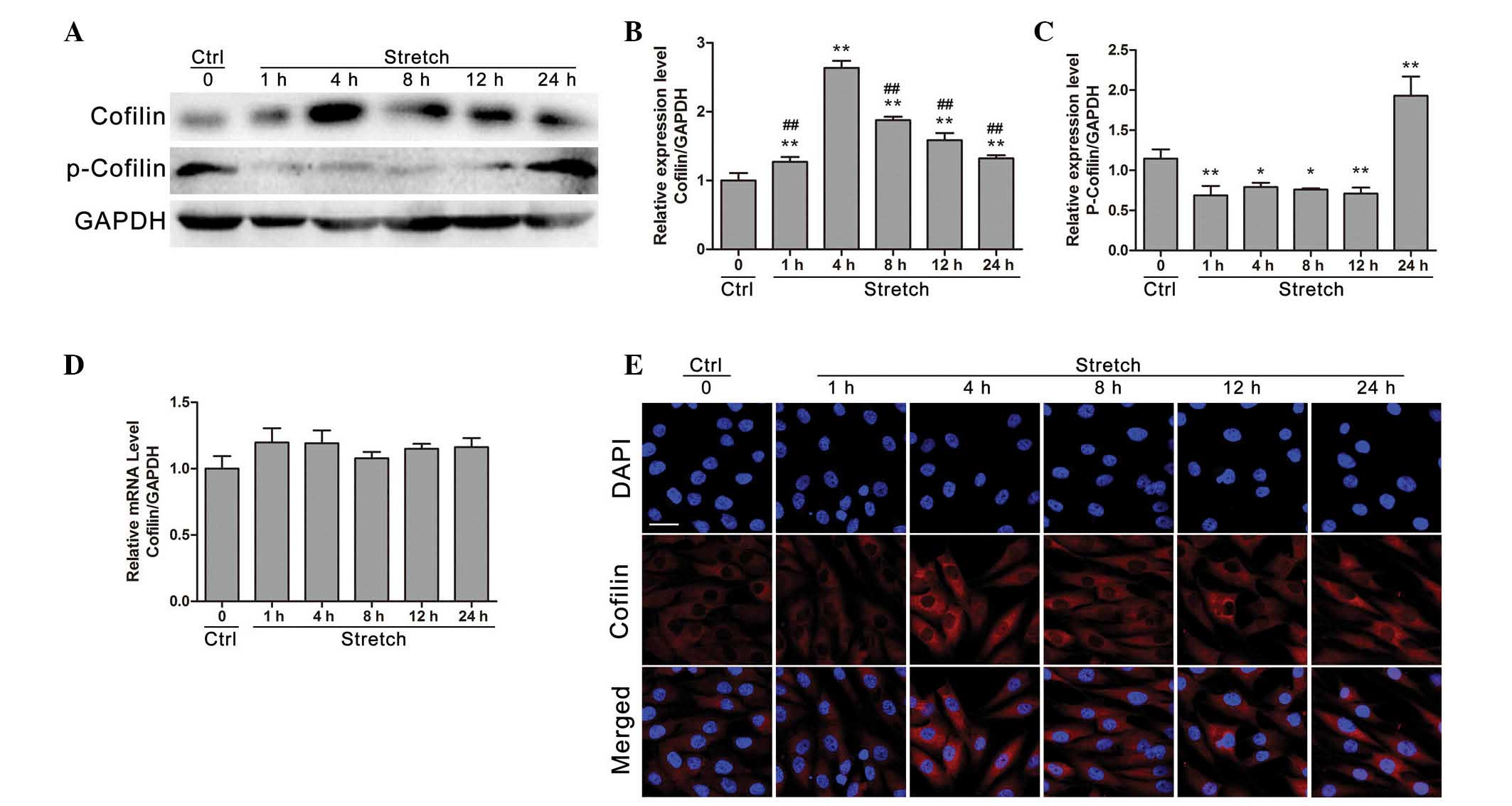
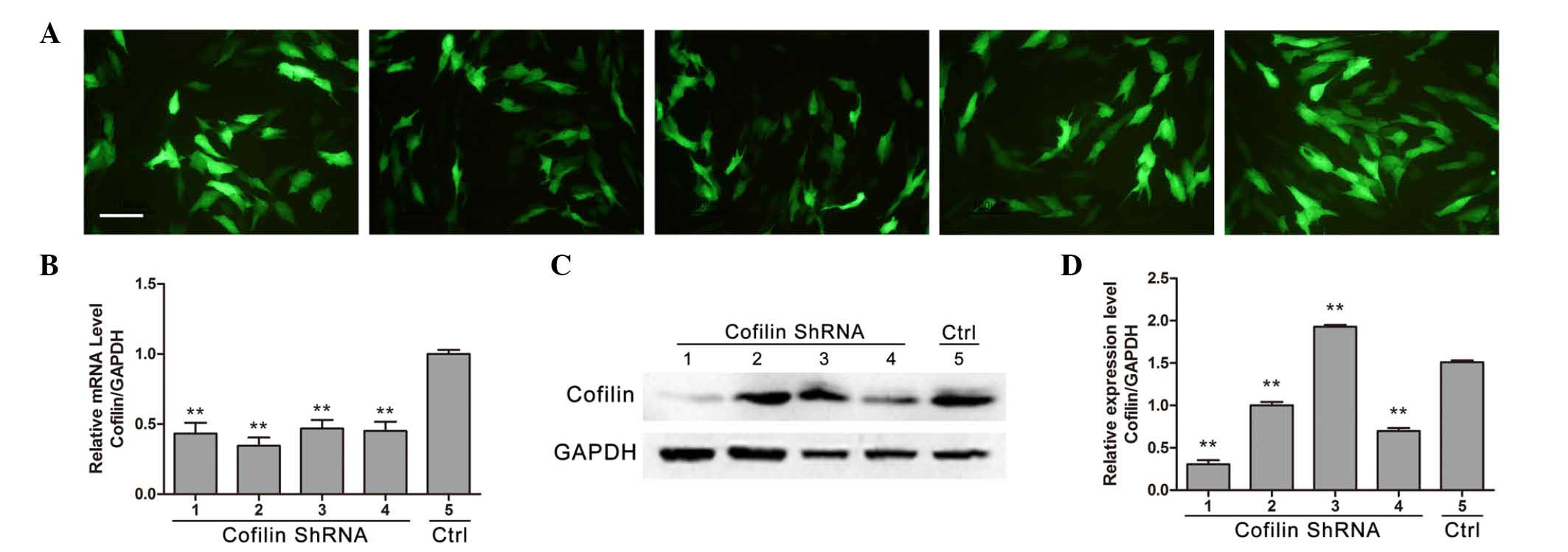
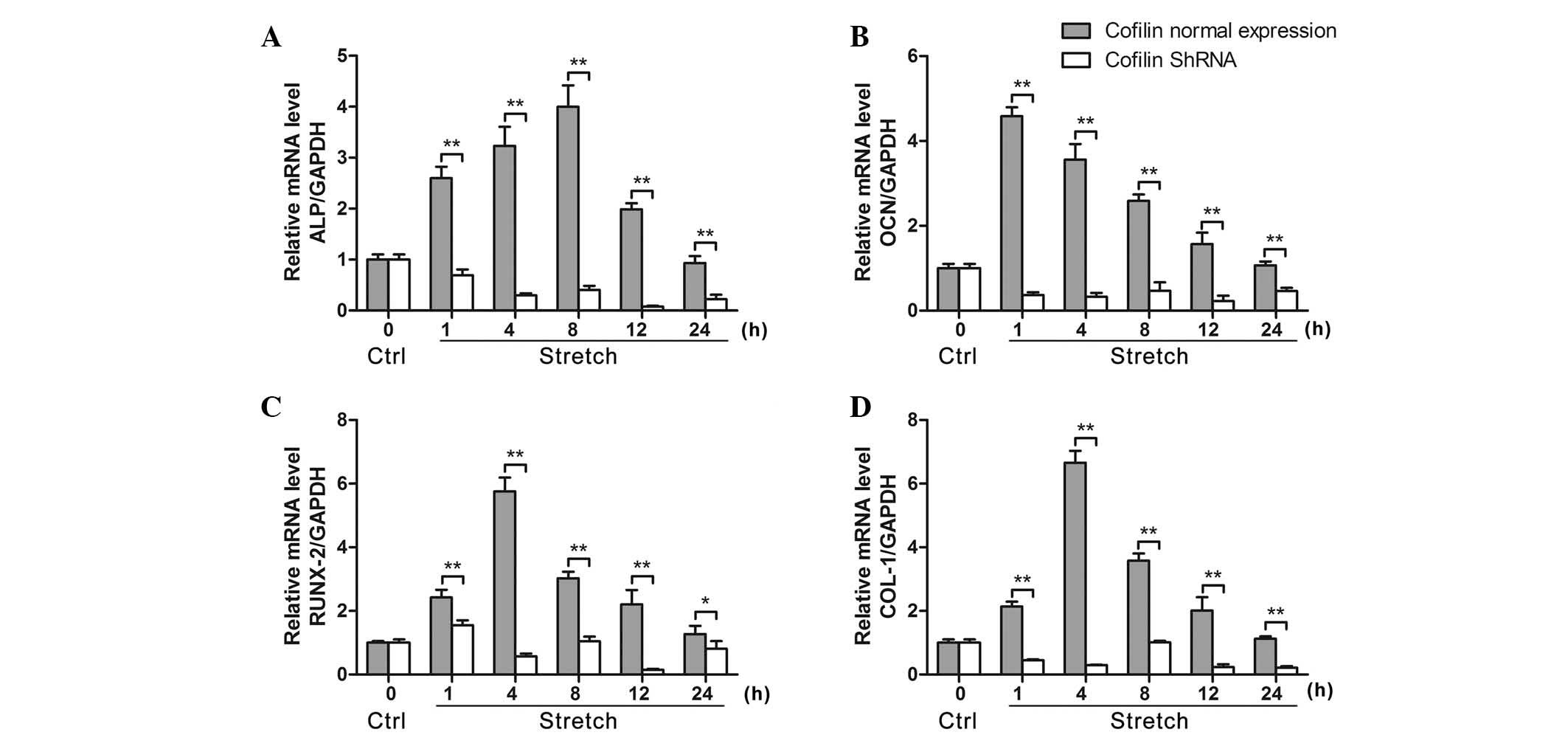
|
1
|
Harter LV, Hruska KA and Duncan RL: Human
osteoblast-like cells respond to mechanical strain with increased
bone matrix protein production independent of hormonal regulation.
Endocrinology. 136:528–535. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Frost HM: Bone's mechanostat: A 2003
update. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 275:1081–1101. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan H, Biechler S, Junor L, Yost MJ, Dean
D, Li J, Potts JD and Goodwin RL: Fluid flow forces and rhoA
regulate fibrous development of the atrioventricular valves. Dev
Biol. 374:345–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yano Y, Geibel J and Sumpio BE: Cyclic
strain induces reorga-nization of integrin alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha
2 beta 1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem.
64:505–513. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Archambault J, Tsuzaki M, Herzog W and
Banes AJ: Stretch and interleukin-1beta induce matrix
metalloproteinases in rabbit tendon cells in vitro. J Orthop Res.
20:36–39. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mayr M, Hu Y, Hainaut H and Xu Q:
Mechanical stress-induced DNA damage and rac-p38MAPK signal
pathways mediate p53-dependent apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle
cells. FASEB J. 16:1423–1425. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang JH and Thampatty BP: An introductory
review of cell mechanobiology. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 5:1–16.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pan J, Wang T, Wang L, Chen W and Song M:
Cyclic strain-induced cytoskeletal rearrangement of human
periodontal ligament cells via the Rho signaling pathway. PLoS One.
9:e915802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi YX, Qu MJ, Long DK, Liu B, Yao QP,
Chien S and Jiang ZL: Rho-GDP dissociation inhibitor alpha
downregulated by low shear stress promotes vascular smooth muscle
cell migration and apoptosis: A proteomic analysis. Cardiovasc Res.
80:114–122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sit ST and Manser E: Rho GTPases and their
role in organizing the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 124:679–683.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bamburg JR and Bernstein BW: ADF/cofilin.
Curr Biol. 18:R273–R275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bamburg JR and Wiggan OP: ADF/cofilin and
actin dynamics in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 12:598–605. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bamburg JR: Proteins of the ADF/cofilin
family: Essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 15:185–230. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maekawa M, Ishizaki T, Boku S, Watanabe N,
Fujita A, Iwamatsu A, Obinata T, Ohashi K, Mizuno K and Narumiya S:
Signaling from Rho to the actin cytoskeleton through protein
kinases ROCK and LIM-kinase. Science. 285:895–898. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM and Gill
GN: Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase
signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol.
1:253–259. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bernstein BW and Bamburg JR: ADF/cofilin:
A functional node in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 20:187–195.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dumas V, Ducharne B, Perrier A, Fournier
C, Guignandon A, Thomas M, Peyroche S, Guyomar D, Vico L and
Rattner A: Extracellular matrix produced by osteoblasts cultured
under low-magnitude, high-frequency stimulation is favourable to
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Calcif Tissue
Int. 87:351–364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Torcasio A, van Lenthe GH and Van
Oosterwyck H: The importance of loading frequency, rate and
vibration for enhancing bone adaptation and implant
osseointegration. Eur Cell Mater. 16:56–68. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zeichen J, van Griensven M and Bosch U:
The proliferative response of isolated human tendon fibroblasts to
cyclic biaxial mechanical strain. Am J Sports Med. 28:888–892.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Watson PA: Function follows form:
Generation of intracellular signals by cell deformation. FASEB J.
5:2013–2019. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mayr M, Hu Y, Hainaut H and Xu Q:
Mechanical stress-induced DNA damage and rac-p38MAPK signal
pathways mediate p53-dependent apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle
cells. FASEB J. 16:1423–1425. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pan J, Wang T, Wang L, Chen W and Song M:
Cyclic strain-induced cytoskeletal rearrangement of human
periodontal ligament cells via the Rho signaling pathway. PLoS One.
9:e915802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Van Troys M, Huyck L, Leyman S, Dhaese S,
Vandekerkhove J and Ampe C: Ins and outs of ADF/cofilin activity
and regulation. Eur J Cell Biol. 87:649–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nishida E, Iida K, Yonezawa N, Koyasu S,
Yahara I and Sakai H: Cofilin is a component of intranuclear and
cytoplasmic actin rods induced in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 84:5262–5266. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin MC, Galletta BJ, Sept D and Cooper JA:
Overlapping and distinct functions for cofilin, coronin and Aip1 in
actin dynamics in vivo. J Cell Sci. 123:1329–1342. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan JS, Han Y, Chen DP, Xu L, Qi YX and
Yan ZQ: Cyclic strain promotes migration of human periodontal
ligament cell via extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
signaling pathway. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 45:80–84.
2010.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu X, Zhang X and Luo ZP: Strain-related
collagen gene expression in human osteoblast-like cells. Cell
Tissue Res. 322:331–334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Larsson T, Aspden RM and Heinegård D:
Effects of mechanical load on cartilage matrix biosynthesis in
vitro. Matrix. 11:388–394. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jing D, Cai J, Wu Y, Shen G, Li F, Xu Q,
Xie K, Tang C, Liu J, Guo W, et al: Pulsed electromagnetic fields
partially preserve bone mass, microarchitecture and strength by
promoting bone formation in hindlimb-suspended rats. J Bone Miner
Res. 29:2250–2261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin T, Zeng L, Liu Y, DeFea K, Schwartz
MA, Chien S and Shyy JY: Rho-ROCK-LIMK-cofilin pathway regulates
shear stress activation of sterol regulatory element binding
proteins. Circ Res. 92:1296–1304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Campbell JJ, Blain EJ, Chowdhury TT and
Knight MM: Loading alters actin dynamics and up-regulates cofilin
gene expression in chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
361:329–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pederson T: As functional nuclear actin
comes into view, is it globular, filamentous, or both? J Cell Biol.
180:1061–1064. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng B, Han M, Bernier M and Wen JK:
Nuclear actin and actin-binding proteins in the regulation of
transcription and gene expression. FEBS J. 276:2669–2685. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iida K, Matsumoto S and Yahara I: The
KKRKK sequence is involved in heat shock-induced nuclear
translocation of the 18-kDa actin-binding protein, cofilin. Cell
Struct Funct. 17:39–46. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Burgos-Rivera B, Ruzicka DR, Deal RB,
McKinney EC, King-Reid L and Meagher RB: ACTIN DEPOLYMERIZING
FACTOR9 controls development and gene expression in Arabidopsis.
Plant Mol Biol. 68:619–632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pendleton A, Pope B, Weeds A and Koffer A:
Latrunculin B or ATP depletion induces cofilin-dependent
translocation of actin into nuclei of mast cells. J Biol Chem.
278:14394–14400. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|