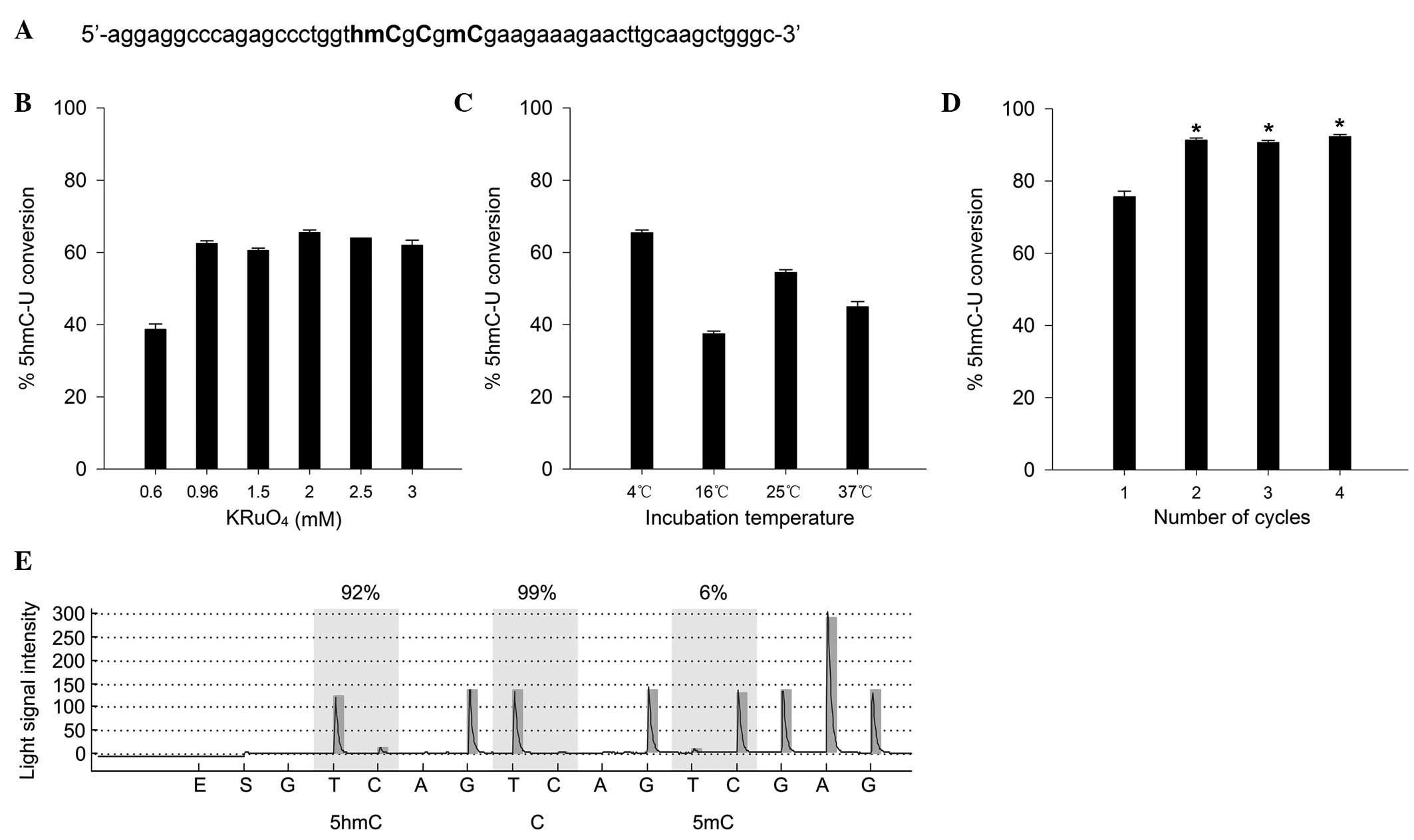
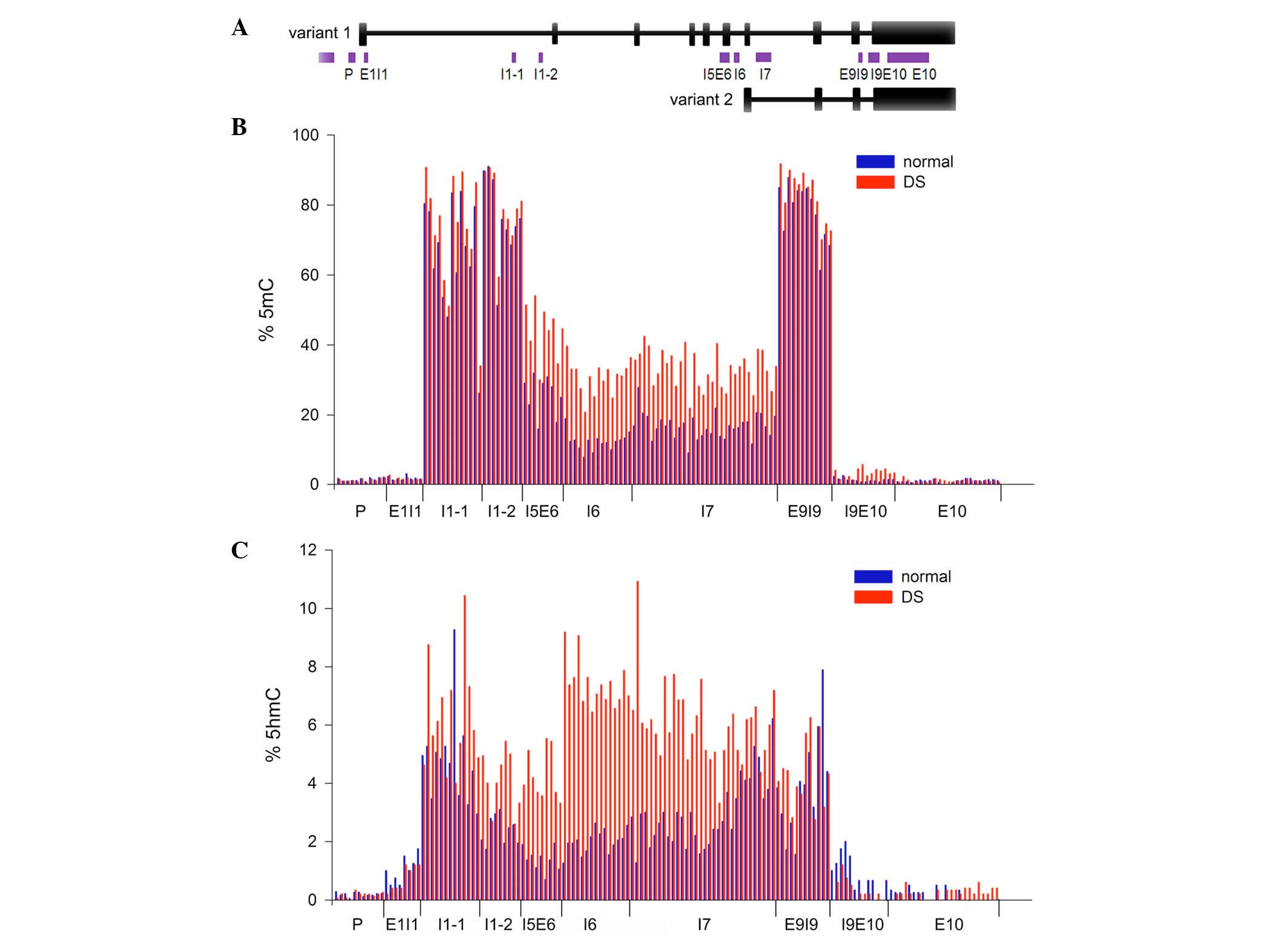
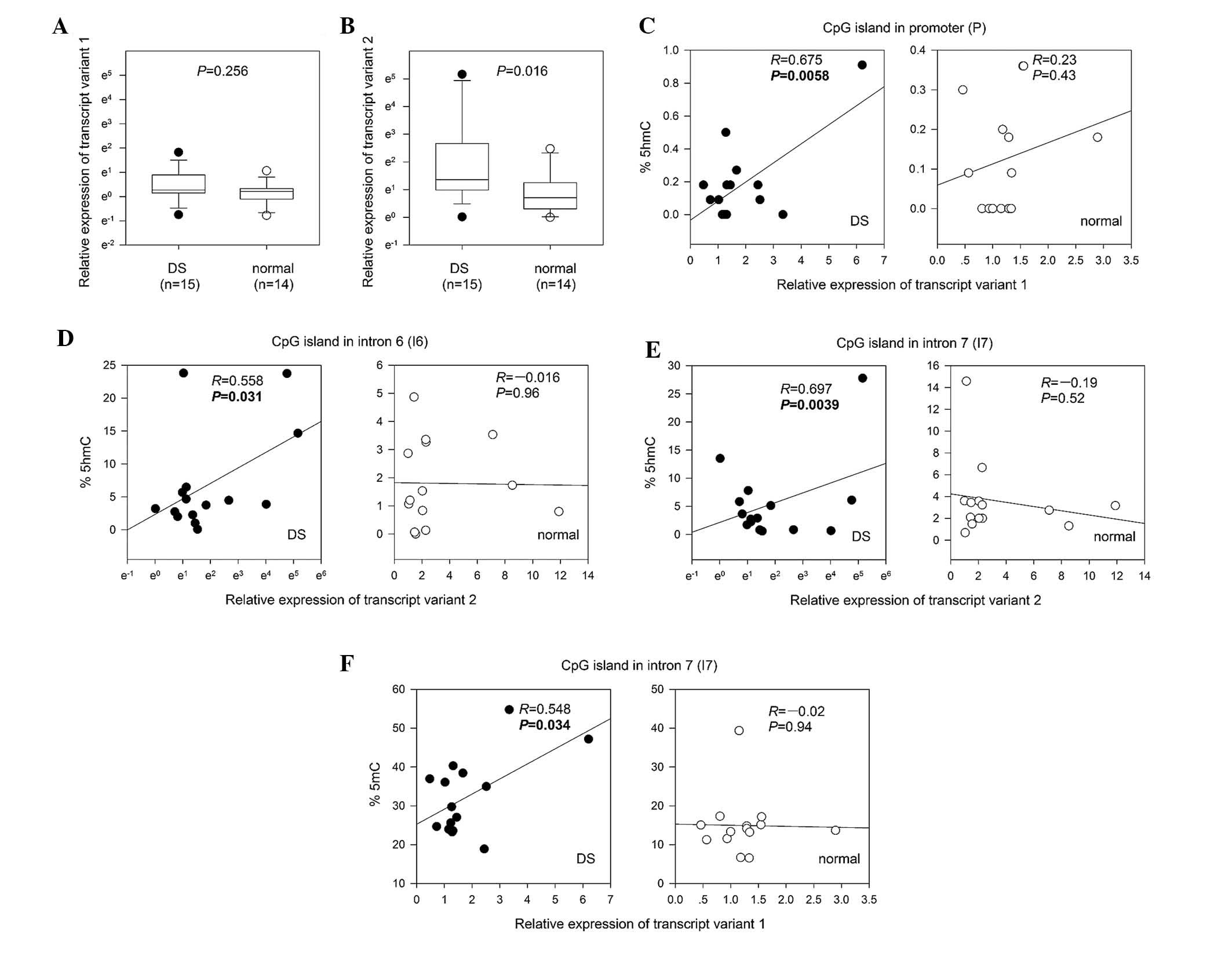
|
1
|
Dierssen M: Down syndrome: The brain in
trisomic mode. Nat Rev Neurosci. 13:844–858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haydar TF and Reeves RH: Trisomy 21 and
early brain development. Trends Neurosci. 35:81–91. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Letourneau A, Santoni FA, Bonilla X,
Sailani MR, Gonzalez D, Kind J, Chevalier C, Thurman R, Sandstrom
RS, Hibaoui Y, et al: Domains of genome-wide gene expression
dysregulation in Down's syndrome. Nature. 508:345–350. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lockstone HE, Harris LW, Swatton JE,
Wayland MT, Holland AJ and Bahn S: Gene expression profiling in the
adult Down syndrome brain. Genomics. 90:647–660. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rozek LS, Dolinoy DC, Sartor MA and Omenn
GS: Epigenetics: Relevance and implications for public health. Annu
Rev Public Health. 35:105–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kerkel K, Schupf N, Hatta K, Pang D, Salas
M, Kratz A, Minden M, Murty V, Zigman WB, Mayeux RP, et al: Altered
DNA methylation in leukocytes with trisomy 21. PLoS Genet.
6:e10012122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin S, Lee YK, Lim YC, Zheng Z, Lin XM, Ng
DP, Holbrook JD, Law HY, Kwek KY, Yeo GS, et al: Global DNA
hypermethylation in down syndrome placenta. PLoS Genet.
9:e10035152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Inoue M, Kuroda T, Honda A,
Komabayashi-Suzuki M, Komai T, Shinkai Y and Mizutani K: Prdm8
regulates the morphological transition at multipolar phase during
neocortical development. PLoS One. 9:e863562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ross SE, McCord AE, Jung C, Atan D, Mok
SI, Hemberg M, Kim TK, Salogiannis J, Hu L, Cohen S, et al: Bhlhb5
and Prdm8 form a repressor complex involved in neuronal circuit
assembly. Neuron. 73:292–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsagaratou A, Äijö T, Lio CW, Yue X, Huang
Y, Jacobsen SE, Lähdesmäki H and Rao A: Dissecting the dynamic
changes of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in T-cell development and
differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E3306–3315. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tahiliani M, Koh KP, Shen Y, Pastor WA,
Bandukwala H, Brudno Y, Agarwal S, Iyer LM, Liu DR, Aravind L, et
al: Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in
mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science. 324:930–935. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB,
Swenberg JA, He C and Zhang Y: Tet proteins can convert
5-methylcytosine to 5-formyl-cytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine.
Science. 333:1300–1303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu H and Zhang Y: Reversing DNA
methylation: Mechanisms, genomics, and biological functions. Cell.
156:45–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li X, Wei W, Zhao QY, Widagdo J,
Baker-Andresen D, Flavell CR, D'Alessio A, Zhang Y and Bredy TW:
Neocortical Tet3-mediated accumulation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
promotes rapid behavioral adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:7120–7125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mikeska T, Felsberg J, Hewitt CA and
Dobrovic A: Analysing DNA methylation using bisulphite
pyrosequencing. Methods Mol Biol. 791:33–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Booth MJ, Ost TW, Beraldi D, Bell NM,
Branco MR, Reik W and Balasubramanian S: Oxidative bisulfite
sequencing of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat
Protoc. 8:1841–1851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Booth MJ, Branco MR, Ficz G, Oxley D,
Krueger F, Reik W and Balasubramanian S: Quantitative sequencing of
5-methyl-cytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine at single-base
resolution. Science. 336:934–937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang Y, Pastor WA, Shen Y, Tahiliani M,
Liu DR and Rao A: The behaviour of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in
bisulfite sequencing. PLoS One. 5:e88882010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pastor WA, Aravind L and Rao A: TETonic
shift: Biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and
transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:341–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stroud H, Feng S, Morey Kinney S, Pradhan
S and Jacobsen SE: 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is associated with
enhancers and gene bodies in human embryonic stem cells. Genome
Biol. 12:R542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang Y, Chavez L, Chang X, Wang X, Pastor
WA, Kang J, Zepeda-Martínez JA, Pape UJ, Jacobsen SE, Peters B, et
al: Distinct roles of the methylcytosine oxidases Tet1 and Tet2 in
mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:1361–1366.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu H, D'Alessio AC, Ito S, Wang Z, Cui K,
Zhao K, Sun YE and Zhang Y: Genome-wide analysis of
5-hydroxymethylcy-tosine distribution reveals its dual function in
transcriptional regulation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Genes
Dev. 25:679–684. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szulwach KE, Li X, Li Y, Song CX, Han JW,
Kim S, Namburi S, Hermetz K, Kim JJ, Rudd MK, et al: Integrating
5-hydroxymethylcytosine into the epigenomic landscape of human
embryonic stem cells. PLoS Genet. 7:e10021542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Colquitt BM, Allen WE, Barnea G and
Lomvardas S: Alteration of genic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine patterning
in olfactory neurons correlates with changes in gene expression and
cell identity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:14682–14687. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wen L, Li X, Yan L, Tan Y, Li R, Zhao Y,
Wang Y, Xie J, Zhang Y, Song C, et al: Whole-genome analysis of
5-hydroxy-methylcytosine and 5-methylcytosine at base resolution in
the human brain. Genome Biol. 15:R492014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gan H, Wen L, Liao S, Lin X, Ma T, Liu J,
Song CX, Wang M, He C, Han C, et al: Dynamics of
5-hydroxymethylcytosine during mouse spermatogenesis. Nat Commun.
4:19952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin SG, Wu X, Li AX and Pfeifer GP:
Genomic mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the human brain.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:5015–5024. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jones PA: Functions of DNA methylation:
Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
13:484–492. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ball MP, Li JB, Gao Y, Lee JH, LeProust
EM, Park IH, Xie B, Daley GQ and Church GM: Targeted and
genome-scale strategies reveal gene-body methylation signatures in
human cells. Nat Biotechnol. 27:361–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Aran D, Toperoff G, Rosenberg M and
Hellman A: Replication timing-related and gene body-specific
methylation of active human genes. Hum Mol Genet. 20:670–680. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|