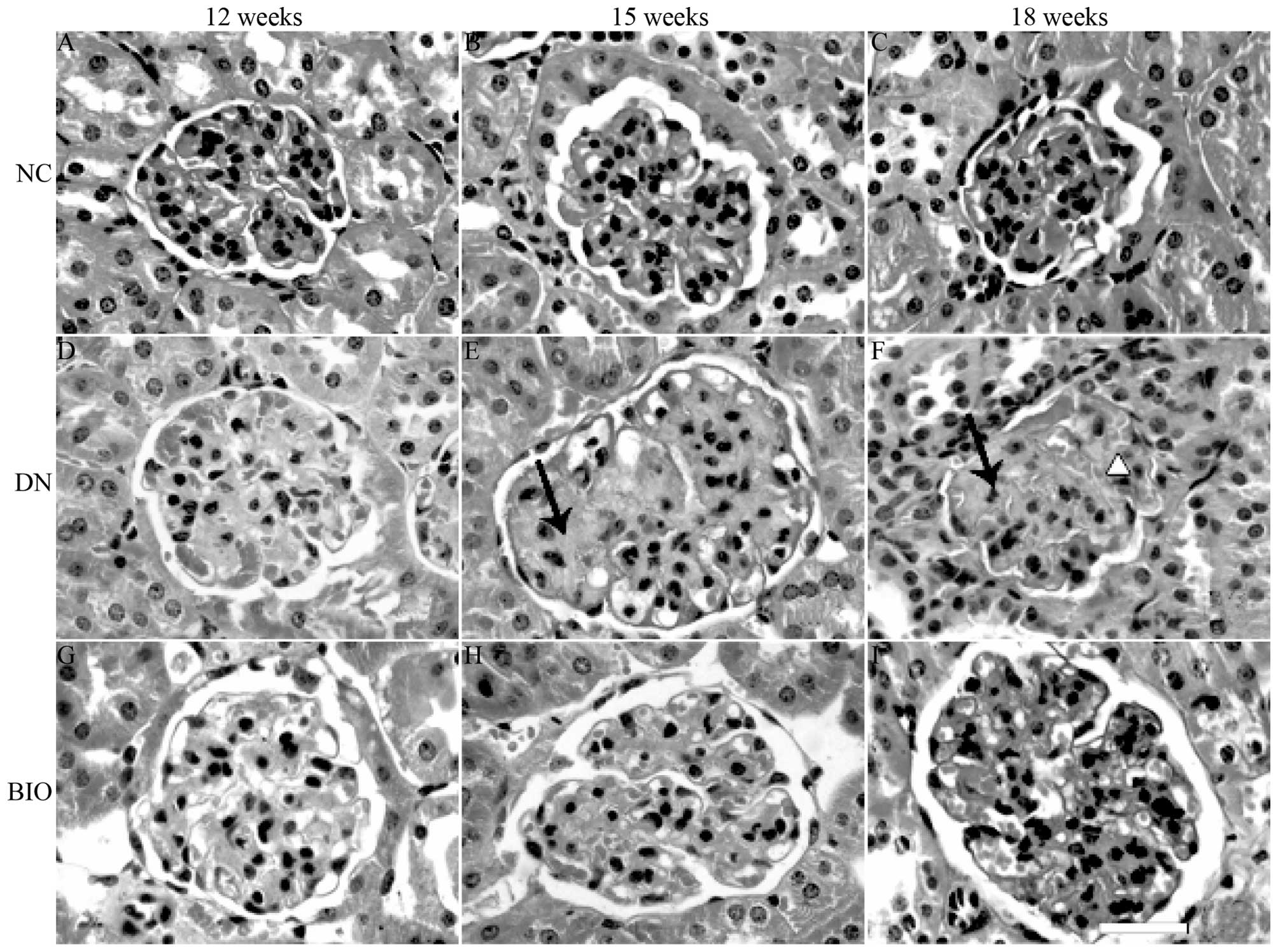
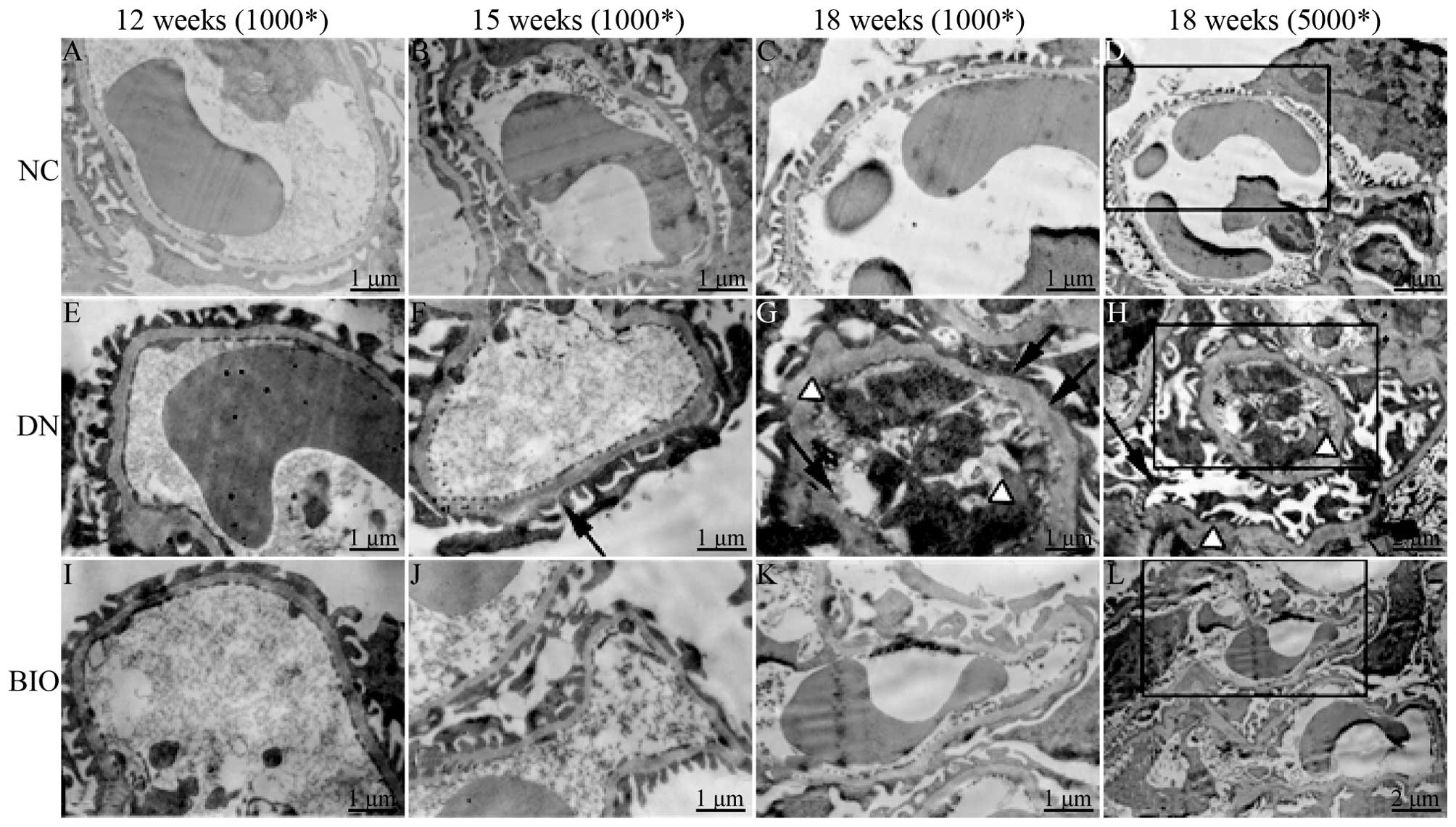
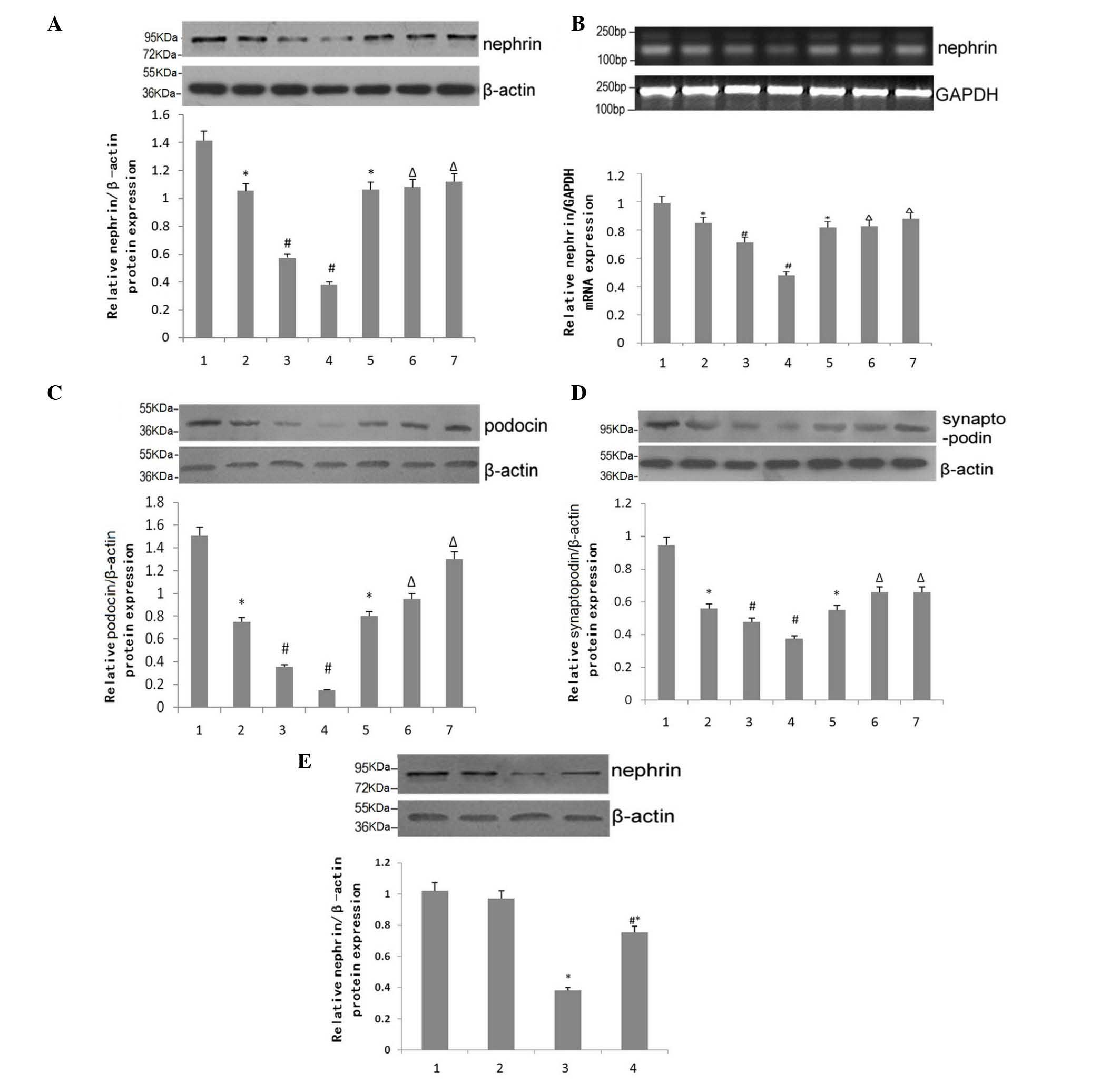
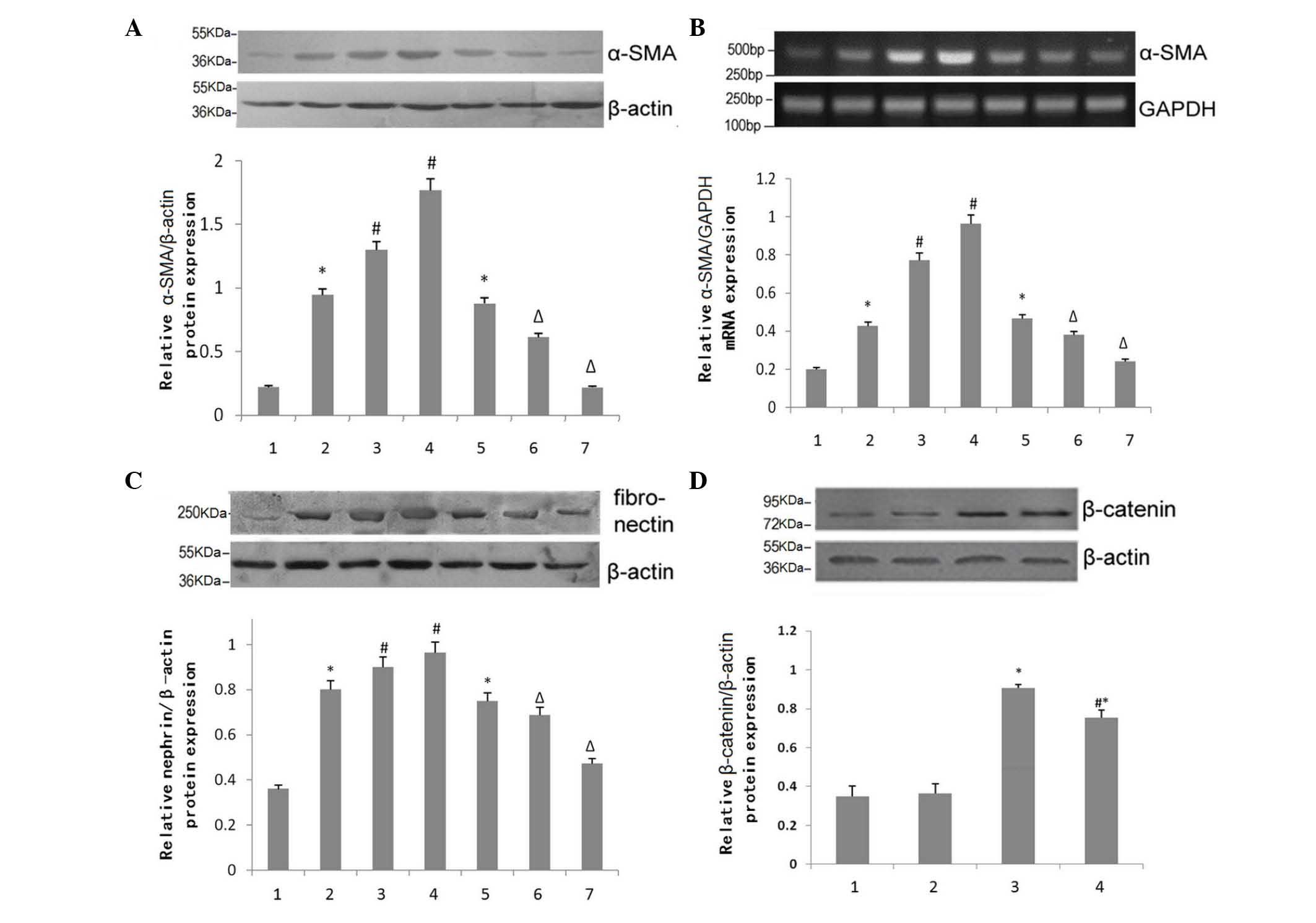
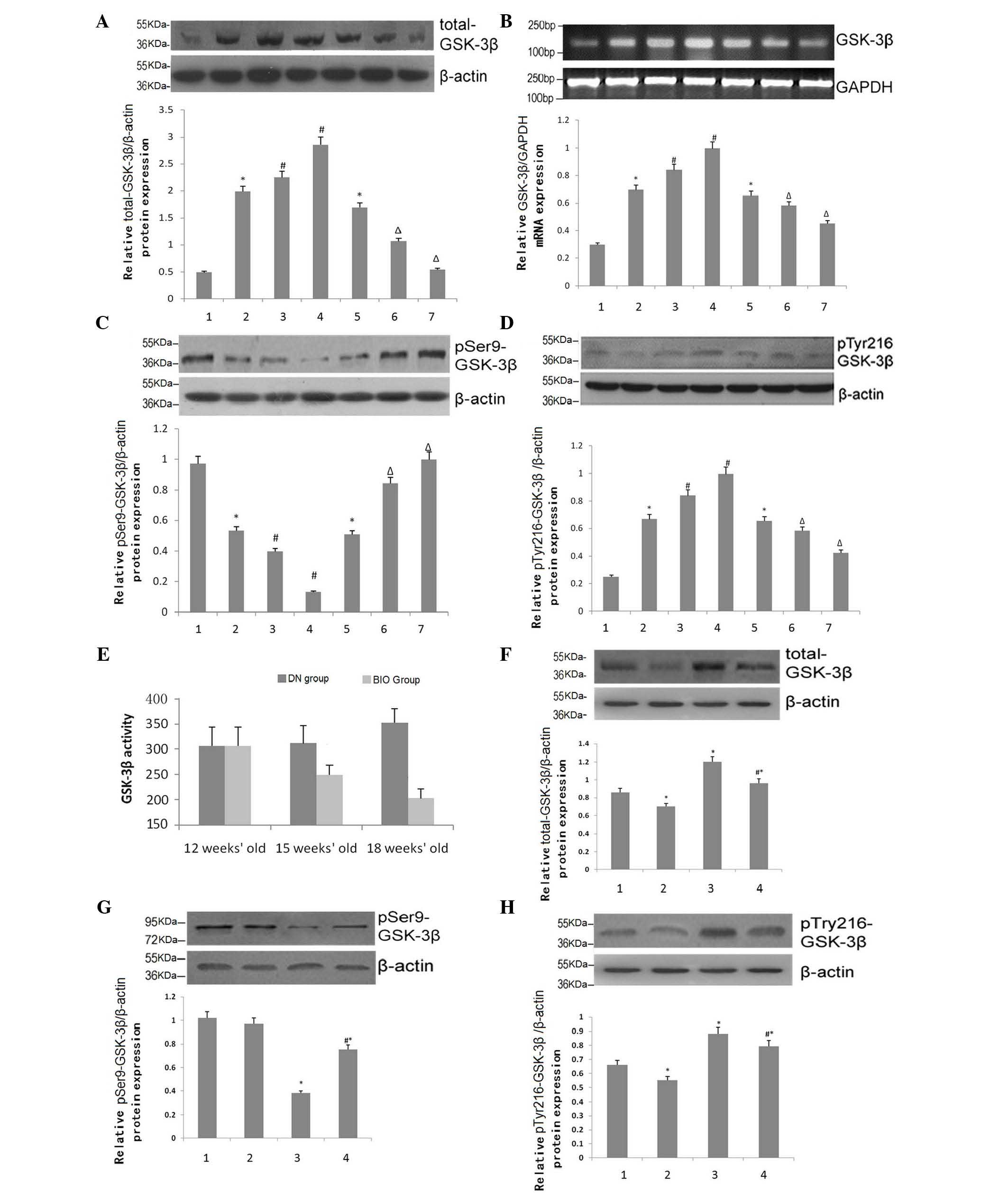
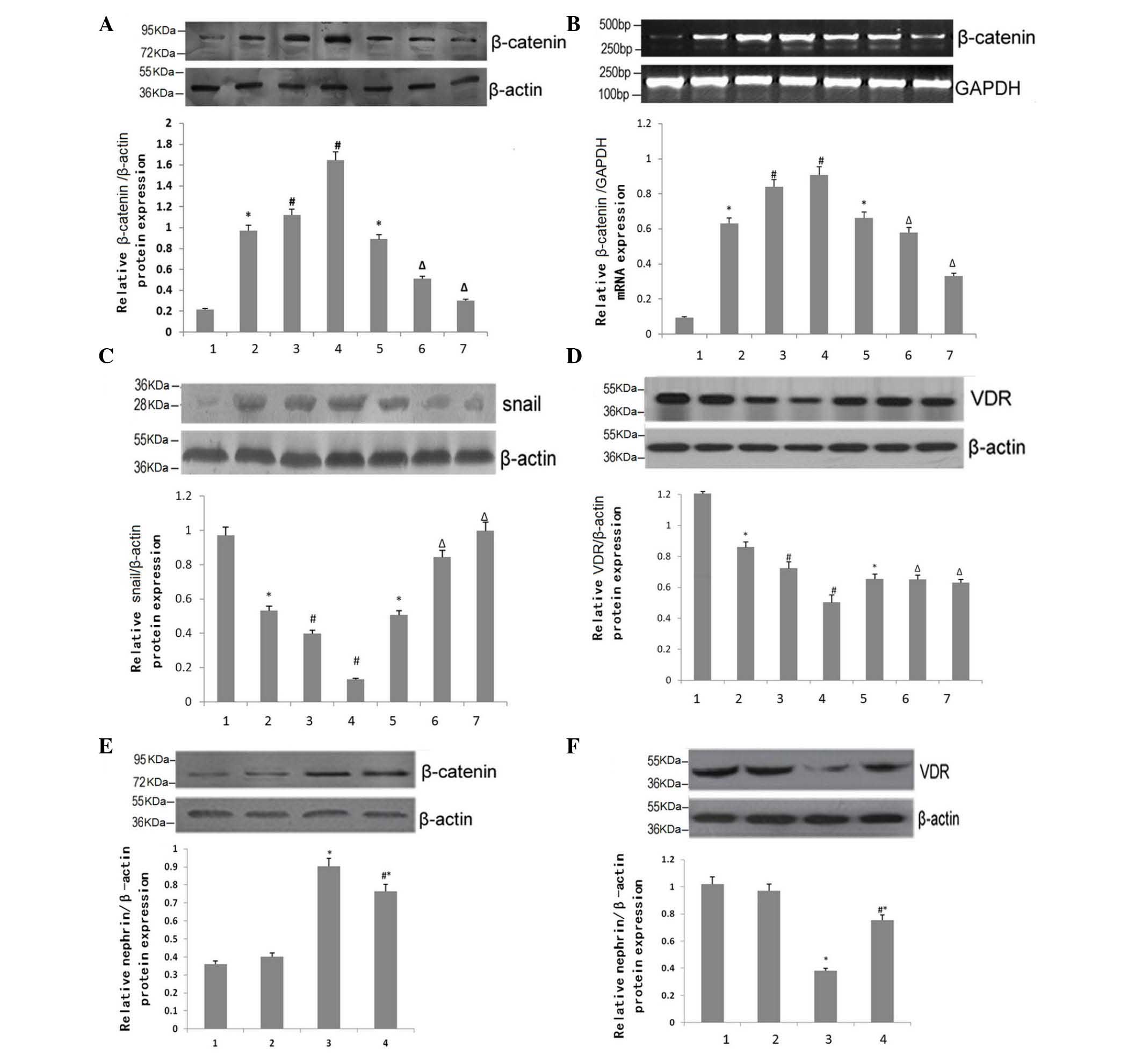
|
1
|
US Renal Data System: 2009 USRDS Annual
Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States.
National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and
Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD: 2009
|
|
2
|
de Boer IH, Rue TC, Hall YN, Heagerty PJ,
Weiss NS and Himmelfarb J: Temporal trends in the prevalence of
diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 305:2532–2539.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Panchapakesan U, Pegg K, Gross S, Komala
MG, Mudaliar H, Forbes J, Pollock C and Mather A: Effects of SGLT2
inhibition in human kidney proximal tubular cells-renoprotection in
diabetic nephropathy? PLoS One. 8:e544422013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dronavalli S, Duka I and Bakris GL: The
pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol
Metab. 4:444–452. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L, Xie P, Wallner
EI, Chen S, Chugh S and Danesh FR: Diabetic nephropathy: Mechanisms
of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 233:4–11.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wolf G and Ziyadeh FN: Molecular
mechanisms of diabetic renal hypertrophy. Kidney Int. 56:393–405.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wolf G and Ziyadeh FN: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy.
Nephron Physiol. 106:p26–p31. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lomelí C, Rosas-Peralta M, Lorenzo A and
Saucedo N; Grupo de investigadores participantes en México para el
estudio I-Search: Microalbuminuria and associated cardiovascular
risk factors in patients with arterial systemic hypertension. A
subanalysis of the I-Search study. Arch Cardiol Mex. 82:93–104.
2012.In Spanish.
|
|
9
|
Monhart V: Microalbuminuria. From diabetes
to cardiovascular risk. Vnitr Lek. 57:293–298. 2011.In Czech.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ozyol A, Yucel O, Ege MR, Zorlu A and
Yilmaz MB: Microalbuminuria is associated with the severity of
coronary artery disease independently of other cardiovascular risk
factors. Angiology. 63:457–460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Udenze IC, Azinge EC, Ebuehi OA, Awolola
NA, Adekola OO, Menkiti I and Irurhe NK: The relationship between
microalbuminuria, cardiovascular risk factors and disease
management in type 2 diabetes. Nig Q J Hosp Med. 22:34–38.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harris RC: Podocyte ACE2 protects against
diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 82:255–256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wiggins RC: The spectrum of
podocytopathies: A unifying view of glomerular diseases. Kidney
Int. 71:1205–1214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reidy K and Susztak K:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and podocyte loss in diabetic
kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 54:590–593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steffes MW, Schmidt D, McCrery R and
Basgen JM; International Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group:
Glomerular cell number in normal subjects and in type 1 diabetic
patients. Kidney Int. 59:2104–2113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M and
Böttinger EP: Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause
apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 55:225–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Thibodeau JF, Holterman CE, Burger D, Read
NC, Reudelhuber TL and Kennedy CR: A novel mouse model of advanced
diabetic kidney disease. PLoS One. 9:e1134592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu P, Wang G, Shen M, Zhang P, Zhang J, Du
J and Liu Q: Intratumoral polymorphonuclear granulocyte is
associated with poor prognosis in squamous esophageal cancer by
promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Future Oncol.
11:771–783. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai HY, Zheng M, Lv LL, Tang RN, Ma KL,
Liu D, Wu M and Liu BC: The roles of connective tissue growth
factor and integrin-linked kinase in high glucose-induced
phenotypic alterations of podocytes. J Cell Biochem. 113:293–301.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liang Y, Jing Z, Deng H, Li Z, Zhuang Z,
Wang S and Wang Y: Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition ameliorates
proteinuria-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating
the PI3K-Akt-GSK-3β signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:70–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Obligado SH, Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Zuk
A, Meijer L and Nelson PJ: CDK/GSK-3 inhibitors as therapeutic
agents for parenchymal renal diseases. Kidney Int. 73:684–690.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zúñiga Mejía Borja A,
Pavenstädt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W and Zeller R: Rearrangements of
the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during
differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell
lines. Exp Cell Res. 236:248–258. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP,
Holzman LB and Liu Y: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte
dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1997–2008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jonathan Ryves W, Dalton EC, Harwood AJ
and Williams RS: GSK-3 activity in neocortical cells is inhibited
by lithium but not carbamazepine or valproic acid. Bipolar Disord.
7:260–265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hummel KP, Dickie MM and Coleman DL:
Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science. 153:1127–1128.
1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen H, Charlat O, Tartaglia LA, Woolf EA,
Weng X, Ellis SJ, Lakey ND, Culpepper J, Moore KJ, Breitbart RE, et
al: Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor:
Identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db
mice. Cell. 84:491–495. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM,
Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI and Friedman JM: Abnormal splicing of the
leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature. 379:632–635. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hummel KP, Coleman DL and Lane PW: The
influence of genetic background on expression of mutations at the
diabetes locus in the mouse. I. C57BL-KsJ and C57BL-6J strains.
Biochem Genet. 7:1–13. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chua S Jr, Liu SM, Li Q, Yang L,
Thassanapaff VT and Fisher P: Differential beta cell responses to
hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance in two novel congenic strains
of diabetes (FVB-Lepr (db)) and obese (DBA-Lep (ob)) mice.
Diabetologia. 45:976–990. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cohen MP, Clements RS, Cohen JA and
Shearman CW: Prevention of decline in renal function in the
diabetic db/db mouse. Diabetologia. 39:270–274. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lim AK, Ma FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Thomas
MC, Hurst LA and Tesch GH: Antibody blockade of c-fms suppresses
the progression of inflammation and injury in early diabetic
nephropathy in obese db/db mice. Diabetologia. 52:1669–1679. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ozols E,
Atkins RC and Tesch GH: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
deficiency is protective against nephropathy in type 2 diabetic
db/db mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1711–1722. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chodavarapu H, Grobe N, Somineni HK, Salem
ES, Madhu M and Elased KM: Rosiglitazone treatment of type 2
diabetic db/db mice attenuates urinary albumin and angiotensin
converting enzyme 2 excretion. PLoS One. 8:e628332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ward SG and Finan P: Isoform-specific
phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors as therapeutic agents. Curr
Opin Pharmacol. 3:426–434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA
and Sugimoto C: PI3 K/Akt and apoptosis: Size matters. Oncogene.
22:8983–8998. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chua S Jr, Li Y, Liu SM, Liu R, Chan KT,
Martino J, Zheng Z, Susztak K, D'Agati VD and Gharavi AG: A
susceptibility gene for kidney disease in an obese mouse model of
type II diabetes maps to chromosome 8. Kidney Int. 78:453–462.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Taneda S, Honda K, Ohno M, Uchida K, Nitta
K and Oda H: Podocyte and endothelial injury in focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis: An ultrastructural analysis. Virchows Arch.
467:449–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lenoir O, Jasiek M, Hénique C, Guyonnet L,
Hartleben B, Bork T, Chipont A, Flosseau K, Bensaada I, Schmitt A,
et al: Endothelial cell and podocyte autophagy synergistically
protect from diabetes-induced glomerulosclerosis. Autophagy.
11:1130–1145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Bastacky SI, St-Arnaud R,
Wu C, Dedhar S and Liu Y: Essential role of integrin-linked kinase
in podocyte biology: Bridging the integrin and slit diaphragm
signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:2164–2175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu W, Chen J, Lin J, Liu D, Mo L, Pan W,
Feng J, Wu W and Zheng D: Exogenous H2S protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury and inflammation by inhibiting
the activation of the NF-κB and IL-1β pathways. Int J Mol Med.
35:177–186. 2015.
|
|
42
|
El-Aouni C, Herbach N, Blattner SM, Henger
A, Rastaldi MP, Jarad G, Miner JH, Moeller MJ, St-Arnaud R, Dedhar
S, et al: Podocyte-specific deletion of integrin-linked kinase
results in severe glomerular basement membrane alterations and
progressive glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1334–1344.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Langham RG, Kelly DJ, Cox AJ, Thomson NM,
Holthöfer H, Zaoui P, Pinel N, Cordonnier DJ and Gilbert RE:
Proteinuria and the expression of the podocyte slit diaphragm
protein, nephrin, in diabetic nephropathy: Effects of angiotensin
converting enzyme inhibition. Diabetologia. 45:1572–1576. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nakatsue T, Koike H, Han GD, Suzuki K,
Miyauchi N, Yuan H, Salant DJ, Gejyo F, Shimizu F and Kawachi H:
Nephrin and podocin dissociate at the onset of proteinuria in
experimental membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 67:2239–2253.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mundel P, Heid HW, Mundel TM, Krüger M,
Reiser J and Kriz W: Synaptopodin: An actin-associated protein in
telencephalic dendrites and renal podocytes. J Cell Biol.
139:193–204. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu W, Hu M, Wang Y, Sun B, Guo Y, Xu Z,
Li J and Han B: Overexpression of interleukin-18 protein reduces
viability and induces apoptosis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma
cells by activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β signaling. Oncol
Rep. 33:1049–1056. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kang YS, Li Y, Dai C, Kiss LP, Wu C and
Liu Y: Inhibition of integrin linked kinase blocks podocyte
epithelial mesenchymal transition and ameliorates proteinuria.
Kidney Int. 78:363–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cai X, Han X, Luo Y and Ji L: Analysis of
insulin doses of Chinese type 2 diabetic patients with intensive
insulin treatment. PLoS One. 7:e389622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tang L, Yi R, Yang B, Li H, Chen H and Liu
Z: Valsartan inhibited HIF-1α pathway and attenuated renal
interstitial fibrosis in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 97:125–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Berwick DC, Hers I, Heesom KJ, Moule SK
and Tavare JM: The identification of ATP-citrate lyase as a protein
kinase B (Akt) substrate in primary adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
277:33895–33900. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo
P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J and Greenberg ME: Akt
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Figueroa C, Tarras S, Taylor J and Vojtek
AB: Akt2 negatively regulates assembly of the POSH-MLK-JNK
signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 278:47922–47927. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kim WY and Snider WD: Functions of GSK-3
Signaling in development of the nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci.
4:442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee J and Kim MS: The role of GSK3 in
glucose homeostasis and the development of insulin resistance.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 77(Suppl 1): S49–S57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yoshino J, Monkawa T, Tsuji M, Inukai M,
Itoh H and Hayashi M: Snail1 is involved in the renal
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
362:63–68. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bachelder RE, Yoon SO, Franci C, de
Herreros AG and Mercurio AM: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an
endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: Implications for the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 168:29–33. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jiang J and Griffin JD: Wnt/β-catenin
pathway modulates the sensitivity of the mutant flt3 receptor
kinase inhibitors in a GSK-3β dependent manner. Genes Cancer.
1:164–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM,
Gunduz M and Hung MC: Dual regulation of Snail by
GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang Y, Feng W, Xue W, Tan Y, Hein DW, Li
XK and Cai L: Inactivation of GSK-3beta by metallothionein prevents
diabetes-related changes in cardiac energy metabolism,
inflammation, nitrosative damage and remodeling. Diabetes.
58:1391–1402. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shi WR, Liu Y, Xie JD, Zhuo S, Tu CX and
Xie ZF: Changes in Wnt pathway inhibiting factors in
nitrosamine-induced esophageal precancerosis lesions and effect of
gexia zhuyu decoction. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 39:3131–3135.
2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mariappan MM, Shetty M, Sataranatarajan K,
Choudhury GG and Kasinath BS: Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is a
novel regulator of high glucose- and high insulin-induced
extracellular matrix protein synthesis in renal proximal tubular
epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 283:30566–30575. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yao CJ, Lai GM, Yeh CT, Lai MT, Shih PH,
Chao WJ, Whang-Peng J, Chuang SE and Lai TY: Honokiol eliminates
human oral cancer stem-like cells accompanied with suppression of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and apoptosis induction. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:1461362013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Li Y, Kang YS, Dai C, Kiss LP, Wen X and
Liu Y: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a potential pathway
leading to podocyte dysfunction and proteinuria. Am J Pathol.
172:299–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Solanas G, Porta-de-la-Riva M, Agustí C,
Casagolda D, Sánchez-Aguilera F, Larriba MJ, Pons F, Peiró S,
Escrivà M, Muñoz A, et al: E-cadherin controls beta-catenin and
NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in mesenchymal gene expression.
J Cell Sci. 121:2224–2234. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cozzolino M, Brenna I, Volpi E, Ciceri P,
Mehmeti F and Cusi D: Restoring the physiology of vitamin D
receptor activation and the concept of selectivity. Contrib
Nephrol. 171:151–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang Y, Deb DK, Kong J, Ning G, Wang Y,
Li G, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Strugnell S, Sabbagh Y, et al: Long-term
therapeutic effect of vitamin D analog doxercalciferol on diabetic
nephropathy: Strong synergism with AT1 receptor antagonist. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 297:F791–F801. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Fretz JA, Zella LA, Kim S, Shevde NK and
Pike JW: 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulates the expression of
low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 via
deoxyribonucleic acid sequence elements located downstream of the
start site of transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 20:2215–2230. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rincon-Choles H, Vasylyeva TL, Pergola PE,
Bhandari B, Bhandari K, Zhang JH, Wang W, Gorin Y, Barnes JL and
Abboud HE: ZO-1 expression and phosphorylation in diabetic
nephropathy. Diabetes. 55:894–900. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xiong M, Gong J, Liu Y, Xiang R and Tan X:
Loss of vitamin D receptor in chronic kidney disease: A potential
mechanism linking inflammation to epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 303:F1107–F1115. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Song H, Deng B, Zou C, Huai W, Zhao R and
Zhao W: GSK3β negatively regulates LPS-induced osteopontin
expression via inhibiting its transcription. Scand J Immunol.
81:186–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu Y: New insights into
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:212–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jope RS, Yuskaitis CJ and Beurel E:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Inflammation, diseases and
therapeutics. Neurochem Res. 32:577–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Lin CL, Wang JY, Huang YT, Kuo YH,
Surendran K and Wang FS: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling modulates
survival of high glucose-stressed mesangial cells. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 17:2812–2820. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Costabile V, Duraturo F, Delrio P, Rega D,
Pace U, Liccardo R, Rossi GB, Genesio R, Nitsch L, Izzo P and de
Rosa M: Lithium chloride induces mesenchymal-to-epithelial
reverting transition in primary colon cancer cell cultures. Int J
Oncol. 46:1913–1923. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|